NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare have been provided below and is also available in Pdf for free download. The NCERT solutions for Class 12 Biology have been prepared as per the latest syllabus, NCERT books and examination pattern suggested in Class 12 by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. Questions given in NCERT book for Class 12 Biology are an important part of exams for Class 12 Biology and if answered properly can help you to get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise answers for NCERT Class 12 Biology and also download more latest study material for all subjects. Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare is an important topic in Class 12, please refer to answers provided below to help you score better in exams
Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare Class 12 Biology NCERT Solutions
Class 12 Biology students should refer to the following NCERT questions with answers for Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare in Class 12. These NCERT Solutions with answers for Class 12 Biology will come in exams and help you to score good marks
Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology
Question. Bacteria cannot be seen with the naked eyes, but these can be seen with the help of a microscope.If you have to carry a sample from your home to your biology laboratory to demonstrate the presence of microbes under a microscope, which sample would you carry and why?
Answer. The most common household product that we would like to carry is curd which contains lactic acid bacteria (Lactobacillus sps.).
Question. Give examples to prove that microbes release gases during metabolism.
Answer. Puffed-up appearance of dough which is used for making ‘dosa’, ‘idli’ and bread is due to gas production. Methanogens (bacteria) in the biogas plant produce methane and carbon dioxide.
Also large holes in the ‘Swiss cheese’ are due to production of a large amount of CO2 during its production.
Question. In which food would you find lactic acid bacteria? Mention some of their useful applications.
Answer. The lactic acid bacteria (LAB) are found in curd. LAB convert the lactose sugar of milk into lactic acid. Lactic acid coagulates the milk protein called casein. It also increases the nutritional quality of curd as the curd contains vitamin B12 along with other vitamins. They also check the growth of other harmful microbes.
Question. Name some traditional Indian foods made of wheat, rice and Bengal gram (or their products)
which involve use of microbes.
Answer. ‘Dosa’ and ‘idli’ (from rice), bread (from wheat) and ‘dhokla’ (from Bengal gram) are the traditional Indian foods which involve use of microbes.
Question. In which way have microbes played a major role in controlling diseases caused by harmful bacteria?
Answer. The major role of microbes in controlling the diseases is the ‘antibiotic production’. Antibiotics have been used against pathogenic bacteria, e.g., penicillin from Penicillium notatum, streptomycin from Streptomyces griseus, etc.
Question. Name any two species of fungus, which are used in the production of the antibiotics.
Answer. Two species of fungus, used in the production of the antibiotics:
(i) Penicillium notatum (for penicillin production).
(ii) Aspergillus fumigatus (for fumagillin production).
Question. What is sewage? In which way can sewage be harmful to us?
Answer. Sewage is the municipal waste water containing large quantities of human excreta and other organic wastes. Sewage could be harmful to us as it contains many pathogenic microbes and produces foul smell. It is the cause of many water-borne diseases. It is also the cause of eutrophication of water bodies thereby killing many aquatic organisms.
Question. What is the key difference between primary and secondary sewage treatment?
Answer. The key difference between primary and secondary treatment of sewage is that primary treatment is the physical process of removing grit and floating debris while secondary treatment is a biological process that involves digestion of organic matter by microbes.
Question. Do you think microbes can also be used as source of energy? If yes, how?
Answer. Yes, microbes can be used to produce energy indirectly. Methanogens (bacteria) like Methanobacterium are involved in the production of biogas which is used as source of energy.
Question. Microbes can be used to decrease the use of chemical fertilisers and pesticides. Explain how this can be accomplished.
Answer. Microbes can be used both as fertilisers and pesticides called biofertilisers and biopesticides, respectively. Microbes are used as biofertilisers to enrich the soil nutrients, e.g., Rhizobium,Azotobacter, Azospirillum, etc., which can fix atmospheric nitrogen in the soil. Bacillus thuringiensis bacteria act as biopesticide to control the growth of insect pests. Trichoderma, fungal species, is an effective bicontrol agent of several plant pathogens. Baculoviruses used as biological control agents in genus Nucleopolyhedrovirus are excellent for species-specific, narrow spectrum insecticidal applications.
Question. Three water samples namely river water, untreated sewage water and secondary effluent discharged from a sewage treatment plant were subjected to BOD test. The samples were labelled A, B and C; but the laboratory attendant did not note which was which. The BOD values of the three samples A, B and C were recorded as 20 mg/L, 8 mg/L and 400 mg/L, respectively. Which sample of the water is most polluted? Can you assign the correct label to each assuming the river water is relatively clean?
Answer. Sample C is most polluted (Highest BOD).
Sample A — River water
Sample B — Secondary effluent (Least BOD)
Sample C — Untreated sewage (Highest BOD)
Question. Find out the name of the microbes from which cyclosporin A (an immuno-suppressive drug) and statins (blood cholesterol lowering agents) are obtained.
Answer. (a) Cyclosporin A is obtained from Trichoderma polysporum.
(b) Statins are obtained from the yeast Monascus purpureus.
Question. Find out the role of microbes in the following and discuss it with your teacher.
(a) Single cell protein (SCP)
(b) Soil
Answer. (a) Single cell protein (SCP): It is a protein-rich microbial biomass which can be used as food.SCP contains essential amino acids and low fat. Bacteria, filamentous fungi, algae, yeast,etc., are used as “single cell proteins” (SCPs). Spirulina is taken as a tablet having 60 per cent proteins, all minerals, vitamins, etc.
(b) Soil: Soil is the habitat of numerous microbes. Microbes in the soil increase the fertility of soil by decomposing organic matter. Some microbes convert nitrates into free nitrogen that escapes into atmosphere for replenishment.
Question. Arrange the following in the decreasing order (most important first) of their importance, for the welfare of human society. Give reasons for your answer.
Biogas, Citric acid, Penicillin and Curd.
Answer. (i) Penicillin: It is an antibiotic used in curing numerous bacterial diseases.
(ii) Biogas: It is a source of energy in rural areas, produced by anaerobic degradation of organic matter.
(iii) Curd: It is vitamin-rich milk preparation which is easily digested.
(iv) Citric acid: It is an organic acid used as preservative in juices, jams and jellies, etc.
Question. How do biofertilisers enrich the fertility of the soil?
Answer. Biofertilisers are microorganisms which bring about nutrient enrichment of soil by enhancing the availability of nutrients to crops. They are of following types:
(i) Nitrogen fixing bacteria and cyanobacteria: They form symbiotic association with plants.
They get food and shelter from plants and on the other hand, plants get nitrogen fixed by these bacteria. For example, Rhizobium.
(ii) Mycorrhiza: It is an association between a fungus and roots of higher plants. It takes part in the solubilisation and absorption of nutrients from organic matter. Many members of the genus Glomus form mycorrhiza.
(iii) Manures: They are semi-decayed organic remains of various types—manure, green manure, compost and vermicompost.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare Multiple Choice Questions
Question. Methanogenic bacteria are not found in
(a) rumen of cattle
(b) gobar gas plant
(c) bottom of water-logged paddy fields
(d) activated sludge.
Answer. D
Question. An organism used as a biofertilizer for raising soyabean crop is
(a) Azotobacter
(b) Azospirillum
(c) Rhizobium
(d) Nostoc
Answer. C
Question. Mycorrhiza does not help the host plant in
(a) enhancing its phosphorus uptake capacity
(b) increasing its tolerance to drought
(c) enhancing its resistance to root pathogens
(d) increasing its resistance to insects.
Answer. D
Question. A good producer of citric acid is
(a) Clostridium
(b) Sacchaaromyces
(c) Aspergillus
(d) Pseudomonas.
Answer. C
Question. Activated sludge should have the ability to settle quickly so that it can
(a) be rapidly pumped back from sedimentation tank to aeration tank
(b) absorb pathogenic bacteria present in waste water while sinking to the bottom of the settling tank
(c) be discarded and anaerobically digested
(d) absorb colloidal organic matter.
Answer. A
Question. The vitamin whose content increases following the conversion of milk into curd by lactic acid bacteria is
(a) vitamin C
(b) vitamin D
(c) vitamin B12
(d) vitamin E.
Answer. C
Question. The residue left after methane production from cattle dung is
(a) burnt
(b) burried in land fills
(c) used as manure
(d) used in civil construction.
Answer. C
Question. Wastewater treatment generates a large quantity of sludge, which can be treated by
(a) anaerobic digesters
(b) floc
(c) chemicals
(d) oxidation pond
Answer. A
Question. Bottled fruit juices from market are clearer than that at home because of
(a) antibiotics
(b) hormones
(c) enzymes
(d) filtration
Answer. C
Question. Select the correct statement from the following
(a) Biogas is produced by the activity of aerobic bacteria on animal waste
(b) Methanobacterium is an aerobic bacterium found in rumen of cattle
(c) Biogas, commonly called gobar gas, is pure methane
(d) Activated sludge-sediment in settlement tanks of sewage treatment plant is a rich source of aerobic bacteria.
Answer. D
Question. A common biocontrol agent for the control of plant diseases is
(a) baculovirus
(b) Bacillus thuringiensis
(c) Glomus
(d) Trichoderma
Answer. A
Question. Match the following list of bioactive substances and their roles
Bioactive Substance Role
A. Statin (i) Removal of oil stains
B. Cyclosporin A (ii) Removal of clots from blood vessels
C. Streptokinase (iii) Lowering of blood cholesterol
D. Lipase (iv) Immuno-suppressive agent
Choose the correct match.
(a) A-(ii), B-(iii), C-(i), D-(iv)
(b) A-(iv), B-(ii), C-(i), D-(iii)
(c) A-(iv), B-(i), C-(ii), D-(iii)
(d) A-(iii), B-(iv), C-(ii), D-(i)
Answer. D
Question. The primary treatment of waste water involves the removal of
(a) dissolved impurities
(b) stable particles
(c) toxic substances
(d) harmful bacteria.
Answer. B
Question. The technology of biogas production from cow dung was developed in India largely due to the efforts of
(a) Gas Authority of India
(b) Oil and Natural Gas Commission
(c) Indian Agricultural Research Institute and Khadi & Village Industries Commission
(d) Indian Oil Corporation.
Answer. C
Question. Secondary sewage treatment is mainly a
(a) physical process
(b) mechanical process
(c) chemical process
(d) biological process
Answer. D
Question. Methanogens do not produce
(a) oxygen
(b) methane
(c) hydrogen sulfide
(d) carbon dioxide.
Answer. A
Question. Which of these is/are symbiotic N2 fixing organisms?
(a) Rhizobium
(b) Clostridium
(c) Azotobacter
(d) All of these
Answer. A
Question. Monascus purpureus is a yeast used commercially in the production of
(a) ethanol
(b) streptokinase for removing clots from the blood vessels
(c) citric acid
(d) blood cholesterol lowering statins.
Answer. D
Question. The free-living fungus Trichoderma can be used for
(a) insects
(b) biological control of plant diseases
(c) controlling butterfly caterpillars
(d) producing antibiotics
Answer. B
Question. Match the items in Column ‘A’ and Column ‘B’ and choose correct answer.
Column I Column II
A. Lady bird (i) Methanobacterium
B. Mycorrhiza (ii) Trichoderma
C. Biological control (iii) Aphids
D. Biogas (iv) Glomus
The correct answer is:
(a) A-(ii), B-(iv), C-(iii), D-(i)
(b) A-(iii), B-(iv), C-(ii), D-(i)
(c) A-(iv), B-(i), C-(ii), D-(iii)
(d) A-(iii), B-(ii), C-(i), D-(iv)
Answer. B
Question. Match the following list of bacteria and their commercially important products
Bacterium Product
A. Aspergillus niger (i) Lactic acid
B. Acetobacter aceti (ii) Butyric acid
C. Clostridium butylicum (iii) Acetic acid
D. Lactobacillus (iv) Citric acid
Choose the correct match.
(a) A-(ii), B-(iii), C-(iv), D-(i)
(b) A-(ii), B-(iv), C-(iii), D-(i)
(c) A-(iv), B-(iii), C-(ii), D-(i)
(d) A-(iv), B-(i), C-(iii), D-(ii)
Answer. C
Question. What would happen if oxygen availability to activated sludge flocs is reduced?
(a) It will slow down the rate of degradation of organic matter
(b) The center of flocs will become anoxic, which would cause death of bacteria and eventually breakage of flocs.
(c) Flocs would increase in size as anaerobic bacteria would grow around flocs.
(d) Protozoa would grow in large numbers.
Answer. B
Question. Big holes in Swiss cheese are made by
(a) a machine
(b) a bacterium that produces methane gas
(c) a bacterium producing a large amount of carbon dioxide
(d) a fungus that releases a lot of gases during its metabolic activities.
Answer. C
Question. Primary treatment of sewage waste involves which processes ?
(a) Filtration and incubation
(b) Sedimentation and decantation
(c) Filtration and sedimentation
(d) Sedimentation and microbial proliferation
Answer. C
Question. BOD of waste water is estimated by measuring the amount of
(a) total organic matter
(b) biodegradable organic matter
(c) oxygen evolution
(d) oxygen consumption
Answer. D
Question. Which one of the following alcoholic drinks is produced without distillation?
(a) Wine
(b) Whisky
(c) Rum
(d) Brandy
Answer. A
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare Assertion-Reason Questions
In the following questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Question. Assertion : For organ transplantation Cyclosporin A needs to be injected to the patient.
Reason : Cyclosporin A inhibits activation of T-cells and interferons.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : Primary treatment of sewage is also called bilogical treatment.
Reason : Primary sewage treatment depends only on density of materials in sewage.
Answer. D
Question. Assertion : Biogas is produced by anaerobic digestion of biomass by methanogenic bacteria.
Reason : Biogas is made up of methane entirely and is the most ecofriendly fuel.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : In mycorrhiza the fungus symbiont absorbs phosphorus for the plant.
Reason : Mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association of fungus with roots of higher plants.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : Acetic acid production involves both aerobic and anaerobic processes.
Reason : First alcohol is produced from glucose by aerobic process which is followed by production of acetic by anaerobic process.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : Baculoviruses control growth of many insects and arthropods.
Reason : Lady bird and Trichoderma are used as biocontrol agents.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : Chemical fertilisers are more preferable than biofertilizers.
Reason : Chemical fertilisers are expensive and hazardous to the environment.
Answer. D
Question. Assertion : A small part of activated sludge is pumped back into aeration tank.
Reason : It serves as inoculum.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : Streptococcus thermophilus increases nutritional value of milk.
Reason : Curd and yoghurt have higher vitamin content than milk.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : Integrated Pest Management (IPM) uses different pest control methods which are ecofriendly.
Reason : Bacillus thuringiensis kill larvae of certain insects.
Answer. B
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare Case-based/Source-based Question
1. Given below is a figure of a biogas plant.
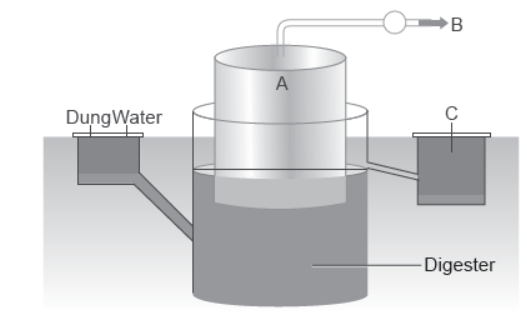
Question. Name the group of organisms and the substrate they act on to produce biogas.
Answer. The organisms are methanogens which act on cellulosic materials like cow dung and agricultural waste.
Question. Identify the products A and B and discuss their significance.
Answer. A is the biogas which is a mixture of gases consisting of methane, hydrogen sulphide and carbon dioxide. It can be used as a source of energy to nearby houses as it is inflammable.B is the spent slurry or sludge which is removed through another outlet and may be used as fertiliser.
Question. What are methanogens? How do they generate biogas?
Answer. Methanogens are anerobic methane producing bacteria which grow anaerobically on cellulosic material in cow dung to decompose it to produce large amount of methane, CO2 and H2. This mixture of gases is biogas.
2. Following is the process of curd formation from milk.
Milk is incubated with curd
↓
LAB grows in milk
↓
(a) production
↓
Coagulation and digestion of milk protein
↓
Improved nutritional quality by (b)
Question. What does (a) and (b) signify in the flow chart.
Answer. (a) Lactic acid;
(b) increased vitamin B12
Question. Expand the word LAB.
Answer. Lactic Acid Bacteria
Question. Milk starts to coagulate when LAB is added to warm milk as a starter. Mention any other two benefits that LAB provides.
Answer. (a) It increases nutritional quality of curd by increasing vitamin B12 content.
(b) It checks the growth of disease-causing organisms in the gut.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare Very Short Answer Questions
Question. Why are antibiotics always sold in combination with Lactobacillus?
Answer. Antibiotics may kill even the useful bacteria present in the digestive tract. LAB is given, which will protect some microbes in the digestive tract and enhance the production and absorption of vitamin B12.
Question. Give the scientific name of the source organism from which the first antibiotic was produced.
Answer. Penicillium notatum
Question. Mention the information that the health workers derive by measuring BOD of a water body.
Answer. (i) By measuring BOD of a water body, health workers find the amount of dissolved oxygen in water. The lesser the amount of dissolved oxygen, the more polluted the water body will be.
(ii) It is also measure of organic matter present in water and uptake of O2 by microbes.
Question. The excreta of cattle does not contain any cellulose but human excreta may contain cellulose. Why?
Answer. The rumen of cattle contains methanogens which help in the digestion of cellulose but these bacteria are not present in human stomach so cellulose is not digested.
Question. Name the pests that ladybird, beetle and dragonflies help to get rid of.
Answer. Ladybird, beetle and dragonflies control aphids and mosquitoes respectively.
Question. What for Nucleopolyhedroviruses are being used nowadays?
Answer. Nucleopolyhedroviruses are used for the biological control of insect pests.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare Short Answer Questions
Question. Name the microbes that help production of the following products commercially:
(a) Statin (b) Citric acid
(c) Penicillin (d) Butyric acid
Answer. (a) Monascus purpureus (b) Aspergillus niger
(c) Penicillium notatum (d) Clostridium butylicum
Question. Name a free-living and a symbiotic bacterium that serve as biofertiliser. Why are they so called?
Answer. Azospirillium/Azotobacter and Rhizobium act as biofertilisers.
They are so called because they enrich soil nutrients by nitrogen fixation.
Question. Why is Rhizobium categorised as a ‘symbiotic bacterium’? How does it act as a biofertiliser?
Answer. Rhizobium is present in the root nodules of leguminous plants. Theirs is a symbiotic relationship in which the bacterium obtains food and shelter from the plant and the plant gets fixed nitrogen in return. These bacteria fix atmospheric nitrogen into organic forms, which is used by the plant as nutrient.
Question. Your advice is sought to improve the nitrogen content of the soil to be used for cultivation of a non-leguminous terrestrial crop.
(a) Recommend two microbes that can enrich the soil with nitrogen.
(b) Why do leguminous crops not require such enrichment of the soil?
Answer. (a) Azospirillum/Azotobacter/Anabaena/Nostoc/Oscillatoria/Frankia. (Any two)
(b) Leguminous crops do not need nitrogen from soil because the nitrogen fixing bacteria (Rhizobium) are present in their root nodules, which can fix atmospheric nitrogen for the crops.
Question. What is Chakravarthy bug? Give its scientific name and its application?
Answer. Chakravarthy bug is a super bug of Pseudomonas with multiple plasmids. They are helpful in removing oil spills.
Question. What does the Ganga Action Plan tend to achieve?
Answer. Ganga Action Plan tends to save the major rivers from pollution like Ganga. Under these plans, a large number of sewage treatment plants were built so that only treated sewage is discharged in the rivers.
Question. To reduce the percentage of population suffering from hunger and malnutrition, microbes are grown on a large scale to act as food supplements. Mention any two microbes used as food supplement and suggest their role.
Answer. Spirulina and Methylophilus methylotrophus are used as food supplements.Spirulina produces large quantities of food rich in protein, minerals, fats, carbohydrates and
vitamins.250 gm of Methylophilus methylotrophus produces 25 tonnes of protein per day
Question. Name the blank spaces a, b, c and d given in the following table:
| Type of microbe | Name | Commercial product |
| Bacterium | a | Clot buster enzyme |
| b | Aspergillus niger | Citric acid |
| Fungus | Trichoderma polysporum | c |
| Bacterium | d | Butyric acid |
Answer. (a) Streptococcus
(b) Fungus
(c) Cyclosporin A
(d) Clostridium butylicum
Question. How do mycorrhizae act as biofertilisers? Explain. Name a genus of fungi that forms a mycorrhizal association with plants.
Answer. Mycorrhizae is a symbiotic association of a fungus with roots of higher plants. The fungus absorbs phosphate from soil and passes it to the plant. It also provides resistance to root-borne pathogen and increase the tolerance of plant to salinity and drought. This way they act as biofertilisers.
Genus of fungi — Glomus.
Question. How does the application of the fungal genus, Glomus, to the agricultural farm increase the farm output?
Answer. Glomus is a fungus which is found in symbiotic relationship with roots of seed plants. It absorbs phosphorus from the soil and passes it on to the plant, and in turn gets sugars from the plant. Due to increased availability of phosphorus there is an increase in farm output.
Question. How does the application of cyanobacteria help to improve agriculture output?
Answer. Cyanobacteria are autotrophic, free-living or symbiotic microbes. They can fix atmospheric nitrogen. Blue-green algae also add organic matter to the soil and increases its fertility. They replenish soil nutrients and reduce dependence on chemical fertilisers.
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 1 Reproduction in Organisms |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Human Reproduction |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 4 Reproductive Health |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 5 Principles of Inheritance and Variation |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 7 Evolution |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles And Processes |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystem |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 16 Environmental Issues |
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare
The above provided NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare is available on our website www.studiestoday.com for free download in Pdf. You can read the solutions to all questions given in your Class 12 Biology textbook online or you can easily download them in pdf. The answers to each question in Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare of Biology Class 12 has been designed based on the latest syllabus released for the current year. We have also provided detailed explanations for all difficult topics in Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare Class 12 chapter of Biology so that it can be easier for students to understand all answers. These solutions of Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare NCERT Questions given in your textbook for Class 12 Biology have been designed to help students understand the difficult topics of Biology in an easy manner. These will also help to build a strong foundation in the Biology. There is a combination of theoretical and practical questions relating to all chapters in Biology to check the overall learning of the students of Class 12.
You can download the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the NCERT Solutions issued for Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare have been made available here for latest academic session
Regular revision of NCERT Solutions given on studiestoday for Class 12 subject Biology Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all latest NCERT Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare Class 12 Biology solutions based on the latest books for the current academic session
Yes, NCERT solutions for Class 12 Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare Biology are available in multiple languages, including English, Hindi
All questions given in the end of the chapter Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare have been answered by our teachers

