NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystem have been provided below and is also available in Pdf for free download. The NCERT solutions for Class 12 Biology have been prepared as per the latest syllabus, NCERT books and examination pattern suggested in Class 12 by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. Questions given in NCERT book for Class 12 Biology are an important part of exams for Class 12 Biology and if answered properly can help you to get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise answers for NCERT Class 12 Biology and also download more latest study material for all subjects. Chapter 14 Ecosystem is an important topic in Class 12, please refer to answers provided below to help you score better in exams
Chapter 14 Ecosystem Class 12 Biology NCERT Solutions
Class 12 Biology students should refer to the following NCERT questions with answers for Chapter 14 Ecosystem in Class 12. These NCERT Solutions with answers for Class 12 Biology will come in exams and help you to score good marks
Chapter 14 Ecosystem NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology
Question. Fill in the blanks.
(a) Plants are called as ___________________ because they fix carbon dioxide.
(b) In an ecosystem dominated by trees, the pyramid (of numbers) is ________________ type.
(c) In aquatic ecosystems, the limiting factor for the productivity is ___________________.
(d) Common detritivores in our ecosystem are ___________________.
(e) The major reservoir of carbon on earth is ___________________.
Answer. (a) producers (b) inverted
(c) light (d) earthworm, ants and mites.
(e) oceans (71% dissolved carbon)
Question. Which one of the following has the largest population in a food chain?
(a) Producers
(b) Primary consumers
(c) Secondary consumers
(d) Decomposers
Answer. (a) Producers
Question. The second trophic level in a lake is
(a) Phytoplankton
(b) Zooplankton
(c) Benthos
(d) Fishes
Answer. (b) Zooplankton
Question. Secondary producers are
(a) Herbivores
(b) Producers
(c) Carnivores
(d) None of the above
Answer. (b) Herbivores
Question. What is the percentage of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR), in the incident solar radiation?
(a) 100%
(b) 50%
(c) 1–5%
(d) 2–10%
Answer. (b) 50%
Question. Distinguish between
(a) Grazing food chain and detritus food chain
(b) Production and decomposition
(c) Litter and detritus
(d) Upright and inverted pyramid
(e) Food chain and food web
(f) Primary and secondary productivity
Answer.
(a) Grazing food chain and detritus food chain:
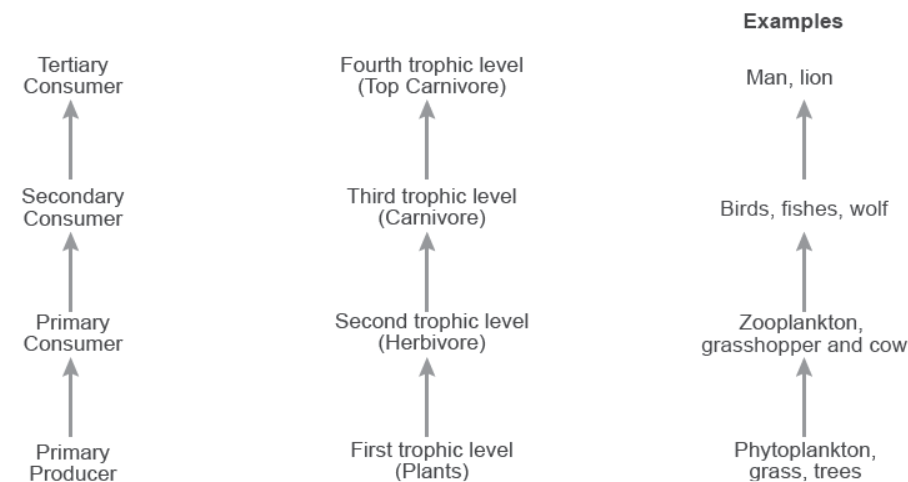
In an ecosystem, an organism occupies a specific place in the food chain called trophic level.
- Each trophic level has a certain mass of living material at a particular time called the standing crop.
- The standing crop is measured as the biomass of living organisms (biomass), or the number in a unit area. Biomass is expressed interms of fresh or dry weight.
(b) Differences between production and decomposition
| Production | Decomposition |
| It is the process of formation of fresh biomass from inorganic matter by producers (plants) using sunlight. |
It is the process of degradation of waste biomass into its constituents by decomposers. |
| It traps energy. | It releases energy. |
| It needs sunlight. | It does not require sunlight. |
| It is an anabolic process. | It is a catabolic process. |
(c) Differences between litter and detritus
| Litter | Detritus |
| It is made of dried fallen plant matter. | It is freshly deposited organic matter, i.e., remains of plants and animals. |
| It is found above the ground. | It is found both above and below the ground. |
(d) Differences between upright and inverted pyramid
| Upright pyramid | Inverted pyramid |
| The base bar comprises of producers in large number. |
The base bar comprises producers in smallest number. |
| The number of consumers decrease and become least in top consumer level. | The number of consumers increase and become largest in top consumer level. |
| Pyramid of energy is always upright. | Pyramid of number and biomass may be inverted. |
(e) Food chain and food web:
| Food chain | Food web |
| The transfer of energy from producers to top consumers through a series of organisms is called food chain. |
A number of food chains are inter-connected with each other, forming a web-like pattern is called food web. |
| One organism holds only one position. | One organism can hold more than one position. |
| The flow of energy can be easily calculated. | The flow of energy is very difficult to calculate. |
| It is always straight and proceed in a progressive straight line. | Instead of straight line it is a series of branching lines. |
| Competition is limited to members of same trophic level. | Competition is amongst members of same and different trophic levels. |
(f) Differences between primary and secondary productivity
| Primary productivity | Secondary productivity |
| It is the rate at which organic matter is built up by producers. | It is the rate at which organic matter is built up by consumers |
| It is the result of synthesis of fresh organic matter from inorganic materials. | It is the result of synthesis of organic matter from plant organic matter. |
Question. Describe the components of an ecosystem.
Answer. An ecosystem consists of two types of components, i.e., biotic or living and abiotic or non-living.
There are three main types of biotic components on the basis of mode of obtaining their food— producers, consumers and decomposers.
(i) Producers (autotrophs): They are photosynthetic or autotrophic plants that synthesise their own organic food from inorganic raw materials with the help of solar radiations. Common producers are algae, plants and photosynthetic bacteria. Phytoplanktons are the producers of aquatic ecosystems.
(ii) Consumers (heterotrophs): They are animals which feed on other organisms or producers for obtaining their nourishment. Common consumers are deer, goat, etc.
(iii) Decomposers: They are saprotrophs which obtain nourishment from organic remains. They release digestive enzymes to digest the organic matter. Common decomposers are detritivores,e.g., earthworm. Abiotic component of ecosystem consists of non-living substances and factors which are as follows:
(a) Temperature
(b) Light
(c) Wind
(d) Humidity
(e) Precipitation
(f) Water, etc.
Question. Define ecological pyramids and describe with examples, pyramids of number and biomass.
Answer. (i) Pyramid of number: The relationship between producers and consumers in an ecosystem can be represented in the form of a pyramid in terms of number of organisms at different trophic levels called pyramid of number.
It is inverted, when you count number of insects feeding on a big tree.
(ii) Pyramid of biomass: The relationship between producers and consumers in an ecosystem can be represented in the form of a pyramid in terms of biomass called pyramid of biomass. It can be
(a) Upright, e.g., in case of grassland ecosystem; or
(b) Inverted, e.g., in case of pond ecosystem as biomass of fishes for exceeds that of phytoplanktons
Question. What is primary productivity? Give brief description of factors that affect primary productivity.
Answer. Primary productivity is the rate of synthesis of biomass by producers, per unit time, per unit area through the process of photosynthesis.
For factors affecting primary productivity,
- Plant species inhabiting a particular area.
- Environmental factors:
(i) Sunlight: The sunlight directly regulates the primary productivity because the plants perform photosynthesis with the help of sunlight. As tropical region receives maximum sunlight so it exhibits higher productivity.
(ii) Temperature: Temperature regulates the activity of enzyme. So, optimum temperature is required for proper functioning of enzyme.
(iii) Moisture: Rain (humidity) is required for higher primary productivity. Deserts have the lowest primary productivity as the soil is deficient in moisture.
- Availability of nutrients: Greater nutrients ensure greater primary productivity.
- Photosynthetic efficiency: Some plants have more efficiency to trap sunlight (sugarcane), so they accumulate more primary productivity.
- Annual Net Primary Productivity of whole biosphere is approx. 170 billion tons (dry weight) of organic matter. Of this, oceans occupy 70% of surface, productivity of oceans are only 55 billion tons. Rest if from land.
Question. Define decomposition and describe the process and products of decomposition.
Answer.
- The process of breaking down complex organic matter into inorganic substances like CO2, water and nutrients is called decomposition.
- The raw materials for decomposition including dead plant remains like leaves, bark, flowers, and animal remains and their faecal matter are called detritus
Steps in Decomposition
(i) Fragmentation: The process of breaking down of detritus into smaller particles is called fragmentation, e.g., as done by earthworm (= farmer’s friend).
(ii) Leaching: The process by which water-soluble inorganic nutrients go down into the soil horizon and get precipitated as unavailable salts is called leaching.
(iii) Catabolism: The enzymatic process by which bacterial and fungal enzymes degrade detritus to simpler inorganic substances is called catabolism.
(iv) Humification: The process of accumulation of a dark coloured amorphous substance, called humus, that is highly resistant to microbial action and undergoes decomposition at an extremely slow rate is called humification. Humus being colloidal is reservoir of nutrients.
(v) Mineralisation: The process by which humus is further degraded by some microbes to release inorganic nutrients is called mineralisation.
Decomposition produces a dark coloured nutrient rich substance called humus which on degradation releases CO2, water and other nutrients in the soil.
Question. Give an account of energy flow in an ecosystem.
Answer.
- The sun is the only source of energy for all ecosystems on earth.
- Out of the total incident solar radiation, only 50 per cent of it is photosynthetically active radiation (PAR).
- Plants capture only 2–10 per cent of the PAR and this small amount of energy sustains the entire living world. So, there is unidirectional flow of energy from the sun to producers and then to consumers.
- The energy is transferred in an ecosystem, in the form of food which is degraded and lose major part of food energy as heat during metabolic activities and only a very small fraction becomes stored as biomass.
- This is correlated to second law of thermodynamics, i.e., ecosystems need a constant supply of energy to synthesize molecules they require, to counteract universal tendency towards increasing disorderliness.
- The green plants in the ecosystem which can trap solar energy to convert it into chemical bond energy are called producers.
- All the animals that depend for food on plants are called consumers or heterotrophs.
- Consumers are divided into the following categories:
(i) Primary consumers: Animals which feed directly on plants, i.e., herbivores.
(ii) Secondary consumers: Consumers that feed on primary consumers, i.e., carnivores.
(iii) Tertiary consumers: Consumers that feed on secondary consumers.
QU Lindeman’s 10 per cent law: At each step of food chain, when food energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next higher trophic level, only about 10 per cent of energy is passed on to the next trophic level. This is known as Lindeman’s 10 per cent law given by Lindeman in 1942.
Question. Write important features of a sedimentary cycle in an ecosystem.
Answer. Sedimentary cycle is circulation of non-gaseous biogeochemical nutrients between abiotic and biotic components of ecosystem with reservoir pool being lithosphere or sediments of earth.
Important features of a sedimentary cycle in an ecosystem are:
(i) Input: Weathering of rocks, industrial processing and mining adds the nutrient to the cycling pool.
(ii) Internal cycling: Nutrients contained in the cycling pool are picked up by producers and the process is called uptake. Organic matter with nutrients is then passed to the next trophic levels.Wastes and dead remains of organisms give rise to detritus which undergoes decomposition.
(iii) Output: It is the loss of nutrients from cycling pool. It occurs through soil erosion, run-off water, etc.
Question. Outline salient features of carbon cycling in an ecosystem.
Answer.
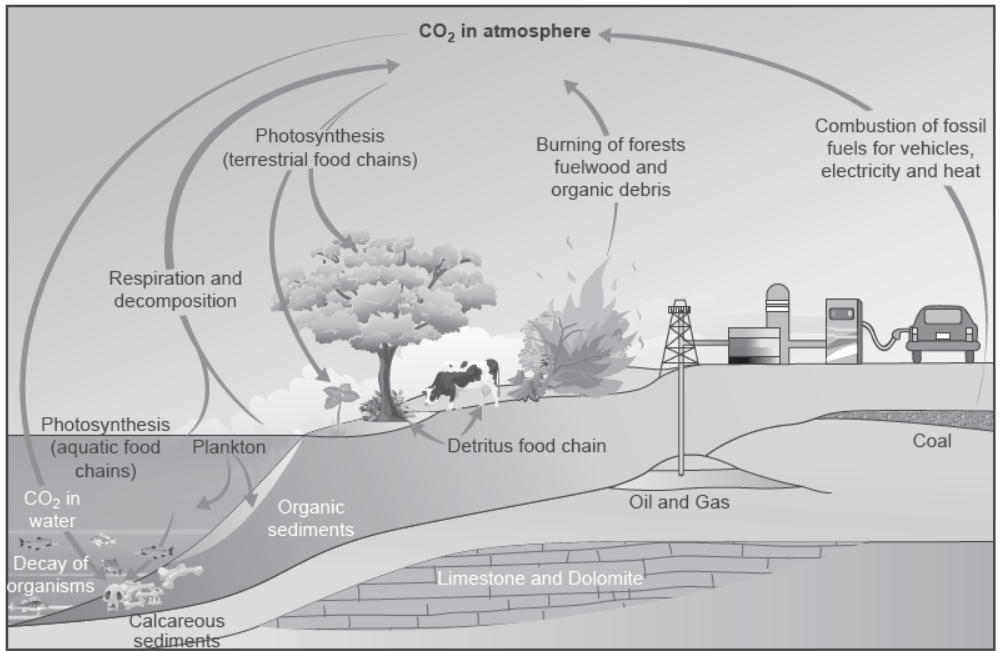
- Carbon constitutes 49 per cent of dry weight of an organism.
- 71 per cent of the carbon is found dissolved in oceans which is responsible for its regulation in atmosphere.
- The carbon cycle occurs through atmosphere, oceans and through living and dead organisms.
- It is estimated that 4 × 1013 kg of carbon is fixed in the biosphere through photosynthesis annually.
- Carbon is returned to atmosphere as CO2 by animals and plants through respiration and the activities of decomposers.
- Some amount of fixed carbon is lost as sediments and removed from circulation.
- Burning of wood, forest fire, volcanic activity and combustion of organic matter and fossil fuels are some additional sources for releasing CO2 in the atmosphere.
- Human activities like deforestation and vehicular burning of fossil fuels have caused an increase in the amount of CO2 in atmosphere.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystem Multiple Choice Questions
Question. Which of the following ecosystems is most productive in terms of net primary production?
(a) Deserts
(b) Tropical rain forests
(c) Oceans
(d) Estuaries
Answer. B
Question. Pyramid of numbers is
(a) always upright
(b) always inverted
(c) either upright or inverted
(d) neither upright nor inverted
Answer. C
Question. The upright pyramid of number is absent in
(a) pond
(b) forest
(c) lake
(d) grassland
Answer. B
Question. Which of the following type of ecosystem is expected in an area where evaporation exceeds precipitation, and mean annual rainfall is below 100 mm?
(a) Grassland
(b) Shrubby forest
(c) Desert
(d) Mangrove
Answer. C
Question. The zone at the edge of a lake or ocean which is alternatively exposed to air and immersed in water is called:
(a) pelagic zone
(b) benthic zone
(c) lentic one
(d) littoral zone
Answer. D
Question. The rate of formation of new organic matter by rabbit in a grassland, is called
(a) net productivity
(b) second productivity
(c) net primary productivity
(d) gross primary productivity
Answer. A
Question. Decomposers like fungi and bacteria are
(i) autotrophs (ii) heterotrophs
(iii) saprotrophs (iv) chemo-autotrophs
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (i) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (ii)
Answer. C
Question. The process of mineralisation by microorganisms helps in the release of
(a) inorganic nutrients from humus
(b) both organic and inorganic nutrients from detritus
(c) organic nutrients from humus
(d) inorganic nutrients from detritus and formation of humus.
Answer. A
Question. Which one of the following is not a functional unit of an ecosystem?
(a) Energy flow
(b) Decomposition
(c) Productivity
(d) Stratification
Answer. D
Question. Productivity is the rate of production of biomass expressed in terms of
(i) (kcal m–3) yr–1 (ii) g–2 yr–1
(iii) g–1 yr–1 (iv) (kcal m–2) yr–1
(a) (ii)
(b) (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iii)
Answer. C
Question. Mass of living matter at a trophic level in an area at any time is called
(a) standing crop
(b) detritus
(c) humus
(d) standing state
Answer. A
Question. Which one of the following is not a gaseous biogeochemical cycle in ecosystem?
(a) Oxygen cycle
(b) Phosphorus cycle
(c) Nitrogen cycle
(d) Carbon cycle
Answer. B
Question. Identify the possible link “A” in the following food chain.
Plant → insect → frog → “A” → eagle
(a) rabbit
(b) wolf
(c) cobra
(d) parrot
Answer. C
Question. An inverted pyramid of biomass can be found in which ecosystem?
(a) Forest
(b) Marine
(c) Grass land
(d) Tundra
Answer. B
Question. What is the difference between a community or group of communities and an ecosystem?
(a) A community and the abiotic environment comprise an ecosystem.
(b) An ecosystem is a type of community.
(c) A biome includes only the plant community or communities present in an environment.
(d) An ecosystem includes only the abiotic aspects of a particular environment.
Answer. A
Question. Of the total amount of energy that passes from one trophic level to another, about 10% is
(a) respired and becomes heat
(b) passed out as faces or urine
(c) stored as body tissue
(d) recycled to autotrophs
Answer. C
Question. Which of the following is an ecosystem service provided by a natural ecosystem?
(a) Cycling of nutrients
(b) Prevention of soil erosion
(c) Pollutant absorption and reduction of the threat of global warming
(d) All of the above
Answer. D
Question. A succession of communities on barren land, is known as
(a) secondary succession
(b) primary succession
(c) tertiary succession
(d) none of these
Answer. B
Question. During the process of ecological succession the changes that take place in communities are
(a) orderly and sequential
(b) random
(c) very quick
(d) not influenced by the physical environment.
Answer. A
Question. Climax community is in a state of
(a) non-equilibrium
(b) equilibrium
(c) disorder
(d) constant change.
Answer. A
Question. Among the following bio-geo-chemical cycles which one does not have losses due to respiration?
(a) Phosphorus
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Sulphur
(d) All of the above
Answer. B
Question. If the carbon atoms fixed by producers already have passed through three species, the trophic level of the last species would be:
(a) scavenger
(b) tertiary producer
(c) tertiary consumer
(d) secondary consumer
Answer. B
Question. Humans benefit from ecosystems because ecosystems provide
(a) buffers from natural disasters such as floods.
(b) maintenance of a clean water supply.
(c) climate moderation.
(d) All of the above
Answer. C
Question. Edaphic factor refers to:
(a) water
(b) soil
(c) relative humidity
(d) altitude
Answer. B
Question. The sequence of communities of primary succession in water is
(a) phytoplankton, sedges, free-floating hydrophytes, rooted hydrophytes, grasses and trees.
(b) phytoplankton, free-floating hydrophytes, rooted hydrophytes, sedges, grasses and trees.
(c) free-floating hydrophytes, sedges, phytoplankton, rooted hydrophytes, grasses and trees.
(d) phytoplankton, rooted submerged hydrophytes, floating hydrophytes, reed swamp, sedges, meadow and trees.
Answer. D
Question. The reservoir for the gaseous type of bio-geo chemical cycle exists in
(a) stratosphere
(b) atmosphere
(c) ionosphere
(d) lithosphere
Answer. B
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystem Assertion-Reason Questions
In the following questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Question. Assertion : In a food chain the members of the successive trophic levels are fewer.
Reason : Number of organisms at any trophic level is independent of the availability of organisms which serve as food at the lower level.
Answer. D
Question. Assertion : Ecological succession occurs when older communities of plants and animals are replaced by newer communities.
Reason : The natural process of replacement of one vegetation community in a given habitat by the other vegetation community.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : Vertical distribution of different species occupying different levels is called stratification.
Reason : Trees occupy top vertical strata, shrub the second, herbs and grasses occupy the bottom layers.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : The decomposers feed on detritus, or decaying organic matter, derived from all levels.
Reason : At each level of energy flow in the food web, energy is lost to respiration.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : In a terrestrial ecosystem, detritus food chain is the major conduit for energy flow.
Reason : Solar energy is the direct source for energy supply in a detritus food chain.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : A network of food chains existing together in an ecosystem is known as a food web.
Reason : An animal like kite cannot be part of a food web.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : In open water zone upto the depth to which light can penetrate is called photic zone.
Reason : The photic zone contains autotrophs.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : Net primary productivity is gross primary productivity minus respiration.
Reason : Secondary productivity is produced by heterotrophs.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : Primary succession takes very long time.
Reason : Soil is absent at the time of beginning of primary succession.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : Pyramid of energy is always upright.
Reason : When energy flows from a particular trophic level to the next trophic level, some energy is always lost at heat at each step.
Answer. A
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystem Case-based/Source-based Question
1. Study the diagram given below and answer the questions that follow.
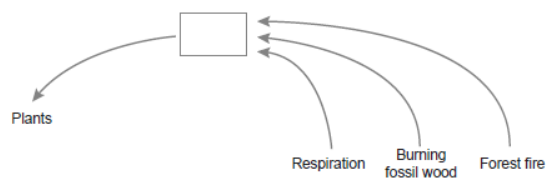
Question. Name the biogeochemical (nutrient) cycle shown above.
Answer. The biogeochemical cycle shown is carbon cycle.
Question. Name an activity of the living organisms not depicted in the cycle by which this nutrient is returned to the atmosphere.
Answer. Volcanic activity and mining/Microbial decomposition of organic matter.
Question. How would the flow of the nutrient in the cycle be affected due to large scale deforestation?
Explain giving reasons.
Answer. Due to large scale deforestation, the flow of carbon in the environment will be disturbed because plants are the major consumers which utilise carbon for photosynthesis. This would lead to accumulation of carbon in the atmosphere.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystem Very Short Answer Questions
Question. Name an omnivore which occurs in both grazing food chain and the decomposer food chain.
Answer. Sparrow/crow
Question. Standing crop and biomass are related to each other, how?
Answer. The standing crop is measured as the mass of living organisms or the number of plants in a unit area. The biomass of a species is expressed in terms of fresh or dry weight.
Question. All the primary productivity is not available to a herbivore. Give one reason.
Answer. All the primary productivity is not available to a herbivore because a considerable amount is utilised by the plant by respiration.
Question. Differentiate between standing state and standing crop in an ecosystem.
Answer. In an ecosystem, standing crop is the mass of living material in each trophic level at a particular time. Whereas standing state refers to the amount of nutrients in the soil at any given time.
Question. Why is the pyramid of biomass inverted in a pond ecosystem?
Answer. The pyramid of biomass is inverted in a pond ecosystem because the biomass of fish (top consumer) is far larger than the producers (phytoplanktons).
Question. Mention the role of pioneer species in primary succession on rocks.
Answer. The pioneer species invade a bare area and pave way for other species.
Question. Why is a food web formed in nature?
Answer. Many organisms occupy positions in different food chains and several food chains become interconnected to form a food web.
Question. What is a detritus food chain made up of? How do they meet their energy and nutritional requirements?
Answer. Dead plant and animal remains and their faecal matter constitute Detritus. DFC includes decomposers which obtain energy by decomposing the dead materials.
Question. Define mineralisation.
Answer. It is the process in which the humus is degraded by certain microbes and thus inorganic nutrients are released in the soil.
Question. Climax stage is achieved quickly in secondary succession as compared to primary succession. Why?
Answer. The rate of succession is much faster in secondary succession as the substratum (soil) is already present as compared to primary succession where the process starts from a bare area (rock).
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystem Short Answer Questions
Question. Differentiate between two different types of pyramids of biomass with the help of one example of each.
Answer. Differences between upright and inverted pyramids of biomass
| Upright pyramid of biomass | Inverted pyramid of biomass |
| The biomass of producers is more than that of consumers. |
The biomass of the producers (phytoplankton) is less than that of consumers (fish). |
| For example, forest ecosystem. | For example, aquatic ecosystem. |
Question. Construct a pyramid of biomass starting with phytoplanktons. Label three trophic levels. Is the pyramid upright or inverted? Why?
Answer.

The pyramid is inverted because the biomass of fishes is much more than that of the phytoplanktons.
Question. Why is earthworm considered a farmer’s friend? Explain humification and mineralisation occurring in a decomposition cycle.
Answer. Earthworms help in breakdown of complex organic matter as well as loosening of the soil. This helps in the proper growth of the crops. Therefore, they are considered farmer’s friend.
Humification: The process of accumulation of a dark coloured amorphous substance, called humus, that is highly resistant to microbial action and undergoes decomposition at an extremely slow rate is called humification. Humus being colloidal is reservoir of nutrients.
Mineralisation: The process by which humus is further degraded by some microbes to release inorganic nutrients is called mineralisation.
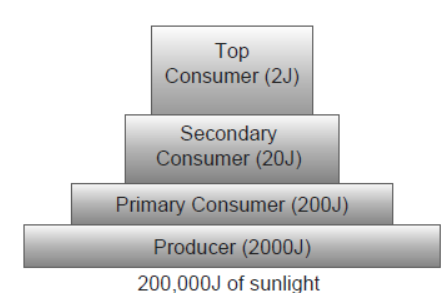
Question. Compare the two ecological pyramids of biomass given below and explain the situations in which this is possible. Also, construct an ideal pyramid of energy, if 200,000 joules of sunlight is available.
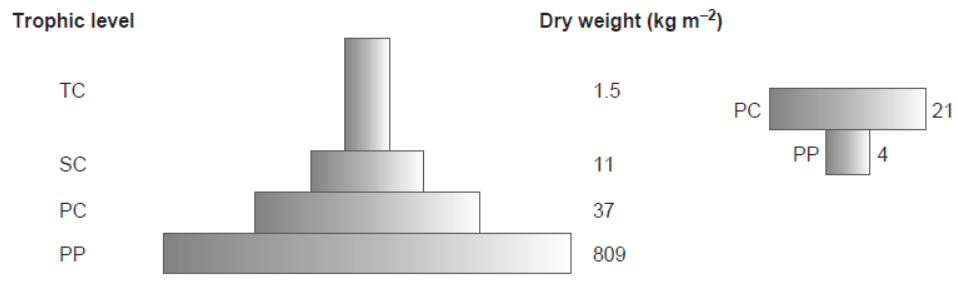
Answer. The first pyramid of biomass corresponds to a terrestrial ecosystem. Second pyramid refers to a small standing crop of phytoplankton supporting a large standing crop of zooplankton or an aquatic ecosystem.
Question. “In a food-chain, a trophic level represents a functional level, not a species.” Explain.
Answer. A given species may occupy more than one trophic level in the same ecosystem (in different food chains) at the given time. If the function of the mode of nutrition of species changes, its position shall change in the trophic levels. The same species can be at primary consumer level in one food chain and at secondary consumer level in another food chain in the same ecosystem at the given time.
Question.

Identify the type of the given ecological pyramid and give one example each of pyramid of number and pyramid of biomass in such cases.
Answer. The given ecological pyramid is the inverted pyramid.
Inverted pyramid of biomass in a lake: Phytoplankton → Zooplankton → fishes.
Inverted pyramid of number: Tree → insects → birds.
Question. What could be the reason for the faster rate of decomposition in the tropics?
Answer. The rate of decomposition is regulated by climatic factors like temperature and soil moisture as they have an effect on the activities of soil microbes. The tropics with its hot and humid climatic condition provides an environment which is ideal for the microbes to speed up the process of decomposition.
Question. Name the pioneer and the climax species in a water body. Mention the changes observed in the biomass and the biodiversity of the successive seral communities developing in the water body.
Answer. Pioneer species — Phytoplanktons
Climax species — Forest or trees
Biomass will be gradually increased and phytoplanktons are replaced by free-floating angiosperms then by rooted hydrophytes followed by different seral communities thus, biodiversity also increases.
Question. Explain the function of ‘reservoir’ in a nutrient cycle. List the two types of nutrient cycles in nature.
Answer. The function of the reservoir is to meet the deficit of nutrients which occurs due to imbalance in the rate of influx and efflux.
The two types of nutrient cycles are:
(i) Gaseous, and (ii) Sedimentary
Question. How are productivity, gross productivity, net primary productivity and secondary productivity interrelated?
Answer. Productivity is the rate of biomass production. GPP is rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis.
GPP – R = NPP = 1
Where NPP is biomass available to consumers for secondary productivity. Secondary productivity is rate of formation of new organic matter by consumers.
Question. Explain with the help of two examples, how the pyramid of number and the pyramid of biomass can look inverted.
Answer. The pyramid of biomass in sea is generally inverted because the biomass of fishes far exceeds that of phytoplankton and the number of big fishes eating the small fishes is also greater than the small ones. Also in pyramid of number, the number of insects feeding on a big tree is far greater than the number of trees. Now the number of small birds depending on the insects and the number of larger birds eating the smaller ones also increases in the order.
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 1 Reproduction in Organisms |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Human Reproduction |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 4 Reproductive Health |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 5 Principles of Inheritance and Variation |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 7 Evolution |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles And Processes |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystem |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 16 Environmental Issues |
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystem
The above provided NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystem is available on our website www.studiestoday.com for free download in Pdf. You can read the solutions to all questions given in your Class 12 Biology textbook online or you can easily download them in pdf. The answers to each question in Chapter 14 Ecosystem of Biology Class 12 has been designed based on the latest syllabus released for the current year. We have also provided detailed explanations for all difficult topics in Chapter 14 Ecosystem Class 12 chapter of Biology so that it can be easier for students to understand all answers. These solutions of Chapter 14 Ecosystem NCERT Questions given in your textbook for Class 12 Biology have been designed to help students understand the difficult topics of Biology in an easy manner. These will also help to build a strong foundation in the Biology. There is a combination of theoretical and practical questions relating to all chapters in Biology to check the overall learning of the students of Class 12.
You can download the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystem for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the NCERT Solutions issued for Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystem have been made available here for latest academic session
Regular revision of NCERT Solutions given on studiestoday for Class 12 subject Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystem can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all latest NCERT Chapter 14 Ecosystem Class 12 Biology solutions based on the latest books for the current academic session
Yes, NCERT solutions for Class 12 Chapter 14 Ecosystem Biology are available in multiple languages, including English, Hindi
All questions given in the end of the chapter Chapter 14 Ecosystem have been answered by our teachers

