NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease have been provided below and is also available in Pdf for free download. The NCERT solutions for Class 12 Biology have been prepared as per the latest syllabus, NCERT books and examination pattern suggested in Class 12 by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. Questions given in NCERT book for Class 12 Biology are an important part of exams for Class 12 Biology and if answered properly can help you to get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise answers for NCERT Class 12 Biology and also download more latest study material for all subjects. Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease is an important topic in Class 12, please refer to answers provided below to help you score better in exams
Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease Class 12 Biology NCERT Solutions
Class 12 Biology students should refer to the following NCERT questions with answers for Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease in Class 12. These NCERT Solutions with answers for Class 12 Biology will come in exams and help you to score good marks
Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology
Question. What are the various public health measures which you would suggest as safeguard against infectious disease?
Answer. The common preventive measures are as follows:
(i) Education: People should be educated about communicable diseases to protect themselves from such diseases.
(ii) Isolation: The infected person should be isolated to minimise the spread of infection.
(iii) Vaccination: People should get vaccination on time to avoid infection.
(iv) Sanitation: The sanitation condition should be improved to avoid infection from polluted water, contaminated food, etc.
(v) Eradication of vectors: The breeding places of vectors should be destroyed and adult vectors should be killed by suitable methods.
(vi) Sterilisation: The patient’s surroundings and articles of use should be completely sterilised so as to reduce the chances of infection.
Question. In which way has the study of biology helped us to control infectious diseases?
Answer. Study of biology helps us to diagnose the pathogen in following ways:
(i) The life cycle of many pathogens is studied.
(ii) Alternate and reservoir hosts are known.
(iii) The mechanisms of transmission of disease is known.
(iv) The protective measures are suggested against disease and pathogen based on above studies.
(v) Suitable medicines against infectious diseases are suggested.
(vi) The preparation of vaccines against many pathogens also entitle the use of study of biology.
Question. How does the transmission of each of following diseases take place?
(a) Amoebiasis (b) Malaria
(c) Ascariasis (d) Pneumonia.
Answer. (a) Amoebiosis
Caused by Entamoeba histolytica (Protozoan parasite).
Transmission:
(i) By ingesting cysts with food and water.
(ii) The cysts are carried by flies from faeces to food and drinks.
(b) Malaria
Caused by Plasmodium sps.
Transmission:
(i) Transmitted by female Anopheles mosquito.
(ii) Female Anopheles injects sporozoites along with saliva while sucking blood.
(c) Ascariasis
Caused by Ascaris lumbricoides. Is transmitted through contaminated food and water with Ascaris eggs.
(d) Pneumonia
Caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae. Transmission is through sputum, droplets or aerosols of the patient.
Question. What measures would you take to prevent water-borne diseases?
Answer. Measures to prevent water-borne diseases are:
(i) Use clean drinking water.
(ii) Periodic cleaning and disinfection of water reservoirs, pools and tanks.
(iii) Proper sanitary conditions.
(iv) Prevention of passage of garbage and sewage into water reservoirs.
Question. Discuss with your teacher what does ‘a suitable gene’ mean, in the context of DNA vaccines.
Answer. The term ‘suitable gene’ refers to that specific segment of DNA which forms immunogenic protein.Such genes can be cloned and then integrated with vector for introducing into an individual to be immunised for certain disorder producing a particular vaccine against the pathogen.
Question. Name the primary and secondary lymphoid orgAnswer.
Answer. Primary lymphoid organs are bone marrow and thymus. Secondary lymphoid organs are spleen,lymph nodes, tonsils, Peyer’s patches of small intestine and appendix.
Question. The following are some well-known abbreviations, which have been used in this chapter.
Expand each one to its full form:
(a) MALT (b) CMI (c) AIDS (d) NACO (e) HIV
Answer. (a) MALT—Mucosal associated lymphoid tissues.
(b) CMI—Cell-mediated immunity.
(c) AIDS—Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome.
(d) NACO—National AIDS Control Organisation.
(e) HIV—Human Immunodeficiency Virus.
Question. Differentiate the following and give examples of each:
(a) Innate and acquired immunity
(b) Active and passive immunity
Answer. (a) Differences between innate and acquired immunity
| Innate immunity | Acquired immunity |
| It is present from birth and is inherited from parents. | It is not present from the birth. |
| It is non-specific. | It is pathogen specific. |
| The various physical, physiological, cellular, cytokine barriers are the basis of innate immunity. |
The memory cells formed by B and T-cells are the basis of acquired immunity. |
| The innate immunity remains throughout life. | The acquired immunity can be short-lived or life long. |
(b) Active and passive immunity:
| Active immunity | passive immunity |
| These are easily transmitted from one infected person to the other. | These are not transmitted from one person to the other. |
| Such diseases are due to extrinsic factors, i.e.,pathogens. | Extrinsic as well as intrinsic factors, like deficiencies and hereditary factors, can cause these diseases. |
| Public health and personal hygiene reduces the probability of disease. | Public health and personal hygiene are ineffective. |
| For example, HIV, tetanus, hepatitis-B. | For example, cancer. |
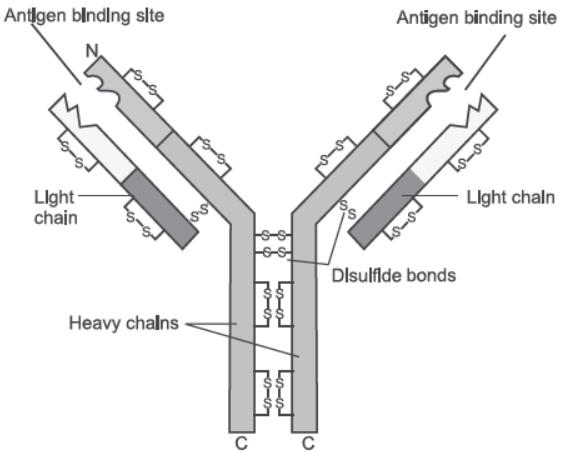
Question. Draw a well labelled diagram of an antibody molecule.
Answer.
Question. What are the various routes by which transmission of human immunodeficiency virus takes place?
Answer. Various routes by which transmission of HIV takes place:
(i) Transfusion of contaminated blood and blood products.
(ii) By sharing infected needles in case of intravenous drug abusers.
(iii) Sexual contact with an infected person.
(iv) From mother to child through placenta.
Question. What is the mechanism by which the AIDS virus causes deficiency in the immune system of the infected person?
Answer. The virus enters macrophages after getting into the body of individual where RNA forms viral DNA by reverse transcription. The viral DNA gets incorporated in the host cell’s DNA and directs the infected cells to produce viral copies. The newly produced virus particles attack helper T-cells and thus the number of T-cells decrease. Since the helper T-cells are essential for functioning of immune system, the person suffers from various diseases due to deficient immune system.
Question. How is a cancerous cell different from a normal cell?
Answer. (i) There is no adherence in cancerous cell whereas normal cells remain adhered to one another.
(ii) Tumour is formed in cancerous cells due to repeated uncontrolled cell division whereas it is absent in normal cells.
(iii) Cancerous cells have no definite lifespan but normal cells have definite lifespan and old cells are replaced by new cells.
Question. Explain what is meant by metastasis.
Answer. Metastasis is the spread of cancerous cells through migration from one tissue to other tissue and organs resulting in formation of secondary tumour. Malignant tumour is a mass of proliferating cells called neoplastic cells. They grow rapidly and invade surrounding unaffected normal cells or tissues. Cells get sloughed off from such tumour and migrate to distant sites through blood.
A new place of infection is thus established and a new tumour is formed. This property is called metastasis.
Question. List the harmful effects caused by alcohol/drug abuse.
Answer. The following are the harmful effects caused by alcohol/drug abuse:
(i) It affects the nervous system resulting in loss of judgement, will power and self-control,visual problem, etc.
(ii) It may cause peptic ulcer, gastric carcinoma, etc.
(iii) It may affect liver by causing hepatitis, liver failure, liver cell carcinoma, etc.
(iv) Reckless behaviour, vandalism and violence, isolation, depression, fatigue, aggressive, fluctuations in weight, appetite, etc.
(v) Those who take drugs intravenously are much more likely to acquire serious infections like AIDS and hepatitis-B.
(vi) Damages nervous system and may cause liver cirrhosis.
Question. Do you think that friends can influence one to take alcohol/drugs? If yes, how may one protect himself/herself from such an influence?
Answer. Yes, friends can influence a person to take alcohol or drugs. It can be avoided by
(i) avoiding addicted friends.
(ii) avoiding experimental use of alcohol/drug just for curiosity and pressure.
Question. Why is that once a person starts taking alcohol or drugs, it is difficult to get rid of this habit?
Discuss it with your teacher.
Answer. The repeated use of alcohol or drugs increases the tolerance level of the receptors present in our body. Therefore, the receptors respond only to higher doses of alcohol or drugs. This leads to greater intake and addiction. Addiction drives the people to consume more knowing that their use makes them destructive. Hence, it is difficult to get rid of this habit.
Question. In your view what motivates youngsters to take to alcohol or drugs and how can this be avoided?
Answer. Reasons for alcohol abuse in children:
(i) Social pressure.
(ii) Curiosity and need for adventure, excitement and experiments.
(iii) To overcome hardships of daily life.
(iv) In order to escape from stress, depression and frustration.
(v) Unsupportive family structure.
Alcohol and drugs can be avoided by following ways:
(i) Avoiding undue peer pressure.
(ii) Educating and counselling problems and stresses to avoid disappointments and failure in life.
(iii) Seeking help from parents and peers.
(iv) Seeking professional and medical help whenever required
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease Multiple Choice Questions
Question. Antibodies in our body are complex
(a) glycoproteins
(b) lipoproteins
(c) steroids
(d) prostaglandins
Answer. A
Question. Lysozyme that is present in perspiration, saliva and tears, destroys
(a) certain types of bacteria
(b) all viruses
(c) most virus-infected cells
(d) certain fungi
Answer. A
Question. Increased asthmatic attacks in certain seasons are related to
(a) eating fruits preserved in tin containers
(b) inhalation of seasonal pollen
(c) low temperature
(d) hot and humid environment.
Answer. B
Question. Which of the following antibodies form innate immunity?
(a) IgE
(b) IgD
(c) IgM
(d) IgG
Answer. D
Question. Tobacco consumption is known to stimulate secretion of adrenaline and nor-adrenaline. The component causing this could be
(a) nicotine
(b) tannic acid
(c) curamin
(d) catechin
Answer. A
Question. Which of the following is not a lymphoid tissue?
(a) Spleen
(b) Tonsils
(c) Pancreas
(d) Thymus
Answer. C
Question. Which of the following glands is large sized at birth but reduces in size with ageing?
(a) Pineal
(b) Pituitary
(c) Thymus
(d) Thyroid
Answer. C
Question. Haemozoin is a
(a) precursor of hemoglobin
(b) toxin released from Streptococcus infected cells
(c) toxin released from Plasmodium infected cells
(d) toxin released from Haemophilus infected cells
Answer. C
Question. To which type of barriers under innate immunity, do the saliva in the mouth and the tears from the eyes, belong?
(a) Physiological barriers
(b) Physical barriers
(c) Cytokine barriers
(d) Cellular barriers.
Answer. A
Question. A person likely to develop tetanus us immunized by administering
(a) performed antibodies
(b) wide spectrum antibotics
(c) weakened germs
(d) dead germs.
Answer. A
Question.The term ‘Health’ is defined in many ways. The most accurate definition of the health would be:
(a) Health is the state of body and mind in a balanced condition
(b) Health is the reflection of a smiling face
(c) Health is a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being
(d) Health is the symbol of economic prosperity.
Answer. C
Question. The clinical test that is used for diagnosis of typhoid is
(a) ELISA
(b) ESR
(c) PCR
(d) Widal
Answer. D
Question. Diseases are broadly grouped into infectious and non-infectious diseases.
In the list given below, identify the infectious diseases.
(i) Cancer (ii) Influenza (iii) Allergy (iv) Small pox
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Answer. D
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease Assertion-Reason Questions
In the following questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Question. Assertion : Interferons are glycoproteins which are produced by virally infected cells.
Reason : Interferons stimulate inflammation at the site of injury.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : Tapeworm, roundworm and pinworm are endoparasites of human intestine.
Reason : Improperly cooked food is the source of intestinal infections.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : Dope test is blood test to know whether a person taking part in a competition used and drug.
Reason : A drunken person usually feels tense and less talkative.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : Mast cells in the human body release excessive amounts of inflammatory chemicals,which cause allergic reactions.
Reason : Allergens in the environment on reaching human body stimulate mast cells in certain individuals.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : Second infection of the same pathogen is quickly eliminated.
Reason : Preformed memory B and T-cells elicit a quick and vigorous attack on pathogens.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : Immunisation is done by successful delivery of vaccines.
Reason : Vaccines are microbial preparations used to induce protective immunity.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : Proto-oncogenes are cellular genes required for normal growth.
Reason : Under certain conditions they lead to the oncogenic transformation of the cell.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : Morphine is useful for patients under depression.
Reason : Morphine is a very effective sedative painkiller.
Answer. D
Question. Assertion : Tobacco contains nicotine which stimulates the adrenal gland.
Reason : Nicotine increases the blood pressure and the heart rate.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : Opioids help to enhance respiratory activity.
Reason : Opioids bind to the receptors in the central nervous system and gastrointestinal tract.
Answer. D
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease Case-based/Source-based Question
1. Study the diagram showing replication of HIV in humans and answer the following questions accordingly:
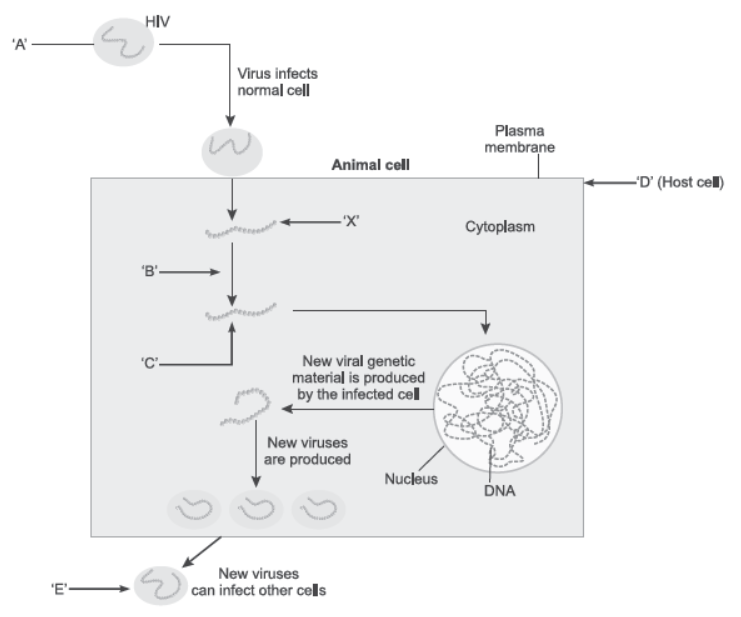
Question. What type of virus causes AIDS? Name its genetic material.
Answer. Retrovirus causes AIDS. RNA is its genetic material.
Question. Name the enzyme ‘B’ acting on ‘X’ to produce molecule ‘C’. Name ‘C’.
Answer. The enzyme ‘B’ is reverse transcriptase, ‘C’ is viral DNA.
Question. Name the type of cells the AIDS virus enters into after getting in the human body.
Answer. Monocytes and helper T-lymphocytes.
2. Study the figures given below and answer the questions that follow.
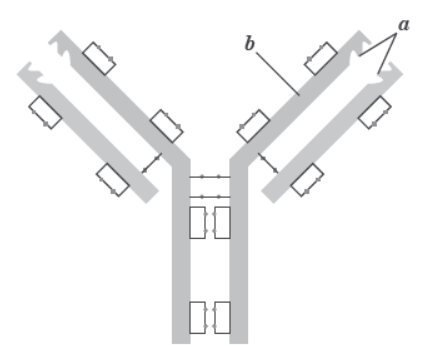
Question. Identify (a) and (b) in the diagram of an antibody molecule given below.
Answer. (a) Antige binding site (b) Heavy chainn
Question. Name the type of cells that produce this molecule.
Answer. B-lymphocytes (B-cells).
Question. Why is an antibody represented as ‘H2L2’ ?
Answer. Each antibody molecule has four polypeptide chains. The two smaller chains are called light chains while the two longer chains are called heavy chains. Therefore an antibody is represented as H2L2.
3. Given below is the structure of an antibody.
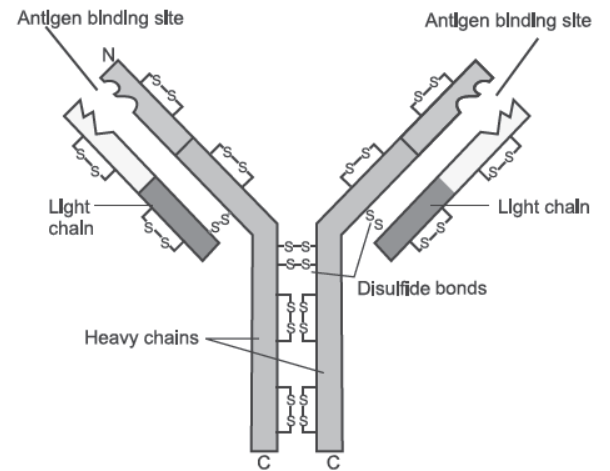
Question. A boy of ten years had chicken pox. He is not expected to have the same disease for the rest of his life. Mention how it is possible.
Answer. The boy when encounters a pathogen for the first time, his body produces antibodies that results in the memory of the first encounter, to protect the body in future.
Question. Why is secondary immune response more intense than the primary immune response in humans?
Answer. This is because of presence of antibodies developed during primary.
Question.(iii) Some allergens trigger sneezing and wheezing in human beings. What causes this type of response by the body?
Answer. The exaggerated response of the immune systems to certain antigens (allergens) present in the environment is the cause of this type of response.
4. Study the figures given below and answer the questions that follow.
Question. Why do sports persons often fall a victim to cocaine addiction?
Answer. Plant source of cocaine is Erythroxylum coca. It has a potent stimulating action on central nervous system, producing a sense of euphoria and increased energy. Excessive dosage of cocaine causes hallucinations.
Question. Why sharing of injection needles between two individuals is not recommended?
Answer. Sharing of needles can transmit diseases like HIV, AIDS, Hepatitis B or C from infected to non-infected individuals.
Question. Mention the useful as well as the harmful drug obtained from the latex of Poppy plant.
Answer. Useful drug—morphine, Harmful drug—heroin.
5. Observe the life cycle of HIV given in the diagram in Q. 1 above, and answer the questions below.
Question. Retroviruses have no DNA. However, the DNA of the infected host cell does possess viral DNA. How is it possible?
Answer. On infecting the host cell, the viral RNA transforms into viral DNA by reverse transcription.
This viral DNA then incorporates into the host DNA.
Question. Name the group of viruses responsible for causing AIDS in humans. Why are these viruses so named?
Answer. Retrovirus cause AIDS in humans. These are named so because they have RNA genome and reverse transcriptase enzyme which carries on the processes RNA → DNA → RNA.
Question. List any two ways of transmission of HIV infection in humans, other than sexual contact.
Answer. Infected blood transfusion, sharing syringes/needles, children born to HIV mothers.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease Very Short Answer Questions
Question. Name two diseases whose spread can be controlled by the eradication of Aedes mosquitoes.
Answer. Dengue/Chikungunya/yellow fever/Eastern equine encephalitis/West Nile fever/Zika virus disease.
Question. What are interferons?
Answer. Virus infected cells secrete proteins called interferons which protect non-infected cells from further viral infection.
Question. “Pranay suffered from measles at the age of 10 years. There are rare chances of his getting infected with the same disease for the rest of his life.” Give reason for the statement.
Answer. First exposure to the infection works as vaccination, the immune system of the body gets familiar with the nature of microorganisms and specific antibodies can be produced against infection.
Question. In what way are monocytes a cellular barrier in immunity?
Answer. Monocytes can phagocytose (by the process called phagocytosis) and thereby destroy the pathogens.
Question. High fever, loss of appetite, stomach pain and constipation are some of the symptoms seen in a patient. How would the doctor confirm that the patient is suffering from typhoid and not amoebiasis?
Answer. By performing Widal test.
Question. Malaria, typhoid, pneumonia and amoebiasis are some of the human infectious diseases.
Which ones of these are transmitted through mechanical carriers?
Answer. Malaria and amoebiasis are transmitted through mechanical carriers.
Question. Name the two intermediate hosts which the human liver fluke depends on to complete its life cycle so as to facilitate parasitization of its primary host.
Answer. Snail and Fish
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease Short Answer Questions
Question. List the two types of immunity a human baby is born with. Explain the differences between the two types.
Answer. The two types of immunity a human baby is born with are innate and passive/acquired immunity.Innate immunity is a non-specific type of defence that provides barrier to the entry of antigens. Passive immunity is a pathogen-specific type of defence in which readymade antibodies are directly given to protect body against foreign agents. The foetus receives antibodies through the placenta.
Question. Name the two types of immune systems in a human body. Why are cell-mediated and humoral immunities so called?
Answer. The two types of immune systems in a human body are innate and adaptive immunity.
Humoral immunity is called so because it consists of antibodies that are present in humors or body fluids, whereas cell-mediated immunity is provided by T-cells and defends body against viruses, fungi and some bacteria which enter host cells. T-cells recognise non-self cells and kill them.
Question. Explain the relationship between B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes in developing an immune response.
Answer. B-lymphocytes produce antibodies to fight pathogen.
T-lymphocytes do not produce antibodies but help B cells to produce them. They can also destroy pathogen directly.
Question. Name the two special types of lymphocytes in humans. How do they differ in their roles in immune response?
Answer. B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes are the lymphocytes in humans.
B-cells produce pathogen specific antibodies and are responsible for humoral immune response.
T-cells help the B-cells to produce antibodies and are responsible for cell-mediated immunity.
Question. What is colostrum? Why is it important to be given to the newborn infants?
Answer. The milk that comes out of the mammary glands during initial days of lactation is called colostrum.
It contains several antibodies (IgA most abundantly), absolutely essential for developing resistance in the new-born babies.
Question. Write the biological (binomial) names of causal organisms of the following diseases:
(a) Typhoid (b) Pneumonia
Answer. (a) Salmonella typhi
(b) Streptococcus pneumoniae
Question. Write the biological (binomial) names of causal organisms of the following diseases:
(a) Elephantiatis (Filariasis) (b) Amoebiasis
Answer. (a) Wuchereria bancrofti and Wuchereria malayi
(b) Entamoeba histolytica
Question. Name the host and the site where the following occur in the life-cycle of a malarial parasite:
(a) Formation of gametocytes]
(b) Fusion of gametocytes
Answer.
| Host | Site of occurrence | |
| (a) Formation of gametocytes | Human | Red blood cells |
| (b) Fusion of gametocytes | Anopheles mosquito | Intestine |
Question. Why does a doctor administer tetanus antitoxin and not a tetanus vaccine to a child injured in a roadside accident with a bleeding wound? Explain.
OR
Why is a person with cuts and bruises following an accident administered tetanus antitoxin?
Give reasons.
Answer. Tetanus is caused by a microbe which has a deadly and fast action. Action of vaccine is slow and this delay may become fatal. Therefore, antitoxins are administered which neutralise the effect of the bacterial toxin.
Question. Name the plant source of the drug popularly called “smack’. How does it affect the body of the abuser?
Answer. Plant source of ‘smack’ is Papaver somniferum or poppy.
Smack is a depressant and slows down body functions.
Question. Name the plant source of cocaine. How does it affect the human body?
OR
Name the drug obtained from Erythroxylum coca and write its effects on the human body.
Answer. Plant source of cocaine is Erythroxylum coca. It has a potent stimulating action on central nervous system, producing a sense of euphoria and increased energy. Excessive dosage of cocaine causes hallucinations.
Question. Name the plant source of ganja. How does it affect the body of the abuser?
OR
From which plant are cannabinoids obtained? Name any two cannabinoids. Which part of the body is affected by consuming these substances? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer. Cannabinoids are obtained from the inflorescence of the plant Cannabis sativa. Marijuana, hashish,charas, ganja are some cannabinoids. These chemicals interact with cannabinoid receptors of the body, mainly present in the brain. Cardiovascular system is affected adversely.
Question. Name the blank spaces a, b, c and d in the table given below:
| Name of the drug | Plant source | Organ system affected |
| a | Poppy plant | b |
| Marijuana | c | d |
Answer. (a) Morphine
(b) Central nervous system
(c) Cannabis sativa
(d) Cardiovascular system.
Question. If a regular dose of drugs or alcohol is not provided to an addicted person, he shows some
withdrawal symptoms. List any four such withdrawal symptoms.
Answer. The withdrawal symptoms are:
(a) Anxiety
(b) Shakiness
(c) Nausea
(d) Sweating
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease Long Answer Questions
Question. Name any two organisms that are responsible for ringworms in humans. Mention two diagnostic symptoms. Name the specific parts of the human body where these organisms thrive and explain why.
Answer. Microsporum/Trichophyton/Epideromophyton.
Symptoms: Dry/scaly lesion on skin/nails/scalp, intense itching.
These organisms thrive in body groin or between toes. They thrive better in heat/moisture/ perspiration.
Question. Study a part of the life cycle of malarial parasite given alongside. Answer the questions that follow:
(a) Mention the roles of ‘A’ in the life cycle of the malarial parasite.
(b) Name the event ‘C’ and the organ where this event occurs.
(c) Identify the organ ‘B’ and name the cells being released from it.
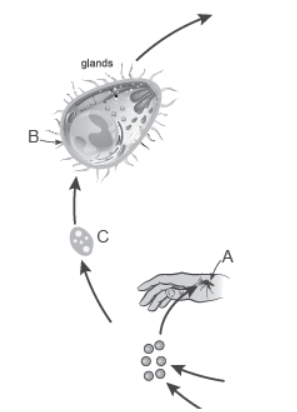
Answer. (a) A—Gametocytes of Plasmodium enter the mosquito when it bites a malarial patient and feed on blood.
(b) C—Fertilisation. It occurs in the intestine of mosquito.
(c) B—Salivary gland of the female Anopheles mosquito. These release sporozoites of Plasmodium.
Question. Write the events that take place when a vaccine for any disease is introduced into the human body.
Answer. The vaccine contains proteins of pathogen or inactivated/weakened pathogen. When a dose of vaccine is introduced into the human body, it behaves as an antigen and the body produces antibodies in response to the antigen. This response generates active immunity. The antibodies thus produced will neutralise the pathogenic agents during actual infection. The vaccines also generate memory B-cells and T-cells that recognise the pathogen quickly on subsequent exposure and overwhelm the invaders with a massive production of antibodies.
Question. Trace the life-cycle of malarial parasite in the human body when bitten by an infected female Anopheles.
Answer. Plasmodium falciparum is the malarial parasite.
(i) Malaria
- It is caused by a protozoan Plasmodium (P. vivax, P. malaria and P. falciparum).
- P. falciparum causes the most serious and fatal malignant malaria.
- The vector of Plasmodium is female Anopheles mosquito which transfers the sporozoites (infectious form).
- Treatment is by antimalarial drugs like quinine, chloroquin.
- Malaria can be prevented by killing mosquitoes by spraying DDT, BHC, etc., and using insect repellents, mosquito nets, etc.
Life cycle of Plasmodium
- Plasmodium requires two hosts to complete its life cycle—human and mosquito.
- The infected female Anopheles mosquito transfers the infectious form of Plasmodium, i.e.,sporozoites to the human body by biting.
- The sporozoites reach the liver cells, where they multiply.
- This is followed by their attack on red blood cells resulting in their rupture.
- The ruptured RBCs release a toxin called haemozoin, which is responsible for high recurring fever, chills and shivering.
- Sexual stages (gametocytes) develop in red blood cells, from where these parasites enter the female Anopheles mosquitoes when they bite an infected person.
- In the body of mosquitoes, they fertilise and multiply in the stomach wall.
- Sporozoites are now stored in the salivary gland of mosquito till it is again transferred to human body by a mosquito bite. After entering the human body, all the events are repeated.
Question. When someone buys packets of cigarettes, cannot miss the statutory warning that is present on the packing which warns against smoking and says how it is injurious to health. Yet, smoking is very prevalent in our society, both among young and old. Advise the adolescents about the importance of avoiding smoking. (Mention any six points.)
Answer. (i) Tobacco in cigarettes contains a large number of chemical substances including nicotine, an alkaloid. Nicotine stimulates adrenal gland to release adrenaline and nor-adrenaline into blood circulation, both of which raise blood pressure and increase heart rate.
(ii) Smoking is associated with increased incidence of cancers of lung, urinary bladder, throat and oral cavity.
(iii) It is responsible for bronchitis and emphysema.
(iv) It is associated with increased risk of coronary heart disease, gastric ulcer, etc.
(v) Smoking increases carbon monoxide (CO) content in blood and reduces the concentration of haem-bound oxygen. This causes oxygen deficiency in the body.
Question. A doctor prescribed morphine as a sedative and pain killer to your cousin who had undergone surgery. Even after recovery, he craved for the prescribed medicine. What do you conclude about his condition, had he continued with the same medication? After appraising yourself,what measures will you suggest to him to overcome this problem? Briefly explain any two.
Answer. His condition is drug dependence. It is the tendency of the body to manifest a characteristic and unpleasant withdrawal syndrome if regular dose of drugs is abruptly discontinued. Because of perceived benefits, drugs are frequently used repeatedly from which the person may not be able to get out.
Following measures can be taken to overcome this problem:
(i) Education and counseling to face problems and stresses and to channelise the energy into healthy pursuits like reading, music, yoga and other extracurricular activities.
(ii) Seeking help from parents to guide the person appropriately and immediately.
(iii) Seeking professional and medical help to the person to get rid of the problem completely with sufficient efforts and will power (any two).
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 1 Reproduction in Organisms |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Human Reproduction |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 4 Reproductive Health |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 5 Principles of Inheritance and Variation |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 7 Evolution |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles And Processes |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystem |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 16 Environmental Issues |
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease
The above provided NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease is available on our website www.studiestoday.com for free download in Pdf. You can read the solutions to all questions given in your Class 12 Biology textbook online or you can easily download them in pdf. The answers to each question in Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease of Biology Class 12 has been designed based on the latest syllabus released for the current year. We have also provided detailed explanations for all difficult topics in Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease Class 12 chapter of Biology so that it can be easier for students to understand all answers. These solutions of Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease NCERT Questions given in your textbook for Class 12 Biology have been designed to help students understand the difficult topics of Biology in an easy manner. These will also help to build a strong foundation in the Biology. There is a combination of theoretical and practical questions relating to all chapters in Biology to check the overall learning of the students of Class 12.
You can download the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the NCERT Solutions issued for Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease have been made available here for latest academic session
Regular revision of NCERT Solutions given on studiestoday for Class 12 subject Biology Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all latest NCERT Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease Class 12 Biology solutions based on the latest books for the current academic session
Yes, NCERT solutions for Class 12 Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease Biology are available in multiple languages, including English, Hindi
All questions given in the end of the chapter Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease have been answered by our teachers

