I- Text Book Question & Answer
1. What is inert pair effect?
In heavier post transition metals, the outermost electrons (ns) have a tendency to remain inert and show reductance to take part in the bonding which is known as inert pair effect.
2. Chalcogens belongs to p - block give reason?
1 Their outer electronic configuration is ns2np4.
2 In these elements, the last electron enter np orbital.
3 Hence they belong to p-block elements.
4 Since the outer most electron of Chalcogens enter into ‘p’ orbital it belongs to ‘p’ block. Its group number is16.
3. Explain why fluorine always exhibit an oxidation state of -1?
1. Since fluorine is the most electronegative element, it exhibits only a negative oxidation state of -1.
2. Due to the absence of d-orbital, fluorine does not show positive oxidation state.
4. Give the oxidation state of halogen in the following
a) OF2, b) O2F2, c) Cl2O3, d) I2O4
Fluorine shows only -1 oxidation state. Hence
a) Oxidation state of‘F’ inOF2 is-1
b) Oxidation state of ‘F’ in O2F2 is -1
c) Cl2O3
2x + 3(-2) = 0
2x - 6 = 0
2x = 6
X=3
Oxidation state of Cl is +3
d) I2O4
2x + 4(-2) = 0
2x - 8 = 0
2x = 8
X=4
Oxidation state of Iodine is +4
5. What are interhalogen compounds? Give example?
Each halogen combines with other halogen to form a series of compounds called interhalogen compounds
Eg : ClF, BrCl, IF7
6. Why fluorine is more reactive than other halogens?
Fluorine is the most reactive element among halogen. This is due to the low value of F-F bond dissociation energy.
7. Give the uses of helium.
1. It is much less denser than air and hence used for filling air balloons.
2.Helium has lowest boiling paint and hence used in cryogenics.
3.Helium is used to provide inert atmosphere in electric arc welding metals.
4.Helium and oxygen mixture is used by the divers in place of air oxygen
mixture. This prevents the painful dangerous condition called bends.
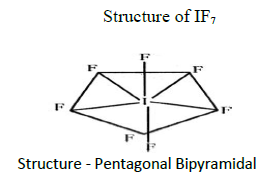
8. What is the hybridisation of iodine in IF7? Give its structure?
Hybridisation of IF7 is sp3d3
9. Give the balanced equation for the reaction between chlorine with cold NaOH and hot NaOH.
1. Chlorine reacts with cold NaOH to give sodium chloride and sodium hypochlorite.
Cl2 + 2 NaOH → NaOCl + NaCl + H2O
Sodium hypochlorite
2. Chlorine reacts with hot NaOH to give sodium chloride and sodium chlorate.
3Cl2 + 6NaOH → NaClO3 + 5 NaCl +3H2O
Sodium chlorate
10. How will you prepare chlorine in the laboratory?
In the laboratory, chlorine is prepared by the oxidation of hydrochloric acid by KMnO4.
2KMnO4 + 16HCl→ 2 KCl + 2 MnCl2 +8H2O + 5Cl2↑
11. Give the uses of sulphuric acid ?
i. Sulphuric acid is used in the manufacture of fertilizers, ammonium sulphate and super phosphates and other chemicals such as hydrochloric acid, nitric acid etc.
ii. It is used as a drying agent and also used in the preparation of pigments, explosives etc.
12. Give a reason to support that sulphuric acid is a dehydrating agent?
It is highly soluble in water and has strong affinity towards water and hence it can be used as a dehydrating agent.
The dehydrating property can also be illustrated by its reaction with organic compounds such as sugar, oxalic acid and formic acid.
C12H22O11+H2SO4→ 12C + H2SO4. 11H2O
(COOH)2+ H2SO4 → CO + CO2 + H2SO4. H2O
HCOOH + H2SO4→ CO + H2SO4. H2O
13. Write the reason for the anamolous behaviour of nitrogen?
1. Small size
2. High ionisation enthalpy and high electronegativity.
3. Absence of d-orbitals in their valence shell.
4. Nitrogen is a diatomic gas unlike the other members of the group.
14. Write the molecular and structural formula for the following molecules?
a) Nitric Acid
b) Dinitrogen Pentoxide
c) Phosphoric acid
d) Phosphine
15. Give the uses of Argon?
Argon prevents the oxidation of hot filament and prolongs the life in filament bulbs
16. Write the valence shell electronic configuration of group 15elements?
Valence shell electronic configuration of group 15 elements ns2np3
17. Give two equations to illustrate the chemical behaviour of phosphine?
(i) Basic nature : Phosphine is weakly basic and forms phosphonium salts with halogen acids.
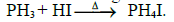
ii) Reducing property : Phosphine precipitates some metal from their salt solutions
3AgNO3 + PH3→Ag3P + 3HNO3
18. Give a reaction between nitric acid and a basic oxide?
Nitric acid reacts with basic oxides to form salt and water.
ZnO + 2HNO3 → Zn (NO3)2 + H2O
3FeO + 10 HNO3 →3Fe (NO3)3 + NO + 5 H2O
19. What happens when PCl5 is heated?
On heating phosphorous penta chloride, it decomposes into phosphorous trichloride and chlorine.
PCl5(g) → PCl3(g) + Cl2(g)
20. Suggest a reason why HF is a weak acid, whereas binary acids of the all other halogens are strong acids?
Hydrofluoric acid is a weak acid due to the presence of intermolecular hydrogen bonding in it and it cannot be completely ionized and hydrogen ion concentration will not be increased. But other hydrohalic acids are completely ionized and therefore they are strong acids.
21. Deduce the Oxidation number of Oxygen in Hypofluorous acid -HOF?
HOF
+1 + x - 1= 0
x =0
Hence oxidation number of oxygen in HOF is zero.
22. What type of hybridisation occur in a) BrF5 b)BrF3
a) BrF5 -sp3d2
b) BrF3 -sp3d
23. Complete the following reactions
Ans:
II. EVALUATE YOURSELF
Write the products formed in the reaction of nitric acid (both dilute and concentrated) with Zinc.
4Zn + 10HNO3→4Zn (NO3)2 + N2O + 5H2O
(dilute)
4Zn + 10HNO3→4Zn (NO3)2 + NH4NO3 + 3H2O
(very dilute)
Zn+ 4HNO3→ Zn (NO3)2 + 2NO2 + 2H2O
(Conc.)
II. ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS
1) How is pure nitrogen gas prepared?
Thermal decomposition of sodium azide about 573K gives pure nitrogen gas.
2NaN3→2Na+2N2.
2) Give reason for the chemically inert character of nitrogen.
Nitrogen is chemically inert due to
i) High bonding energy of the molecules (225 cal mol-1 (or)945kJmol-1).
ii) Triply bonded N≡N.
3) Mention the only metal that reacts with nitrogen at room temperature and give its reaction.
Only metal that reacts with nitrogen at room temperature is lithium.
6Li + N2→2Li3N.
4) How does nitrogen reacts with the following elements at hightemperature?
(i) Calcium (ii) Boron
1. 3Ca + N2→ Ca3N2
2. 2B +N2 →2BN
5) Give the uses of nitrogen.
i) Nitrogen is used for the manufacture of ammonia, nitric acid and calcium cyanamide.
ii) Liquid nitrogen is used for producing low temperature required in cryosurgery and so in biological preservation.
6) Write the reaction of hydrolysis of urea.
Hydrolysis of Urea gives ammonia.
NH2CONH2+H2O→2NH3+CO2
7) How is ammonia prepared in the laboratory?
Ammonia is prepared in the laboratory by heating ammonium salts with a base.
2NH4+ + OH--→ 2NH3 + H2O
2NH4Cl + CaO → CaCl2 + 2NH3 + H2O
8) How is ammonia prepared from magnesium nitride?
Mg3N2 + 6 H2O →3Mg(OH)2+2NH3
By heating magnesium nitride with water ammonia is formed.
9) What happens when ammonia is heated above500°C?
When ammonia is heated above 500°C, it decomposes into Nitrogen and hydrogen.
10) Illustrate the reducing property of ammonia with an example
When Ammonia is passed over heated lead oxide, it is reduced into lead
3PbO + 2NH3 → 3Pb +N2+3H2O
11) The Affinity of ammonia for proton is greater than that of water .Justify it.
When treated with acids ammonia forms ammonium salts. This reaction shows that the affinity of ammonia for proton is greater than that of water.
12) What happens when nitric acid is exposed to sunlight (or) heating? (or) Colourless pure concentrated nitric acid turns yellow on standing. why?
Nitric acid decomposes on exposure to sunlight (or) on being heated.
4HNO3→4NO2 + 2H2O + O2`
13) Mention the uses of nitricacid
i) Nitric acid is used as a oxidizing agent in the preparation of aquaregia
ii) Salts of nitric acid are used in photography (AgNO3) and gun powder for firearms(NaNO3)
14) Mention the three common allotropic forms of phosphorous.
The three common allotropic forms of phosphorous are white, red and black phosphorous.
15) How do you convert
i) White phosphorous → Red Phosphorous
ii) Red phosphorous → White phosphorous
i) The White phosphorous can be changed into red phosphorous by heating it to 420°C in the absence of air and light
ii) The red phosphorous can be converted back into white phosphorous by boiling it in an inert atmosphere and condensing the vapour underwater.
16) Mention the uses of phosphorous.
1. The red phosphorous is used in the matchboxes.
2. It is also used for the production of certain alloys such as phosphorbronze.
17) What happens when phosphorous acid is heated?
By heating phosphorous acid phosphine is prepared in pure form.
4H3PO3→ 3H3PO4+PH3 ↑
18) What is the reaction of phosphonium iodide with caustic soda solution?
A pure sample of phosphine is prepared by heating phosphonium iodide with caustic soda solution
19) Write the reaction of phosphine with Lewisacid
BCl3 + PH3→ [Cl3 B← : PH3]
Phosphine reacts with lewis acid like boron trichloride and gives co-ordination compound.
20) What is known as Holme’s signal?
In a ship, a pierced container with a mixture of calcium carbide and calcium phosphide liberates phosphine and acetylene when thrown into sea. The liberated phosphine catches fire and ignites acetylene. These burning gases serves as a signal to the approaching ships. This is known as holme’s signal.
21) Prove that phosphorous trichloride is a chlorinating agent.
C2H5OH + PCl3→ C2H5Cl+ H3PO3
C2H5COOH + PCl3→ C2H5COCl + H3PO3
Above reactions prove that phosphorous trichloride is a good chlorinating agent.
22) Mention the allotropic forms of oxygen.
Oxygen exists in two allotropic forms namely dioxygen (O2) and ozone or trioxygen (O3).
23) What are known as pyrophoricmetals?
Some of less reactive metals react when powdered finely and made to react exothermically with oxygen at room temperature, but a lump of metal is unaffected under same condition. These finely divided metals are known as pyrophoric and when set the powder on fire, heat is liberated during a reaction.
24) What happens when SO2 is dissolved in water?
Sulphur dioxide dissolves in water to give sulphurous acid
25) Give the allotropic forms of Sulphur .
Sulphur exists in crystalline as well as amorphous allotropic forms. The crystalline form includes rhombic sulphur (α sulphur) and monoclinic sulphur (β sulphur). Amorphous allotropic form includes plastic sulphur (γ sulphur), milk of sulphur and colloidal sulphur.
26) Why H2SO4 is used as a dehydratingagent?
It is highly soluble in water and has strong affinity towards water and hence it can be used as a dehydrating agent.
27) Illustrate the dehydrating property of con.H2SO4 with
(i) sucrose
(ii) formic acid
(iii) oxalic acid?
C12H22O11 + H2SO4→ 12C + H2SO4.11H2O
HCOOH + H2SO4→ CO + H2SO4.H2O
(COOH)2+ H2SO4→ CO+CO2+ H2SO4.H2O
28) What happens when H2SO4 is heated to high temperature?
Sulphuric acid is stable, however, it decomposes at high temperature to sulphur trioxide.
H2SO4→ H2O + SO3
29) What is the reaction of H2SO4 with NH3?
H2SO4 +2NH3→ (NH4)2SO4
30) Prove the oxidizing property of H2SO4 with twoexamples.
Sulphuric acid is an oxidizing agent as it produces nascent oxygen. Sulphuric acid oxidises elements such as C, S and P. It also oxidizes bromide and Iodide to Bromine and Iodine respectively
H2SO4→ H2O + SO2+(O) C+2H2SO4→ 2SO2 + 2H2O + CO2 S+2H2SO4→ 3SO2 + 2H2O
31) What is the role of H2SO4 in the conversion of H2S to S? Give the reaction.
It acts as an oxidizing agent in the conversion of H2S to S.
H2S + H2SO4→ SO2 + 2H2O+S
32) What happens when benzene reacts with con.H2SO4?
It reacts with organic compounds such as benzene to give sulphonic acids.
C6H6 + H2SO4→ C6H5 SO3H + H2O
33) How is ammonia prepared by Haber’s process?
Nitrogen reacts with hydrogen under high pressure and optimum temperature in presence of iron catalyst to give ammonia.
34) Explain the following reactions.
i) Reaction of excess of ammonia with chlorine
ii) Reaction of ammonia with excess of chlorine
i) Chlorine with excess of ammonia
2NH3 + 3Cl2 → N2 + 6HCl
6HCl + 6NH3 → 6NH4Cl
OVER ALL REACTIONS
8NH3 + 3Cl2→ N2 + 6NH4Cl
ii. Ammonia with excess of chlorine
NH3 + 3Cl2→ NCl3 + 3HCl
3NH3 + 3HCl → 3NH4Cl
OVER ALL REACTIONS
4NH3 + 3Cl2→ NCl3 + 3NH4Cl
35) How does ammonia react with metallic salts?
i) Fe3+ ii)Cu2+
Ammonia reacts with metallic salts to give metal hydroxides (in case of Fe) (or) forming complexes (in case of Cu).
Fe 3+ + 3NH4+ → Fe(OH)3 + 3NH4+
Cu2+ + 4NH3→ [(Cu(NH3)4]+2
Tetraamminecopper(II)ion
36) Prove that nitric acid is an oxidizing agent.
C+4HNO3 → 2H2O + 4 NO2 + CO2
S + 2HNO3 → H2SO4 + 2 NO
37) Write a note on nitration of benzene.
In organic compounds replacement of a - H atom with NO2 is referred to as nitration.
H2SO4
C6H6 + HNO3 → C6H5NO2 + H2O
Nitration takes place due to the formation of nitronium ion.
HNO3 + H2SO4→ N3O2 + + H3O+ + HSO4-
38) Write the reaction of conc.HNO3 with copper.
Cu + 4HNO3→ Cu (NO3)2+ 2 NO2+2H2O
39) What is called phosphorescence?
The freshly prepared white phosphorous is colourless but becomes pale yellow due to the formation of a layer of red phosphorous on standing. It is poisonous and has a characteristic garlic smell. It glows in the dark due to oxidation which is called phosphorescence.
40) Give an account on structure of phosphorous.
Phosphorous has a layer structure. The four atoms in phosphorous have polymeric structure with chains of P4 linked tetrahedrally. P≡P is less stable than P-P single bonds. Hence phosphorous atoms are linked through single bonds rather than triple bonds.
41) How is phosphine obtained from yellow phosphorous?
Yellow phosphorous reacts with alkali on boiling in an inert atmosphere and it liberates phosphine.
P4 + 3NaOH + 3H2O → 3NaH2PO2 + PH3↑
42) How do you prepare orthophosphoric acid from phosphorous?
When phosphorous is treated with conc.nitric acid in presence of iodine catalyst ortho phosphoric acid is formed.
P4 + 20HNO3→ 4H3PO4 + 20NO2 + 4H2O
43) Mention the hydride of phosphorous and give its hybridization and structure.
The hydride of phosphorous is phosphine (PH3).The hybridization of phosphorous in phosphine is sp3.
Three orbitals are occupied by bond pair with fourth corner occupied by lone pair of electrons. Hence bond angle is reduced to 94°. It has pyramidal shape.
44) How do you prepare phosphine from metallic phosphides?
Metallic phosphides on hydrolysis with water (or) dilute mineral acids give phosphine.
Ca3P2 + 6H2O →2PH3↑+3Ca(OH)2
AlP + 3HCl → PH3↑+ AlCl3
45) How is phosphine converted into meta phosphoricacid?
When phosphine is heated with air or oxygen it burns to give meta phosphoric acid
46) Show that phosphine is weakly basic in nature.
Phosphine forms phosphonium salts with halogen acids. It shows that phosphine is weakly basic in nature.
47) Mention the phosphorous compound which has the smell of rotten fish and what is the action of heat on it in the absence of air?
Phosphine has rotten fish smell. Phosphine decomposes into its elements , when heated in absence of air at 317K.
317K
4PH3→ P4 + 6H2
48) Illustrate the reducing property of phosphine.
Phosphine precipitates some metal from their salt solutions. It illustrates the reducing property of phosphine.
3AgNO3 + PH3→ Ag3P + 3HNO3
49) Mention the uses ofphosphine.
i) Phosphine is used for producing smokescreen.
ii) It is used in the Holme’s signal (i.e) signal to the approaching ships.
50) What is the action of PCl3on
i) Ethyl alcohol ii) Acetic acid
i) C2H5OH + PCl3→C2H5Cl +H3PO3
ii) C2H5COOH + PCl3→ C2H5COCl +H3PO3
51) How is O2 prepared in the laboratory fromH2O2
The decomposition of H2O2 in the presence of catalyst (MnO2) or by the oxidation with potassium permanganate produces oxygen.
2H2O2→ 2H2O + O2
5H2O2 + 2MnO4 - + 6H+→ 5O2+8H2O + 2Mn2+
52) How is ozone prepared in the laboratory?
In the laboratory ozone is prepared by passing electrical discharge through oxygen at a potential of 20,000V about 10% of oxygen is converted into ozone. It gives a mixture known as ozonised oxygen. Pure ozone is obtained as a pale blue gas by the fractional distillation of liquefied ozonised oxygen.
O2→2(O)
O2 + (O) → O3
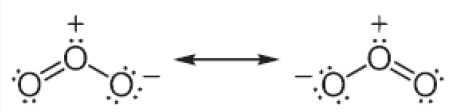
53) Write briefly on the structure ofozone?
The ozone molecule have a bent shape and symmetrical with delocalized bonding between the oxygen atoms.
54) Mention the uses ofO3
i) Oxygen is one of the essential components for the survival of living organisms.
ii) It is used in welding (oxy acetylene welding)
iii) Liquid oxygen is used as fuel in rockets etc.
55) Write the reaction which is used in the estimation of O3.
Ozone is a powerful oxidizing agent and it reacts with many substances under conditions where oxygen will not react. For example, it oxidizes potassium iodide to iodine. This reaction is Quantitative and can be used for estimation of ozone.
O3 + 2KI + H2O → 2KOH + O2 + I2
56) Illustrate the oxidizing property of SO2.
SO2 oxidizes hydrogen sulphide to sulphur and Magnesium to Magnesium oxide. 2H2S + SO2→ 3S + 2H2O
2Mg + SO2→ 2MgO + S
57) How is sulphur dioxide prepared in the laboratory?
Sulphur dioxide is prepared in the laboratory by treating a metal or metal sulphite with sulphuric acid.
Cu + 2H2SO4→CuSO4 + SO2 + 2H2O
SO3- + 2H+ → H2O + SO2
58) Illustrate the reducing property of SO2 with an example.
As it can be readily oxidized, it acts as a reducing agent. It reduces chlorine into hydrochloride acid.
SO2+2H2O +Cl2→ H2SO4 + 2HCl
59) What happens when SO2 is passed through acidified K2Cr2O7?
It reduces acidified K2Cr2O7 to Cr3+.
K2Cr2O7 + 3SO2 + H2SO4→ K2SO4 + Cr2(SO4)3+H2O
60) How is SO3 prepared by contact process and mention the Inorganic acid obtained from it?
Sulphur dioxide is oxidised to sulphur trioxide upon heating with oxygen at high temperature in the presence of V2O5 catalyst
V2O5
2SO2 + O2 → 2SO3
This reaction is used for the manufacture of sulphuric acid by contact process.
61) Give an account on bleaching action of SO2.
In the presence of water, SO2 bleaches coloured wool, silk, sponges & straw into colourless product due to its reducing property.
SO2 + 2H2O → H2SO4 + 2[H]
X+2[H] → XH2
(coloured) (colourless)
However,when the bleached product (colourless) is allowed to stand in air, it is reoxidised by atmospheric oxygen to its original colour. Hence bleaching action of SO2 is temporary.
62) Mention the uses of SO2.
1. Sulphurdioxide is used in bleaching hair, silk, wool etc.,
2. It can be used for disinfecting crops and plants in agriculture.
63) Mention the hybridization of S in SO2 and give its structure.
In sulphur dioxide, sulphur atom undergoes, sp2 hybridization. A double bond arises between S and O is due to pπ- dπoverlapping.
64) Prove that sulphuric acid is a strong dibasicacid.
It forms two types of salts namely sulphates and bisulphates with sodium hydroxide and hence it is a dibasic acid.
H2SO4 + NaOH → NaHSO4 + H2O
Sodium bisulphate
H2SO4 + 2NaOH → Na2SO4 + 2H2O
Sodium Sulphate
65) Give two test for sulphuric acid /sulphates?
Dilute solution of sulphuric acid / aqueous solution of sulphate gives white precipitates (barium sulphate) with barium chloride solution. It can also be detected using lead acetate solution. Here a white precipitate of lead sulphate is obtained.
BaCl2 + H2SO4→ BaSO4 + 2HCl
(CH3COO)2Pb + H2SO4→ PbSO4 + 2CH3COOH
Group 17 (Halogen group) Elements
66) Name the halogen liberated from bleaching powder on reaction with mineral acids. Give reaction
Chlorine is liberated from bleaching powder on reaction with mineral acids
CaOCl2 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + H2O + Cl2
67) What is the action of hydrochloric acid on potassiumdichromate
K2Cr2O7 + 14HCl → 2KCl + 2CrCl3 + 7H2O + 3Cl2
68) What happens when chlorine is burnt with turpeatine
When Chlorine is burnt with turpentine it forms carbon and hydrochloric acid
C10H16 + SCl2→ 10C + 16HCl
69) When chlorine water is exposed to sunlight it loses its colour and smell. Give reason
Chlorine is converted into hydrochloric acid when chlorine water is exposed to sunlight. Hence it loses it’s colour and smell
2Cl2 + H2O → O2+4HCl
70) Show that chlorine is a strong bleaching agent
Chlorine is a strong bleaching agent because of the nascent oxygen
H2O + Cl2→ HCl + HOCl - Hypochlorous acid
HOCl → HCl + (O)
Colouring matter + Nascent oxygen → Colourless oxidation product
71) Show that chlorine is a strong oxidizing agent
Chlorine is a strong oxidizing agent because of the nascent oxygen. It oxidizes ferrous sulphate to ferric sulphate
2FeSO4 + H2SO4 + Cl2→ Fe2 (SO4)3 +2HCl
72) How is bleaching powder prepared?
Bleaching Powder is prepared by passing chlorine gas through dry slaked time (Calcium hydroxide)
Ca(OH)2 + Cl2→ CaOCl2 + H2O
73) Write two displacement redox reactions of chlorine
Chlorine displaces bromine from bromides and iodine from iodide salts
Cl2 + 2KBr → 2KCl + Br2
Cl2 + 2KI → 2KCl + I2
74) Give the uses of chlorine
Chlorine is used in
i) Purification of drinking water
ii) Bleaching of cotton textiles paper and rayon
iii) Extraction of gold and platinum
75) What is aqua regia (Royal water) mention it’s use
When three parts of concentrated hydrochloric acid and one part of concentrated Nitric acid are mixed aquar egia is obtained. It is used for gold, platinum etc.,
76) What is the action of gold on aquaregia
Au + 4H+ + NO3- + 4Cl-→ AuCl4- + NO + 2H2O
77) Give the reaction of platinum on aquaregia
Pt + 8H+ + 4NO3- + 6Cl-→ [Pt Cl6]2- + 4 NO2 + 4 H2O
78) Give the uses of hydrochloric acid
i) Hydrochloric acid is used for the manufacture of chlorine, ammonium chloride, glucose from corn starch etc.,
ii) It is used in the extraction of glue from bone and also for purification of bone black
79) Thermal stability of hydrogen halide decreases from hydrogen fluoride to iodide Give reason
Bond dissociation enthalpy decreases from hydrogen fluoride to hydrogen iodide and hence thermal stability decreases. For eg, hydrogen iodide decomposes at 400°C while hydrogen fluoride and hydrogen chloride are stable at this temperature.
80) Hydrofluoric acid is a weak acid whereas other hydrohalic acids are strong acids Give reason
Hydrofluoric acid is a weak acid due to the presence of intermolecular hydrogen bonding in it and it cannot be completely ionized and hydrogen ion concentration will not be increased. But other hydrohalic acids are completely ionized and hydrogen therefore they are strong acids.
81) Hydrofluoric acid is a weak acid at low concentration, but becomes stronger as the concentration increases why?
0.1M HF is only 10% ionized and hence it is a weak acid but 5M and 15M solution of HF is stronger acid due to the equilibrium
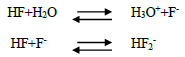
At high concentration, the equilibrium involves the removal of fluoride ions. It affects the dissociation of hydrogen fluoride and increases the hydrogen ion concentration and hence HF becomes stronger acid.
82) Hydrofluoric acid cannot be stored in silica and glass bottles why?
Moist hydrofluoric acid rapidly reacts with silica and glass and thus it cannot be stored init
SiO2 + 4HF → SiF4 + 2H2O
Na2SiO3 + 6HF → Na2 SiF6 + 3H2O
83) Show that hydrogen iodide is a good reducing agent, and how is it tested?
Hydrogen iodide is readily oxidized to iodine hence it is a good reducing agent
2HI → 2H+ + I2 + 2C-
Liberated iodine gives blue-black colouration with starch (Test for Iodine).
84) Give the conditions for formation of interhalogen compounds
i) The central atom must be less electronegative and larger insize
ii) It can be formed only between two halogens and not with more than two halogens.
85) Fluorine cannot act as central atom in inter halogen compoundsWhy?
Fluorine cannot act as central atom in inter halogen compounds because it is highly electronegative and smallest among halogens.
Group 18 (Inert Gases) Elements
86) How are xenon fluorides prepared?
Xenon fluorides are prepared by direct reaction of xenon and fluorine under different conditions.
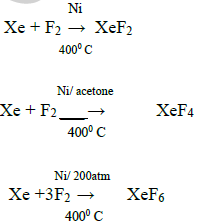
87) What happens when XeF6 is hydrolysed?
On hydrolysis of X6F6 with water vapour it gives
XeO3 XeF6 + 3H2O → XeO3 + 6HF
88) How is sodium per xenate obtained fromXeF6?
When XeF6 reacts with 2.5m NaOH, sodium perxenate is obtained
2XeF6 + 16 NaOH → Na4XeO6 + Xe+O2 + 12 NaF + 8H2O
(Sodium per xenate)
89) Show that sodium per xenate is has strong oxidizing property?
Sodium per xenate oxidises manganese(II) ion into permanganate ion even in the absence of catalyst
5XeO6 4- + 2Mn2+ 14H+ → 2MnO4-+ 5XeO3 + 7 H2O
90) Xenon is used in high speed electronic flash bulbs used by photographers Why?
Xenon emits an intense light in discharge tubes instantly. Due to this it is used in high speed electronic flash bulbs used by photographers.
ADDITIONAL 5 MARK QUESTIONS
1) Explain commercial method of preparation of nitric acid by ostwald’s process.
2) Write the primary, secondary and tertiary reactions of metals with nitric acid.
3) Give the various steps involved in the reaction of dilute nitric acid with
i. copper
ii. magnesium
4) Mention the oxides of nitrogen and give their preparation.
5) Give the structures of oxides of nitrogen.
6) Give the structures of oxoacids of nitrogen.
7) Mention the oxoacids of nitrogen and give their method of preparation.
8) Give one method of preparation for each oxyacids of phosphorous.
9) Write briefly on allotropic form of Sulphur.
10) Explain any three methods of preparation of sulphur dioxide with equations.
11) Phosphorous compound ‘A’ which is poisonous and has the smell of rotten fish reacts with chlorine and gives ‘B’ ‘B’ reacts with water to give an oxyacid of phosphorous ‘C’ which is tribasic in nature Identify the compounds A, B and C and explain the reactions.
12) How is chlorine manufactured by the electrolysis of brine solution?
13) Explain deacon’s process of manufacture of Chlorine
14) Mention the hybridization, geometry and number of bond pair and lone pairs of electrons present in different types of inter halogen compounds.

