• Unit of rate of reaction : mol L-1 s-1
• The rate measured over a long time interval is called average rate and the rate measured for an infinitesimally small time interval is called instantaneous rate.
• In a chemical change, reactants and products are involved. As the chemical reaction proceeds, the concentration of the reactants decreases, i.e., products are produced.
• The rate of reaction (average rate) is defined as the change of concentration of any one of its reactants (or products) per unit time.
Order of Reaction
For reaction aA + bB + ….. → cC+ ….
R ∝[A]m[B]n or R = k[A]m[B]n….
Where m and n may or may not be equal to a & b.
m is order of reaction with respect to A and n is the order of reaction with respect to B.
m + n +… is the overall order of the reaction.
Elementary Reaction:
• It is the reaction which completes in a single step.
• A reaction may involve more than one elementary reactions or steps also.
• Overall rate of reaction depends on the slowest elementary step and thus it is known as rate determining step.
Molecularity of Reaction:
• Number of molecules taking part in an elementary step is known as its molecularity.
• Order of an elementary reaction is always equal to its molecularity.
• Elementary reactions with molecularity greater than three are not known because collisions in which more than three particles come together simultaneously are rare.
Differential and Integrated Rate Laws:
Zero Order Reactions:
Examples:
• Enzyme catalyzed reactions are zero order with respect to substrate concentration.
• Decomposition of gases on the surface of metallic catalysts like decomposition of HI on gold surface.
Pseudo First Order Reactions:
These are the reactions in which more than one species is involved in the rate determining step but still the order of reaction is one.
Examples:
• Acid hydrolysis of ester: CH3COOEt + H3O+ →CH3COOH + EtOH
• Inversion of cane sugar:
• Decomposition of benzenediazonium halides C6H5N=NCl +H2O → C6H5OH +N2 +HCl
Half – Life of a nth Order Reaction:
kt1/2 = (2n-1-1)/(n-1)[A0]n-1
Where, n = order of reaction ≠1
Parallel Reactions:
The reactions in which a substance reacts or decomposes in more than one way are called parallel or side reactions.
This means that irrespective of how much time is elapsed, the ratio of concentration of B to that of C from the start (assuming no B and C in the beginning ) is a constant equal to k1/k2.
Sequential Reactions:
This reaction is defined as that reaction which proceeds from reactants to final products through one or more intermediate stages. The overall reaction is a result of several successive or consecutive steps.
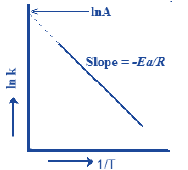
Arrhenius Equation:
k = A exp(-Ea/RT)
Where, k = Rate constant
A = pre-exponential factor
Ea = Activation energy
Temperature Coefficient:
The temperature coefficient of a chemical reaction is defined as the ratio of the specific reaction rates of a reaction at two temperature differing by 10oC.
μ = Temperature coefficient= k(r+10)/kt
Let temperature coefficient of a reaction be ' μ ' when temperature is raised from T1 to T2; then the ratio of rate constants or rate may be calculated as
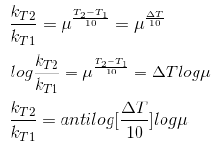
Its value lies generally between 2 and 3.
Collision Theory of Reaction Rate
• A chemical reaction takes place due to collision among reactant molecules.
• The number of collisions taking place per second per unit volume of the reaction mixture is known as collision frequency (Z).
• The value of collision frequency is very high, of the order of 1025 to 1028 in case of binary collisions.
• Every collision does not bring a chemical change.
• The collisions that actually produce the products are effective collisions.
• The effective collisions which bring chemical change are few in comparison to the form a product are ineffective elastic collisions, i.e., molecules just collide and
• disperse in different directions with different velocities.
• For a collision to be effective, the following two barriers are to be cleared.
1. Energy Barrier
2. Orientation Barrier
Radioactivity:
All radioactive decay follow 1st order kinetics
For radioactive decay A ->B
-(dNA/dt) =l NA
Where, l = decay constant of reaction
NA = number of nuclei of the radioactive substance at the time when rate is calculated. Arrhenius equation is not valid for radioactive decay.
Units: dps or Becquerrel

