Refer to BITSAT Physics Mechanical Properties Of Fluids MCQs provided below available for download in Pdf. The MCQ Questions for Full Syllabus Physics with answers are aligned as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern suggested by BITSAT, NCERT and KVS. Mechanical Properties Of Fluids Full Syllabus MCQ are an important part of exams for Full Syllabus Physics and if practiced properly can help you to improve your understanding and get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise MCQs for BITSAT Full Syllabus Physics and also download more latest study material for all subjects
MCQ for Full Syllabus Physics Mechanical Properties Of Fluids
Full Syllabus Physics students should refer to the following multiple-choice questions with answers for Mechanical Properties Of Fluids in Full Syllabus.
Mechanical Properties Of Fluids MCQ Questions Full Syllabus Physics with Answers
Question: A mercury drop of radius 1 cm is sprayed into 106 drops of equal size. The energy expressed in joule is (surface tension of Mercury is 460 × 10–3 N/m)
- a) 0.057
- b) 5.7
- c) 5.7 × 10–4
- d) 5.7 × 10–6
Answer: 0.057
Question: A capillary tube of radius R is immersed in water and water rises in it to a height H. Mass of water in the capillary tube is M. If the radius of the tube is doubled, mass of water that will rise in the capillary tube will now be :
- a) M
- b) 2 M
- c) M/2
- d) 4 M
Answer: 2 M
Question: A capillary tube of radius r is immersed vertically in a liquid such that liquid rises in it to height h (less than the length of the tube). Mass of liquid in the capillary tube is m. If radius of the capillary tube is increased by 50%, then mass of liquid that will rise in the tube, is
- a)
- b) m
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: The approximate depth of an ocean is 2700 m. The compressibility of water is 45.4 × 10–11 Pa–1 and density of water is 103 kg/m3.What fractional compression of water will be obtained at the bottom of the ocean ?
- a) 1.0 × 10–2
- b) (1.2 × 10–2
- c) 1.4 × 10–2
- d) 0.8 × 10–2
Answer: (1.2 × 10–2
Question: A glass capillary tube of internal radius r = 0.25 mm is immersed in water. The top end of the tube projected by 2 cm above the surface of the water. At what angle does the liquid meet the tube? Surface tension of water = 0.7 N/m.
- a) 90°
- b) 70°
- c) 45°
- d) 35°
Answer: 70°
Question: Water is flowing on a horizontal fixed surface, such that its flow velocity varies with y (vertical direction) as 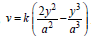 If coefficient of viscosity for water is h, what will be shear stress between layers of water at y =a.
If coefficient of viscosity for water is h, what will be shear stress between layers of water at y =a.
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d) None of these
Answer:
Question: A square gate of size 1 m × 1m is hinged at its mid-point. A fluid of density r fills the space to the left of the gate. The force F required to hold the gate stationary is
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: Two capillary tubes are of the same diameters. One is dipped in a liquid of relative density 0.8 while the other in a liquid of relative density 0.6. If surface tensions of these liquids are 60 and 50 milli N/m, respectively, and the angles of the contact are equal, compare the rise of liquids in the capillary tubes.
- a) 9 : 10
- b) 7 : 10
- c) 3 : 10
- d) 1 : 10
Answer: 9 : 10
Question: Two liquids of densities d1 and d2 are flowing in identical capillary tubes uder the same pressure difference. If t1 and t2 are time taken for the flow of equal quantities (mass) of liquids, then the ratio of coefficient of viscosity of liquids must be
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: An ice block floats in a liquid whose density is less than water. A part of block is outside the liquid. When whole of ice has melted, the liquid level will
- a) Rise
- b) Go down
- c) Remain same
- d) First rise then go down
Answer: Go down
Question: A large drop of oil (density 0.8 g/cm3 and viscosity η0) floats up through a column of another liquid (density 1.2 g/cm3 and viscosity ηL ). Assuming that the two liquids do not mix, the velocity with which the oil drop rises will depend on :
- a) η0 only
- b) ηLonly
- c) both on η0 and hL
- d) neither η0 nor ηL
Answer: ηLonly
Question: Viscosity is the property of a liquid due to which it :
- a) Occupies minimum surface area
- b) Opposes relative motion between its adjacent layers
- c) Becomes spherical in shape
- d) Tends to regain its deformed position
Answer: Opposes relative motion between its adjacent layers
Question: A spherical ball is dropped in a long column of a viscous liquid. The speed (n) of the ball as a function of time (t) may be best represented by
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: Two mercury drops (each of radius r) merge to form a bigger drop. The surface energy of the bigger drop, if T is the surface tension, is
- a) 25/3 πr2T
- b) 4 πr2T
- c) 2 πr2T
- d) 28/3 πr2T
Answer: 28/3 πr2T
Question: Two circular plates of radius 5 cm each, have a 0.01 mm thick water film between them. Then what will be the force required to separate these plate (S.T. of water = 73 dyne/cm) ?
- a) 125 N
- b) 95 N
- c) 115 N
- d) 105 N
Answer: 115 N
Question: A liquid is flowing through a non-sectional tube with its axis horizontally. If two points X and Y on the axis of tube has a sectional area 2.0 cm3 and 25 mm2 respectively then find the flow velocity at Y when the flow velocity at X is 10m/s.
- a) 20 m/s
- b) 40 m/s
- c) 80 m/s
- d) 60 m/s
Answer: 80 m/s
Question: A cylindrical vessel filled with water is released on an inclined surface of angle θ as shown in figure. Fixed The friction coefficient of surface with vessel is μ (< tan θ). Then the contact angle made by the surface of water with the incline will be –
- a) tan–1 μ
- b) q – tan–1 μ
- c) q + tan–1 μ
- d) cot–1 μ
Answer: tan–1 μ
Question: The lift of an air plane is based on
- a) Torricelli's theorem
- b) Bernoulli's theorem
- c) Law of gravitation
- d) Conservation of linear momentum
Answer: Bernoulli's theorem
Question: A vertical glass capillary tube of radius r open at both ends contains some water (surface tension T and density ρ). If L be the length of the water column, then :
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: Two pieces of metals are suspended from the arms of a balance and are found to be in equilibrium when kept immersed in water. The mass of one piece is 32 g and its density 8 g cm–3. The density of the other is 5 g per cm3. Then the mass of the other is
- a) 28 g
- b) 35 g
- c) 21 g
- d) 33.6 g
Answer: 35 g
MCQs for Mechanical Properties Of Fluids Physics Full Syllabus
Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to NCERT book for Full Syllabus Physics to develop the Physics Full Syllabus MCQs. If you download MCQs with answers for the above chapter you will get higher and better marks in Full Syllabus test and exams in the current year as you will be able to have stronger understanding of all concepts. Daily Multiple Choice Questions practice of Physics will help students to have stronger understanding of all concepts and also make them expert on all critical topics. After solving the questions given in the MCQs which have been developed as per latest books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Full Syllabus Physics. We have also provided lot of MCQ questions for Full Syllabus Physics so that you can solve questions relating to all topics given in each chapter. After solving these you should also refer to Full Syllabus Physics MCQ Test for the same chapter.
You can download the BITSAT MCQs for Full Syllabus Physics Mechanical Properties Of Fluids for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the MCQs issued by BITSAT for Full Syllabus Physics Mechanical Properties Of Fluids have been made available here for latest academic session
You can find BITSAT Full Syllabus Physics Mechanical Properties Of Fluids MCQs on educational websites like studiestoday.com, online tutoring platforms, and in sample question papers provided on this website.
To prepare for Mechanical Properties Of Fluids MCQs, refer to the concepts links provided by our teachers and download sample papers for free.
Yes, there are many online resources that we have provided on studiestoday.com available such as practice worksheets, question papers, and online tests for learning MCQs for Full Syllabus Physics Mechanical Properties Of Fluids

