Chemical Bonding
Chemical bond:-
Chemical bond is the attractive force which holds various constituents together in a molecule. There are three types of chemical bonds: Ionic Bond, Covalent Bond, Co-ordinate Bond.
Octet Rule:
Atoms form chemical bonds in order to complete their octet i.e. eight electrons in their valence shell.
Lewis Structures:
• Pair of bonded electrons is by means of a ‘dash’ (-) usually called a ‘bond’.
• Lone pairs or ‘non-bonded’ electrons are represented by ‘dots’.
• Electrons present in the last shell of atoms are called valence electrons.
Exceptions to the Octet Rule:
• Species with odd number of electrons: NO, NO2,
• Incomplete octet for the central atom: LiCl, BeH2 and BCl3
• Expanded octet for the central atom: PF5, SF6 and H2SO4
Formal Charge:
• Formal charge is the difference between the number of valence electrons in an isolated atom and number of electrons assigned to that atoms in Lewis structure.
• Formal charge = [Total number of valence electrons in the free atom ) - (Total number of lone pairs of electrons) -1/2(Total number of shared electrons i.e. bonding electrons)]
Resonance:
• For molecules and ions showing resonance it is not possible to draw a single Lewis structure.
• All the properties of such species can only be explained by two or more Lewis structures. Example: Resonance of O3
A and B are resonating or canonical structures and C is the resonance hybrid Some other examples
(i) CO32– ion
Example
(ii) Carbon-oxygen bond lengths in carboxylate ion are equal due to resonance.
(iii) Benzene
(iv) Vinyl Chloride
Ionic Bonding:
Formation of Ionic Bond:
• Formation of ionic bond takes place between a metal and a non-metal by transfer of electron.
• Steps involved in formation of an ionic bond:
Conditions required of formation of ionic bonds:
• Low I.E of cation.
• High E.A of anion.
• High lattice energy.
Covalent Bonding:
• Covalent bond is formed between two non-metals by sharing of electrons.
• Electron pairs which participate in bonding are called bond pairs.
• Electron pairs which do not participate in bonding are called lone pairs.
• There could be single, double or triple covalent bonds between two elements depending on the number of electrons being shared
VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) Theory:
• The shape of the molecule is determined by repulsions between all of the electron pairs present in the valence shell.
• Order of the repulsion: Lone pair↔ Lone pair > Lone pair↔ Bond pair > Bond pair↔ Bond pair.
• Repulsion among the bond pairs is directly proportional to the bond order and electro negativity difference between the central atom and the other atoms.
Determination of shape of molecules using VSEPR theory:
• Calculate X using following method.
X = (No. of valence electrons of central atom) + (No. of other atoms) + (Negative charge on the
molecule) – (Positive charge on the molecule)
Use the following chart to find the shape.
Rule:
It accounts for the covalent character in ionic compounds.
Covalency is favoured by
• Smaller cation .
• Larger anion and
• Large charge on either ion.
Dipole Moment:
• Dipole moment of any bond is the product of the net positive or negative charge and distance between the two charged ends, i.e., the bond length. i.e. Dipole moment (m) = electronic charge (e) × Distance (d) Dipole moment is measured in debye unit (D);
• Dipole moment of a molecule is vector addition of all the individual bond moments.
Percentage Ionic Character:
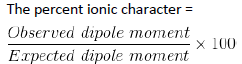
Hydrogen Bonding:
• Hydrogen bond is an electrostatic attractive force between covalently bonded hydrogen atom of one molecule or a part of a molecule and an electronegative atom (such as F,O, N) of another molecule (Inter-molecular hydrogen bonding) or another part of the same molecule
(intramolecular hydrogen bonding).
• Intermolecular hydrogen bonding increases boiling point of the compound and also its water solubility
• Intramolecular hydrogen bonding decreases the boiling point of the compound and also its water solubility
Valence bond theory (VBT):
• A covalent bond is formed by overlapping of valence shell atomic orbital of the two atoms having unpaired electron.
• There is maximum electron density between the bonding atoms.
• Greater the overlapping of atomic orbital higher is the strength of chemical bond.
• The bond formed by lateral overlap of two atomic orbitals having maximum overlapping on both sides of the line connecting the centres of the atoms is called a π-bond. A π-bond possess a plane of symmetry, often referred to as the nodal plane.
• σ-Bond : When covalent bond is formed by overlapping of atomic orbitals along the same axis it is called s - bond. Such type of bond is symmetrical about the line joining the two nuclei e.g.
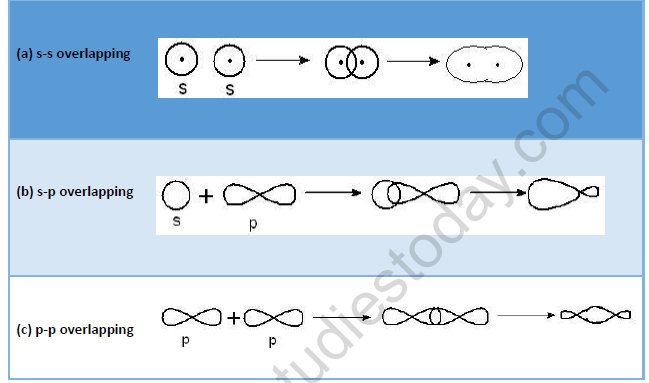
• π - Bond: This type of bond is formed by the sidewise or lateral overlapping of two half filled atomic orbitals.
• The strength of a bond depends upon the extent of overlapping of half-filled atomic orbitals. The extent of overlapping is between two atoms is always greater when there is end to end overlapping of orbitals than, when there is sidewise overlapping of orbitals. Hence s-bond is always stronger than p-bond.
• The average distance between the nuclei of the two bonded atoms in a molecule is called bond length and the energy required to break one mole of bonds of particular type in gaseous state is called Bond energy or Bond strength. The same amount of energy is released in formation of one mole of particular bond.
Hybridization:
• The mixing of dissimilar orbital of similar energies to form new set of hybrid orbital.
• Number of hybrid orbital formed is equal to the no. of orbital taking part in hybridization.
• Depending upon the different combination of s and p orbitals, these types of hybridization are known.
sp3 hybridization: In this case, one s and three p orbitals hybridize to form four sp3 hybrid orbitals. These four sp3 hybrid orbitals are oriented in a tetrahedral arrangement.
sp2 hybridization: In this case one s and two p orbitals mix together to form three sp2 hybrid orbitals and are oriented in a trigonal planar geometry.
The remaining p orbital if required form side ways overlapping with the other unhybridized p orbital of other C atom and leads to formation of p2C = CH2 bond as in H
sp hybridization: In this case, one s and one p orbital mix together to form two sp hybrid orbitals and are oriented in a linear shape.
The remaining two unhybridised p orbitals overlap with another unhybridised p orbital leading to the formation of triple bond as in
Bond Characteristics:
Bond Length:
• The distance between the nuclei of two atoms bonded together is called bond length.
• It is expressed in angstrom (Å) units or picometer (pm).
• Bond length in ionic compound = rc + + ra –
• Bond length in covalent compound (AB) = rA + rB
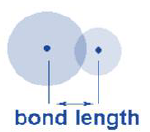
Important features of bond length
1. The bond length of the homonuclear diatomic molecules are twice the covalent radii.
2. The lengths of double bonds are less than the lengths of single bonds between the same two atoms, and triple bonds are even shorter than double bonds.Single bond > Double bond > Triple
bond (decreasing bond length)
3. Bond length decreases with increase in s-character since s-orbital is smaller than a p – orbital.
4. Bond length of polar bond is smaller than the theoretical non-polar bond length.
Bond Angle:
Bond angel is the angle between two adjacent bonds at an atom in a molecule made up of three or more atoms.
Bond angles mainly depend on the following three factors:
• Hybridization: Bond angle depends on the state of hybridization of the central atom
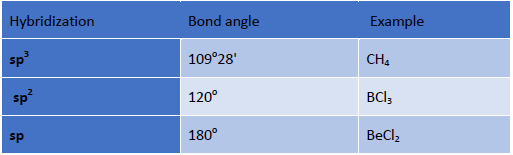
Generally s- character increase in the hybrid bond, the bond angle increases.
• Lone pair repulsion: Bond angle is affected by the presence of lone pair of electrons at the central atom. A lone pair of electrons at the central atom always tries to repel the shared pair (bonded pair) of electrons. Due to this, the bonds are displaced slightly inside resulting in a decrease of bond angle.
• Electronegativity: If the electronegativity of the central atom decreases, bond angle decreases.
Bond Energy or Bond Strength:
• The amount of energy required to break a bond in molecule is called bond energy.
• Bond energy of sigma bond is more than that of a π-bond.
• Bond energy increases with decrease in bond length
C ≡ C > C = C > C – C (decreasing bond length)
s < p < sp < sp2 < sp3
• The bond energy decreases with increase in number of lone pairs on the bonded atom.
Molecular Orbital Theory:
• Molecular orbital are formed by linear combination of atomic orbital (LCAO)
• Atomic orbital of all the atoms are assumed to interfere with each other in the form of waves.
• Bonding molecular orbital are formed by constructive interference of atomic orbital.
• Anti-bonding orbital are formed by destructive interference of atomic orbital.
• Anti-bonding MO is of higher energy than Bonding MO.
• In simple homonuclear diatomic molecules the order of MO's based on increasing energy is
• For molecules including O2 and above, the order is
• Bond Order: Bond-order = 1/2 (no. of bonding electrons - No. of anti-bonding electrons).
Application of MOT to Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules
Application of MOT to Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules

