Refer to BITSAT Physics Ray Optics and Optical Instruments MCQs provided below available for download in Pdf. The MCQ Questions for Full Syllabus Physics with answers are aligned as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern suggested by BITSAT, NCERT and KVS. Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Full Syllabus MCQ are an important part of exams for Full Syllabus Physics and if practiced properly can help you to improve your understanding and get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise MCQs for BITSAT Full Syllabus Physics and also download more latest study material for all subjects
MCQ for Full Syllabus Physics Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Full Syllabus Physics students should refer to the following multiple-choice questions with answers for Ray Optics and Optical Instruments in Full Syllabus.
Ray Optics and Optical Instruments MCQ Questions Full Syllabus Physics with Answers
Question: Two plano-concave lenses (1 and 2) of glass of refractive index 1.5 have radii of curvature 25 cm and 20 cm. They are placed in contact with their curved surface towards each other and the space between them is filled with liquid of refractive index 4/3. Then the combination is
- a) Convex lens of focal length 70 cm
- b) Concave lens of focal length 70 cm
- c) Concave lens of focal length 66.6 cm
- d) Convex lens of focal length 66.6 cm
Answer: Concave lens of focal length 66.6 cm
Question: On a hypotenuse of a right angle prism (30° – 60° – 90°) of refractive index 1.50, a drop of liquid is placed as shown in figure. Light is allowed to fall normally on the short face of the prism. In order that the ray of light may get totally reflected, the maximum value of refractive index is :
- a) 1.30
- b) 1.47
- c) 1.20
- d) 1.25
Answer: 1.30
Question: A biconvex lens has a radius of curvature of magnitude 20 cm. Which one of the following options best describe the image formed of an object of height 2 cm placed 30 cm from the lens?
- a) Virtual, upright, height = 1 cm
- b) Virtual, upright, height = 0.5 cm
- c) Real, inverted, height = 4 cm
- d) Real, inverted, height = 1cm
Answer: Real, inverted, height = 4 cm
Question: For the angle of minimum deviation of a prism to be equal to its refracting angle, the prism must be made of a material whose refractive index :
- a) lies between √2 and 1
- b) lies between 2 and √2
- c) is less than 1
- d) is greater than 2
Answer: lies between 2 and √2
Question: A lens having focal length f and aperture of diameter d forms an image of intensity I. Aperture of diameter 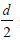 in central region of lens is covered by a black paper. Focal length of lens and intensity of image now will be respectively;
in central region of lens is covered by a black paper. Focal length of lens and intensity of image now will be respectively;
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: A ray parallel to principal axis is incident at 30° from normal on concave mirror having radius of curvature R. The point on principal axis where rays are focussed is Q such that PQ is
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: A planoconvex lens fits exactly into a planoconcave lens. Their plane surface are parallel to each other. If the lenses are made of different materials of refractive indices μ1 & μ2 and R is the radius of curvature of the curved surface of the lenses, then focal length of combination is
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: The magnifying power of a telescope is 9. When it is adjusted for parallel rays, the distance between the objective and the eye piece is found to be 20 cm. The focal length of lenses are
- a) 18 cm, 2 cm
- b) 11 cm, 9 cm
- c) 10 cm, 10 cm
- d) 15 cm, 5 cm
Answer: 18 cm, 2 cm
Question: When light is refracted, which of the following does not change ?
- a) Wavelength
- b) Frequency
- c) Velocity
- d) Amplitude
Answer: Frequency
Question: A Convex lens of crown glass (μ = 1.525) will behave as a divergent lens if immersed in
- a) water (μ = 1.33)
- b) in a medium of μ = 1.525
- c) carbon disulphide (μ = 1.66)
- d) it cannot act as a divergent lens
Answer: carbon disulphide (μ = 1.66)
Question: Wavelength of light used in an optical instrument are λ1 = 4000Å and λ2 = 5000 Å, then ratio of their respective resolving powers (corresponding to λ1 and λ2) is
- a) 16 : 25
- b) 9 : 1
- c) 4 : 5
- d) 5 : 4
Answer: 5 : 4
Question: A thin convergent glass lens (μg = 1.5) has a power of + 5.0 D. When this lens is immersed in a liquid of refractive index m, it acts as a divergent lens of focal length 100 cm. The value of m must be
- a) 4/3
- b) 5/3
- c) 5/4
- d) 6/5
Answer: 5/3
Question: A vessel of depth 2d cm. is half filled with a liquid of refractive index μ1 and the upper half with a liquid of refractive index μ2. The apparent depth of the vessel seen perpendicularly is –
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: A plano-convex lens of focal length 30 cm has its plane surface silvered. An object is placed 40 cm from the lens on the convex side. The distance of the image from the lens is
- a) 18 cm
- b) 24 cm
- c) 30 cm
- d) 40 cm
Answer: 24 cm
Question: Time taken to cross a 4 mm window glass of refractive index 1.5 will be-
- a) 2 × 10–8 sec
- b) 2 × 108 sec
- c) 2 × 10–11 sec
- d) 2 × 1011 sec
Answer: 2 × 10–11 sec
Question: A fish looking up through the water sees the outside world contained in a circular horizon. If the refractive index of water is 4/3 and the fish is 12 cm. below the surface, the radius of this circle in cm is –
- a) 36 √5
- b) 4 √5
- c) 36 √7
- d) 36/ √7
Answer: 36/ √7
Question: An air bubble under water shines brightly because of the phenomenon of :
- a) Diffraction
- b) Dispersion
- c) Interference
- d) Total internal reflection
Answer: Total internal reflection
Question: A vessel is half filled with a liquid of refractive index μ. The other half of the vessel is filled with an immiscible liquid of refrative index 1.5 μ. The apparent depth of the vessel is 50% of the actual depth. Then μ is
- a) 1.4
- b) 1.5
- c) 1.6
- d) 1.67
Answer: 1.67
Question: A biconvex lens has a radius of curvature of magnitude 20 cm. Which one of the following options best describe the image formed of an object of height 2 cm placed 30 cm from the lens?
- a) Virtual, upright, height = 1 cm
- b) Virtual, upright, height = 0.5 cm
- c) Real, inverted, height = 4 cm
- d) Real, inverted, height = 1cm
Answer: Real, inverted, height = 4 cm
Question: When light is refracted, which of the following does not change ?
- a) Wavelength
- b) Frequency
- c) Velocity
- d) Amplitude
Answer: Frequency
MCQs for Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Physics Full Syllabus
Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to NCERT book for Full Syllabus Physics to develop the Physics Full Syllabus MCQs. If you download MCQs with answers for the above chapter you will get higher and better marks in Full Syllabus test and exams in the current year as you will be able to have stronger understanding of all concepts. Daily Multiple Choice Questions practice of Physics will help students to have stronger understanding of all concepts and also make them expert on all critical topics. After solving the questions given in the MCQs which have been developed as per latest books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Full Syllabus Physics. We have also provided lot of MCQ questions for Full Syllabus Physics so that you can solve questions relating to all topics given in each chapter. After solving these you should also refer to Full Syllabus Physics MCQ Test for the same chapter.
You can download the BITSAT MCQs for Full Syllabus Physics Ray Optics and Optical Instruments for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the MCQs issued by BITSAT for Full Syllabus Physics Ray Optics and Optical Instruments have been made available here for latest academic session
You can find BITSAT Full Syllabus Physics Ray Optics and Optical Instruments MCQs on educational websites like studiestoday.com, online tutoring platforms, and in sample question papers provided on this website.
To prepare for Ray Optics and Optical Instruments MCQs, refer to the concepts links provided by our teachers and download sample papers for free.
Yes, there are many online resources that we have provided on studiestoday.com available such as practice worksheets, question papers, and online tests for learning MCQs for Full Syllabus Physics Ray Optics and Optical Instruments

