Revision Notes on Solid State
Classification of solids:
Crystalline and Amorphous solids:
Based on binding forces:
Bragg Equation:
nλ = 2dsinθ,
Where
• d= distance between the planes
• n = order of refraction
• θ= angel of refraction
• λ = wavelength
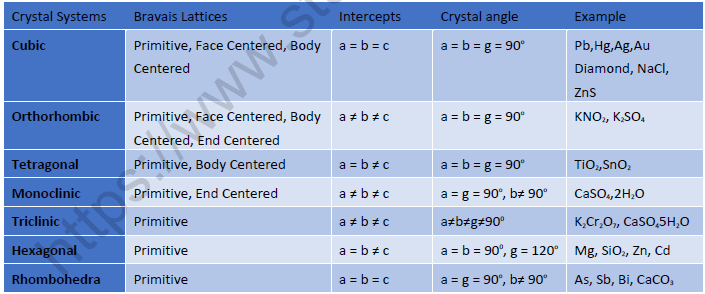
Crystal Systems:
• Total number of crystal systems: 7
• Total number of Bravais Lattices: 14
Number of atoms in unit cells.
Primitive cubic unit cell:
• Number of atoms at corners = 8×1/8 =1
• Number of atoms in faces = 0
• Number of atoms at body-centre: = 0
• Total number of atoms = 1
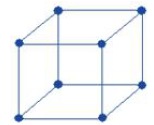
Body-centred cubic unit cell:
• Number of atoms at corners = 8×1/8 =1
• Number of atoms in faces = 0
• Number of atoms at body-centre: =1
• Total number of atoms = 2
Face-centred cubic or cubic-close packed unit cell:
• Number of atoms at corners = 8×1/8 =1
• Number of atoms in faces = 6×1/2 = 3
• Number of atoms at body-centre: = 0
• Total number of atoms = 4
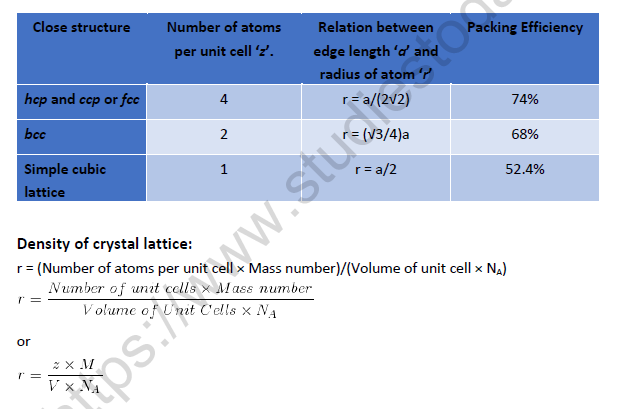
Packing Efficiency
Packing Efficiency = (Volume occupied by all the atoms present in unit cell / Total volume of unit cell)×100
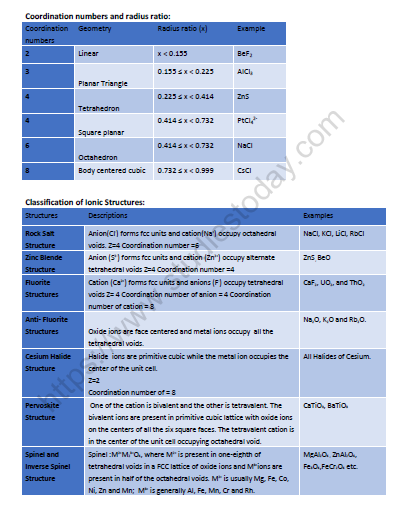
Octahedral and Tetrahedral Voids:
Number of octahedral voids = Number of effective atoms present in unit cell
Number of tetrahedral voids = 2×Number of effective atoms present in unit cell
So, Number of tetrahedral voids = 2× Number of octahedral voids.
Defects in crystal:
Stoichiometric Defects
1. Schottky Defects
• Some of the lattice points in a crystal are unoccupied.
• Appears in ionic compounds in which anions and cations are of nearly same size.
• Decreases the density of lattice
• Examples: NaCl and KCl
2. Frenkel Defects
• Ion dislocate from its position and occupies an interstitial position between the lattice points
• Appears in crystals in which the negative ions are much larger than the positive ion.
• Does not affect density of the crystal.
• Examples: AgBr, ZnS
Non-Stoichiometric Defects
1. Metal Excess defect:
• Metal excess defect occurs due to
• anionic vacancies or
• presence of extra cation.
• F-Centres: hole produced due to absence of anion which is occupied by an electron.
2. Metal deficiency defect:
• Metal deficiency defect occurs
• Due to variable valency of metals
• When one of the positive ions is missing from its lattice site and the extra negative charge is balanced by some nearby metal ion acquiring two charges instead of one
Please click the link below to download pdf file of NEET Chemistry Solid State Revision Notes

