NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications have been provided below and is also available in Pdf for free download. The NCERT solutions for Class 12 Biology have been prepared as per the latest syllabus, NCERT books and examination pattern suggested in Class 12 by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. Questions given in NCERT book for Class 12 Biology are an important part of exams for Class 12 Biology and if answered properly can help you to get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise answers for NCERT Class 12 Biology and also download more latest study material for all subjects. Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications is an important topic in Class 12, please refer to answers provided below to help you score better in exams
Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications Class 12 Biology NCERT Solutions
Class 12 Biology students should refer to the following NCERT questions with answers for Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications in Class 12. These NCERT Solutions with answers for Class 12 Biology will come in exams and help you to score good marks
Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology
Question. Crystals of Bt toxin produced by some bacteria do not kill the bacteria themselves because—
(a) bacteria are resistant to the toxin;
(b) toxin is immature;
(c) toxin is inactive;
(d) bacteria encloses toxin in a special sac.
Answer. (c) toxin is inactive.
Question. What are transgenic bacteria? Illustrate using any one example.
Answer. The bacteria whose DNA is manipulated to carry and express a foreign DNA is called transgenic bacteria. These microbes are used for producing important biochemicals. They have been synthesising alcohol, enzymes, steroids and antibiotics. Example, Bacillus thuringiensis for Bt cotton. For details refer basic concept point 1(i) and 2(i).
Question. Compare and contrast the advantages and disadvantages of production of genetically modified crops.
Answer. Advantages of genetically modified crops:
- Reduces the use of chemical fertilisers and pesticides which cause pollution (air, water and soil).
- Production of new resistant varieties against pathogen, droughts, salinity, etc.
- Provides raw materials to industries like pharmaceuticals.
- Genetically modified crops have enhanced nutritional quality and yield.
- These crops grow fast and produce high yield through modifications.
Disadvantages of genetically modified crops:
- Proteins produced by GM organisms might cause allergy and other reactions.
- Resistance characters might develop in intestinal bacteria against antibiotics.
- Resistant genes transferred by pollen to the weeds may also become resistant to pests.
Question. What are Cry proteins? Name an organism that produce it. How has man exploited this protein to his benefit?
Answer. Cry protein (crystal protein) is a toxin coded by a gene cry and is poisonous to some insects, thus giving resistant characters to the plants. Bacillus thuringiensis produces Cry protein. Cry protein producing gene is transferred to the plants to provide resistance against insect larvae. Man has developed several transgenic crops by introducing these genes from bacteria to crop plants such as Bt cotton, Bt corn, etc.
Question. What is gene therapy? Illustrate using the example of adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency.
Answer. Gene therapy is a method which corrects or replaces the defective genes. In 1900, first clinical gene therapy was given to a 4-year old girl with adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency. This enzyme plays an important role in functioning of immune system. This disorder is caused due to the deletion of the gene for adenosine deaminase. In gene therapy, lymphocytes from the blood of the patient are grown in a culture outside the body. A functional ADA cDNA (using a retroviral vector) is then introduced into these lymphocytes, which are returned to the patients. However, as these cells are not immortal, hence the patient requires periodic infusion of such genetically engineered lymphocytes.
Question. Diagrammatically represent the experimental steps in cloning and expressing a human gene (say the gene for growth hormone) into bacterium like E. coli.
Answer. It is possible to produce HGH (human growth hormone) by recombinant DNA technology. This is represented diagrammatically as follows:
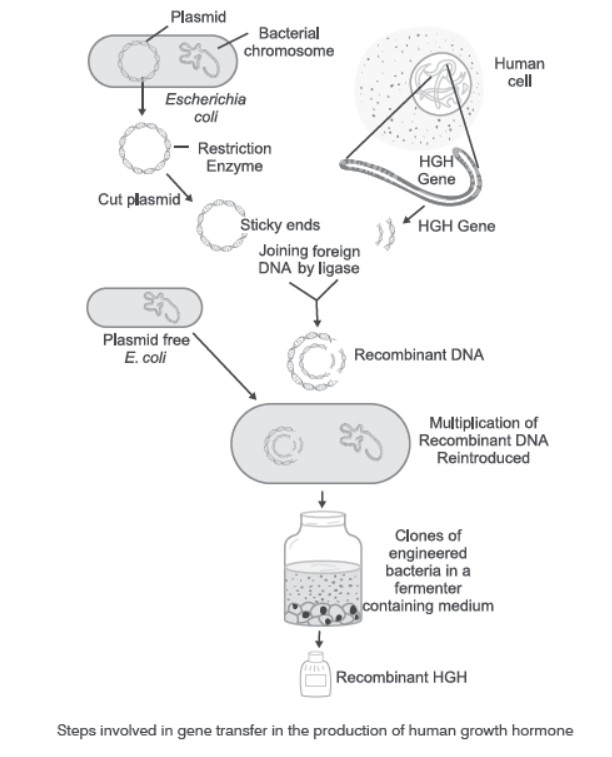
Question. Can you suggest a method to remove oil (hydrocarbon) from seeds based on your understanding of rDNA technology and chemistry of oil?
Answer. To remove oil from seeds, the genes responsible for formation of glycerol or fatty acids need to be identified and removed by using restriction endonucleases. The restricted DNA of the seed then needs to be ligated using the enzyme ligase and allowed to grow in nutrient media under aseptic condition.
Question. Find out from internet what is golden rice.
Answer. Golden rice is a genetically modified rice that contains b-carotene (provitamin A). This provitamin A is converted into vitamin A inside the body and gives the rice grain its characteristic golden colour. It produces two new enzymes that completes the b-carotene expression in the grain. It is intended to complement current strategies in the fight against vitamin A deficiency.
Question. Does our blood have proteases and nucleases?
Answer. Blood does not contain proteases and nucleases because their function is to breakdown proteins and nucleic acids.
Question. Consult internet and find out how to make orally active protein pharmaceutical. What is the major problem to be encountered?
Answer. Orally active protein pharmaceutical can be made by lining it with a substance that will dissolve after it has passed through the stomach.
The major problem encountered is that the stomach enzymes and acids may denature the therapeutic protein and render it ineffective.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications Multiple Choice Questions
Question. The site of production of ADA in the body is
(a) erythrocytes
(b) lymphocytes
(c) blood plasma
(d) osteocytes
Answer. B
Question. What is true about Bt toxin?
(a) Bt protein exists as active toxin in the Bacillus.
(b) The activated toxin enters the ovaries of the pest to sterilise it and thus prevent its multiplication.
(c) The concerned Bacillus has antitoxins.
(d) The inactive protoxin gets converted into active form in the insect gut.
Answer. D
Question. Biopiracy means
(a) use of biopatents
(b) thefts of plants and animals
(c) stealing of bioresources
(d) exploitation of bioresources without authentic permission
Answer. D
Question. A probe which is a molecule used to locate homologous sequences in a mixture of DNA or RNA molecules could be:
(a) a ssRNA
(b) a ssDNA
(c) either RNA or DNA
(d) can be ssDNA but not ssRNA
Answer. C
Question. During the processing of ‘proinsulin’ into mature ‘insulin’
(a) A – chain is removed
(b) C – chain is removed
(c) B – chain is removed
(d) No peptide chain is removed
Answer. B
Question. Genetic engineering has been successfully used for producing
(a) transgenic mice for testing safety of polio vaccine before use in humans
(b) transgenic models for studying new treatments for certain cardiac diseases
(c) transgenic cow-Rosie which produces high fat milk for making ghee
(d) animals like bulls for farm work as they have super power
Answer. A
Question. Pathophysiology is the
(a) study of physiology of pathogen
(b) study of normal physiology of host
(c) study of altered physiology of host
(d) none of the above
Answer. C
Question. Bt cotton is not
(a) a GM plant
(b) insect resistant
(c) a bacterial gene expressing system
(d) resistant to all pesticides
Answer. D
Question. C-peptide of human insulin is
(a) a part of mature insulin molecule
(b) responsible for formation of disulphide bridges
(c) removed during maturation of proinsulin to insulin
(d) tesponsible for its biological activity.
Answer. C
Question. GEAC stands for
(a) Genome Engineering Action Committee
(b) Ground Environment Action Committee
(c) Genetic Engineering Approval Committee
(d) Genetic and Environment Approval committee
Answer. C
Question. A protoxin is
(a) a primitive toxin
(b) a denatured toxin
(c) toxin produced by protozoa
(d) inactive toxin
Answer. D
Question. The trigger for activation of toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis is
(a) acidic pH of stomach
(b) high temperature
(c) alkaline pH of gut
(d) mechanical action in the insect gut
Answer. C
Question. a-1-antitrypsin is
(a) an antacid
(b) an enzyme
(c) used to treat arthritis
(d) used to treat emphysema
Answer. D
Question. What is antisense technology?
(a) When a piece of RNA that is complementary in sequence is used to stop expression of a specific gene.
(b) RNA polymerase producing DNA.
(c) A cell displaying a foreign antigen used for synthesis of antigens.
(d) Production of somaclonal variants in tissue cultures.
Answer. A
Question. Cry I endotoxins obtained from Bacillus thuringiensis are effective against
(a) nematodes
(b) bollworms
(c) mosquitoes
(d) flies
Answer. B
Question. Human insulin is being commercially produced from a transgenic species of
(a) Rhizobium
(b) Saccharomyces
(c) Escherichia
(d) Mycobacterium
Answer. C
Question. Human insulin is being commercially produced from a transgenic species of
(a) Rhizobium
(b) Saccharomyces
(c) Escherichia
(d) Mycobacterium
Answer. C
Question. Choose the correct option regarding retrovirus.
(a) An RNA virus that synthesises DNA during infection
(b) A DNA virus that synthesises RNA during infection
(c) A ssDNA virus
(d) A dsRNA virus
Answer. A
Question. Which one of the following is commonly used in transfer of foreign DNA into crop plants?
(a) Meloidogyne incognita
(b) Agrobacterium tumefaciens
(c) Penicillium expansum
(d) Trichoderma harzianum
Answer. B
Question. Bt corn has been made resistant from corn borer disease by introduction of the gene
(a) cryIAb
(b) ampR
(c) cryIIAb
(d) trp
Answer. A
Question. A bioreactor refers to
(a) fermentation tank
(b) tank for biochemical reactions
(c) organisms reacting to a stimulus
(d) tank for biochemical waste
Answer. A
Question. Golden rice is
(a) a variety of rice grown along the yellow river in China
(b) long stored rice having yellow colour tint
(c) a transgenic rice having gene for b-carotene
(d) wild variety of rice with yellow coloured grains
Answer. C
Question. In RNAi, genes are silenced using
(a) ssDNA
(b) dsDNA
(c) dsRNA
(d) ssRNA
Answer. C
Question. Silencing of a gene could be achieved through the use of
(a) RNAi only
(b) antisense RNA only
(c) both RNAi and antisense RNA
(d) none of the above
Answer. C
Question. The first clinical gene therapy was done for the treatment of
(a) AIDS
(b) Cancer
(c) Cystic fibrosis
(d) SCID (Severe Combined Immuno Deficiency resulting form deficiency of ADA)
Answer. D
Question. ADA is an enzyme which is deficient in a genetic disorder SCID. What is the full form of ADA?
(a) Adenosine deoxyaminase
(b) Adenosine deaminase
(c) Aspartate deaminase
(d) Arginine deaminase
Answer. B
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications Assertion-Reason Questions
In the following questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Question. Assertion : Agrobacterium tumefaciens is popular in genetic engineering because it spontaneously transfers tumour inducing gene to broad leaf dicot plants.
Reason : A gene incorporated in the bacterial chromosomal genome gets autonomically transferred to be crop with which the bacterium is associated.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : Genetic engineering is mainly involved in production of transgenic animals that produce proteins.
Reason : Transgenic plants can be obtained by combination of tissue culture and genetic engineering.
Answer. D
Question. Assertion : The first gene therapy was given for ADA deficiency.
Reason : The normal gene for ADA was delivered to patient’s cells using retroviral vector.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : Orgnisations like Genetic Engineering Approval Committee (GAEC) monitor GM researches.
Reason : Some ethical standards are required to evaluate the morality of all human activities.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : Human insulin is produced in E. coli.
Reason : In mammals, insulin is synthesised as a pro-hormone which contains an extra stretch of protein.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : The RNAi can be introduced in an organism only by inserting the gene encoding complementary RNA.
Reason : The complement of the mRNA sense strand usually contains the sequence of codons for producing functional protein.
Answer. D
Question. Assertion : ‘Cry’ proteins are named so because they are crystal proteins.
Reason : ‘Cry’ proteins solubilise in alkaline pH of the insect’s gut and activate Bt toxin.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : Patents are granted by government to an inventor.
Reason : Patent prevents other from commercial use of an invention.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : Stem cells are undifferentiated biological cells found in multicellular organisms.
Reason : They are obtained from only umbilical cord blood just after birth.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : Indian Patents Bill takes cases of biopiracy in consideration.
Reason : Biopiracy is the use of bioresources by multinational companies without proper authorisation from concerned persons and countries.
Answer. B
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications Case-based/Source-based Question
1. Refer to the diagram of maturation of proinsulin into insulin to answer the following questions
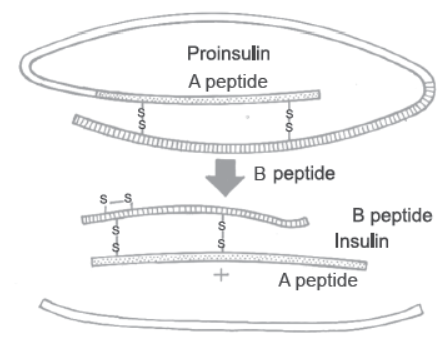
Question. How are two short polypeptide chains of insulin linked together?
Answer. Two short polypeptide chains of insulin are linked together by disulphide bridges.
Question. State the role of C-peptide in human insulin.
Answer. C-peptide (extra stretch of polypeptide) makes the insulin inactive.
Question. Mention the chemical change that proinsulin undergoes, to be able to act as mature insulin.
Answer. An extra stretch called C-peptide is removed from pro-insulin during maturation.
2.
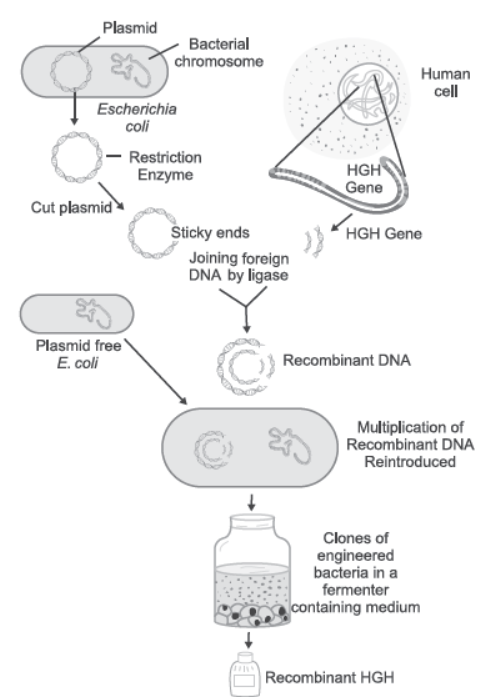
Human growth hormone can be cloned and expressed experimentally with the steps shown above.
Question. What is the host called that produces a foreign gene product? What is this product called?
Answer. The host that produces a foreign gene product is called competent host. The product is called recombinant protein.
Question. Write the name of the enzymes that are used for isolation of DNA from bacterial and fungal cells respectively for Recombinant DNA technology.
Answer. Bacterial cell is treated with enzyme lysozyme.
Fungal cell is treated with chitinase.
Question. How can bacterial DNA be released from the bacterial cell for biotechnology experiments?
Answer. The bacterial cell wall is digested by the enzyme lysozyme to release DNA from the cell.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications Very Short Answer Questions
Question. PCR requires very high temperature conditions where most of the enzymes get denatured.
How was this problem resolved in a PCR?
Answer. This problem was resolved by the use of a thermostable DNA polymerase, Taq polymerase derived from Thermus aquaticus which remains active during the high temperature and induces denaturation of double stranded DNA.
Question. Why is the gene encoding for ‘Cry’ protein inserted into a crop plant?
Answer. Cry protein producing gene is transferred to the plant to provide resistance against insect larvae.
Question. Name any two techniques that serve the purpose of early diagnosis of some bacterial/viral human diseases.
Answer. Enzyme linked immuno sorbent (ELISA) and Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) serve the purpose of early diagnosis of human diseases.
Question. What is the significance of the process of RNA interference (RNAi) in eukaryotic organisms?
Answer. RNA interference in all eukaryotic organisms is a method of cellular defence.
Question. Name the first transgenic cow. Which gene was introduced in this cow?
Answer. Rosie was the first transgenic cow. Human a-lactalbumin gene was introduced.
Question. Name the specific type of gene that is incorporated in a cotton plant to protect the plant against cotton boll worm infestation.
Answer. Cry IAc/Cry IIAb genes are incorporated in a cotton plant.
Question. State a method of cellular defence which works in all eukaryotic organisms.
Answer. RNA interference.
Question. State the role of transposons in silencing of mRNA in eukaryotic cells.
Answer. Transposons or mobile genetic elements in viruses are the sources of the complementary dsRNA,which in turn bind to specific mRNA and cause RNA interference of the parasite.
Question. A boy has been diagnosed with ADA deficiency. Suggest any one possible treatment.
Answer. Bone marrow transplant/enzyme replacement therapy/gene therapy.
Question. Why do children cured by enzyme-replacement therapy for adenosine deaminase deficiency need periodic treatment?
Answer. As enzyme replacement therapy does not cure the disease completely, it requires periodic treatment.
Question. Name two genetically modified hormones.
Answer. Insulin and human growth hormones.
Question. Give the name of HGH (Human Growth Hormones), developed during recombinant DNA technology and used for treating hypopituitary dwarfism in human.
Answer. Somatotropin.
Question. Mention the source organism of the gene cryIAc and its target pest.
Answer. Source organism — Bacillus thuringiensis
Target pest — Cotton bollworms
Question. What are transgenic animals? Give an example.
Answer. Animals that have had their DNA manipulated, to possess and express an extra (foreign) gene are known as transgenic animals. Example, Rosie is a transgenic cow.
Question. What was the speciality of the milk produced by the transgenic cow Rosie?
Answer. The first transgenic cow, Rosie, produced milk with human alpha-lactalbumin (2.4 g protein/ litre of milk) which was nutritionally, more balanced product for human babies than natural cow milk.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications Short Answer Questions
Question. Explain the process of RNA interference.
Answer. RNA interference takes place in all eukaryotic organisms as a method of cellular defence. It involves silencing of a specific mRNA due to complementary dsRNA molecule that binds to and prevents translation of the mRNA.
Question. Name the source and the types of cry genes isolated from it for incorporation into crops by biotechnologists. Explain how have these genes brought beneficial changes in the genetically modified crops.
Answer. Source of cry gene is Bacillus thuringiensis.
The following type of cry genes are isolated from it: cryIAc, cryIIAb, cryIAb.
The introduction of cry gene acts as biopesticide. The cry gene produce crystals of toxic insecticidal protein. The activated toxin causes death of the insect.
Question. cryIAb is introduced in a plant to control infestation by corn borer.
(a) Name the resultant plant after successful insertion of the gene desired.
(b) Summarise the action of the gene introduced.
Answer. (a) Bt corn
(b) CryIAb/Bt toxin gene codes for crystal protein; the Bt toxin protein exists as an inactive protein, but once an insect ingests it, it gets converted into an active form due to the alkaline pH of the gut which solubilises the crystal. The activated toxin binds to the surface of mid gut and creates pores that cause swelling, lysis and eventually death of the insect.
Question. Bt cotton is resistant to pest, such as lepidopteran, dipterans and coleopterAnswer. Is Bt cotton resistant to other pests as well?
Answer. Bt cotton is made resistant to only certain specific taxa of pests. It is quite likely that in future, some other pests may infest the Bt cotton plants. It is similar to immunisation against small-pox which does not provide immunity against other pathogens like those that cause cholera, typhoid, etc.
Question. Why are yeasts used extensively for functional expression of eukaryotic genes?
Answer. Yeasts are simplest unicellular eukaryotic organisms and like bacteria they are genetically well characterised, easy to grow and manipulate. They can be readily cultured in small culture vessels as well as in large-scale bioreactors.
Question. What is GEAC and what are its objectives?
Answer. GEAC (Genetic Engineering Approval Committee) is an Indian government organisation. Its objective are to:
(a) examine the validity of GM (Genetic modification of organism) research.
(b) inspect the safety of introducing GM for public services and for their large scale use.
Question. Gene therapy is an attempt to correct a genetic defect by providing a normal gene into the individual. By this the normal function can be restored. Alternate method would be to provide the gene product (protein/enzyme) known as enzyme replacement therapy, which would also restore the function. Which in your opinion is a better option? Give reason for your answer.
Answer. Gene therapy would be a better option because it has the potential to completely cure the patient.
It is because the correct gene once introduced in the patient, can continue to produce the correct protein enzyme. Enzyme therapy does not offer permanent cure as it needs to be given to the patient on regular basis. It is also more expensive.
Question. (a) How does cryIAc gene express itself in its host?
(b) State the role of this gene in controlling the infestation of bollworm.
OR
Name the insect pest that is killed by the products of cryIAc gene. Explain how the gene makes the plant resistant to the insect pest.
Answer. (a) cryIAc gene codes for a toxic insecticidal protein that controls the cotton bollworms.
(b) This gene codes for a toxin that becomes active when ingested by the insect. The activated toxin binds to the surface of mid-gut epithelial cells thus creating pores which causes cell swelling and lysis, further leading to death of the insects.
Question. How has the bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis helped us in controlling caterpillars of insect pests?
Answer. Bacillus thuringiensis products are endotoxin which when ingested and released in the gut of the larvae of insect pest disrupts the insect gut lining thereby killing them.
Question. How has recombinant technology helped in large scale production of vaccines? Explain giving one example.
Answer. Production of insulin by rDNA techniques was achieved by an American company, Eli Lilly, in 1983. It prepared two DNA sequences corresponding to A and B chains of human insulin and introduced them in plasmids of E. coli for production. The A and B chains produced were separated, extracted and combined by creating disulfide bonds to form human insulin.
Question. Why do the toxic insecticidal proteins secreted by Bacillus thuringiensis kill the insect and not the bacteria itself?
Answer. The Bt toxin protein exists as inactive protoxins but once an insect ingests the inactive toxin, it is converted into an active form of toxin due to the alkaline pH of the gut which solubilise the crystals. Therefore, it does not kill the bacteria.
Question. Why is the introduction of genetically engineered lymphocytes into an ADA deficiency patient not a permanent cure? Suggest a possible permanent cure.
Answer. Introduction of genetically engineered lymphocytes into an ADA deficiency patient is not a permanent cure because these cells are not immortal and the patient requires periodic infusion of such genetically engineered lymphocytes. A possible permanent cure can be isolating the gene producing adenosine deaminase (ADA) from bone marrow cells and introducing it into cells at early embryonic stages.
Question. Name the genes responsible for making Bt cotton plants resistant to bollworm attack.
How do such plants attain resistance against bollworm attacks? Explain.
Answer. Bt cotton has cryIAc/cryIIAb genes. These genes produce crystals of protoxin.
When bollworm bites the cotton fruits, it consumes the toxic insecticidal protein. The alkaline pH in its gut activates the toxin. The activated toxin binds to mid-gut epithelial cells resulting in the lysis of cells leading to the death of the insect.
Question. What is gene therapy? Name the first clinical case where it was used.
Answer. Gene therapy is a collection of methods that allows correction of a gene defect that has been diagnosed in a child/embryo.
Genes are inserted into an individual’s cells and tissues to treat disease.
The first clinical case where it was used was for caring Adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency.
Question. (a) Given below is a single stranded DNA molecule. Frame and label its sense and antisense RNA molecule.
5′ ATGGGGCTC 3′
(b) How the RNA molecules made from above DNA strand help in silencing of the specific RNA molecules?
Answer. (a) 5′ ATGGGGCTC 3′ sense
3′ TACCCCGAG 5′ antisense
5′AUGGGGCUC 3′ sense
3′UACCCCGAG 5′ antisense
(b) The two strands of RNA (i.e., sense and antisense) being complementary will bind with each other and form double stranded RNA as a result its translation and protein expression would be inhibited.
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 1 Reproduction in Organisms |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Human Reproduction |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 4 Reproductive Health |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 5 Principles of Inheritance and Variation |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 7 Evolution |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles And Processes |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystem |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 16 Environmental Issues |
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications
The above provided NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications is available on our website www.studiestoday.com for free download in Pdf. You can read the solutions to all questions given in your Class 12 Biology textbook online or you can easily download them in pdf. The answers to each question in Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications of Biology Class 12 has been designed based on the latest syllabus released for the current year. We have also provided detailed explanations for all difficult topics in Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications Class 12 chapter of Biology so that it can be easier for students to understand all answers. These solutions of Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications NCERT Questions given in your textbook for Class 12 Biology have been designed to help students understand the difficult topics of Biology in an easy manner. These will also help to build a strong foundation in the Biology. There is a combination of theoretical and practical questions relating to all chapters in Biology to check the overall learning of the students of Class 12.
You can download the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the NCERT Solutions issued for Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications have been made available here for latest academic session
Regular revision of NCERT Solutions given on studiestoday for Class 12 subject Biology Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all latest NCERT Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications Class 12 Biology solutions based on the latest books for the current academic session
Yes, NCERT solutions for Class 12 Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications Biology are available in multiple languages, including English, Hindi
All questions given in the end of the chapter Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications have been answered by our teachers

