NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations have been provided below and is also available in Pdf for free download. The NCERT solutions for Class 12 Biology have been prepared as per the latest syllabus, NCERT books and examination pattern suggested in Class 12 by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. Questions given in NCERT book for Class 12 Biology are an important part of exams for Class 12 Biology and if answered properly can help you to get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise answers for NCERT Class 12 Biology and also download more latest study material for all subjects. Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations is an important topic in Class 12, please refer to answers provided below to help you score better in exams
Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations Class 12 Biology NCERT Solutions
Class 12 Biology students should refer to the following NCERT questions with answers for Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations in Class 12. These NCERT Solutions with answers for Class 12 Biology will come in exams and help you to score good marks
Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology
Question. How is diapause different from hibernation?
Answer. Differences between hibernation and diapause
| Hibernation | Diapause |
| Under unfavourable conditions, the animals that fail to migrate, avoid the stress by escaping in time and showing winter sleep is called hibernation. |
Under unfavourable conditions, many species in lakes and ponds are known to enter a stage of suspended development called diapause |
| It occurs usually in winters. | It occurs both in summers and winters. |
| Example, bear goes into hibernation during winter. |
Example, zooplanktons undergo diapause in lakes and ponds under unfavourable conditions. |
Question. If a marine fish is placed in a freshwater aquarium, will the fish be able to survive? Why or why not?
Answer. A marine fish if kept in freshwater aquarium will not be able to survive because:
(a) water will enter the body of fish through endosmosis.
(b) it does not have mechanism of salt absorption as in freshwater fishes.
(c) its drinking water habit will cause excess of water to enter the body.
So, the marine fish will fail to maintain the osmolarity and hence will die.
Question. Most living organisms cannot survive at temperature above 45°C. How are some microbes able to live in habitats with temperatures exceeding 100°C?
Answer. Most living organisms cannot survive above 45°C because
(a) Above 45°C enzymes get denatured.
(b) Protoplasm precipitates at high temperature.
However, some microbes (Archaebacteria) are found at 100°C because of
(a) reduced fluidity of cell membrane due to presence of branched chain lipids in their cell membrane.
(b) presence of heat-tolerant enzymes.
Question. List the attributes that populations, but not individuals possess.
Answer. The attributes that populations but not individuals possess are:
(i) Population density (ii) Population growth
(iii) Mortality or death rate (iv) Natality or birth rate
(v) Sex ratio (vi) Age distribution
Question. If a population growing exponentially doubles in size in 3 years, what is the intrinsic rate of increase (r) of the population?
Answer. t= r log2N/r
or r = log2N/t
=0.7931/3
=0.2643
Intrinsic rate of increase = 0.2643 × 100 = 26.43%
Question. An orchid plant is growing on the branch of mango tree. How do you describe this interaction between the orchid and the mango tree?
Answer. The interaction between an orchid and the mango tree is commensalism, because orchid is benefited by getting shelter from mango tree whereas the mango tree is neither harmed nor benefited.
Question. What is the ecological principle behind the biological control method of managing with pest insects?
Answer. The ecological principle operating in the biological control method of managing with pest insect is through their natural enemies, i.e., predators and parasites.
Question. Distinguish between the following:
(a) Hibernation and aestivation
(b) Ectotherms and endotherms
Answer. (a) Differences between hibernation and aestivation
| Hibernation | Aestivation |
| It is the condition of passing the winter in a resting or dormant condition. |
It is the state of inactivity during hot dry summer. |
| Animals rest in a warm place. | Animals rest in a cool and shady place. |
| It lasts usually for the whole winter season. | It generally last for hot dry day-time because nights are often cooler. |
| It is also called winter sleep. | It is also called summer sleep. |
(b) Differences between ectotherms and endotherms
| Ectotherms | Endotherms |
| They are also called cold-blooded animals. | They are also called warm-blooded animals. |
| They are unable to regulate their body temperature, body temperature changes with temperature of environment. |
They can regulate their body temperature. |
| They exhibit both hibernation and aestivation. | Their activities are uncommon. |
| They are less active animals. | They are more active animals. |
Question. Write a short note on:
(a) Adaptations of desert plants and animals
(b) Adaptations of plants to water scarcity
(c) Behavioural adaptations in animals
(d) Importance of light to plants
(e) Effect of temperature or water scarcity and the adaptations of animals.
Answer. (a) Adaptations of desert plants are as follows:
(i) Desert plants have cuticles to minimise transpiration.
(ii) In some desert plants, leaves are modified into spines to minimise loss of water.
(iii) They have long roots and adaptations to reduce transpiration, e.g., Acacia.
(iv) Stomata are present in deeppits.
Adaptations of desert animals are as follows:
(i) Desert animals have concentrated their urine for minimum loss of water, e.g., Kangaroo rat.
(ii) Desert animals absorb heat from the sun, when the body temperature drops below the comfort zone.
(iii) They live in burrows during hot season and have little water requirement, e.g., camel.
(iv) Meet water requirement by interval fat oxidation.
(b) Adaptations of plants to water scarcity
(i) Some desert plants develop special photosynthetic pathway (CAM) to minimise the loss of water and close stomata during day.
(ii) Some desert plants have sunken stomata to minimise the loss of water.
(iii) Epidermis is thick walled with thick cuticles and often possess wax, thus, reducing the surface transpiration.
(iv) Roots are deep-seated, almost reaching the water table, e.g., Prosopis.
(v) These xerophytes possess hard and pointed spines (modified leaves) to reduce transpiration.
(c) Behavioural adaptations in animals
(i) Desert lizards bask in the sun and absorb heat when their body temperature drops below the comfort zone, but move into shade when the ambient temperature starts increasing.
(ii) Some species are capable of burrowing into the soil to hide and escape from ground heat.
(iii) Hibernation and aestivation are quite common in ectothermal animals.
(d) Importance of light to plants
(i) Light is important for manufacturing food by the process of photosynthesis.
(ii) Duration of light determines flowering and fruit formation.
(iii) Light also determines the temperature which is associated with functioning of enzymes.
(iv) Light is essential for growth and development of plant because it provides organic materials.
(e) Effect of temperature or water scarcity and the adaptations of animals.
(i) Animals living in arid areas reduce water loss to minimum. For example, Kangaroo Rat feeds on dry seeds and seldom drink water.
ii) The requirement of water is often compensated by food and metabolic water. Water loss is prevented by burrowing into the soil to hide and escape from the above ground heat,
concentration of urine and solid faeces. Camel stops producing urine when water is not available and can remain without water for many days.
(iii) Animals protect themselves from excessive cold by deposition of fat, fur, etc. Bears undergo hibernation during winters.
Question. List the various abiotic environmental factors.
Answer. (i) Atmospheric factors: Light, temperature, wind and water.
(ii) Lithosphere: Rock, soil.
(iii) Hydrosphere: Pond, river, lake and ocean.
(iv) Edaphic factors: Soil texture, soil water, soil air, soil micro-organisms, soil pH, minerals.
(v) Topographic factors: Slope, altitude, valley.
Question. Give an example for:
(a) An endothermic animal
(b) Ectothermal animal
(c) An organism of benthic zone.
Answer.
(a) Monkey
(b) Snake
(c) Angler fish.
Question. Define population and community.
Answer. Population: Population is a group of individuals of same species, which can reproduce among themselves and occupy a particular area in a given time.
Community: It is an assemblage of several populations in a particular area and time and exhibit interaction and interdependence through trophic relationships.
Question. Define the following terms and give one example for each:
(a) Commensalism (b) Parasitism (c) Camouflage
(d) Mutualism (e) Interspecific competition.
Answer.
(a) Commensalism: It is an interaction between two different species where one is benefited and other remains unaffected, e.g., clown fish and sea anemone. Here, the clown fish gets protection from predators which stay away from stinging tentacles of anemone but anemone does not derive any benefit from fish.
(b) Parasitism: It is an interaction between two organisms in which one is benefited and the other is harmed, i.e., one organism lives at the cost of other organism. e.g., Cuscuta, a parasitic plant that is found growing on hedge plants, do not have chlorophyll and thus derives its nutrition from the host.
(c) Camouflage: It is a phenomenon of blending of an organism with the surrounding due to similar colour, marking and shape so as to avoid the predators, e.g., leaf-like insect such as grasshopper.
(d) Mutualism: It is the interaction between two species in which both organisms are benefited to maintain the life process, e.g., lichen (association between algae and fungi). Here, fungi helps in absorption of nutrients and water while the algal partner manufactures food.
(e) Interspecific competition: It is the competition among the members of different species for limited natural resources. The Abingdon tortoise in Galapagos Islands became extinct within a decade after goats were introduced on the Island, apparently due to the greater browsing efficiency of the goats.
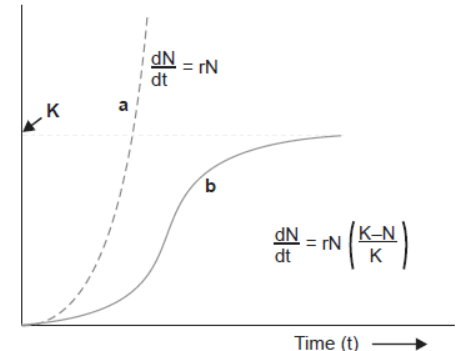
Question. With the help of suitable diagram describe the logistic population growth curve.
Answer.
- The resources become limited at certain point of time, so no population can grow exponentially.
- This growth model is more realistic.
- Every ecosystem or environment or habitat has limited resources to support a particular maximum number of individuals called its carrying capacity (K).
- When N is plotted in relation to time t, the logistic growth show sigmoid curve and is also called Verhulst–Pearl logistic growth. It is given by the following equation:
dN/dt= rN [K – N/K]
where N = population density at time t
r = intrinsic rate of natural increase
K = carrying capacity.
QQ Graph shows lag phase, followed by phases of acceleration and deceleration and finally an asymptote when population density reaches the carrying capacity.
Question. Select the statement which explains parasitism best.
(a) One organism is benefited.
(b) Both the organisms are benefited.
(c) One organism is benefited, other is not affected.
(d) One organism is benefited, other is affected.
Answer. (d).
Question. List any three important characteristics of a population and explain them.
Answer. The three important characteristics of a population are as follows:
(i) Population density: Population density of a species is the number of individuals of a species per unit area or volume.
PD = N/s
where, PD = Population density
N = Number of individuals in a region
S = Number of unit area in a region.
(ii) Birth rate: It is expressed as the number of births per 1,000 individuals of a population per year.
(iii) Death rate: It is expressed as the number of deaths per 1,000 individuals of a population per year.
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations Multiple Choice Questions
Question. What type of human population is represented by the following age pyramid?
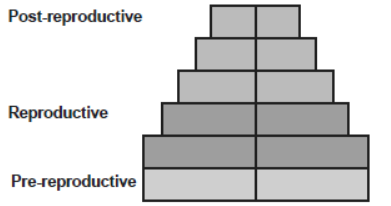
(a) Vanishing population
(b) Stable population
(c) Declining population
(d) Expanding population
Answer. B
Question. A sedentary sea anemone gets attached to the shell lining of hermit crab. The association is
(a) commensalism
(b) amensalism
(c) ectoparasitism
(d) symbiosis
Answer. D
Question. Which of the following is the most accurate comment on Earth’s carrying capacity (K)?
(a) K is smaller now than it was a thousand years ago.
(b) The human population is still a long way from K.
(c) Our technology has allowed us to keep increasing K.
(d) When it comes to humans, the concept of K is irrelevant.
Answer. C
Question. Which of the following would be true of a species with an opportunistic life history?
(a) Members of the species take a relatively long time to reach reproductive age.
(b) They are regulated mostly by density-dependent factors.
(c) They produce large numbers of offspring.
(d) The population usually stabilizes near carrying capacity.
Answer. C
Question. A particular species of tropical fish has only a few offspring and takes care of them for an extended period. We might also expect the fish population to
(a) be controlled mostly by density independent factors.
(b) show exponential growth.
(c) live in a harsh environment.
(d) be relatively stable near carrying capacity.
Answer. D
Question. Ecological niche is
(a) the surface area of the ocean
(b) an ecologically adapted zone
(c) the physical position and functional role of a species within the community
(d) formed of all plants and animals living at the bottom of a lake
Answer. C
Question. Reduction in vascular tissue, mechanical tissue and cuticle are characteristics of
(a) mesophytes
(b) epiphytes
(c) hydrophytes
(d) xerophytes
Answer. D
Question. Which of the following is a characteristic of biological community?
(a) Startification
(b) Natality
(c) Morality
(d) Sex-ratio
Answer. A
Question. When birth rate equals death rate,
(a) a population grows rapidly.
(b) the size of a population remains constant.
(c) density-dependent limiting factors do not affect the population.
(d) a population is in danger of extinction.
Answer. B
Question. According to Allen’s Rule, the mammals from colder climates have
(a) shorter ears and longer limbs
(b) longer ears and shorter limbs
(c) longer ears and longer limbs
(d) shorter ears and shorter limbs
Answer. D
Question. Which of the following forest plants controls the light conditions at the ground?
(a) Lianas and climbers
(b) Shrubs
(c) Tall trees
(d) Herbs
Answer. C
Question. The birth and death rates of four countries are given below. Which one will have the least population growth rate?
Country Birth rate/1000 Death rate/1000
M 15 5
N 25 10
O 35 18
P 48 41
(a) M
(b) N
(c) O
(d) P
Answer. D
Question. According to population scientists, one of the factors responsible for limiting population is the
(a) availability of food.
(b) daily variation of environmental temperature.
(c) time required for ecological succession.
(d) life span of members of the population.
Answer. A
Question. The logistics population growth is expressed by the equation
(a) dt/dN= Nr [K – N/K]
(b) dN/dt= rN [K – N/K]
(c) dN/dt= rN
(d) dN/dt= rN [N – K/K]
Answer. B
Question. Cuscuta is an example of
(a) ectoparasitism
(b) brood parasitims
(c) predation
(d) endoparasitims
Answer. A
Question. For a population that is stable in size, the following age distribution indicates that
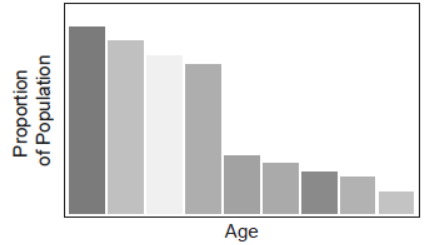
(a) The population’s birth and death rates are both high.
(b) The population’s birth and death rates are both low.
(c) The population’s birth rate is low but its death rate is high.
(d) The population’s birth rate is high but its death rate is low.
Answer. A
Question. Amensalism is an association between two species where
(a) one species is harmed and other is benefitted
(b) one species is harmed and other is unaffected
(c) one species is benefitted and other is unaffected
(d) both the species are harmed.
Answer. B
Question. What will happen to a well growing herbaceous plant in the forest if it is transplanted outside the forest in a park?
(a) It will grow normally
(b) It will grow well because it is planted in the same locality
(c) It may not survive because of change in its micro climate
(d) It grows very well because the plant gets more sunlight
Answer. C
Question. What would be the per cent growth or birth rate per individual per hour for the same population mentioned in the previous question (Question 17)?
(a) 100
(b) 200
(c) 50
(d) 150
Answer. B
Question. A population has more young individuals compared to the older individuals. What would be the status of the population after some years?
(a) It will decline
(b) It will stabilise
(c) It will increase
(d) It will first decline and then stabilise
Answer. C
Question. At which point in the graph shown below would there be zero population growth (DN/Dt = 0)?
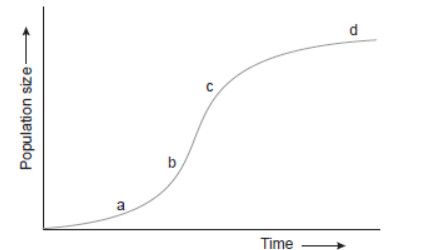
(a) a
(b) b
(c) c
(d) d
Answer. D
Question. Lichens are association of
(a) bacteria and fungus
(b) alga and bacterium
(c) fungus and alga
(d) fungus and virus
Answer. C
Question. Which of the following is a partial root parasite?
(a) Sandalwood
(b) Mistletoe
(c) Orobanche
(d) Ganoderma
Answer. A
Question. Salt concentration (Salinity) of the sea measured in parts per thousand is
(a) 10 – 15
(b) 30 – 70
(c) 0 – 5
(d) 30 – 35
Answer. D
Question. Formation of tropical forests needs mean annual temperature and mean annual precipitation as
(a) 18–25°C and 150–400 cm
(b) 5–15°C and 50–100 cm
(c) 30–50°C and 100–150 cm
(d) 5–15°C and 100–200 cm
Answer. A
Question. If a population of 50 Paramecium present in a pool increases to 150 after an hour, what would be the growth rate of population?
(a) 50 per hour
(b) 200 per hour
(c) 5 per hour
(d) 100 per hour
Answer. D
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations Assertion-Reason Questions
In the following questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Question. Assertion : Species are groups of potentially interbreeding natural populations which are isolated from other such groups.
Reason : Distinctive morphological features are displayed due to reproductive isolation.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : Leaf butterfly and stick insect show mimicry to dodge their enemies.
Reason : Mimicry is a method to acquire body colour blending with the surroundings.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : Small sized animals are rarely found in polar regions.
Reason : Small sized animal have larger surface area relative to their volume and have to spend energy to generate body heat.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : A stable population is depicted by bell-shaped age pyramid.
Reason : The proportion of individuals in reproductive age group is higher than those in pre reproductive age group.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : Plant-animal interactions do not generally involve co-evolution of the mutualist organisms.
Reason : Evolution of plants and animals go side by side.
Answer. D
Question. Assertion : Predators are organisms which feed on other individuals.
Reason : Prey species have evolved various defences to lessen the impact of predation.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : Population pyramid (graphically) depicts the rate at which population will grow in future.
Reason : A triangular population pyramid depicts population size is stable.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : Epiphytes growing on branches of the tree exhibit commensalism.
Reason : In commensalism on organism benefits from the association while the other has no effect.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : Coral reefs are found in regions of West Bengal and Andhra Pradesh.
Reason : Coral reef require low fresh water inflow, high salinity and optimal temperature to propagate.
Answer. D
Question. Assertion : Verhulst-Pearl Logistic growth curve is sigmoid in nature.
Reason : A population growing in habitat with limited resources shows an initial lag phase,followed by acceleration and deceleration and finally an asymptote.
Answer. B
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations Case-based/Source-based Question
1. The graph shown alongside represents the organismic response to a certain environmental condition (e.g., temperature):
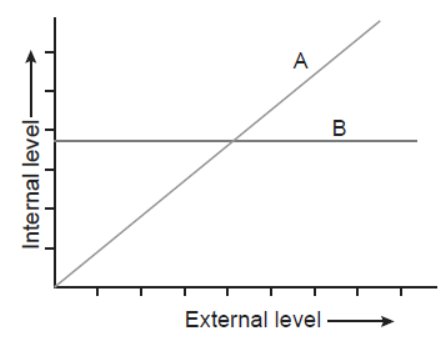
Question. Which one of these, ‘A’ or ‘B’, depicts conformers?
Answer. ‘A’ depicts conformers.
Question. What does the other line graph depict?
Answer. The other line depicts response of the regulators.
Question. How do these organisms differ from each other with reference to homeostasis?
Answer.
Conformers
Aquatic animals and plants in which the osmotic concentration or body temperature of body fluids changes according to the ambient conditions or environment of water are called conformers.
Regulators
Some organisms are able to maintain homeostasis by physiological means which ensures constant body temperature, constant osmotic concentration, etc.
2. Study the three different age pyramids for human population given below and answer the questions that follow:
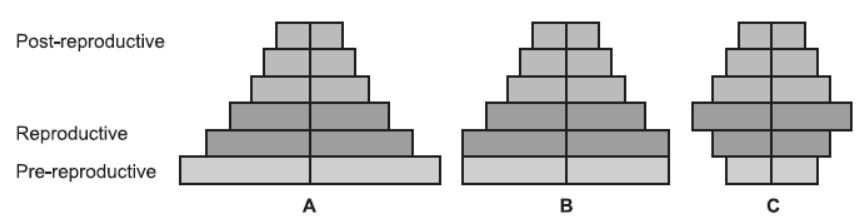
Question. Write the names given to each of these age pyramids.
Answer. A — Expanding pyramid B — Stable pyramid
C — Declining pyramid
Question. Mention the one which is ideal for human population and why.
Answer. Stable pyramid is ideal for human population because it maintains the stability in all population phases.
Question. What would be the growth rate pattern when the resources are unlimited?
Answer. Exponential.
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations Very Short Answer Questions
Question. Give two reasons as to why a weed such a Calotropis flourishes in abandoned fields.
Answer. Calotropis flourishes in abandoned fields because of:
(i) It has dry hairy seeds which help in dissemination
(ii) Its have xerophytic adaptations like thick hair on leaves and stems.
(iii) It is not grazed by animals as it produces poisonous substances like cardiac glycosides.
Question. What does sigmoid growth curve of a population indicate?
Answer. Sigmoid growth curve of a population indicates following characteristics:
(i) Initially the growth is slow.
(ii) The growth becomes rapid and the curve becomes steady due to environmental resistance.
Question. Pollinating species of wasps show mutualism with specific fig plants. Mention the benefits the female wasps derive from the fig trees from such an interaction.
Answer. The wasp uses the fruit as oviposition, i.e., egg laying and the developing seeds for nourishing its larvae.
Question. Give an example of an organism that enters ‘diapause’ and why.
Answer. Many species of Zooplankton under unfavourable conditions enters diapause which delay overall development and hence they can pass unfavourable conditions.
Question. Name a ‘photoperiod’ dependent process, one each in plants and in animals.
Answer. In plants, flowering and in animals, migration/foraging are photoperiod dependent processes.
Question. When and why do some animals like snails go into aestivation?
Answer. Snails undergo aestivation if they are unable to migrate in order to avoid stressful condition of high temperature.
Question. Between amphibians and birds, which will be able to cope with global warming? Give reasons.
Answer. Birds being eurythermals can tolerate a wide range of temperature and thus will be able to cope with global warming more efficiently.
Question. What is an interaction called when an orchid grows on a mango plant?
Answer. Commensalism
Question. What is Allen’s rule?
Answer. According to Allen’s rule, mammals in colder climate have shorter ears and shorter limbs to minimise heat loss.
Question. Name the interaction between sea anemone and the hermit crab that grows on it.
Answer. Commensalism
Question. What is the interaction called between Cuscuta and shoe flower bush?
Answer. Parasitism
Question. In a pond there were 20 Hydrilla plants. Through reproduction 10 new Hydrilla plants were added in a year. Calculate the birth rate of the population.
Answer. Birth rate= Number of individuals born/Total number of individuals 10/20= 0.5
Birth rate is 0.5 plants per year.
Question. What does J-shaped growth curve of a population indicate?
Answer. The J-shaped growth curve indicates the minimum or absence of environmental resistance.
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations Short Answer Questions
Question. Categorise the following plants into hydrophytes, xerophytes, halophytes and mesophytes.
Write the type of plant against the following examples.
(a) Salvinia
(b) Opuntia
(c) Rhizophora
(d) Mangifera
Answer. (a) Hydrophyte
(b) Xerophyte
(c) Halophyte
(d) Mesophyte
Question. In a pond, we see plants which are free-floating, rooted-submerged, rooted emergent, rooted
with floating leaves. Write the type of plants against each of them.
(a) Hydrilla, (b) Typha, (c) Nymphaea, (d) Lemna, (e) Vallisnaria
Answer. (a) Submerged
(b) Rooted emergent
(c) Rooted with floating leave
(d) free-floating
(e) Rooted Submerged
Question. Why are coral reefs not found from West Bengal to Andhra Pradesh but found in Tamil Nadu on the east coast of India?
Answer. High salinity, optimal temperature and less siltation are essential to colonise corals. If siltation and fresh water inflow are very high, the corals don’t colonise. In contrast when the siltation and fresh water in flow by the rivers are very less, the corals do colonise.
Question. In a sea shore, the benthic animals live in sandy, muddy and rocky substrata and accordingly developed the following adaptations. Find the suitable substratum against each adaptation.
(a) Burrowing ______________________
(b) Building cubes ______________________
(c) Holdfasts/peduncle ______________________
Answer. (a) Sandy, (b) Muddy, (c) Rocky.
Question. Name two basic types of competition found amongst organisms. Which one of them is more intense and why?
Answer. The two basic types of competitions are:
(i) Interspecific competition
(ii) Intraspecific competition
The intraspecific competition is more intense because the requirement of the individual of the species are similar.
Question. Mention four adaptive features that help cacti survive in xeric environment.
Answer. Adaptation in desert plants:
(i) Desert plants have thick waxy coating on leaf called cuticle for minimum loss of water, through transpiration.
(ii) They have special photosynthetic pathway (CAM) that enables minimum loss of water during day time because stomata remain closed.
(iii) Some desert plants develop spines instead of leaf and photosynthetic function is carried out by the flattened stem.
(iv) Stomata are arranged in deep pits to minimise loss, through transpiration.
Question. In certain seasons we sweat profusely while in some other season we shiver. Explain.
Answer. Human beings maintain a constant body temperature of 37°C.
- In summers: The outside temperature is much higher than our body temperature. Therefore,we sweat profusely. This results in evaporative cooling and our body temperature is brought down to normal (37°C).
- In winters: The outside temperature is much lower than our body temperature. Therefore,we start to shiver; this action (of shivering) is a kind of exercise (work) that produces heat and raises the body temperature.
Question. Why are small animals rarely found in the polar regions? Explain.
OR
Why are small birds like humming birds not found in polar regions? Explain.
Answer. Small animals like humming birds have a large surface area relative to their volume. So they tend to lose body heat very fast when it is cold outside. Then, these animals have to use their energy (generated by metabolic reactions) to generate body heat. That is the reason why small sized animals are rarely found in the polar regions.
Question. Why the plants that inhabit a desert are not found in a mangrove? Give reasons.
Answer. In mangroves the soil is oxygen deficit because of excess water present. Plants in mangroves develop special roots called breathing roots or pneumatophores for respiration. This adaptation is not present in desert plants because of which they cannot survive in mangroves.
Question. Bear hibernates whereas some species of zooplanktons enter diapause to avoid stressful external conditions. How are these two ways different from each other?
Answer. Hibernation is the winter sleep, seen in cold-blooded animals in polar regions, in which they suspend their metabolic activities when external temperature becomes unfavourable. Whereas, diapause is the phenomenon seen in insects during their developmental stages, in which metabolic activities are suspended due to unfavourable conditions.
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 1 Reproduction in Organisms |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Human Reproduction |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 4 Reproductive Health |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 5 Principles of Inheritance and Variation |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 7 Evolution |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles And Processes |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystem |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 16 Environmental Issues |
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations
The above provided NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations is available on our website www.studiestoday.com for free download in Pdf. You can read the solutions to all questions given in your Class 12 Biology textbook online or you can easily download them in pdf. The answers to each question in Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations of Biology Class 12 has been designed based on the latest syllabus released for the current year. We have also provided detailed explanations for all difficult topics in Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations Class 12 chapter of Biology so that it can be easier for students to understand all answers. These solutions of Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations NCERT Questions given in your textbook for Class 12 Biology have been designed to help students understand the difficult topics of Biology in an easy manner. These will also help to build a strong foundation in the Biology. There is a combination of theoretical and practical questions relating to all chapters in Biology to check the overall learning of the students of Class 12.
You can download the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the NCERT Solutions issued for Class 12 Biology Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations have been made available here for latest academic session
Regular revision of NCERT Solutions given on studiestoday for Class 12 subject Biology Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all latest NCERT Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations Class 12 Biology solutions based on the latest books for the current academic session
Yes, NCERT solutions for Class 12 Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations Biology are available in multiple languages, including English, Hindi
All questions given in the end of the chapter Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations have been answered by our teachers

