Refer to BITSAT Physics Electric Charges and Fields MCQs provided below available for download in Pdf. The MCQ Questions for Full Syllabus Physics with answers are aligned as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern suggested by BITSAT, NCERT and KVS. Electric Charges and Fields Full Syllabus MCQ are an important part of exams for Full Syllabus Physics and if practiced properly can help you to improve your understanding and get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise MCQs for BITSAT Full Syllabus Physics and also download more latest study material for all subjects
MCQ for Full Syllabus Physics Electric Charges and Fields
Full Syllabus Physics students should refer to the following multiple-choice questions with answers for Electric Charges and Fields in Full Syllabus.
Electric Charges and Fields MCQ Questions Full Syllabus Physics with Answers
Question: A disk of radius a/4 having a uniformly distributed charge 6 C is placed in the x - y plane with its centre at (–a/2, 0, 0). A rod of length a carrying a uniformly distributed charge 8 C is placed on the x-axis from x = a /4 to x = 5a/4. Two point charges – 7 C and 3 C are placed at (a/4, – a/4, 0) and (– 3a/4, 3a/4, 0), respectively. Consider a cubical surface formed by six surfaces x = ± a/2, y = ± a/2, z = ± a/2. The electric flux through this cubical surface is
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: Two concentric conducting thin spherical shells A, and B having radii rA and rB ((rB > rA) are charged to QA and –QB (|QB| > |QA|). The electric field along a line passing through the centre is
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: Two identical charged spheres suspended from a common point by two massless strings of lengths l, are initially at a distance d (d << l) apart because of their mutual repulsion. The charges begin to leak from both the spheres at a constant rate. As a result, the spheres approach each other with a velocity v. Then v varies as a function of the distance x between the spheres, as :
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: The surface charge density of a thin charged disc of radius R is σ. The value of the electric field at the centre of the disc is 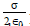 With respect to the field at the centre, the electric field along the axis at a distance R from the centre of the disc
With respect to the field at the centre, the electric field along the axis at a distance R from the centre of the disc
- a) Reduces by 70.7%
- b) Reduces by 29.3%
- c) Reduces by 9.7%
- d) Reduces by 14.6%
Answer: Reduces by 70.7%
Question: At the corners of an equilateral triangle of side a (1 metre), three point charges are placed (each of 0.1 C). If this system is supplied energy at the rate of 1 kw, then calculate the time required to move one of the mid-point of the line joining the other two.
- a) 50 h
- b) 60 h
- c) 48 h
- d) 54 h
Answer: 50 h
Question: A solid sphere of radius R has a charge Q distributed in its volume with a charge density r = kra, where k and a are constants and r is the distance from its centre. If the electric field at r =
times that at r = R, the value of a is
- a) 3
- b) 5
- c) 2
- d) 7
Answer: 2
Question: Two point dipoles 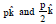 are located at (0, 0, 0) and (1m, 0, 2m) respectively. The resultant electric field due to the two dipoles at the point (1m, 0, 0) is
are located at (0, 0, 0) and (1m, 0, 2m) respectively. The resultant electric field due to the two dipoles at the point (1m, 0, 0) is
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d) None of these
Answer:
Question: Three equal charges (q) are placed at corners of an equilateral triangle. The force on any charge is
- a) zero
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: In a region of space having a uniform electric field E, a hemispherical bowl of radius r is placed. The electric flux Φthrough the bowl is
- a) 2πRE
- b) 4πR2E
- c) 2πR2E
- d) πR2E
Answer: 4πR2E
Question: The electric field intensity just sufficient to balance the earth’s gravitational attraction on an electron will be: (given mass and charge of an electron respectively are 9.1 × 10–31 kg and 1.6 × 10–19 C.)
- a) –5.6 × 10–11 N/C
- b) –4.8 × 10–15 N / C
- c) –1.6 × 10–19 N/C
- d) –3.2 × 10–19 N / C
Answer: –5.6 × 10–11 N/C
Question: In an uniformly charged sphere of total charge Q and radius R, the electric field E is plotted as function of distance from the centre. The graph which would correspond to the above will be
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: A charge Q1 exerts some force on a second charge Q2. If a 3rd charge Q3 is brought near, then the force of Q1 exerted on Q2 –
- a) Will increase
- b) Will decrease
- c) Will remain unchanged
- d) will increase if Q3 is of the same sign as Q1 and will decrease if Q3 is of opposite sign
Answer: Will remain unchanged
Question: A charge +q is at a distance L/2 above a square of side L. Then what is the flux linked with the surface?
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: Two metallic spheres of radii 1 cm and 3 cm are given charges of –1 × 10–2 C and 5×10–2 C, respectively. If these are connected by a conducting wire, the final charge on the bigger sphere is
- a) 2 × 10–2 C
- b) 3 × 10–2 C
- c) 4 × 10–2 C
- d) 1 × 10–2 C
Answer: 3 × 10–2 C
Question: If an electron has an initial velocity in a direction different from that of an electric field, the path of the electron is
- a) A straight line
- b) A circle
- c) An ellipse
- d) A parabola
Answer: A parabola
Question: The ratio of magnitudes of electric field due to an electric dipole on the axis and on the equatorial line at equal distances will be
- a) 4 : 1
- b) 1 : 2
- c) 2 : 1
- d) 1 : 1
Answer: 2 : 1
Question: A square surface of side L meter in the plane of the paper is placed in a uniform electric field E (volt/m) acting along the same plane at an angle θ with the horizontal side of the square as shown in Figure. The electric flux linked to the surface, in units of volt m, is
- a) EL2
- b) EL2 cos θ
- c) EL2 sin θ
- d) zero
Answer: zero
Question: Charge Q is distributed to two different metallic spheres having radii R and 2R such that both spheres have equal surface charge density, then charge on large sphere is
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: A charge q is placed at the centre of the open end of a cylindrical vessel. The flux of the electric field through the surface of the vessel is
- a) zero
- b) (q/ε0)
- c) (q/2ε0)
- d) (2q/ε0)
Answer: (q/2ε0)
Question: A solid spherical conductor of radius R has a spherical cavity of radius a (a < R) at its centre. A charge + Q is kept at the centre. The cahrge at the inner surface, outer and at a position r (a < r < R) are respectively
- a) + Q, – Q, 0
- b) – Q, + Q, 0
- c) 0, – Q, 0
- d) + Q , 0, 0
Answer: 0, – Q, 0
MCQs for Electric Charges and Fields Physics Full Syllabus
Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to NCERT book for Full Syllabus Physics to develop the Physics Full Syllabus MCQs. If you download MCQs with answers for the above chapter you will get higher and better marks in Full Syllabus test and exams in the current year as you will be able to have stronger understanding of all concepts. Daily Multiple Choice Questions practice of Physics will help students to have stronger understanding of all concepts and also make them expert on all critical topics. After solving the questions given in the MCQs which have been developed as per latest books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Full Syllabus Physics. We have also provided lot of MCQ questions for Full Syllabus Physics so that you can solve questions relating to all topics given in each chapter. After solving these you should also refer to Full Syllabus Physics MCQ Test for the same chapter.
You can download the BITSAT MCQs for Full Syllabus Physics Electric Charges and Fields for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the MCQs issued by BITSAT for Full Syllabus Physics Electric Charges and Fields have been made available here for latest academic session
You can find BITSAT Full Syllabus Physics Electric Charges and Fields MCQs on educational websites like studiestoday.com, online tutoring platforms, and in sample question papers provided on this website.
To prepare for Electric Charges and Fields MCQs, refer to the concepts links provided by our teachers and download sample papers for free.
Yes, there are many online resources that we have provided on studiestoday.com available such as practice worksheets, question papers, and online tests for learning MCQs for Full Syllabus Physics Electric Charges and Fields

