Refer to BITSAT Physics Moving Charges and Magnetism MCQs provided below available for download in Pdf. The MCQ Questions for Full Syllabus Physics with answers are aligned as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern suggested by BITSAT, NCERT and KVS. Moving Charges and Magnetism Full Syllabus MCQ are an important part of exams for Full Syllabus Physics and if practiced properly can help you to improve your understanding and get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise MCQs for BITSAT Full Syllabus Physics and also download more latest study material for all subjects
MCQ for Full Syllabus Physics Moving Charges and Magnetism
Full Syllabus Physics students should refer to the following multiple-choice questions with answers for Moving Charges and Magnetism in Full Syllabus.
Moving Charges and Magnetism MCQ Questions Full Syllabus Physics with Answers
Question: Two very long, straight, parallel wires carry steady currents I and -I respectively. The distance between the wires is d. At a certain instant of time, a point charge q is at a point equidistant from the two wires, in the plane of the wires. Its instantaneous velocity v is perpendicular to this plane. The magnitude of the force due to the magnetic field acting on the charge at this instant is
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d) 0
Answer: 0
Question: A charged particle moves through a magnetic field perpendicular to its direction. Then
- a) Kinetic energy changes but the momentum is constant
- b) The momentum changes but the kinetic energy is constant
- c) Both momentum and kinetic energy of the particle are not constant
- d) Both momentum and kinetic energy of the particle are constant
Answer: The momentum changes but the kinetic energy is constant
Question: A wire carrying current I has the shape as shown in adjoining figure. Linear parts of the wire are very long and parallel to X-axis while semicircular portion of radius R is lying in Y-Z plane. Magnetic field at point O is :
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: A deuteron of kinetic energy 50 keV is describing a circular orbit of radius 0.5 metre in a plane perpendicular to the magnetic field B. The kinetic energy of the proton that describes a circular orbit of radius 0.5 metre in the same plane with the same B is
- a) 25 keV
- b) 50 keV
- c) 200 keV
- d) 100 keV
Answer: 100 keV
Question: A long straight wire along the Z-axis carries a current I in the negative Z-direction. The magnetic vector field B r at a point having coordinates (x, y) in the Z = 0 plane is
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: A charged particle with velocity 2 × 103 m/s passes undeflected through electric and magnetic field. Magnetic field is 1.5 tesla. The electric field intensity would be
- a) 2 × 103 N/C
- b) 1.5 × 103 N/C
- c) 3 × 103 N/C
- d) 4/3 × 10–3 N/C
Answer: 3 × 103 N/C
Question: A small current element of length dl and carryingcurrent is placed at (1, 1, 0) and is carrying current in ‘+z’ direction. If magnetic field at origin be 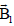 and at point (2, 2, 0) be
and at point (2, 2, 0) be 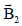 then
then
- a)
=
- b)
|
| = |2
|
- c)
= -
- d)
= -2
Answer:
= -
Question: Field inside a solenoid is
- a) Directly proportional to its length
- b) Directly proportional to current
- c) Inversely proportional to number of turns
- d) Inversely proportional to current
Answer: Directly proportional to current
Question: A uniform electric field and uniform magnetic field are acting along the same direction in a certain region. If an electron is projected in the region such that its velocity is pointed along the direction of fields, then the electron
- a) Will turn towards right of direction of motion
- b) Speed will decrease
- c) Speed will increase
- d) Will turn towards left direction of motion
Answer: Speed will decrease
Question: A horizontal overhead powerline is at height of 4m from the ground and carries a current of 100A from east to west. The magnetic field directly below it on the ground is (μ0 = 4π × 10–7 Tm A–1)
- a) 2.5×10–7 T southward
- b) 5 × 10–6 T northward
- c) 5 × 10–6 T southward
- d) 2.5 × 10–7 T northward
Answer: 5 × 10–6 T southward
Question: If m is magnetic moment and B is the magnetic field, then the torque is given by
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: A steady current is set up in a cubic network composed of wires of equal resistance and length d as shown in figure. What is the magnetic field at the centre P due to the cubic network
- a)
- b)
- c) 0
- d)
Answer: 0
Question: The magnetic field at the origin due to the current flowing in the wire is –
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: A conducting circular loop of radius r carries a constant current i. It is placed in a uniform magnetic field such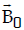 that
that 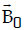 is perpendicular to the plane of the loop. The magnetic force acting on the loop is
is perpendicular to the plane of the loop. The magnetic force acting on the loop is
- a)
- b)
- c) zero
- d)
Answer: zero
Question: An ammeter reads upto 1 ampere. Its internal resistance is 0.81ohm. To increase the range to 10 A the value of the required shunt is
- a) 0.03Ω
- b) 0.3Ω
- c) 0.9Ω
- d) 0.09Ω
Answer: 0.09Ω
Question: Two parallel wires carrying currents in the same direction attract each other because of
- a) Mutual inductance between them
- b) Potential difference between them
- c) Electric forces between them
- d) Magnetic forces between them
Answer: Magnetic forces between them
Question: Calculate the magnetic field at the centre of a coil in the form of a square of side 2a carrying a current I.
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: The work done by a magnetic field, on a moving charge is
- a) zero because
acts parallel to
- b) Positive because
acts perpendicular to
- c) Zero because
acts perpendicular to
- d) Negative because
acts parallel to
Answer: Zero because acts perpendicular to
Question: A circular loop of radius 0.3 cm lies parallel to a much bigger circular loop of radius 20 cm. The centre of the smaller loop is on the axis of the bigger loop. The distance between their centres is 15 cm. If a current of 2.0 A flows through the smaller loop, then the flux linked with bigger loop
- a) 9.1 × 10–11 weber
- b) 6 × 10–11 weber
- c) 3.3 × 10–11 weber
- d) 6.6 × 10–9 weber
Answer: 9.1 × 10–11 weber
Question: A particle is moving with velocity 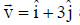 and it produces an electric field at a point given by
and it produces an electric field at a point given by 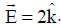 . It will produce magnetic field at that point equal to (all quantities are in SI units) [
. It will produce magnetic field at that point equal to (all quantities are in SI units) [
- a)
- b)
- c) zero
- d) cannot be determined from the given data
Answer:
MCQs for Moving Charges and Magnetism Physics Full Syllabus
Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to NCERT book for Full Syllabus Physics to develop the Physics Full Syllabus MCQs. If you download MCQs with answers for the above chapter you will get higher and better marks in Full Syllabus test and exams in the current year as you will be able to have stronger understanding of all concepts. Daily Multiple Choice Questions practice of Physics will help students to have stronger understanding of all concepts and also make them expert on all critical topics. After solving the questions given in the MCQs which have been developed as per latest books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Full Syllabus Physics. We have also provided lot of MCQ questions for Full Syllabus Physics so that you can solve questions relating to all topics given in each chapter. After solving these you should also refer to Full Syllabus Physics MCQ Test for the same chapter.
You can download the BITSAT MCQs for Full Syllabus Physics Moving Charges and Magnetism for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the MCQs issued by BITSAT for Full Syllabus Physics Moving Charges and Magnetism have been made available here for latest academic session
You can find BITSAT Full Syllabus Physics Moving Charges and Magnetism MCQs on educational websites like studiestoday.com, online tutoring platforms, and in sample question papers provided on this website.
To prepare for Moving Charges and Magnetism MCQs, refer to the concepts links provided by our teachers and download sample papers for free.
Yes, there are many online resources that we have provided on studiestoday.com available such as practice worksheets, question papers, and online tests for learning MCQs for Full Syllabus Physics Moving Charges and Magnetism

