NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles And Processes have been provided below and is also available in Pdf for free download. The NCERT solutions for Class 12 Biology have been prepared as per the latest syllabus, NCERT books and examination pattern suggested in Class 12 by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. Questions given in NCERT book for Class 12 Biology are an important part of exams for Class 12 Biology and if answered properly can help you to get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise answers for NCERT Class 12 Biology and also download more latest study material for all subjects. Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles And Processes is an important topic in Class 12, please refer to answers provided below to help you score better in exams
Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles And Processes Class 12 Biology NCERT Solutions
Class 12 Biology students should refer to the following NCERT questions with answers for Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles And Processes in Class 12. These NCERT Solutions with answers for Class 12 Biology will come in exams and help you to score good marks
Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles And Processes NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology
Question. Can you list 10 recombinant proteins which are used in medical practice? Find out where they are used as therapeutics (use the internet).
Answer.Recombinant proteins Therapeutic uses
(i) Human Insulin (Humulin) Treatment of diabetes type 1.
(ii) Tissue Plasminogen Activator Treatment for acute myocardial infarction; dissolves
blood clot after heart attack and stroke.
(iii) DNase Treatment of cystic fibrosis.
(iv) Platelet Growth Factor Stimulation of wound healing.
(v) Calcitonin Treatment of rickets.
(vi) Reo Pro Prevention of blood clots.
(vii) Hirudin Used as an anticoagulant.
(viii) Interferon (α, β and γ) Treatment of viral infection and cancer.
(ix) Chorionic Gonadotropin reatment of infertility.
(x) Interleukins Enhancing activity of immune system.
Question. Make a chart (with diagrammatic representation) showing a restriction enzyme, the substrate DNA on which it acts, the site at which it cuts DNA and the product it produces.
Answer.
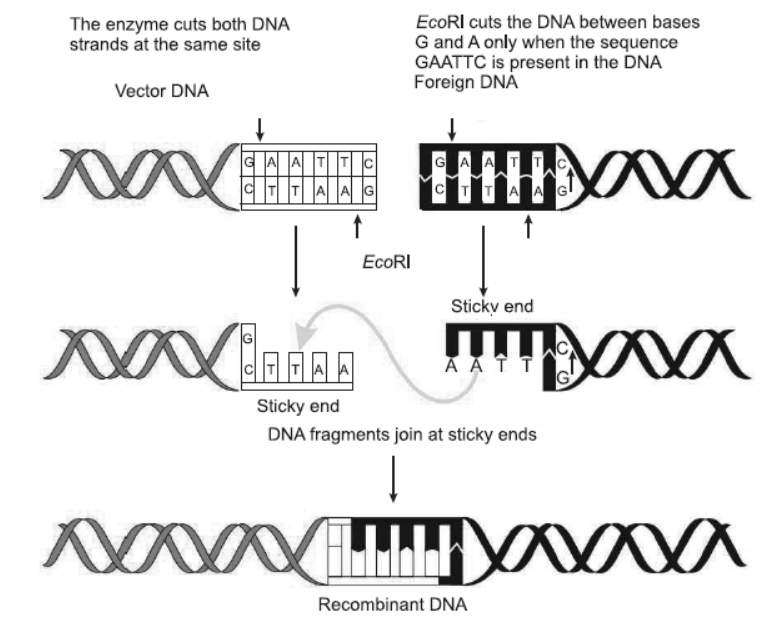
Question. From what you have learnt, can you tell whether enzymes are bigger or DNA is bigger in molecular size? How did you come to know?
Answer. DNA is bigger in molecular size. DNA is made up of sugar, phosphate and nitrogenous bases. An enzyme is made up of only protein (one or few polypeptides), so there is no complexity of molecules.
Question. What would be the molar concentration of human DNA in a human cell? Consult your teacher.
Answer. The average molecular weight of a nucleotide pair is 330 dalton. Genome size of a diploid human cell is around 6 × 109 bp. The concentration of DNA will be 330 × 6 × 109g/mol.The molarity can then be calculated as:
Sample DNA concentration (in g)/330×6×109 g/mol
Question. Do eukaryotic cells have restriction endonucleases? Justify your answer.
Answer. Eukaryotic cells have no restriction enzymes as the DNA molecules of eukaryotes are heavily methylated. It is present in prokaryotic cell (like bacteria) where these act as defence mechanism to restrict the growth of bacteriophages.
Question. Besides better aeration and mixing properties, what other advantages do stirred tank bioreactors have over shake flasks?
Answer. Other advantages of stirred tank bioreactors over shake flasks are that these facilitate temperature
control system, pH control system, foam control system and sampling ports from where small
volume of the cultures can be obtained and tested time to time.
Question. Collect 5 examples of palindromic DNA sequences by consulting your teacher. Better try to create a palindromic sequence by following base-pair rules.
Answer. (i) 5′ G A A T T C 3′ (ii) 5′ G G A T C C 3′
3′ C T T A A G 5′ 3′ C C T A G G 5′
(iii) 5′ A C T A G T 3′ (iv) 5′ A A G C T T 3′
3′ T G A T C A 5′ 3′ T T C G A A 5′
(v) 5′ A G G C C T 3′
3′ T C C G G A 5′
Question. Can you recall meiosis and indicate at what stage a recombinant DNA is made?
Answer. A recombinant DNA is made during pachytene stage of meiosis-I by crossing over.
Question. Can you think and answer how a reporter enzyme can be used to monitor transformation of host cells by foreign DNA in addition to a selectable marker?
Answer. A reporter gene encodes an enzyme, with an easily transcriptional activity of a gene of interest.
A reporter gene is the one whose phenotypic expression can be monitored and thus it reports about activity or change in advance of the effect of modification, in addition to eliminating non-transformed cells by selectable markers.
Question. Describe briefly the following:
(a) Origin of replication
(b) Bioreactors
(c) Downstream processing
Answer. (a) Origin of replication is a DNA sequence that initiates any piece of linked DNA to replicate and is also called ori site. It controls the copy numbers of the linked DNA.
(b) Refer to Basic Concepts Point 9.
(c) Refer to Basic Concepts Point 8 (ix).
Question. Explain briefly
(a) PCR
(b) Restriction enzymes and DNA
(c) Chitinase
Answer. (a) PCR stands for Polymerase Chain Reaction, which is a method for amplification of small segments of DNA.
(b) Restriction enzymes are also called ‘molecular scissors’ because they cut the helix of DNA at a specific site. DNA is the genetic material, which carries and pass the genetic characters or information from one generation to other.
(c) Chitinase is an enzyme which is used to cut or break the cell wall of fungi to release its cellular components.
Question. Discuss with your teacher and find out how to distinguish between
(a) Plasmid DNA and chromosomal DNA
(b) RNA and DNA
(c) Exonuclease and endonuclease
Answer. (a) Differences between Plasmid DNA and Chromosomal DNA
| Plasmid DNA | Chromosomal DNA |
| This is present in prokaryotic cells (bacteria). | This is present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. |
| This is the circular extra-chromosomal DNA not associated with histone proteins. |
It is linear and associated with histones proteins in eukaryotes but is double stranded and circular in prokaryotes. |
| It gives the cell extra characters like antibiotic resistance. | It contains genes for characters essential for life of organism. |
(b) Differences between DNA and RNA
| DNA | RNA |
| It has deoxyribose sugar. | It has ribose sugar. |
| It is the genetic material in almost all organisms. | It is the genetic material in only some viruses. |
| It is double stranded | It is single stranded. |
| It has A, G, C, T bases. | It has A, G, C, U bases. |
(c) Differences between Exonuclease and Endonuclease
| Exonuclease | Endonuclease |
| These cut the end regions of the DNA. | These cut at specific regions within the DNA. |
| These act on single strand of DNA. | These act on both strands as well as on DNA strand. |
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles And Processes Multiple Choice Questions
Question. Given below is a sample of a portion of DNA strand giving the base sequence on the opposite strands. What is so special shown in it?
5′_____GAATTC_____3′
3′_____CTTAAG_____5′
(a) Replication completed
(b) Deletion mutation
(c) Start codon at the 5′ level
(d) Palindromic sequence of base pairs
Answer. D
Question. There is a restriction endonuclease called Eco RI. What does “co” part in it stand for?
(a) Colon
(b) Coelom
(c) Coenzyme
(d) Coli
Answer. D
Question. Agarose extracted from sea weeds is used in
(a) spectrophotometry
(b) tissue culture
(c) PCR
(d) gel electrophoresis
Answer. D
Question. An enzyme catalysing the removal of nucleotides from the ends of DNA is
(a) endonuclease
(b) exonuclease
(c) DNA ligase
(d) Hind-II
Answer. B
Question. The transfer of genetic material from one bacterium to another through the mediation of a viral vector is termed as:
(a) transduction
(b) conjugation
(c) transformation
(d) translation
Answer. A
Question. A bacterial cell was transformed with a recombinant DNA molecule that was generated using a human gene. However, the transformed cells did not produce the desired protein. Reasons could be:
(a) Human gene may have intron which bacteria cannot process
(b) Amino acid codons for humans and bacteria are different
(c) Human protein is formed but degraded by bacteria
(d) All of the above
Answer. A
Question. Which of the given statements is correct in the context of observing DNA separated by agarose gel electrophoresis?
(a) DNA can be seen in visible light
(b) DNA can be seen without staining in visible light
(c) Ethidium bromide stained DNA can be seen in visible light
(d) Ethidium bromide stained DNA can be seen under exposure to UV light
Answer. D
Question. Select the correct sequence of processing of PCR.
(a) Extension, primer annealing, denaturation
(b) Denaturation, primer annealing, extension
(c) Denaturation, extension, primer annealing
(d) Primer annealing, denatturatiotn, extension
Answer. B
Question. Which of the following is/are used in recombinant DNA technology ?
1. Agarose gel 2. Restriction endonuclease
3. Plasmid vector 4. Ethidium bromide
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 3 and 4
(d) All of these
Answer. D
Question. Which of the following is not a characterstic of the plasmids ?
(a) Extranuclear
(b) Single-stranded
(c) Independent replication
(d) Circular DNA
Answer. B
Question. Restriction endonuclease
(a) synthesizes DNA
(b) cuts the DNA molecues randomly
(c) cuts the DNA molecule at specific sites
(d) restricts the synethesis of DNA inside the nuclease
Answer. C
Question. In genetic engineering, the antibiotics are used
(a) as selectable markers
(b) to keep the cultures free of inection
(c) to select healthy vectors
(d) as sequence from where replication starts
Answer. A
Question. The linking of antibiotic resistance gene with the plasmid vector became possible with
(a) DNA polymerase
(b) exonucleases
(c) DNA ligase
(d) endonucleases
Answer. C
Question. DNA fragments generated by the restriction endonuclease in a chemical reaction can be separated by
(a) Gel electrophoresis
(b) Restriction mapping
(c) Centrifugation
(d) PCR
Answer. A
Question. Which of the following is not required in the preparation of a recombinant DNA molecule?
(a) Restriction endonuclease
(b) DNA ligase
(c) DNA fragments
(d) E.coli
Answer. D
Question. Stirred-tank bioreactors have been designed for
(a) addition of preservatives to the product
(b) purification of the product
(c) ensuring anaerobic conditions in the culture vessel
(d) availability of oxygen throughout the process
Answer. D
Question. In agarose gel electrophoresis, DNA molecules are separated on the basis of their
(a) charge only
(b) size only
(c) charge to size ratio
(d) All of the above
Answer. D
Question. Which of these is not correctly matched?
(a) Gene gun—biolistic gun
(b) Plasmids—extrachromosomal DNA
(c) DNA ligase—biological scissors
(d) Bacteriophages—viruses
Answer. C
Question. Which of the following statements does not hold true for restriction enzyme?
(a) It recognises a palindromic nucleotide sequence
(b) It is an endonuclease
(c) It is isolated from viruses
(d) It can produce the same kind of sticky ends in different DNA molecules
Answer. C
Question. The most important feature in a plasmid to be used as a vector is
(a) origin of replication (ori)
(b) presence of a selectable marker
(c) presence of sites for restriction endonuclease
(d) its size
Answer. A
Question. Which of the following has popularised the PCR (polymerase chain reactions)?
(a) Easy availability of DNA template
(b) Availability of synthetic primers
(c) Availability of cheap deoxyribonucleotides
(d) Availability of ‘Thermostable’ DNA polymerase
Answer. D
Question. Significance of ‘heat shock’ method in bacterial transformation is to facilitate
(a) binding of DNA to the cell wall
(b) uptake of DNA through membrane transport proteins
(c) uptake of DNA through transient pores in the bacterial cell wall
(d) expression of antibiotic resistance gene
Answer. C
Question. The role of DNA ligase in the construction of a recombinant DNA molecule is
(a) formation of phosphodiester bond between two DNA fragments
(b) formation of hydrogen bonds between sticky ends of DNA fragments
(c) ligation of all purine and pyrimidine bases
(d) None of the above
Answer. A
Question. Which of the following steps are catalysed by Taq DNA polymerase in a PCR reaction?
(a) Denaturation of template DNA
(b) Annealing of primers to template DNA
(c) Extension of primer end on the template DNA
(d) All of the above
Answer. C
Question. While isolating DNA from bacteria, which of the following enzymes is not required?
(a) Lysozyme
(b) Ribonuclease
(c) Deoxyribonuclease
(d) Protease
Answer. C
Question. An antibiotic resistance gene in a vector usually helps in the selection of
(a) competent cells
(b) transformed cells
(c) recombinant cells
(d) none of the above
Answer. B
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles And Processes Assertion-Reason Questions
In the following questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Question. Assertion : In recombinant DNA technology both ligase and nuclease play an important role.
Reason : Ligase cuts the DNA at specific sites and nuclease joins the DNA fragments.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : Insertion of recombinant DNA within the coding sequence of beta-galactosidase results in colourless colonies.
Reason : Presence of insert results in inactivation of enzyme beta-galactosidase known as insertional inactivation.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : Restriction enzymes recognise palindromic sequences.
Reason : Palindromic sequences read the same in both directions of the strands.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : For isolating DNA from yeast cell, chitinase enzyme is necessary.
Reason : Cell wall of fungi are made up of chitin.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : E.coli having pBR322 with DNA insert at BamHI site cannot grow in medium containing tetracycline.
Reason : Recognition site for BamHI is present in tetr region of pBR322.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : In recombinant DNA technology, human genes are often transferred into bacteria (prokaryotes) or yeast (eukaryote).
Reason : Both bacteria and yeast multiply very fast to form huge population which express the desired gene.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : Downstream processing include separation and purification of product.
Reason : Before release of the product, it needs to be tested for quality control.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : Plasmids are single stranded extrachromosomal DNA.
Reason : Plasmids are found in eukaryotic cells.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : Plasmids are extrachromosomal DNA.
Reason : Plasmids are found in bacteria and are useful in genetic engineering.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : PCR primers do not have self complementary regions.
Reason : PCR involves use of Taq polymerase as it can withstand the high temperature of the process.
Answer. D
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles And Processes Case-based/Source-based Question
1.
Question. Name the organism in which the vector shown is inserted to get the copies of the desired gene.
Answer. Escherichia coli.
Question. Mention the area labelled in the vector responsible for controlling the copy number of the inserted gene.
Answer. Origin of replication or ‘ori’ controls copy number of inserted gene.
Question. Name and explain the role of a selectable marker in the vector shown.
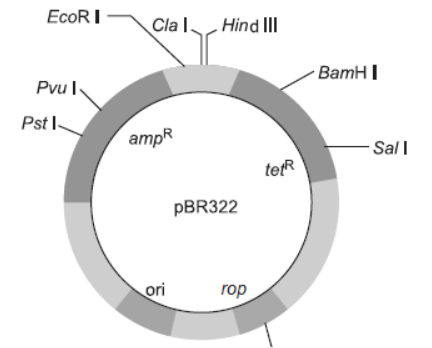
Answer.
The selectable markers are ampR and tetR (resistance to ampicillin, tetracycline). Selectable markers help to select the host cells which contain the vector (transformants) and eliminate non-transformants. If a foreign DNA ligates at the BamHI site of tetracycline resistance gene in the vector pBR322, the recombinant plasmid loses the tetracycline resistance due to insertion of DNA. It can still be selected out from non-recombinant.
2. Rajesh was doing gel electrophoresis to purify DNA fragments. Given below is the sketch of the observations of the experiment performed by him.
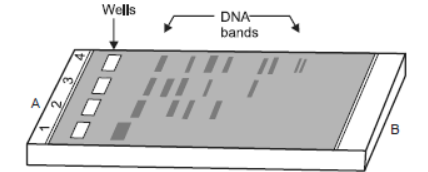
Question. At which end he would have loaded the samples and where?
Answer. He would have loaded the samples near end A; in the wells.
Question. Analyse the reason for different positions taken up by the DNA bands.
Answer. The DNA fragments separate (resolve) according to their size through sieving effect provided by the agarose gel. Hence, the smaller the fragment size, the farther it moves.
Question. Elaborate the step he would have followed to visualise DNA bands.
Answer. After staining the DNA with ethidium bromide followed by exposure to UV radiations the DNA bands appear coloured.
3. Study the diagram given below and answer the questions that follow:
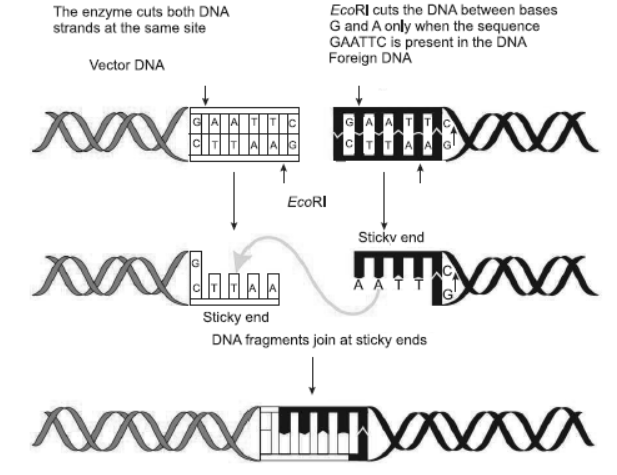
Question. What is EcoRI?
Answer. EcoRI is a restriction endonuclease enzyme.
Question. How is the action of exonuclease different from that of endonuclease?
Answer. Exonucleases cleave the DNA molecules at their ends whereas endonucleases cleave DNA molecules internally.
Question. How are ‘sticky ends’ formed on a DNA strand? Why are they so called?
Answer. Restriction enzymes cut the strands of the DNA, a little away from the centre of the palindromic sites, but between the same two bases on opposite strands. This leaves sticky single stranded position at the ends. These overhanging stretches are aids. These are named so because they form hydrogen bonds with their complementary cut counterparts very easily.
4. Observe the diagram of the first artificial plasmid vector pBR322.
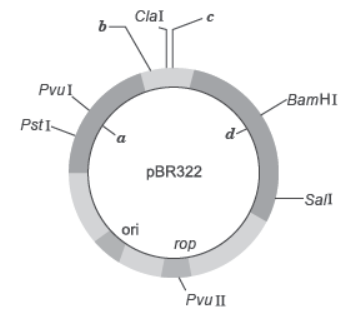
Question. Identify the selectable markers in the diagram of E. coli vector shown above.
Answer. a—gene for ampicillin resistance d—gene for tetracycline resistance.
Question. How is the coding sequence of β-galactosidase considered a better marker than the ones identified by you in the diagram? Explain.
Answer. The insertion of rDNA into the coding sequence of an enzyme β-galactosidase leads to the inactivation of the enzyme. This is called insertional inactivation. The recombinants do not produce blue-coloured colonies in the presence of chromogenic substrate while the nonrecombinants produce a blue colour. Thus, coding sequence of β-galactosidase is a better marker.
Question. Why is it essential to have a ‘selectable marker’ in a cloning vector?
Answer. Selectable markers are essential to identify and eliminate non-transformants, by selectively permitting the growth of the transformant.
5. Bioreactors are vessels for production of large-scale gene products.
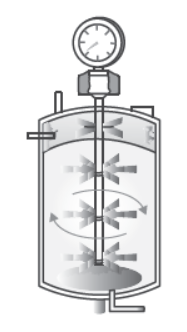
Answer the following questions based on the above information.
Question. How has the development of bioreactors helped in biotechnology?
Answer. In bioreactors large volume of culture can be processed which results in higher yields of the desired specific products (protein/enzyme). The entire process takes place under the controlled conditions of temperature, pH and raw materials.
Question. What are recombinant proteins?
Answer. The protein produced by genetically altered gene in a host is called recombinant protein.
Bioreactors are vessels in which raw materials are biologically converted into specific products by microbes.
Question. How do bioreactors help in their production?
Answer. It provides optimum growth conditions such as temperature, pH, substrate, vitamins, oxygen and salts.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles And Processes Very Short Answer Questions
Question. What is the cell that receives a recombinant gene called?
Answer. Competent host cell/recipient cell.
Question. Mention the type of host cells suitable for the gene guns to introduce an alien DNA.
Answer. Plant cells
Question. Why is a thermostable DNA polymerase needed in amplification (genetic engineering)?
Answer. Because thermostable DNA polymerase remains active even at high temperature required for extension step of PCR.
Question. Why does DNA move towards the anode in gel electrophoresis?
Answer. The DNA fragments are negatively charged so they move towards the positively charged anode.
Question. Suggest a technique to a researcher who needs to separate fragments of DNA.
Answer. Gel electrophoresis is used to separate DNA fragments.
Question. Name the first plasmid used as vector.
Answer. pBR322.
Question. Identify the reason for selection of DNA polymerase from Thermus aquaticus for Polymerase Chain Reaction.
Answer. DNA polymerase from Thermus aquaticus remains active during the high temperature induced denaturation of double stranded DNA.
Question. Write the two components of the first artificial recombinant DNA molecule constructed by Cohen and Boyer.
Answer. The two components were—antibiotic resistance gene and plasmid vector of Salmonella typhimurium.
Question. What is the host called that produces a foreign gene product? What is this product called?
Answer. The host that produces a foreign gene product is called competent host. The product is called recombinant protein.
Question. Give any two microbes that are useful in biotechnology.
Answer. E. coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Question. How is repetitive/satellite DNA separated from bulk genomic DNA for various genetic experiments?
Answer. By density gradient centrifugation.
Question. How can bacterial DNA be released from the bacterial cell for biotechnology experiments?
Answer. The bacterial cell wall is digested by the enzyme lysozyme to release DNA from the cell.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles And Processes Short Answer Questions
Question. Name the source of the DNA polymerase used in PCR technique. Mention why it is used.
Answer. The source is the bacterium Thermus aquaticus. It is used because it is thermostable and do not denature at high temperatures.
Question. How is insertional inactivation of an enzyme used as a selectable marker to differentiate recombinants from non-recombinants?
Answer. When a recombinant DNA is inserted within the coding sequence of an enzyme β-galactosidase, it results into inactivation of the enzyme. The bacterial colonies having recombinant plasmid,show no colouration while those without recombinant plasmid show blue colour.
Question. Explain any two methods of vectorless gene transfer.
Answer. The two methods of vectorless gene transfer are:
(i) Micro-injection: The technique of introducing foreign gene in a target cell by injecting the DNA, directly into the nucleus, by micro-needle is called micro-injection.
(ii) Electroporation: It is the process in which transient holes are produced in the plasma membrane of the target cell, to incorporate foreign DNA.
Question. Explain palindromic nucleotide sequence with the help of a suitable example.
Answer. The palindrome in DNA is a sequence of base pairs that reads same on the two strands when orientation of reading is kept the same. For example, the following sequences reads the same on the two strands in 5′ → 3′ direction. This is also true if it is read in the 3′→ 5′ direction.

Question. Why are molecular scissors so called? Write their use in biotechnology.
Answer. (a) The restriction endonucleases are called molecular scissors, as they cut the DNA segments at
particular locations, e.g., EcoRI.
(b) The restriction enzymes cut the DNA strands a little away from the centre of the palindromic sites, but between the same two bases on the opposite strands. This leaves single stranded portions with overhanging stretches called sticky ends on each strand as they form hydrogen bonds with their complementary cut counterparts. This stickiness at the ends facilitates the action of the enzyme DNA ligase.
Question. Write the convention used for naming restriction enzymes.
OR
Explain with the help of a suitable example the naming of a restriction endonuclease.
Answer. The convention for naming restriction enzymes is that the first letter to the name comes from the Genus and the second two letters come from species and third letter indicates the strain of the prokaryotic cell from which they are isolated e.g., EcoRI comes from Escherichia coli RI, here R stands for the strain and I follows the order in which the enzyme was isolated.
Question. State how has Agrobacterium tumefaciens been made a useful cloning vector to transfer DNA to plant cells.
Answer. Agrobacterium tumifaciens is known to be a natural vector and consists of a pathogenic plasmid.It is capable of passing its DNA to plants and induce tumour by integrating its DNA with host genome. The tumour causing gene in the plasmid of this bacteria is replaced by gene of interest and is now used as a cloning vector to transfer the DNA into plant cells.
Question. You have created a recombinant DNA molecule by ligating a gene to a plasmid vector. By mistake, your friend adds exonuclease enzyme to the tube containing the recombinant DNA.
How will your experiment get affected as you plan to go for transformation now?
Answer. The experiment will not likely be affected as recombinant DNA molecule is circular and closed, with no free ends. Hence, it will not be a substrate for exonuclease enzyme which removes nucleotides from the free ends of DNA.
Question. What are ‘cloning sites’ in a cloning vector? Explain their role. Name any two such sites in pBR322.
Answer. Cloning sites are the recognition sites on plasmid. The restriction enzymes recognise these sites
for cutting and ligation of alien DNA at this place. For example, EcoRI, BamHI.
Question. A wine maker and a molecular biologist who has developed a recombinant vaccine, both claim themselves to be biotechnologist. Who in your opinion is right?
Answer. Both are right because biotechnology is a very wide area which deals with techniques of using a ‘natural’ organism (or its parts) as well as genetically modified organism to produce products and processes useful for mankind. A wine maker employs a strain of yeast to produce wine by fermentation (a natural phenomenon), while the molecular biologist has cloned gene for the antigen (that is used as vaccine) in an organism which allows the production of the antigen in large amount.
Question. For producing a recombinant protein (for therapeutic purpose) in large scale, which vector would you choose—a low copy number or high-copy number?
Answer. High-copy number, because higher the copy number of vector plasmid, higher the copy number of gene and consequently, protein coded by the gene is produced in high amount.
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 1 Reproduction in Organisms |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Human Reproduction |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 4 Reproductive Health |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 5 Principles of Inheritance and Variation |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 7 Evolution |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles And Processes |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystem |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 16 Environmental Issues |
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles And Processes
The above provided NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles And Processes is available on our website www.studiestoday.com for free download in Pdf. You can read the solutions to all questions given in your Class 12 Biology textbook online or you can easily download them in pdf. The answers to each question in Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles And Processes of Biology Class 12 has been designed based on the latest syllabus released for the current year. We have also provided detailed explanations for all difficult topics in Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles And Processes Class 12 chapter of Biology so that it can be easier for students to understand all answers. These solutions of Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles And Processes NCERT Questions given in your textbook for Class 12 Biology have been designed to help students understand the difficult topics of Biology in an easy manner. These will also help to build a strong foundation in the Biology. There is a combination of theoretical and practical questions relating to all chapters in Biology to check the overall learning of the students of Class 12.
You can download the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles And Processes for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the NCERT Solutions issued for Class 12 Biology Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles And Processes have been made available here for latest academic session
Regular revision of NCERT Solutions given on studiestoday for Class 12 subject Biology Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles And Processes can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all latest NCERT Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles And Processes Class 12 Biology solutions based on the latest books for the current academic session
Yes, NCERT solutions for Class 12 Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles And Processes Biology are available in multiple languages, including English, Hindi
All questions given in the end of the chapter Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles And Processes have been answered by our teachers

