NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Human Reproduction have been provided below and is also available in Pdf for free download. The NCERT solutions for Class 12 Biology have been prepared as per the latest syllabus, NCERT books and examination pattern suggested in Class 12 by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. Questions given in NCERT book for Class 12 Biology are an important part of exams for Class 12 Biology and if answered properly can help you to get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise answers for NCERT Class 12 Biology and also download more latest study material for all subjects. Chapter 3 Human Reproduction is an important topic in Class 12, please refer to answers provided below to help you score better in exams
Chapter 3 Human Reproduction Class 12 Biology NCERT Solutions
Class 12 Biology students should refer to the following NCERT questions with answers for Chapter 3 Human Reproduction in Class 12. These NCERT Solutions with answers for Class 12 Biology will come in exams and help you to score good marks
Chapter 3 Human Reproduction NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology
Question. Fill in the blanks.
(a) Humans reproduce _____________________. (asexually/sexually)
(b) Humans are _____________________. (oviparous, viviparous, ovoviviparous)
(c) Fertilisation is _____________________ in humAnswer. (external/internal)
(d) Male and female gametes are _____________________. (diploid/haploid)
(e) Zygote is _____________________. (diploid/haploid)
(f) The process of release of ovum from a mature follicle is called _____________________.
(g) Ovulation is induced by a hormone called _____________________.
(h) The fusion of male and female gametes is called _____________________.
(i) Fertilisation takes place in _____________________.
(j) Zygote divides to form _____________________ which is implanted in the uterus.
(k) The structure which provides vascular connection between foetus and uterus is called_____________.
Answer.
(a) sexually,
(b) viviparous,
(c) internal,
(d) haploid,
(e) diploid,
(f) ovulation,
(g) luteinising hormone,
(h) fertilisation,
(i) oviduct (ampullary–isthmic junction),
(j) blastocyst,
(k) placenta.
Question. Draw a labelled diagram of male reproductive system.
Answer.
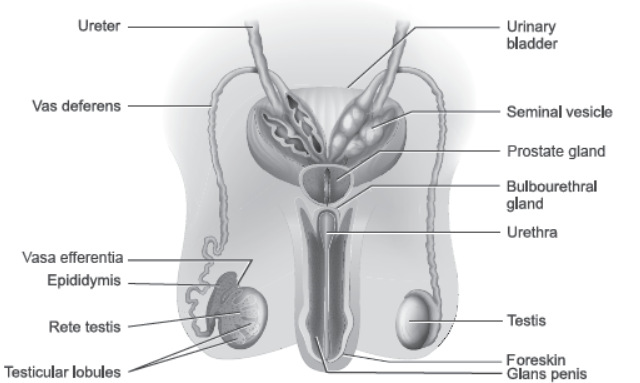
Question. Draw a labelled diagram of the human female reproductive system.
Answer.
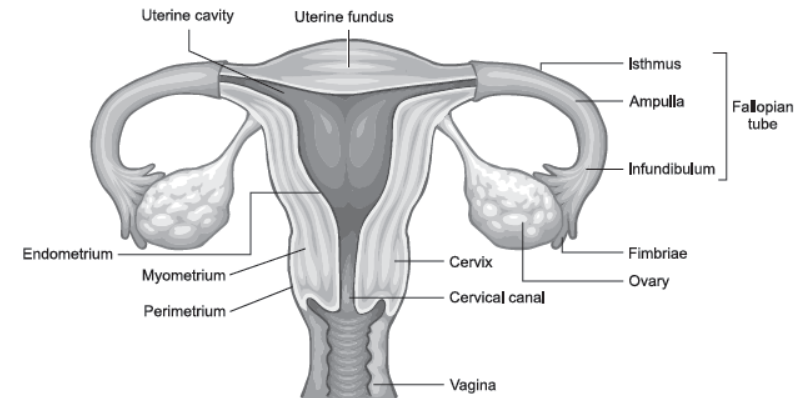
Question. Write two major functions each of testis and ovary.
Answer. Functions of testis:
(i) Production of sperms by seminiferous tubules.
(ii) Production of male sex hormone, testosterone, by Leydig cells.
Functions of ovary:
(i) Production of ova (eggs).
(ii) Production of female sex hormones, estrogen and progesterone.
Question. Describe the structure of a seminiferous tubule.
Answer. A seminiferous tubule is made up of layer of male germ cells and large Sertoli cells (nurse cells). The male germ cells undergo spermatogenesis to produce spermatocytes, spermatids and sperms. The regions outside the seminiferous tubules called interstitial spaces have connective tissue which includes blood vessels and Leydig cells (interstitial cells). Leydig cells synthesise and secrete the male sex hormones called androgens, of which testosterone is the principle one.
For diagram,
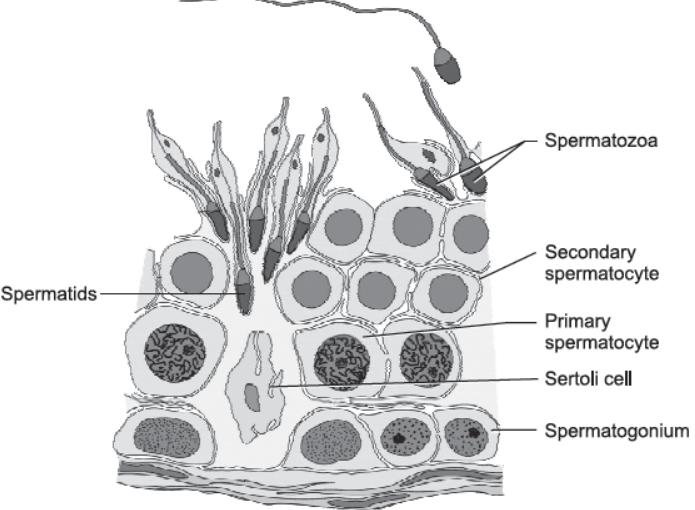
Question. What is spermatogenesis? Briefly describe the process of spermatogenesis.
Answer. The process of formation of spermatozoa (sperms) from diploid spermatogonia is called spermatogenesis. The male germ cells of seminiferous tubules multiply mitotically to increase in numbers. Spermatogonia grow and increase in size to form primary spermatocyte (2n). The primary spermatocytes undergo the first meiotic division and produce two haploid secondary spermatocytes (n). Each secondary spermatocyte undergoes the second meiotic division and produces 4 equal haploid spermatids. The spermatids are finally transformed into spermatozoa by the process of spermiogenesis.
Question. Name the hormones involved in regulation of spermatogenesis.
Answer. GnRH (Gonadotropin releasing hormone), LH (Luteinising hormone), FSH (Follicle stimulating hormone), androgen-binding protein (ABP), inhibin and androgens.
Question. Define spermiogenesis and spermiation.
Answer. Spermiogenesis: The process involving transformation of spermatids into spermatozoa is called spermiogenesis.
Spermiation: After spermiogenesis, sperm heads become embedded in the Sertoli cells and are finally released from the seminiferous tubules by the process called spermiation.
Question. Draw a labelled diagram of sperm.
Answer.
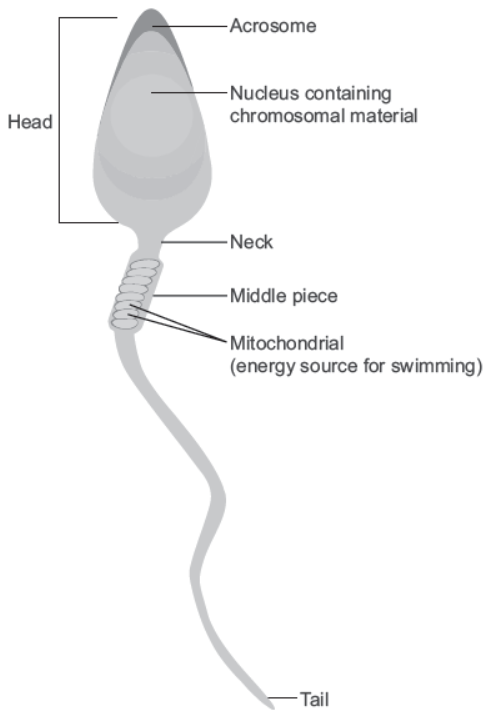
Question. What are the major components of seminal plasma?
Answer. Seminal plasma is the mixture of secretions of male accessory glands which include paired seminal vesicles, a prostate gland and a pair of bulbourethral glands.
Question. What are the major functions of male accessory ducts and glands?
Answer. Male accessory ducts include rete testes, vasa efferentia, epididymis and vas deferens. These ducts store and transport the sperms from the testes to the outside through urethra. Male accessory glands include paired seminal vesicles, prostate gland and paired bulbourethral glands. Secretion of these glands constitute the seminal plasma which is rich in fructose, calcium and certain enzymes. The secretions of bulbourethral glands also help in the lubrication of the penis.
Question. What is oogenesis? Give a brief account of oogenesis.
Answer. OO The process of formation of a mature female gamete is called oogenesis. It occurs in the ovaries.
It consists of the following three phases:
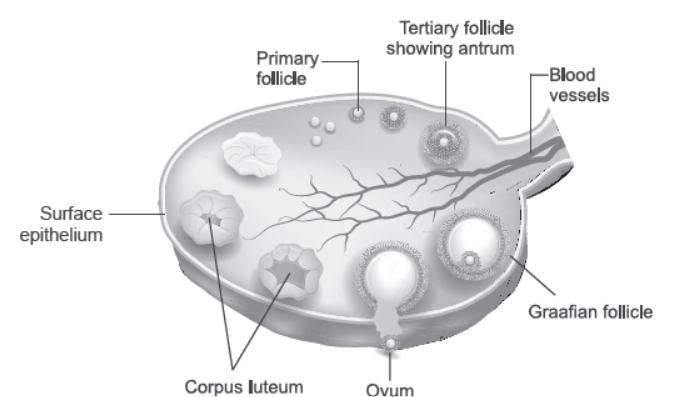
(a) Multiplication phase: Oogenesis is initiated during the embryonic development stage when a couple of million gamete mother cells (oogonia) are formed within each foetal ovary. No more oogonia are formed and added after birth. These cells start division and enter into prophase-I of the meiotic division. They get temporarily arrested at this stage and are called primary oocytes.
(b) Growth phase: Each primary oocyte then gets surrounded by a layer of granulosa cells. This structure is called the primary follicle. A large number of these follicles degenerate during the phase from birth to puberty. At puberty, only 60,000 to 80,000 primary follicles are left in each ovary. The primary follicles get surrounded by more layers of granulosa cells and a new theca to form secondary follicles.
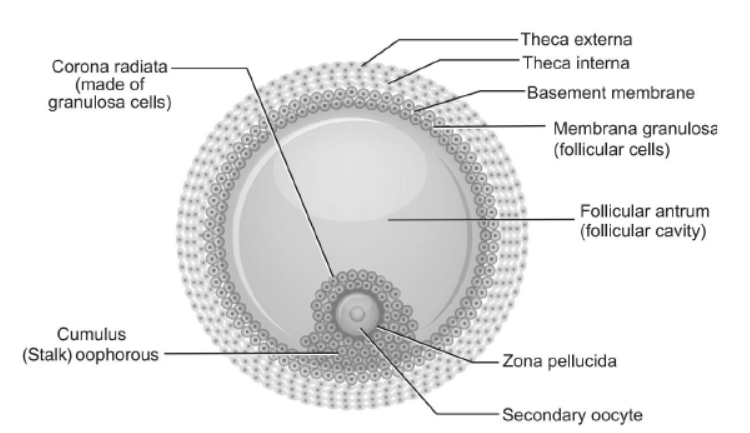
(c) Maturation phase: In the first maturation phase, the secondary follicle soon transforms into a tertiary follicle. The primary oocyte within the tertiary follicle grows in size and completes its first meiotic division to form a large, haploid, secondary oocyte and a tiny first polar body. The tertiary follicle changes into a mature follicle—the Graafian follicle—which ruptures to release the secondary oocyte (ovum) from the ovary by a process called ovulation. The second maturation phase occurs after fertilisation when the meiotic division of the secondary oocyte is complete. This second meiotic division results in the formation of a second polar body and a haploid ovum (ootid).
Question. Draw a labelled diagram of a section through ovary.
Answer.
Question. Draw a labelled diagram of a Graafian follicle.
Answer.
Question. Name the functions of the following:
(a) Corpus luteum (b) Endometrium
(c) Acrosome (d) Sperm tail
(e) Fimbriae
Answer.
(a) Corpus luteum: It acts as an endocrine gland and secretes progesterone which is essential for maintenance of the endometrium.
(b) Endometrium: It is the innermost layer of uterus responsible for nutrition and development of the foetus. It undergoes cyclic changes during menstrual cycle. Implantation of blastocyst takes place on the endometrium.
(c) Acrosome: It contains hydrolytic enzymes that help in dissolving membranes of the ovum for fertilisation.
(d) Sperm tail: It helps in the sperm movement in the female genital tract for fertilisation.
(e) Fimbriae: It is present at the opening of oviduct which helps in the collection of the eggs after ovulation.
Question. Identify True/False statements. Correct each false statement to make it true.
(a) Androgens are produced by Sertoli cells. (True/False)
(b) Spermatozoa get nutrition from Sertoli cells. (True/False)
(c) Leydig cells are found in ovary. (True/False)
(d) Leydig cells synthesise androgens. (True/False)
(e) Oogenesis takes place in corpus luteum. (True/False)
(f) Menstrual cycle ceases during pregnancy. (True/False)
(g) Presence or absence of hymen is not a reliable indicator of virginity or sexual experience. (True/False)
Answer. (a) False—Androgens are produced by Leydig cells or interstitial cells.
(b) True
(c) False—Leydig cells are found in testes.
(d) True
(e) False—Oogenesis takes place in Graafian follicles.
(f) True
(g) True
Question. What is menstrual cycle? Which hormones regulate menstrual cycle?
Answer. The reproductive cycle in the female primates is called menstrual cycle. The uterus lining becomes thick and spongy to receive fertilised egg. If the egg is not fertilised this lining is not needed any longer so, it slowly breaks and comes out through vagina as along with blood and mucous and is called menstruation.
Menstrual cycle is regulated by FSH (Follicle stimulating hormone), LH (Lutenising hormone), estrogen and progesterone.
Question. What is parturition? Which hormones are involved in induction of parturition?
Answer. The process of delivery of the foetus (child birth) at the end of the pregnancy is called parturition.The signals for parturition originate from the fully developed foetus and the placenta, which trigger the release of oxytocin from the maternal pituitary. Oxytocin acts on the uterine muscles and induces stronger uterine contractions leading to expulsion of the baby. Relaxin hormone released by the ovary widens the vagina to facilitate birth.
Question. In our society the women are often blamed for giving birth to daughters. Can you explain why this is not correct?
Answer. It is not correct to blame women for giving birth to daughters. The male sperm contains either X or Y chromosome whereas the female egg contains only X chromosomes. At the time of fertilisation when sperm carrying X chromosome combines with egg carrying X chromosome of female, XXzygote is formed which would be a female and when sperm with Y chromosome combines with egg containing X chromosome, XY-zygote is formed which would be a male. Thus, scientifically sex of the baby is determined by the father and not by the mother as blamed in our society.
Question. How many eggs are released by a human ovary in a month? How many eggs do you think would have been released if the mother gave birth to identical twins? Would your answer change if the twins born were fraternal?
Answer. Only one egg is released by a human (female) ovary in a month.
Only one egg is released if the mother gave birth to identical twins.
Yes. Two or more eggs are released in case fraternal twins are born.
Question. How many eggs do you think were released by the ovary of a female dog which gave birth to 6 puppies?
Answer. Six eggs are released by the ovary of a female dog if it gave birth to six puppies.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Human ReproductionMCQs
Choose and write the correct option in the following questions.
Question. The immature male germs cell undergo division to produce sperms by the process of spermatogenesis. Choose the correct one with reference to above.
(a) Spermatogonia have 46 chromosomes and always undergo meiotic cell division
(b) Primary spermatocytes divide by mitotic cell division
(c) Secondary spermatocytes have 23 chromosomes and undergo second meiotic division
(d) Spermatozoa are transformed into spermatids
Answer. C
Question. Urethral meatus refers to the
(a) urinogenital duct
(b) opening of vas deferens into urethra
(c) external opening of the urinogenital duct
(d) muscles surrounding the urinogenial duct
Answer. C
Question. The correct sequence of stages in spermatogenesis are:
(a) spermatogonia → spermatid → spermatocyte → sperm
(b) spermatocyte → spermatogonia → spermatid → sperm
(c) spermatogonia → spermatocyte → spermatid → sperm
(d) spermatid → spermatocyte → spermatogonia → sperm
Answer. C
Question. Seminal plasma in humans is rich in
(a) fructose and calcium
(b) glucose and calcium
(c) Progesterone and testosterone
(d) potassium and calcium
Answer. A
Question. The Leydig cells are a source of
(a) fructose
(b) androgens
(c) progesterone
(d) mucus
Answer. D
Question. Choose the incorrect statement from the following.
(a) In birds and mammals internal fertilisation takes place.
(b) Colostrum contains antibodies and nutrients.
(c) Polyspermy in mammals is prevented by the chemical changes in the egg surface.
(d) In the human female implantation occurs almost seven days after fertilisation.
Answer. C
Question. Morula is a developmental stage
(a) between the zygote and blastocyst
(b) between the blastocyst and gastrula
(c) after the implantation
(d) between implantation and parturition
Answer. A
Question. Identify the correct statement from the following.
(a) High levels of estrogen triggers the ovulatory surge.
(b) Oogonial cells start to proliferate and give rise to functional ova in regular cycles from puberty onwards.
(c) Sperms released from seminiferous tubules are highly motile/non-motile.
(d) Progesterone level is high during the post ovulatory phase of menstrual cycle.
Answer. B
Question. Spot the odd one out from the following structures with reference to the male reproductive system.
(a) Rete testis
(b) Epididymis
(c) Vasa efferentia
(d) Isthmus
Answer. D
Question. The vas deferens receives duct from the seminal vesicle and opens into urethra as
(a) epididymis
(b) ejaculatory duct
(c) efferent ductule
(d) ureter
Answer. B
Question. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
(a) GnRH stimulates secretion of FSH and LH
(b) LH stimulates the Leydig cells to secrete androgen
(c) FSH acts on the Sertoli cells and stimulates spermiogenesis
(d) None of these
Answer. D
Question. The membranous cover of the ovum at ovulation is
(a) corona radiata
(b) zona radiata
(c) zona pellucida
(d) chorion
Answer. A
Question. Number of chromosomes in polar body of human is
(a) 23
(b) 46
(c) 21
(d) 1
Answer. A
Question. Identify the odd one from the following.
(a) Labia minora
(b) Fimbriae
(c) Infundibulum
(d) Isthmus
Answer. A
Question. Spermiation is the process of the release of sperms from.
(a) Seminiferous tubules
(b) Vas deferens
(c) Epididymis
(d) Prostate gland
Answer. A
Question. The signals of parturition originate from
(a) placenta
(b) fully developed foetus
(c) oxytocin released from pituitary
(d) both placenta and fully developed foetus
Answer. B
Question. Mature Graafian follicle is generally present in the ovary of a healthy human female around.
(a) 5 – 8 day of menstrual cycle
(b) 11 – 17 day of menstrual cycle
(c) 18 – 23 day of menstrual cycle
(d) 24 – 28 day of menstrual cycle
Answer. B
Question. Which hormone of pituitary gland regulates Sertoli cells?
(a) LH
(b) FSH
(c) GH
(d) prolactin
Answer. B
Question. Which one of the following is not a male accessory gland?
(a) Seminal vesicle
(b) Ampulla
(c) Prostate
(d) Bulbourethral gland
Answer. B
Question. Which among the following has 23 chromosomes?
(a) Spermatogonia
(b) Zygote
(c) Secondary oocyte
(d) Oogonia
Answer. C
Question. The function of corpus luteum is to produce
(a) estrogen
(b) progesterone
(c) HCG
(d) relaxin
Answer. B
Question. Which of the following hormones is not secreted by human placenta?
(a) hCG
(b) Estrogens
(c) Progesterone
(d) LH
Answer. D
Question. Acrosomal reaction of the sperm occurs due to
(a) its contact with zona pellucida of the ova
(b) reactions within the uterine environment of the female
(c) reactions within the epididymal environment of the male
(d) androgens produced in the uterus
Answer. A
Question. Seminal plasma, the fluid part of semen, is contributed by.
(i) Seminal vesicle (ii) Prostate gland
(iii) Urethra (iv) Bulbourethral gland
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(c) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Answer. B
Question. Match the following and choose the correct options
Column I Column II
(A) Trophoblast (i) Embedding of blastocyst in the endome trium
(B) Cleavage (ii) Group of cells that would differentiate as embryo
(C) Inner cell mass (iii) Outer layer of blastocyst attached to the endometrium
(D) Implantation (iv) Mitotic division of zygote
Options:
(a) A-(ii), B-(i), C-(iii), D-(iv)
(b) A-(iii), B-(iv), C-(ii), D-(i)
(c) A-(iii), B-(i), C-(ii), D-(iv)
(d) A-(ii), B-(iv), C-(iii), D-(i)
Answer. B
Question. Match between the following representing parts of the sperm and their functions and choose the correct option.
Column I Column II
(A) Head (i) Enzymes
(B) Middle piece (ii) Sperm motility
(C) Acrosome (iii) Energy
(D) Tail (iv) Genetic material
options:
(a) A-(ii), B-(iv), C-(i), D-(iii)
(b) A-(iv), B-(iii), C-(i), D-(ii)
(c) A-(iv), B-(i), C-(ii), D-(iii)
(d) A-(ii), B-(i), C-(iii), D-(iv)
Answer. B
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Human Reproduction Assertion-Reason Questions
In the following questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Question. Assertion : A decrease in temperature has no effect on spermatogenesis.
Reason : Spermatogonia cannot survive the high body temperature.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : The uterus is shaped like an inverted pear.
Reason : The inner glandular layer lining the uterine cavity is called as myometrium.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : The middle piece of the sperm is called its powerhouse.
Reason : Numerous mitochondria in the middle piece produce energy for the movement of the tail.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : All sperms released at a time do not fertilise the ovum.
Reason : Fertilisation occur only when ovum and sperm fuse at the ampullary-isthmic junction.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : The embryo with 8 to 16 blastomeres is called a morula.
Reason : The morula continuously divides to transform into trophoblast.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : After implantation, finger-like projections appear on the trophoblast called chorionic villi.
Reason : Chorionic villi are surrounded by the uterine tissue and the maternal blood.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : The regions inside the seminiferous tubules contain Leydig cell.
Reason : Leydig cells synthesise and secrete androgens.
Answer. D
Question. Assertion : The endometrium undergoes cyclical changes during the menstrual cycle.
Reason : Perimetrium contracts strongly during delivery of the baby.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : The signals for parturition, originating from the foetus, trigger release of oxytocin which stimulates uterine contraction.
Reason : Vigorous contraction of the uterus at the end of pregnancy causes expulsion.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : In human beings, ovum is released from the ovary in the ootid stage.
Reason : The secondary oocyte divides into unequal daughter cells, a large ootid and a small polar body.
Answer. D
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Human Reproduction Case-based/Source-based Question
1. Study the graph given below and answer the questions that follow:
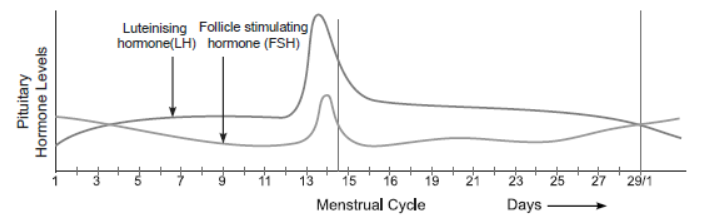
Question. What is the importance of LH surge?
Answer. LH surge is essential for the events leading to ovulation.
Question. Identify the ovarian phases during the menstrual cycle.
(a) 5th day to 12th day of the cycle.
(b) 14th day of the cycle.
Answer. (a) 5th day to 12th day of the cycle: Follicular phase (Proliferative phase).
(b) 14th day of the cycle: Ovulatory phase (release of ovum) followed by luteal phase.
Question. Menstrual cycles are absent during pregnancy. Why?
Answer. The high levels of progesterone and estrogens during pregnancy suppress the release of gonadotropins required for the development of new follicles. Therefore, new cycle cannot be initiated.
2. Study the figure given below:
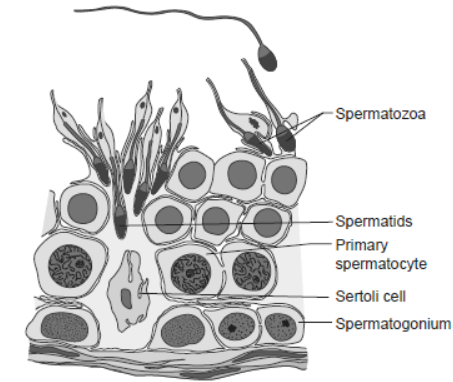
Question. Pick out and name the cells that undergo spermiogenesis.
Answer. Spermatids undergo spermiogenesis.
Question. Differentiate between spermiogenesis and spermiation?
Answer. Spermiogenesis: It is the transformation of spermatids into spermatozoa or sperms.
Spermiation: It is the release of sperms from the sertoli cells in the seminiferous tubules.
Question. How many sperms will be produced from 50 primary spermatocytes?
Answer. One primary spermatocyte undergoes meiosis to form four sperms. So, primary spermatocyte will produce 200 sperms.
3. Study the figure given below and answer the questions that follow:
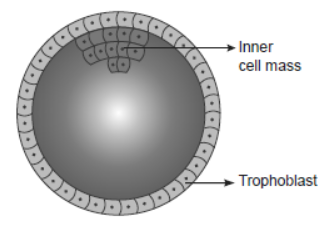
Question. Name the stage of human embryo the figure represents.
Answer. Blastocyst
Question. Mention the fate of the inner cell mass after implantation in the uterus.
Answer. The inner cell mass differentiates into an outer layer of ectoderm and an inner layer of endoderm.
Question. Where are the stem cells located in this embryo?
Answer. Inner cell mass.
4. Study the figures given below and answer the questions that follow.
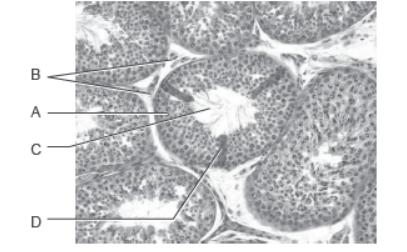
Question. During reproduction, the chromosome number (2n) reduces to half (n) in the gametes and again resume the original number (2n) in the offspring, what are the processes through which these events take place?
Answer. Halving of chromosomal number takes place during gametogenesis by meosis and regaining the 2n number occur as a result of fertilisation by fusion of male and female gametes.
Question. Write the functions of A and D.
Answer. A : The spermatogonia or male germ cells undergo meiotic divisions leading to sperm formation.
D : Sertoli cells provide nutrition to the germ cells.
Question. Mention the function of mitochondria in sperm.
Answer. Provide energy for the movement of sperm tail.
5. The following is the illustration of the sequence of ovarian events (a – i) in a human female.
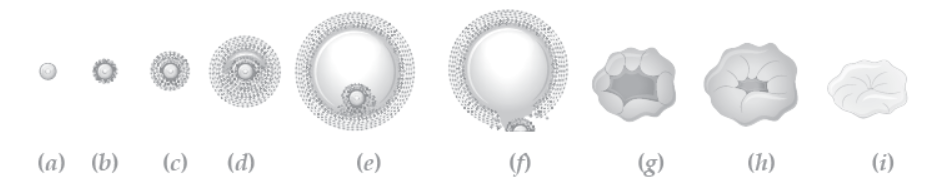
Question. Identify the figure that illustrates ovulation and mention the stage of oogenesis it represents.
Answer. f ; secondary oocyte.
Question. Name the ovarian hormone and the pituitary hormone that have caused the above mentioned event.
Answer. Estrogen and luteinising hormone (LH)
Question. Explain the changes that occur in the uterus simultaneously in anticipation.
Answer. Endometrium proliferate (glands become cork-screw shaped) highly vascularised, high regeneration anticipating implantation of the fertilised ovum.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Human Reproduction Very Short Answer Questions
Question. Write the location and function of the Sertoli cells in humans.
Answer. Sertoli cells are present in seminiferous tubules. They provide nutrition to the germ cells or sperms.
Question. Mention the location and the function of Leydig cells in humans.
Answer. Leydig cells are present in the regions called interstitial spaces outside the seminiferous tubules.
They synthesise and secrete androgens (testosterone).
Question. Mention the function of mitochondria in sperm.
Answer. Provide energy for the movement of sperm tail.
Question. When do the oogenesis and the spermatogenesis initiate in human females and males respectively?
Answer. Oogenesis in human females initiate at the foetal/embryonic stage.
Spermatogenesis in human males starts at puberty.
Question. Males in whom testes fail to descend to the scrotum are generally infertile. Why?
Answer. If the testes fail to descend to the scrotum, gametogenesis could be inhibited. The process of spermatogenesis requires a marginally lesser (2°C less) ambient temperature than that in the abdominal cavity.
Question. The path of sperm transport is given below. Provide the missing steps in blank boxes.
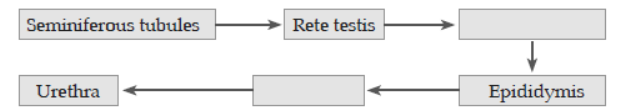
Answer. Vasa efferentia, Vas deferens.
Question. What is the role of cervix of the human female system in reproduction?
Answer. Cervix helps in regulating the passage of sperms into the uterus and forms the birth canal to facilitate parturition.
Question. Name the important mammary gland secretions that help in resistance of the new born baby.
Answer. Colostrum
Question. Name the hormones produced only during pregnancy in a human female. Mention their source organ.
Answer. During pregnancy, placenta produces hormones like human chorionic gonadotropin and human placental lactogen and ovary produces relaxin.
Question. List the changes that the primary ooctye undergoes in the tertiary follicular stage in the human ovary.
Answer. The primary oocyte within the tertiary follicle grows in size and completes its first meiotic division to form secondary oocyte and first polar body.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Human Reproduction Short Answer Questions
Question. Why are the human testes located outside the abdominal cavity? Name the pouch in which they are present.
Answer. The human testes need lower temperature, 2 – 2.5°C less than the body temperature, for the formation of sperms which is provided outside the body.
Testes are present in scrotal sac or scrotum.
Question. What is the number of chromosomes in the following cells of a human male?
(i) Spermatogonial cells (ii) Spermatids
(iii) Primary spermatocytes (iv) Sertoli cells
Answer. (i) 46 (ii) 23
(iii) 46 (iv) 46.
Question. (i) How many spermatozoa are formed from one secondary spermatocyte?
(ii) Where does the first cleavage division of zygote take place?
Answer. (i) Two
(ii) During the passage of zygote from fallopian tube to the uterus.
Question. Draw a diagram of a human sperm. Label only those parts along with their functions, that assist the sperm to reach and gain entry into the female gamete.
Answer.
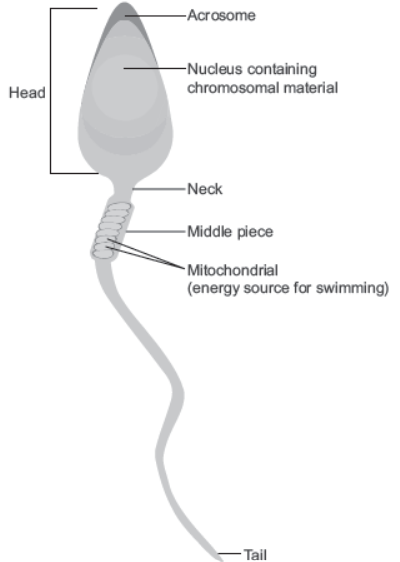
Question. Where is acrosome present in humans? Write its function.
Answer. Acrosome is present on the sperm head. It has enzymes to help the sperm enter into the cytoplasm of ovum through zona pellucida and plasma membrane to facilitate entry of sperm nucleus for fertilisation.
Question. Write the function of each of the following:
(a) Middle piece in human sperm.
(b) Luteinising hormone in human males.
Answer. (a) Provides energy for movement as it contains mitochondria.
(b) Stimulates synthesis and secretion of androgens or male hormones for spermatogenesis.
Question. Write the function of each of the following:
(a) Seminal vesicle
(b) Acrosome of human sperm.
Answer. (a) It is responsible for storage and transport of sperms. It provides secretions for motility and nourishment of sperms.
(b) It helps the sperm to enter into the cytoplasm of the ovum through the zona pellucida and provides enzymes for fertilisation.
Question. Spermatogenesis in human males is a hormone regulated process. Justify.
Answer. Spermatogenesis: Formation of haploid spermatozoa (sperms) from diploid spermatogonia in males.
Question. Write the location and functions of myometrium and endometrium.
Answer. Endometrium is the inner layer of uterus. It assists in cyclic changes during menstruation and implantation of embryo.
Myometrium is the middle layer of uterus. It consist of smooth muscles and thus assists in contractions of the uterus during parturition.
Question. Where are fimbriae present in a human female reproductive system? Give their function.
Answer. The fimbriae are the finger-like projections present on the edges of infundibulum (fallopian tubes). They help in collection of ovum after ovulation.
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 1 Reproduction in Organisms |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Human Reproduction |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 4 Reproductive Health |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 5 Principles of Inheritance and Variation |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 7 Evolution |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles And Processes |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystem |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 16 Environmental Issues |
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Human Reproduction
The above provided NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Human Reproduction is available on our website www.studiestoday.com for free download in Pdf. You can read the solutions to all questions given in your Class 12 Biology textbook online or you can easily download them in pdf. The answers to each question in Chapter 3 Human Reproduction of Biology Class 12 has been designed based on the latest syllabus released for the current year. We have also provided detailed explanations for all difficult topics in Chapter 3 Human Reproduction Class 12 chapter of Biology so that it can be easier for students to understand all answers. These solutions of Chapter 3 Human Reproduction NCERT Questions given in your textbook for Class 12 Biology have been designed to help students understand the difficult topics of Biology in an easy manner. These will also help to build a strong foundation in the Biology. There is a combination of theoretical and practical questions relating to all chapters in Biology to check the overall learning of the students of Class 12.
You can download the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Human Reproduction for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the NCERT Solutions issued for Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Human Reproduction have been made available here for latest academic session
Regular revision of NCERT Solutions given on studiestoday for Class 12 subject Biology Chapter 3 Human Reproduction can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all latest NCERT Chapter 3 Human Reproduction Class 12 Biology solutions based on the latest books for the current academic session
Yes, NCERT solutions for Class 12 Chapter 3 Human Reproduction Biology are available in multiple languages, including English, Hindi
All questions given in the end of the chapter Chapter 3 Human Reproduction have been answered by our teachers

