a) Homolytic fission: Each atom separates with one electron, leading to the formation of highly reactive entities called radicals, owing their reactivity to their unpaired electron.
b) Heterolytic fission: One atom holds on to electrons, leaving none for the other, the result in the above case being a negative and positive ion, respectively, the result being the formation of an ion pair.
Reactions involving radicals tend to occur in the gas phase and in solution in non-polar solvents, and to be catalyzed by light and by the addition of other radicals. Reactions involving ionic intermediates take place more readily in solution in polar solvents, because of the greater ease of separation of charges therein and very often because of the stabilization of the resultant ion pairs through solvation.
Mesomeric Effect or Resonance Effect:
In conjugated systems, p-electrons shifting takes place consecutively giving permanent polarity on the chain.
a) Positive Mesomeric Effect (+M): A group or atom is said to have +M effect when the direction of electron -displacement is away from it.
This effect extends the degree of delocalization and imparts stability to the molecule
a) Negative Mesomeric Effect (–M): A group or atom is said to have +M effect when the direction of electron -displacement is toward it.
a) Resonance Energy: The difference in energy between the hybrid and the most stable canonical structure is called as Resonance energy
Electromeric Effect:
Complete transfer of p-electrons from one atom to other to produce temporary polarity on atoms joined by multiple bonds, in the presence of an electrophile is known as electromeric effect. Effect is reversible and temporary.
a) Positive Electromeric Effect:
p-electrons transfer takes place C to C (as alkenes, alkynes etc.)
b) Negative Electromeric Effect:
p-electrons transfer takes place to more electronegative atom (O,N,S) joined by multiple bonds.
Hyperconjugation:
Delocalization of sigma electrons also known as sigma-pi – conjugation or no bond resonance.
It is a permanent effect.
a) Occurrence
Alkene, alkynes
Free radicals (saturated type) carbonium ions (saturated type)
b) Condition
Presence of a–H with respect to double bond, triple bond carbon containing positive charge (in carbonium ion) or unpaired electron (in free radicals)
Note: Number of hyperconjugative structures = number of a-Hydrogen. Hence, in above examples structures I,ii,iii,iv are hyperconjugate structures (H-structures).
a) Effects of Hyperconjugation:
Bond Length: Hyperconjugation also affects bond lengths because during the process the single bond in compound acquires some double bond character and vice-versa
Dipole moment: Since hyperconjugation causes this development of charges, it also affects the dipole moment of the molecule.
Stability of carbonium Ions: Tertiary > Secondary > Primary
Stability of Free radicals:
Reactive Intermediates:
Isomerism :
Geometrical Isomerism:
The isomers possess the same structural formula containing a double bond and differ only in respect of the arrangement of atoms or groups about the double bond.
This isomerism is shown by alkenes or their derivatives in which two different atoms or groups are attached to each carbon containing the double bond.
Thus the compounds having the formula abC = Cxy or the simple structure abC = Cab occur in two forms and exhibit geometrical isomerism.
a) The trans isomers of alkenes are usually more stable than their corresponding cis isomers.
b) The trans isomers have normally less dipole moments than their corresponding cis isomers.
c) The trans isomer has greater symmetry than the corresponding cis isomer. Thus it packs more easily in the crystal lattice and hence has higher melting points.
Optical Isomerism:
a) Optical Activity: The property of a substance of rotating the plane of polarized light.
b) Specific Rotation: The number of degrees of rotation observed when light is passed through 1 decimeter (10 centimeters) of its solution having concentration 1 gram per milliliter.
a) Laevorotatory or (-) - form: rotates the plane of polarized light to the left.
b) Dextrorotatory or (+)- form : rotates the plane of polarized light to the right.
c) Racimic Mixture or (±)– mixture : An inactive from which does not rotate the plane of polarized light at all. This is a mixture of equal amounts of (+)– and (–)– forms and hence its optical inactivity
Asymmetric Carbon atom: A carbon atom which is attached to four different atoms
Chirality:
a) All organic compounds which contain an asymmetric carbon (C* abde) atom are chiral and exist in two tetrahedral forms.
b) A molecule must have chirality in order to show optical activity.
Enantiomers: Two optical isomers which are non superimposable mirror images of each other.
a) Meso compounds: Compound containing two or more chiral carbon which do not show optical activity due to presence of centre of symmetry (indicated by thick dot).
b) Compounds which have unsymmetrical molecule with one or more chiral centres: In such compounds if ’n’ is the number of chiral carbons, then
No. of optically active isomers (a) = 2n
No. of racemic forms (r) = a/2
No. of meso forms (m) = 0
c) compounds having a symmetrical molecule (compounds having chiral carbons but molecule as a whole is achiral): (a) compounds with even number of carbons atoms: In such compounds if number of chiral carbons in n, we have a = 2n–1, r = a/2, and m=2(n/2-1)
d) Compounds with odd number of carbon atoms: In such compounds if n is the number of asymmetric carbons then total optical isomers are given by 2n-1 whereas m = 2(n-2)/2). Thus, a = 2n–1 –2(n-1)/2).
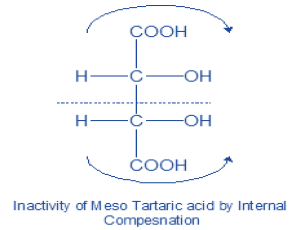
The force of rotation due to one half of the molecule is balanced by the opposite and equal force due to the other half. The optical inactivity so produced is said to be due to internal compensation. It occurs whenever a compound containing two or more
Fischer Projections:
a) Representing three dimensional structures on a two dimensional surface.
b) Asymmetric carbon atom drawn in a prescribed orientation and then projected into a planar surface.
c) Planar formulas of the asymmetric carbon are obtained by placing it so that the two substituents are horizontal and project out towards the viewer (shown by thick wedge-like bonds), while the two other substituents are vertical and project away from the viewer (shown by dotted bonds).
D and L configuration:
a) The configuration of an enantiomer is related to a standard, glyceraldehydes.
b) If the configuration at the asymmetric carbon atom of a compound can be related to D (+)- glyceraldehyde, it belongs to D-series.
c) By convention for sugars, the configuration of the highest numbered asymmetric carbon is referred to glyceraldehyde to determine the overall configuration of the molecule.
R and S System:
The sequence rules to determine the order of priorities of groups are :
The atoms or groups directly bonded to the asymmetric carbon are arranged in order of decreasing atomic number and assigned priority 1, 2, 3, 4, accordingly
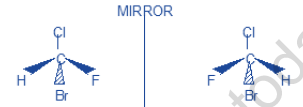
a) Thus in chlorobromofluoromethane (CHClBrF), the substituents Br (at no = 35), Cl (at no = 17),
F (at no = 9) and H (at no = 1) give the order of priorities.
Br > Cl > F > H
(1) (2) (3) (4)
b) When two or more groups have identical first atoms attached to asymmetric carbon, the priority order is determined by considering the atomic numbers of the second atoms; and if the second atoms are also identical the third atoms along the chain are examined.
c) If the first atoms of the two groups have same substituents of higher atomic number, the one with more substituents takes priority.
Thus ––CHCl2 has a higher priority than ––CH2Cl.
d) A doubly or triply bonded atom 'A' present in a group appended to asymmetric carbon, is considered equivalent to two or three singly bonded 'A's, respectively. Thus, R= A equals A-R-A.
If in a molecule, order of priority for groups a,b,c,d, & e is a > b > d > e

