ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS
1. Define average rate and instantaneous rate.
2. Define rate law and rate constant.
Rate Law
Rate is given in terms of molar concentration of reactants raised to the power which may or may not equal to stoichiometric coefficient.
Rate constant
Rate constant is same as rate of reaction when concentration of all the reactants is unity.
3. Derive integrated rate law for a zero order reaction A ⎯⎯→ product.
Rate is independent of the concentration of reactant is called zero order reaction.

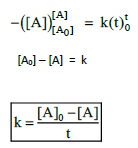
4. Define half life of a reaction. Show that for a first order reaction half life is independent of initial concentration.
Time required for the reactant concentration to reach one half its of initial value is called half life of a reaction.
First order reaction half-life
No concentration terms involved, so half life is independent on initial concentration of reactant.
5. What is an elementary reaction? Give the differences between order and molecularity of a reaction.
Each and every single step in a reaction mechanism is called an elementary reaction.
6. Explain the rate determining step with an example.
7. Describe the graphical representation of first order reaction.
8. Write the rate law for the following reactions.
(a) A reaction that is 3/2 order in x and zero order in y.
(b) A reaction that is second order in NO and first order in Br2.
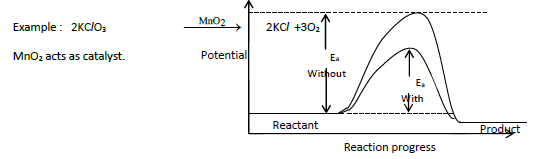
9. Explain the effect of catalyst on reaction rate with an example.
1. A catalyst is a substance which alters the rate of a reaction without itself undergoing any permanent chemical change.
2. It may participate in a reaction but regenerated at the end of reaction.
3. A catalyst increases rate of reaction by lowering the activation energy.
10. The rate law for a reaction of A, B and L has been found to be rate = k [A]2 [B] [L]3/2.
How would the rate of reaction change when
(i) Concentration of [L] is quadrupled
(ii) Concentration of both [A] and [B] are doubled
(iii) Concentration of [A] is halved
(iv) Concentration of [A] is reduced to (1/3) and concentration of [L] is quadrupled.
11. The rate of formation of a dimer in a second order reaction is 7.5 × 10 –3 mol L–1 s–1 at 0.05 mol L–1 monomer concentration. Calculate the rate constant.
rate = k [monomer]2
12. For a reaction X + Y + Z ⎯⎯→ products the rate law is given by rate = k [X3/2 [Y]1/2 .
What is the overall order of the reaction and what is the order of the reactionwith respect to z.
13.Explain briefly the collision theory of bimolecular reactions. (or) Derive 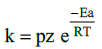
Consider a bimolecular reaction between A2 and B2 proceeds through collision betweenthem which is proportional to number of collision per second
Collision rate in gas phase reaction is calculated from kinetic theory of gas and its value is 109collision per seconds at 298K and 1 atm pressure.
All these collisions are not effective and in order for reaction to takes place, the colliding molecules must possess activation energy.
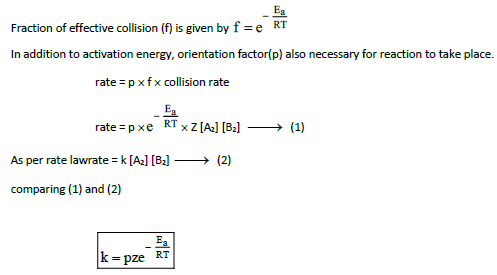
14. Write Arrhenius equation and explains the terms involved.
k is rate constant
A is Frequency factor
Ea is Activation energy( Jmol-1)
T is Temperature in Kelvin
R is gas constant (8.314 JK–1 mol–1)
15. The decomposition of Cl2O7 at 500 K in the gas phase to Cl2 and O2 is a first order reaction.
After 1 minute at 500K, the pressure of Cl2O7 falls from 0.08 to 0.04 atm.
Calculate the rate constant in s – 1.
17. Explain pseudo first order reaction with an example.
A second order reaction can be altered to a first order reaction by taking one of the reactants in large excess, such reaction is called pseudo first order reaction.
Example : Acid hydrolysis of ester
18. Identify the order for the following reactions
(i) Rusting of Iron
(ii) Radioactive disintegration of 92U238
(iii) 2A + 3B ⎯⎯→ products ; rate = [A]1/2 [B]2
(i) First order
(ii) First order
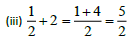
19. A gas phase reaction has energy of activation 200 kJ mol–1. If the frequency factor of the reaction is 1.6 × 1013 s–1. Calculate the rate constant at 600 K.( e−40.09 = 3.8 × 10–18)
Ea = 200 kJ mol–1
A = 1.6×1013 s –1
T = 600 K andR = 8.314 J K–1 mol–1
k = ?
20. For the reaction 2x + y ⎯⎯→ L. Find the rate law from the following data.
21. How do concentrations of the reactant influence the rate of reaction?
Rate of reaction increases with increases of concentration of reactant.
rateα[Reactant]
As reactant concentration is more, which leads to more collision of reactant molecules which increases the rate of reaction.
22. How do nature of the reactant influence rate of reaction. (or)
Titration between potassium per mangate and oxalic acid is carried out at 60°C where as titration between potassium per manganate and ferrous ammonium sulphate at room temperature. Give reason.
Chemical reaction involves bond breaking and bond formation. The net energy involved in this process depends on nature of reactants and hence rate differs for different reactants.
For example, titration between KMnO4 vs FAS takes place at room temperature whereas titration between KMnO4 vs Oxalic acid is heated to 60°C. This is because oxidation of oxalate ion by KMnO4 is slow compared to reaction between KMnO4 and Fe2+.
23. The rate constant for a first order reaction is 1.54 × 10–3 s–1. Calculate its half life time.
k = 1.54 × 10–3 s–1
t1/2 = ?
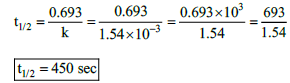
24. The half life of the homogeneous gaseous reaction SO2Cl2 ⎯⎯→ SO2 + Cl2 which obeys first orderkinetics is 8.0 minutes. How long will it take for the concentration of SO2Cl2 to be reduced to 1% of the initial value?
25. The time for half change in a first order decomposition of a substance A is 60 seconds.Calculate the rate constant. How much of A will be left after 180 seconds.
(i) t1/2 = 60sec k = ?
(ii) t = 180 sec [A] = ?
[A0] = 100

26. A zero order reaction is 20% complete in 20 minutes. Calculate the value of the rate constant.
In what time will the reaction be 80% complete?
(i) [A0] = 100 [A] = 80
t = 20 min k = ?
(ii) t = ? [A] = 20
27. The activation energy of a reaction is 225 k cal mol –1 and the value of rate constant at 40°C is 1.8 × 10–5 s –1. Calculate the frequency factor A.
Ea = 225 k cal.mol–1 = 225000 cal .mol–1
k = 1.8 × 10–5 s–1
R = 1.987 cal K –1 mol –1
T = 40°C = 40 + 273 = 313 K
A = ?


28. Benzene diazonium chloride in aqueous solution decomposes according to the equation C6H5N2Cl ⎯⎯→ C6H5Cl + N2. Starting with an initial concentration of 10 g L–1, the volume of N2 gas obtained at 50°C at different intervals of time was found to be as under:
Show that the above reaction follows the first order kinetics. What is the value of the rate constant?
29. From the following data, show that the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide is a reaction of the first order :
Where t is the time in minutes and V is the volume of standard KMnO4 solution required for titrating the same volume of the reaction mixture.
30. A first order reaction is 40% complete in 50 minutes. Calculate the value of the rate constant.In what time will the reaction be 80% complete?
(i) t = 50 min [A0] = 100 [A] = 60 k = ?
(ii) [A] = 20 t = ?
II. EXAMPLES
Example-1
Consider the oxidation of nitric oxide to form NO2
2NO(g) + O2(g) ⎯⎯→ 2NO2 (g)
(a) Express the rate of the reaction in terms of changes in the concentration of NO, O2 and NO2.
(b) At a particular instant, when [O2] is decreasing at 0.2 mol L–1 s–1 at what rate is [NO2] increasing at that instant?
Example-2
What is the order with respect to each of the reactant and overall order of the following reaction?
(a)Order w.t.to Br – is 1
Order w.t.to 3 BrO − is 1
Order w.t.to H+ is 2
Overall order is 1 + 1 + 2 = 4
(b)order = 3/2
Example-3
The rate of the reaction x + 2y → product is 4 × 10 –3 mol L –1 s –1, if [x] = [y] = 0.2 M and rate constant at 400 K is 2 × 10 –2 s –1, What is the overall order of the reaction.
rate = k [X]9 [Y]6
4× 10 –3 = 2 × 10 –2× (0.2)a (0.2)b
Comparing the powers a + b = 1
Overall order = a + b = 1
Example-4
A first order reaction takes 8 hours for 90% completion. Calculate the time required for 80% completion. (log 5 = 0.6989 ; log 10 = 1)
t = 8 hr
[A0] = 100
[A] = 10
t = ?for [A] = 20 (80% completion)
Example-5
The half life of a first order reaction x → products is 6.932 × 104 s at 500 K. What percentage of x would be decomposed on heating at 500 K for 100 min. (e0.06 = 1.06)
t1/2 = 6.932 × 104 s
t = 100 min = 100 × 60 = 6000 s
Example-6
Show that in case of first order reaction, the time required for 99.9% completion is nearly ten times the time required for half completion of the reaction.
t99.9%
Example-7
The rate constant of a reaction of a reaction at 400 and 200 K are 0.04 and 0.02 s –1 respectively. Calculate the value of activation energy.
T1 = 200 K k1 = 0.02 s –1
T2 = 400 K k1 = 0.04 s –1
R = 8.314 JK –1mol –1
Ea= ?
Example-8
Rate constant k of a reaction varies with temperature T according to the following Arrhenius equation
Where Ea is the activation energy. When a graph is plotted for log k Vs 1/T astraight line with a slope of –4000 K is obtained. Calculate the activation energy Slope = –4000 K
Ea= ?
III EVALUATE YOURSELF
Evaluate Yourself-1
(1) Write the rate expression for the following reactions, assuming them as elementary reactions.
(i) 3A + 5B2 ⎯⎯→ 4CD (ii) X2 + Y2 ⎯⎯→2XY
(2) Consider the decomposition of N2O5(g) to form NO2(g) and O2(g). At a particular instant N2O5 disappears at a rate of 2.5 × 10 –2 mol dm –3 s –1. At what rate are NO2 and O2 formed? What is the rate of the reaction?
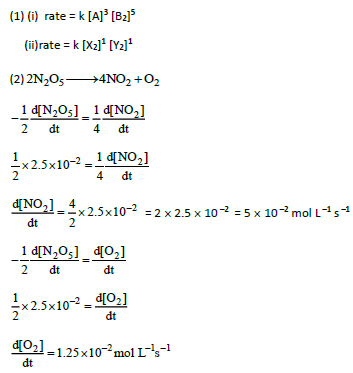
Evaluate Yourself-2
(1) For a reaction, X + Y ⎯⎯→ product ; quadrupling [x], increases the rate by a factor of 8.
Quadrupling both [x] and [y], increases the rate by a factor 16. Find the order of the reaction with respect to x and y. What is the overall order of the reaction?
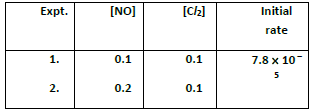
(2) Find the individual and overall order of the following reaction using the given date
2NO(g) +Cl2(g) ⎯⎯→2NOCl(g)
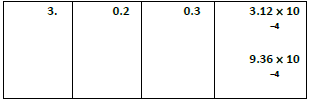
(1)rate = k [X]a [Y]b ⎯ ⎯→ (1)
8 rate = k [4X]a [Y]b ⎯ ⎯→ (2)
16 rate = k [4X]a [Y]b ⎯⎯→ (3)
8=4a
23 = 22a
3 = 2a
a = 3/2
order w.r.to X = 3/2
2=4b
b = 1/2
order w.r.to Y = 1/2
3 = (3− 1 )
3 = 3
Equating the powers
1 = –y
y = –1
order w.r.to O2 = 1
rate = k [NO]2 [O2]–1
overall order = 2 – 1 = 1
Evaluate Yourself-3
(1) In a first order reaction A→ products 60% of the given sample of A decomposes in 40 min.
What is the half life of the reaction?
(2) The rate constant for a first order reaction is 2.3 10 –4 s –1. If the initial concentration of the reactant is 0.01 M. What concentration will remain after 1 hour?
(3) Hydrolysis of an ester in an aqueous solution was studied by titrating the liberated carboxylic acid against sodium hydroxide solution. The concentrations of the ester at different time intervals are given below.
Show that, the reaction follows first order kinetics.
(1) t = 40 min
[A0] = 100
[A] = 40
t1/2 = ?
Evaluate Yourself-4
For a first order reaction the rate constant at 500 K is 8 × 10 –4 s –1. Calculate the frequency factor, if the energy of activation for the reaction is 190 kJ mol –1.
0.9031 – 4 = log A – 19.846
log A = 0.9031 – 4 + 19.846
= 20.7491 – 4
log A = 16.7491
A = Antilog 16.7491
IV ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS
1. Define rate of a reaction.
Rate is defined as change in concentration of reactant or product with respect to time.
2. Give the unit of rate of reaction for (i) aqueous reaction (ii) Gaseous reaction
(i) mol L–1 s–1 (ii) atm s–1
3. How to determine rate of a reaction.
Draw a plot of concentration vs time graph. The slope of the curve between the interval of time gives the average rate.
Instantaneous rate is the rate at a particular time which is calculated by drawing a tangent at that point on the concentration vs time graph. The slope of the tangent gives the instantaneous rate.
4. Differentiate rate and rate constant.
5. Define molecularity.
It is the total number of reactant speciesthat are involved in an elementary step.
6. Define order of a reaction.
aA + bB ⎯⎯→ products
rate = k [A]x [B]y
overall order = x + y
It is the sum of the powers of concentration terms involved in the experimentally determined rate law.
7. Derive an expression of half life of a zero order reaction.
8. Give general expression for half life of nth order reaction.
9. Draw a plot of concentration vs time for zero order reaction.

y = – mx + C
Plot of [A] Vs t gives straight line with negative slope.
Slope equal to –k and intercept equals to [A].
10. Give examples of first order reaction.
(iv) All radioactive decay
(v) Isomerisation of cyclopropane to propene
11. Give two examples of zero order reaction.
12. Give units of rate constant of
(a) first order reaction (b) zero order reaction
(a) sec–1 (b) mol L–1s–1
13. What is collision frequency?
Number of collisions per second per unit volume is called collision frequency.
14. Why molecularity can never be more than 3?
Probability of simultaneous collision of more than three reactants is rare.
So molecularity can never be more than three.
15. Define activation energy?
In order to react, the colliding molecules must possess a minimum energy called activation energy.
16. What is the usefulness of Arrhenius equation.
With the help of Arrhenius equation, we can calculate activation energy of the reaction provided rate constants at two different temperatures are given.
17. Mention the factors affecting rate of reaction.
1. Nature and state of reactant
2. Concentration of reactant.
3. Surface area of reactant.
4. Temperature of reaction.
5. Presence of catalyst.
18. What does the slope represent in the following graphs.
19. Which of the following reaction is fast. Give reason.
Second reaction is fast because the state of reactant is gas. Gaseous reaction is faster than solid state reactants.
20. Which of the two reacts faster? Why?
(i) Powdered CaCO3 with dil. HCl
(ii) Lump of CaCO3 as marble with dil. HCl
First reaction is faster because powdered form of reactant has more surface area.
21. Derive integrated rate law for a first order reaction A ⎯⎯→ product.
Rate is directly proportional to the concentration of one reactant is called first order reaction.
Consider a general first order reaction A ⎯⎯→ Product
At t = 0 concentration of reactant = [A0]
At time t, concentration of reactant left = [A]
Please click on below link to download pdf file for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chemical Kinetics Important Questions and Answers

