Gaseous & Liquid State
Revision Notes on States of Matter
Thus matter is classified mainly into three categories depending upon its physical state namely solid, liquid and gaseous states.
Distinction between three states of matter:
Parameters of Gases
The characteristics of gases are described in terms of following four parameters
• Mass
• Volume
• Pressure
• Temperature
1. Mass (m):
The mass of the gas is related to the number of moles as
n = w/M
Where n = number of moles
w = mass of gas in grams
M = molecular mass of the gas
2. Volume (V):
Since gases occupy the entire space available to them, therefore the gas volume means the volume of the container in which the gas is enclosed.
Units of Volume: Volume is generally expressed in litre (L), cm3 & dm3
1m3 = 103 litre = 103 dm3 = 106 cm3.
3. Pressure:
Pressure of the gas is due to its collisions with walls of its container i.e. the force exerted by the gas per unit area on the walls of the container is equal to its pressure.
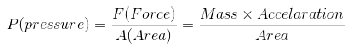
Pressure is exerted by a gas due to kinetic energy of its molecules.
As temperature increases, the kinetic energy of molecules increases, which results in increase in pressure of the gas. So, pressure of any gas is directly proportional to its temperature.
Units of Pressure:
The pressure of a gas is expressed in atm, Pa, Nm–2, bar and lb/In2 (psi).
760 mm = 1 atm = 10132.5 KPa = 101325 Pa = 101325 Nm–2
760 mm of Hg = 1.01325 bar = 1013.25 milli bar = 14.7 lb/2n2 (psi)
4. Temperature (T):
Temperature is defined as the degree of hotness. The SI unit of temperature is Kelvin. oC and oF are the two other units used for measuring temperature. On the Celsius scale water freezes at 0°C and boils at 100°C where as in the Kelvin scale water freezes at 273 K and boils at 373 K.
K = oC + 273.5
F = (9/5) oC + 32
Gas Laws:
1. Boyle’s Law:-
”At constant temperature, the pressure of a fixed amount (i.e., number of moles n) of gas varies inversely with its volume”.
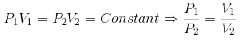
Graphical Representation of Boyle’s Law :
• A plot of P versus 1/V at constant temperature for a fixed mass of gas would be a straight line passing through the origin.
• A plot of P versus V at constant temperature for a fixed mass of a gas would be a rectangular hyperbola.
• A plot of P (or V ) versus PV at constant temperature for a fixed mass of a gas is a straight line parallel to the PV axis.
2. Charles’ Law:-
”At constant pressure, the volume of a given mass of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature”
Or log V – log T = Constant
Graphical Representation of Charles’s Law :
1. For a definite mass of the gas a plot of V vs T (oK) at constant pressure is a straight line passing through the origin.
2. A plot of V vs t (oC) at constant pressure is a straight line cutting the temperature axis at -273 oC
3. Combined Gas Law:-
This law states that “at constant volume, the pressure of a given mass of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature”.
The combination of Boyle’s Law and Charles’ Law:
4. Gay Lussac’s Law:
Where,
P = Pressure of Gas
T = Absolute Temperature
If the pressure and temperature of a gas changes from P1 & T1 to P2 & T2 , volume remaining constant, we have
where,
Pt = Pressure of gas at t oC
Po = Pressure of gas at 0 oC
t = Temperature in oC.
Graphical Representation of Gay-Lussac’s Law
5. Avogadro Law:
“Samples of different gases which contain the same number of molecules (any complexity, size, shape) occupy the same volume at the same temperature and pressure”.
It follows from Avogadro’s hypothesis that
(when T and P are constant).
6. Ideal Gas Equation:
Ideal gas obey all the three laws i.e. Boyle’s, Charles’s, and Avogadro‘s law strictly.
pv = nRT
Where,
where R is the constant of proportionality or universal gas constant
The value of R was found out to be
R = 8.314 J mol–1 K–1
R = 0.0821 litre atm K–1 mol–1
R = 2 cal K–1 mol–1
Ideal gas equation is also known as equation of state.
7. Dalton’s law of partial pressures:
The total pressure of mixture of non-reactive gases at constant temperature and pressure is equal to the sum of the individual partial pressures of the gases.
ptotal = p1 +p2+p3+p4…
p1 = x1 ptotal
p2 = x2 ptotal
p3 = x3 ptotal
Aqueous tension:-
Pressure exerted by saturated water vapour.
pdry gas = pTotal –Aqueous Tension
Gas Eudiometry:
Equation for combustion of hydrocarbons:
CxHy + (x + y/4) O2 ——> xCO2 + y/2 H2O
Kinetic molecular theory of gases:
• Gases are made of large number of identical particles (atoms or molecules), which are very small and perfectly hard spheres.
• The actual volume of the molecules is negligible as compare to the space between them and hence they are considered as the point masses.
• Interaction between the particles is negligible.
• Particles of a gas are always in constant and random motion and the collision between them is perfectly elastic.
• The average kinetic energy of the particles of a gas is directly proportional to the absolute temperature.
• Pressure of the gas is due to the collision between gas molecules and walls of the container.
The Kinetic Equation
Velocities of gas molecules
• Average Velocity
Average velocity =
• Root Mean Square Velocity:-
Maxwell proposed the term Urms as the square root of means of square of all such velocities.
• Most probable velocity:-
It is the velocity which is possessed by maximum no. of molecules.
Kinetic Energy of Gas
As per kinetic equation
For 1 mole m × n = Molecular Mass (M)
Where k is the Boltzmann constant (k = R / N)
Graham’s Law of Diffusion/Effusion:
1. Diffusion: ability of a gas to spread and occupy the whole available volume irrespective of other gases present in the container
2. Effusion: process by which a gas escapes from one chamber of a vessel through a small opening or an orifice
r ∝ 1 / √d
where r is the rate of diffusion and d is the density of the gas.
Now, if there are two gases A and B having r1 and r2 as their rates of diffusion and d1 and d2 their densities respectively. Then
Deviation from ideal gas behavior:
For ideal gas,
Compressibility factor i.e. Z = PV/nRT =1
For non-Ideal gas, Z ≠1
Thus for non-ideal gas,Z can be < 1 or > 1
When Z < 1, it is a negative deviation. It shows that the gas is more compressible than expected from ideal behaviour.
When Z > 1, it is a positive deviation. It shows that the gas is less compressible than expected from ideal behaviour.
1. Causes of deviation from ideal behaviour:
The volume occupied by gas molecules is negligibly small as compared to the volume occupied by the gas.
The forces of attraction between gas molecules are negligible.
2. Van der waals Equation:
a/V2 may be neglected in comparison with P. The Vander Waals equation becomes
PV = RT + Pb
or
PV > RT
This accounts for the rising parts of the PV vs P isotherm at high pressures
Boyle’s Temperature (Tb) :- Temperature at which real gas obeys the gas laws over a wide range of pressure.
Tb = a / Rb = 1/2 T1
Liquefaction of gases:
• Critical temperature (Tc):- temperature at which a gas liquefies. Tc = 8a / 27Rb
• Critical Volume: (Vc) :- volume of one mole of a gas at critical temperature.Vc = 3b
• Critical pressure (pc):- pressure of A gas at its critical temperature. Pc = a/27b2
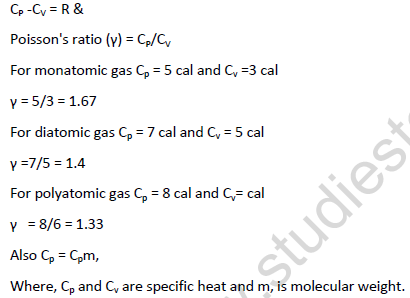
• Molar heat capacity of ideal gases:- the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 mole of a gas trough 10C.
Liquid State:
1) Surface Tension (γ):- It is the force acting at right angles to the surface along one centimeter length of the surface.
Surface tension (γ) = Work done / Change in area
Units: CGS: dcm-1
SI: Nm-1
The surface of the liquid tends to contract to the smallest possible area for a given volume of the liquid i.e. spherical shape.
Surface Tension of liquid decreases with increase of temperature and becomes zero at its critical temperature.
Surface Tension in everyday life:
• Cleansing action of soap and detergents.
• Efficacy of tooth pastes, mouth washes and nasal jellies.
Viscosity:
It is the force of friction which one part of the liquid offers to another part of the liquid.
Coefficient of viscosity: is the force per unit area required to maintain unit difference of velocity between two parallel layers in the liquid one unit apart.
Units: CGS: dscm-1
S.I: Nsm-1
Viscosity of liquid decreases with increase in temperature.

