NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation have been provided below and is also available in Pdf for free download. The NCERT solutions for Class 12 Biology have been prepared as per the latest syllabus, NCERT books and examination pattern suggested in Class 12 by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. Questions given in NCERT book for Class 12 Biology are an important part of exams for Class 12 Biology and if answered properly can help you to get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise answers for NCERT Class 12 Biology and also download more latest study material for all subjects. Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation is an important topic in Class 12, please refer to answers provided below to help you score better in exams
Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation Class 12 Biology NCERT Solutions
Class 12 Biology students should refer to the following NCERT questions with answers for Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation in Class 12. These NCERT Solutions with answers for Class 12 Biology will come in exams and help you to score good marks
Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology
Question. Name the three important components of biodiversity.
Answer. The three important components of biodiversity are: genetic diversity, species diversity and ecological diversity.
Question. How do ecologists estimate the total number of species present in the world?
Answer. There are two methods to estimate the number of species in the world:
(i) By estimating the rate of discovery of new species.
(ii) By statistical comparison of the temperate–tropical species richness of an exhaustively studied group of insects and extrapolate this ratio to other groups of animals and plants to come up with a gross estimate of the number of species on earth.
Question. Write any three hypotheses put forth by ecologists explaining the existence of greater biodiversity in tropical regions than in temperate regions.
Answer. The three hypotheses to explain species richness in tropics are:
(i) The constant environment in tropics promotes niche specialisation and increased species diversity.
(ii) There is longer exposure to solar radiation in the tropical regions that contributes directly to higher productivity and indirectly to greater species diversity.
(iii) There occurred no glaciation in tropical region and it remained undisturbed. Thus organisms living in tropics continued to flourish and evolved more species diversity.
Question. What is the significance of the slope of regression in a species–area relationship?
Answer. Slope of regression in a species–area relationship indicates that species richness decreases with the decrease in area. Regression coefficient (Z) is 0.1–0.2 regardless of the taxonomic group or the region. However, when very large areas like the entire continent is analysed, it was found that slope of the line is much steeper with Z values in the range of 0.6 – 1.2.
Question. What are the major causes of species losses in a geographical region?
Answer. There are four major causes (The Evil Quartet):
(i) Habitat loss and fragmentation (ii) Over-exploitation
(iii) Alien species invasions (iv) Co-extinctions
Question. How is biodiversity important for ecosystem functioning?
Answer. Importance of biodiversity for ecosystem functioning:
(i) Stability: Biodiversity is an important aspect for stability of an ecosystem. Ecologists believe that communities with more species tend to be more stable than those with less species.
(ii) Productivity: Ecosystem with higher biodiversity show more productivity than ecosystems with lower biodiversity. David Tilman’s long-term ecosystem experiments using outdoor plots provide confirmation.
(iii) Ecosystem health: Rich biodiversity is not only essential for ecosystem health but imperative for the survival of the human race on earth. Species are interlinked and so, killing or disappearance of one would effect the others also.
(iv) Resilience: Increased biodiversity provides resilience of the ecosystem against natural or man-made disturbances.
Question. What are sacred groves? What is their role in conservation?
Answer. Sacred groves are forest patches for worship in several parts of India. All the trees and wildlife in them are venerated and given total protection. They are found in Khasi and Jaintia Hills in Meghalaya, Western Ghat regions of Karnataka and Maharashtra, etc. Tribals do not allow anyone to cut even a single branch of tree in these sacred groves, thus sacred groves have been free from all types of exploitations.
Question. Among the ecosystem services are control of floods and soil erosion. How is this achieved by the biotic components of the ecosystem?
Answer. Control of soil erosion: Plant roots hold the soil particles tightly and do not allow the top soil to be drifted away by winds or moving water. Plants increase the porosity and fertility of the soil.
Control of floods: It is carried out by retaining water and preventing run off of rain water. Litter and humus of plants function as sponges thus retaining the water which percolates down and get stored as underground water. Hence, the flood is controlled.
Question. The species diversity of plants (22 per cent) is much less than that of animals (72 per cent).What could be the explanations to how animals achieved greater diversification?
Answer. Animals have achieved greater diversification than plants due to following reasons:
(i) They are mobile and thus can move away from their predators or unfavourable environments.
On the other hand, plants are fixed and have fewer adaptation to obtain optimum amount of raw materials and sunlight therefore, they show lesser diversity.
(ii) Animals have well-developed nervous system to receive stimuli against external factors and thus can respond to them. On the other hand, plants do not exhibit any such mechanism,thus, they show lesser diversity than animals.
Question. Can you think of a situation where we deliberately want to make a species extinct? How would you justify it?
Answer. Species which are harmful to human beings can be made extinct, e.g., HIV, polio virus, etc. Such micro-organisms are not part of any food chain and thus, their extinction would not affect the ecosystem.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation Multiple Choice Questions
Question. Biodiversity of a geographical region represents
(a) endangered species found in the region
(b) the diversity in the organisms living in the region
(c) genetic diversity in the dominant species of the region
(d) species endemic to the region
Answer. B
Question. Which of the following countries has the highest biodiversity?
(a) South America
(b) South Africa
(c) Russia
(d) India
Answer. A
Question. Which one of the following is an example of ex situ conservation?
(a) Wildlife sanctuary
(b) Seed bank
(c) Sacred groves
(d) National park
Answer. B
Question. Which one of the following is correct expanded form of the following acronyms?
(a) IPCC = International Panel for Climate Change
(b) UNEP = United Nations Environmental Policy
(c) EPA = Environmental Pollution Agency
(d) IUCN = International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources
Answer. D
Question. A collection of plants and seed having diverse alleles of all the genes of a crop is called
(a) herbarium
(b) germplasm
(c) gene library
(d) genome
Answer. B
Question. The active chemical drug reserpine is obtained from:
(a) Datura
(b) Rauwolfia
(c) Atropa
(d) Papaver
Answer. B
Question. Which of the following is not a cause for loss of biodiversity?
(a) Destruction of habitat
(b) Invasion by alien species
(c) Keeping animals in zoological parks
(d) Over-exploitation of natural resources
Answer. C
Question. Where among the following will you find pitcher plant?
(a) Rain forest of North-East India
(b) Sunderbans
(c) Thar Desert
(d) Western Ghats
Answer. A
Question. Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) Parthenium is an endemic species of our country.
(b) African catfish is not a threat to indigenous catfishes.
(c) Steller’s sea cow is an extinct animal.
(d) Lantana is popularly known as carrot grass.
Answer. C
Question. Which one of the following is not a major characteristic feature of biodiversity hot spots?
(a) Large number of species
(b) Abundance of endemic species
(c) Mostly located in the tropics
(d) Mostly located in the polar regions
Answer. C
Question. What is common to the following plants: Nepenthes, Psilotum, Rauwolfia and Aconitum?
(a) All are ornamental plants
(b) All are phylogenic link species
(c) All are prone to over exploitation
(d) All are exclusively present in the Eastern Himalayas.
Answer. C
Question. The one-horned rhinoceros is specific to which of the following sanctuary?
(a) Bhitar Kanika
(b) Bandipur
(c) Kaziranga
(d) Corbett park
Answer. C
Question. Which one of the following pairs of organisms are exotic species introduced in India?
(a) Lantana camara, water hyacinth
(b) Water hyacinth, Prosopis cinereria
(c) Nile perch, Ficus religiosa
(d) Ficus religiosa, Lantana camara
Answer. A
Question. Which of the following group exhibit more species diversity?
(a) Gymnosperms
(b) Algae
(c) Bryophytes
(d) Fungi
Answer. D
Question. Which one of the following is not observed in biodiversity hot spots?
(a) Lesser inter-specific competition
(b) Species richness
(c) Endemism
(d) Accelerated species loss
Answer. A
Question. Amongst the animal groups given below, which one appears to be more vulnerable to extinction?
(a) Insects
(b) Mammals
(c) Amphibians
(d) Reptiles
Answer. C
Question. The historic convention on Biological Diversity held in Rio de Janeiro in 1992 is known as
(a) CITES Convention
(b) The Earth Summit
(c) G-16 Summit
(d) MAB Programme
Answer. B
Question. What is common to the techniques (i) in vitro fertilisation, (ii) Cryopreservation and (iii) tissue culture?
(a) All are in situ conservation methods.
(b) All are ex situ conservation methods.
(c) All require ultra modern equipment and large space.
(d) All are methods of conservation of extinct organisms.
Answer. B
Question. Which one of the following is an endangered plant species of India?
(a) Rauwolfia serpentina
(b) Santalum album (Sandal wood)
(c) Cycas beddonei
(d) All of the above
Answer. D
Question. Keystone species deserve protection because these
(a) are capable of surviving in harsh environmental condition
(b) indicate presence of certain mineral in the soil.
(c) have become rare due to overexploitation.
(d) play an important role in supporting other species.
Answer. D
Question. Which of the following is not an invasive alien species in the Indian context?
(a) Lantana
(b) Cynodon
(c) Parthenium
(d) Eichhornia
Answer. B
Question. Among the ecosystem mentioned below, where can one find maximum biodiversity?
(a) Mangroves
(b) Desert
(c) Coral reefs
(d) Alpine meadows
Answer. C
Question. Genetic diversity in agricultural crops is threatened by
(a) intensive use of pesticides
(b) extensive intercropping
(c) intensive use of fertilisers
(d) introduction of high yielding varieties.
Answer. D
Question. What is common to Lantana, Eichhornia and African catfish?
(a) All are endangered species of India.
(b) All are keystone species.
(c) All are mammals found in India.
(d) All the species are neither threatened nor indigenous species of India.
Answer. D
Question. Which of the following forests is known as the ‘lungs of the planet Earth’?
(a) Taiga forest
(b) Tundra forest
(c) Amazon rainforest
(d) Rainforests of North East India
Answer. C
Question. Match the animals given in column I with their location in column II.
Column I Column II
A. Dodo (i) Africa
B. Quagga (ii) Russia
C. Thylacine (iii) Mauritius
D. Stellar’s sea cow (iv) Australia
Choose the correct match from the following.
(a) A-(i), B-(iii), C-(ii), D-(iv)
(b) A-(iv), B-(iii), C-(i), D-(ii)
(c) A-(iii), B-(i), C-(ii), D-(iv)
(d) A-(iii), B-(i), C-(iv), D-(ii)
Answer. D
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation Assertion-Reason Questions
In the following questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Question. Assertion : Tropical rainforests are disappearing fast from developing countries like India.
Reason : No value is attached to these forests because they are poor in biodiversity.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : Tropical rainforest are rich in flora and founa along with microbes on this biosphere.
Reason : The low latitude humid tropics harbor the rainforest ecosystems.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : Biodiversity is declining at an accelerated rate.
Reason : Exotic species cause extinction of endemic species.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : Tropical rainforest are rich in species diversity than temperate forest.
Reason : Frequent glaciation was quite common in temperate region in the part and absent in tropical rainforest.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : IUCN maintains the red list of threatened species to assess conservation of different species.
Reason : Threatened species are those living species which are on the verge of extinction.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : According to broadly utilitarian arguments, biodiversity needs to be conserved as it plays important role in many ecosystem services.
Reason : Species diversity at molecular and genetic levels are explored to obtain products of economic importance.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : Species with high genetic variability are at greater risk of extinction than species with low genetic variability.
Reason : Species with low genetic variability are more vulnerable to predators and environmental challenges.
Answer. D
Question. Assertion : Biodiversity loss of a region is only dependent on the human population around the region.
Reason : Overexploitation of a species reduces the size of its population and can eventually lead to its extinction.
Answer. D
Question. Assertion : Nile Perch introduced into Lake Victoria in east Africa lead to extinction of many species of Cichlid fish.
Reason : When alien species are introduced in a region, they become invasive and cause extinction of indigenous species.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : Traditionally, sacred groves acted as repository for various medicines.
Reason : In modern times, sacred groves have become biodiversity rich areas.
Answer. B
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation Case-based/Source-based Question
1. The following graph shows the species–area relationship. Answer the following questions as directed.
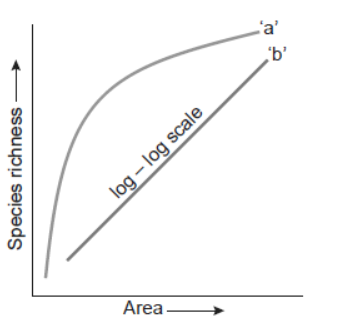
Question. Name the naturalist who studied the kind of relationship shown in the graph. Write the observations made by him.
Answer. Alexander von Humboldt.He observed that within a region, species richness increased with increasing explored area but only up to a limit.
Question. Write the situations as discovered by the ecologists when the value of ‘Z’ (slope of the line) lies between (a) 0.1 and 0.2 (b) 0.6 and 1.2.
What does ‘Z’ stand for?
Answer. (a) The slopes regression lines are similar when unaffected distribution in an area is analysed.
(b) The slope of regression is steeper when we analyse the species area relationship among very large areas like entire continent.
Z (slope of the line) is the regression co-efficient.
Question. When would the slope of the line ‘b’ become steeper?
Answer. If species richness is more, i.e., in the range 0.62-1.2.
2. Observe the global biodiversity distribution of major plant taxa in the diagram alongside and answer the questions that follow.
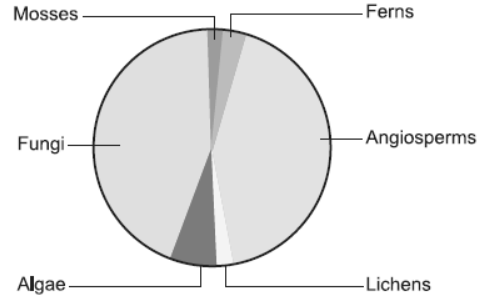
Question. Which group of plants are most endangered?
Answer. Lichens.
Question. Why are mosses/ferns so few? Give reason.
Answer. Mosses and ferns are few as they need humid conditions in forests that are fast disappearing.
Question. How do fungi that are heterotrophs sustain themselves as a large population?
Answer. Fungi are able to sustain themselves as a large population because of their wider adaptability to the changing environmental conditions and they grow on dead organic matter.
Question. Which group of plants is most advanced and which one is most primitive?
Answer. Most advanced group is of angiosperms and most primitive group is of fungi.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation Very Short Answer Questions
Question. What is the difference between endemic and exotic species?
Answer. Endemic species are native species restricted to a particular geographical region. Exotic species are species which are introduced from other geographical regions into an area.
Question. Western Ghats have a greater amphibian diversity than the Eastern Ghats. What do you infer from the above two statements?
Answer. It can be inferred that Western Ghats have a greater species diversity.
Question. India has more than 50,000 strains of rice. Mention the level of biodiversity it represents.
Answer. 50,000 strains of rice represent genetic biodiversity.
Question. What are Ramsar sites?
Answer. Ramsar sites are conserved wetlands which are of international importance.
Question. Name the type of biodiversity represented by the following:
(i) 1000 varieties of mangoes in India.
(ii) Variations in terms of potency and concentration of reserpine in Rauwolfia vomitoria growing in different regions of Himalayas.
Answer. (i) Genetic diversity
(ii) Genetic diversity
Question. What are seed banks?
Answer. The collection of seeds of many different genetic strains of commercially important plants, that are kept viable for longer periods in place are called seed banks.
Question. What is Red Data Book?
Answer. The Red Data Book is a compilation of data on species threatened with extinction and is maintained by IUCN.
Question. Name the unlabelled areas ‘a’ and ‘b’ of the pie chart (given alongside) representing the global biodiversity of invertebrates showing their proportionate number of species of major taxa.
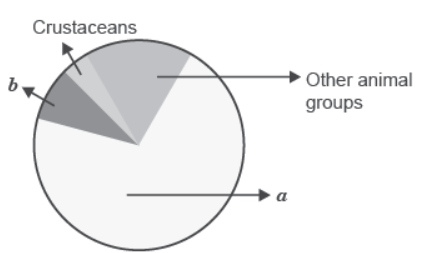
Answer. a → Insects;
b → Molluscs
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation Short Answer Questions
Question. Would the extinction of one insect pollinator affect the ecosystem? Explain.
Answer. It would affect the ecosystem because insect pollinators form a part of food web. It may lead to coextinction of species in the case of a co-evolved plant. It is a case of mutualism where extinction of one invariably leads to the extinction of the other.
Question. Lantana and Eichhornia are examples of two weeds. How do they affect the ecosystem?
Answer. These are examples of Alien species invasions. They threaten the indigenous species and lead to their extinction.
Question. What is IUCN red list? Give any two uses of this list.
Answer. IUCN red list is a catalogue of species and subspecies that are facing the risk of extinction.
The two uses of this list are:
(i) Provides information and develops awareness about the importance of threatened species.
(ii) Identification and documentation of endangered species and so measures can be taken for their protection.
Question. Explain, giving one example, how co-extinction is one of the causes of loss of biodiversity. List the three other causes also (without description).
Answer. When a species becomes extinct, the plant and animal species associated with it in an obligatory may also become extinct. This is called co-extinction. For example, when a host fish species becomes extinct, its unique assemblage of parasites also becomes extinct.
The three other causes are:
(i) Habitat loss and fragmentation,
(ii) Over-exploitation,
(iii) Alien species invasion.
Question. Why should biodiversity be conserved? List any two ethical arguments in its support.
Answer. The biodiversity should be conserved because of the following reasons: (Any two)
(i) Narrowly utilitarian arguments for deriving direct economic benefit from nature.
(ii) Broadly utilitarian arguments as biodiversity plays a major role in many ecosystem services.
(iii) Ethical reasons: There is a need to realise that every species has an intrinsic value and we need to pass on our biological legacy to future generations.
Question. Explain the effect on the characteristics of a river when urban sewage is discharged into it.
Answer. —Rise in organic matter, leads to increased microbial activity/growth of microbes.
—It results in decrease in dissolved oxygen/rise in Biochemical Oxygen Demand.
—Leads to fish mortality/algal bloom/colour change/foul odour/increase in toxicity.
Question. Alien species are highly invasive and are a threat to indigenous species. Substantiate this statement with any three examples.
Answer. Exotic species are defined as species that have been introduced from another geographic region to an area outside its natural range. For example,
(i) Parthenium, Lantana and Eichhornia are the exotic species of plants that have invaded the native species of India and caused environmental damage.
(ii) Introduction of African catfish Clarias gariepinus for aquaculture purpose is posing threat to many indigenous catfish.
(iii) Nile perch introduced into lake Victoria in East Africa led to the extinction of cichlid fish.
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 1 Reproduction in Organisms |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Human Reproduction |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 4 Reproductive Health |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 5 Principles of Inheritance and Variation |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 7 Evolution |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles And Processes |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystem |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 16 Environmental Issues |
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation
The above provided NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation is available on our website www.studiestoday.com for free download in Pdf. You can read the solutions to all questions given in your Class 12 Biology textbook online or you can easily download them in pdf. The answers to each question in Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation of Biology Class 12 has been designed based on the latest syllabus released for the current year. We have also provided detailed explanations for all difficult topics in Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation Class 12 chapter of Biology so that it can be easier for students to understand all answers. These solutions of Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation NCERT Questions given in your textbook for Class 12 Biology have been designed to help students understand the difficult topics of Biology in an easy manner. These will also help to build a strong foundation in the Biology. There is a combination of theoretical and practical questions relating to all chapters in Biology to check the overall learning of the students of Class 12.
You can download the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the NCERT Solutions issued for Class 12 Biology Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation have been made available here for latest academic session
Regular revision of NCERT Solutions given on studiestoday for Class 12 subject Biology Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all latest NCERT Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation Class 12 Biology solutions based on the latest books for the current academic session
Yes, NCERT solutions for Class 12 Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation Biology are available in multiple languages, including English, Hindi
All questions given in the end of the chapter Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation have been answered by our teachers

