CBSE Class 10 Social Science Globalization and Indian Economy VBQs read and download in pdf. Value Based Questions come in exams for Social Science in Class 10 and are easy to learn and helpful in scoring good marks. You can refer to more chapter wise VBQs for Class 10 Social Science and also get latest topic wise very useful study material as per latest NCERT book for Class 10 Social Science and all other subjects for free on Studiestoday designed as per latest Class 10 CBSE, NCERT and KVS syllabus and examination pattern
VBQ for Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy
Class 10 Social Science students should refer to the following value based questions with answers for Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy in Class 10. These VBQ questions with answers for Class 10 Social Science will come in exams and help you to score good marks
Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy VBQ Questions Class 10 Social Science with Answers
Question. Which of the following is a benefit of globalization?
(a) Consumers pay higher amount for goods and services, so producers are better off.
(b) Asymmetric information cannot exist in a globalized market.
(c) Consumers get a wide variety of goods to choose from.
(d) Homogeneous goods are sold in a globalized market.
Answer : (c) Consumers get a wide variety of goods to choose from.
Question. Rajiv has a textile firm. For carrying out production, Rajiv spent money on procuring thread from traders, buying machine and equipment and built a warehouse to store the cloth produced. The expenditure incurred by Rajiv for conducting the production process is termed as _____.
(a) investment
(b) profits
(c) equity
(d) interest
Answer : (a) investment
Question. Which of the following is a reason for the government to impose barriers on trade?
(a) To regulate the type and amount of goods that can enter the country.
(b) To increase competition in domestic market.
(c) To remove monopoly markets from the country.
(d) To improve the performance of domestic producers.
Question. Which of the following can be a benefit to localbusi nesses if they conduct business with MNCs?
(a) Local businesses do not have to invest in the business as MNCs do all the investment.
(b) MNCs provide cheap labour to local businesses.
(c) MNCs can bring advanced techniques of production.
(d) Local businesses earn higher profits as their cost of production becomes nil.
Answer : (c) MNCs can bring advanced techniques of production.
Question. In what way did the pressure of competition affect the workers in the garment industry?
(a) Reduced cost of raw materials
(b) Reduced the labour cost
(c) Decreased the working hours
(d) Protection to workers
Answer : (b) Reduced the labour cost
Question. Which of the following is a reason for the government to impose barriers on trade?
(a) To regulate the type and amount of goods that can enter the country
(b) To increase competition in domestic market
(c) To remove monopoly markets from the country
(d) To improve the performance of domestic producers
Answer : (a) To regulate the type and amount of goods that can enter the country.
Question. Which of the following is an example of a trade barrier?
(a) Remittances to foreigners
(b) Cost of transportation
(c) Tax on imports
(d) Interest on bonds
Answer : (c) Tax on imports
Question. Globalisation helps in exchange of goods and services around the world. (True/False)
Answer : True
Question. The impacts of globalisation is that although it has created a lot of jobs but labour laws are not implemented properly, workers are denied their rights and its benefits have not been shared equally.
Answer : True
Question. Rapid development in technology and its usage and removal of trade barriers has helped to achieve rapid globalisation. (True/False)
Answer : True
Mark the option which is most suitable :
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If both assertion and reason are false.
Question. Assertion : MNCs can exert a strong influence on production at distant locations.
Reason : MNCs set up partnerships with local companies, use local companies for supplies, compete with the local companies or buy them up.
Answer : (a) By setting up partnerships with local companies, by using the local companies for supplies, by closely competing with the local companies or buying them up, MNCs are exerting a strong influence on production at distant locations. As a result, production in widely dispersed locations is getting interlinked.
Question. Assertion : A tax on imports makes the market for imported goods lucrative in terms of earning higher profits.
Reason : Taxes are imposed to ensure smooth trade between nations and higher tax revenues for the governments of the countries.
Answer : (d) Taxes increase the price of imported goods, and so the demand for imports is likely to go down. As a result, the profits of producers who sell imported goods are also likely to reduce. Governments impose taxes to regulate the amount and quality of goods that enter a nation and to protect domestic industry from foreign competition.
Question. Assertion : Due to foreign trade, producers in different countries closely compete with each other.
Reason : Foreign trade leads to similar prices of good across boundaries, and the producers who do not offer competitive prices may lose the market share.
Answer : (a) Due to foreign trade, producers in different countries closely compete with each other. This is because the price of similar goods tends to become equal in different markets. Therefore, if a good is priced higher in domestic market, consumers may prefer importing it from another country at a lower price.
Question. Assertion : Global production has a complex structure.
Reason : Production of one good may take place in different parts of the world. For instance, an equipment may be produced by combining components produced in different countries.
Answer : (a) Globalization leads to connectivity of different countries and goods and services can be transported across the world. Goods, components produced in different parts of the world can be used for production in any country.
Question. Assertion : The removal of barriers to trade is known as liberalisation.
Reason : Liberalisation of trade allows businesses to freely decide which goods to import and export.
Answer : (b) The removal of barriers to trade is known as liberalisation, and the businesses freely deciding which goods to import and export is an outcome of liberalisation not a reason for liberalisation.
Question. Fill in the blanks.
Indian buyers have a greater choice of goods than they did two decades back. This is closely associated with the process of (a) ......... . Markets in India are selling goods produced in many other countries. This means there is increasing (b) ......... with other countries. Moreover, the rising number of brands that we see in the markets might be produced by MNCs in India. MNCs are investing in India because (c) ......... . While consumers have more choices in the market, the effect of rising (d) ......... and (e) ......... has meant greater (f) ......... among the producers.
Answer : (a) globalisation
(b) trade
(c) production costs here are cheaper
(d) demand
(e) purchasing power
(f ) competition.
Question. Match the following:

Ans. (i)—(b) (ii)—(e) (iii)—(d) (iv)—(c) (v)—(a).
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Give examples of industries where production is carried out by small producers around the world.
Answer : Garments, footwear, sports items.
Question. For which purpose can government use trade barriers?
Answer : Government can use trade barriers to increase or decrease (regulate) foreign trade and to decide what kinds of goods and how much of each, should come into the country.
Question. What is an MNC?
Answer : An MNC (Multi-National Corporation) is a company that owns and controls production in more than one nation.
Question. Why do MNCs set up offices and factories in regions where they can get cheap labour and other resources?
Answer : MNCs do this so that the cost of production is low and they can earn greater profits.
Question. What is the aim of World Trade Organisation (WTO)?
Answer : Its aim is to liberalise international trade.
Question. How are Mexico and Eastern Europe useful for the MNCs?
Answer : In these two countries are close to the markets in the US and Europe.
Question. How much did Ford Motors invest in India?
Answer : Ford Motors came to India in 1995 and spend ` 1700 crore to set up a large plant near Chennai.
Question. What do you mean by foreign investment?
Answer : Investment made by MNCs is called foreign investment.
Question. How many countries are currently the members of the World Trade Organisation (WTO)?
Answer : It has 153 member countries as on 23 July, 2008.
Quedtion. Where is the main Head Office of WTO?
Answer : Geneva-Switzerland.
Quedtion. What is Globalisation?
Answer : Globalisation means opening up the economy to facilitate its integration with the world economy
Question. Why had the Indian Government put barrier to foreign trade and foreign investment after independence? State any one reason.
Answer : The Indian government, after Independence, had put barriers to foreign trade and foreign investment because this was considered necessary to protect the producers within the country from foreign competition.
Question. What is the most common route for MNC investments?
Answer : The most common route for MNC investments is to buy up local companies and then to expand production.
Question. How does liberalisation of trade benefit businesses?
Answer : With liberalisation of trade, business are allowed to make decisions freely about what they wish to import or export.
Question. What do you know about Ford Motors?
Answer : It is an American company. It is one of the world’s largest automobile manufactures with production spread over 26 countries of the world.
Question. Until the middle of the twentieth century, production was largely organised within countries. What crossed the boundaries of these countries?
Answer : There were raw materials, food stuff and finished products.
Question. What is basic function of foreign trade?
Answer : Foreign trade creates an opportunity for the producers to reach beyond the domestic markets, i.e., markets of their own countries.
Question. Why is fair globalisation essential?
Answer : Fair globalisation would create opportunities for all, and also ensure that the benefits of globalisation are shared better.
Question. How would flexibility in labour laws help companies?
Answer : Flexibility in labour laws would help to reduce the cost of labour for the company.
Question. Why are Chennai toys more popular in the Indian markets?
Answer : Chennai toys are more popular in the Indian markets because of the cheaper prices and new designs.
Question. In what way does China provide advantage to the MNCs?
Answer : China provides the advantage of being a cheap manufacturing location.
Question. What has been the major factor that has stimulated the globalisation process?
Answer : Rapid improvement in technology has been the major factor that has stimulated the globalisation process.
Question. What was the main channel connecting countries in the past?
Answer : Foreign trade was the main channel connecting countries in the past.
Question. The Indian government removed barriers on foreign trade and foreign investment to a large extent. What does this mean?
Answer : This means that goods could be imported and exported easily and also foreign companies could set up factories and offices here.
Question. Why are MNCs attracted to India?
Answer : India has high skilled engineers who can understand the technical aspects of production. It also has educated English speaking youth who can provide customer care services.
Question. Where do MNCs set up offices and factories for production?
Answer : MNCs set up offices and factories for production in regions where they can get cheap labour and other resources.
Question. What is multinational corporation?
Answer : A multinational corporation is a company that owns or controls the production of its goods in more than one country.
Question. Give the meaning of globalisation.
Answer : Globalisation means integrating the economy of a country with the economies of other countries under conditions of free flow of trade, capital and movement of persons across borders.
Question. Differentiate between investment and foreign investment.
Answer : The money that is spent to buy assets such as land, building, machines etc. is called investment whereas investment made by a MNC to buy such assets is called foreign investment.
Question. Due to what reason are the latest models of different items available within our reach?
Answer : Globalisation
Question. Why had the Indian Government put barriers to foreign trade and foreign investment after independence? State any one reason.
Answer : To protect the producers within the country from foreign competition.
Question. Why do MNCs set up their offices and factories in those regions where they get cheap labour and other resources?
Answer : MNCs set up their offices and factories in those regions where they get cheap labour and other resources because they bring down the cost of production and ensure more profits for themselves.
Question. In which two different forms do we participate in the market?
Answer : We participate in the market as producers and consumers.
Question. Why did the Indian government remove barriers to a large extent on foreign trade and foreign investment?
Answer : The Indian government realised that its domestic industries had established themselves and it was the proper time to face competition and improve the quality of production. So, barriers on foreign trade and investment were removed.
Question. Define the term investment.
Answer : An investment is an asset or item that is purchased with the hope that it will generate income in future.
Question. What is foreign investment?
Answer : Investment made by MNCs is called foreign investment.
Question. What is the meaning of investment?
Answer : The money that is spent to buy assets such as land, building, machines and other equipments is called investment.
Question. How are the MNCs spreading their production across the globe?
Answer : MNCs are spreading their production across the globe by setting up partnerships with local companies, by using the local companies for supplies and by closely competing with local companies or buying them up.
Question. What is meant by trade barrier?
Answer : It refers to the various restrictions which are used by the government of a country to increase or decrease foreign trade such as tax on imports.
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. What is the impact of globalisation on the well-off sections in the urban areas of India?
Answer : Due to globalisation there is greater choice before the people belonging to well- off sections. They now enjoy improved quality and lower prices for several products. As a result, these people today, enjoy much higher standards of living than was possible earlier.
Question. “Globalisation and competition among producers has been of advantage to the consumers.” Give arguments in support of this statement.
Answer : (i) There is greater choice available to the consumers in goods.
(ii) The quality of goods has been improved.
(iii) Prices of goods are lower.
(iv) Consumers are now able to enjoy a better life.
Question. What do you understand by globalisation? Explain in your own words.
Answer : Globalisation is the process of rapid integration or interconnection between countries. Globalisation means integrating an economy with the world economy. As a result of globalisation, the different countries of the world become economically interdependent on each other. This term is also often used to refer to economic globalisation: the integration of national economies into the international economy through trade, foreign direct investments, capital flows, migration and the spread of technology.
Question. How are local companies benefitted by joining hands with MNCs for production?
Answer : At times, MNCs set up production jointly with some local companies. The benefit to the local companies of such joint production is two-fold.
(i) MNCs can provide money for additional investments, like buying new machines for faster production.
(ii) MNCs might bring with them the latest technology for production.
Question. What is WTO? Why it has been formed?
Answer : World Trade Organisation (WTO) is an organisation whose aim is to liberalise international trade. It was set up in early 1995. It helps to remove trade barriers and create a free environment for foreign trade. It establishes rules regarding present members of the WTO.
Though WTO is supposed to allow free trade for all, in practice, it is seen that the developed nations have unfairly retained trade barriers. On the other hand, WTO rules have forced the developing countries to remove trade barriers.
Question. In recent years how our markets have been transformed? Explain with examples.
Answer : Until the middle of the twentieth century, production was largely organised within countries. What crossed the boundaries of these countries were raw materials, food stuffs and finished goods. Trade was the main channel connecting distant countries. But with the emergence of multinational corporations (MNCs), things have been changed. These MNCs are spreading their production and interacting with local producers in various countries across the globe.
Foreign trade integrates markets. It creates an opportunity for the producers to reach beyond the domestic markets. Producers can sell their produce not only in markets located within the country but can also compete in markets located in other countries. Similarly, for the buyers, import of goods produced in another country is one way of expanding the choice of goods beyond what is domestically produced.
Question. Why had the Indian government put barriers to foreign trade and foreign investment after independence? Analyse the reasons.
Answer : The Indian government put barriers on foreign trade and foreign investment after independence because:
(a) It was considered necessary to protect the producers within the country from foreign competition.
(b) In 1950s and 1960s, the industries were in nascent stage and competition from imports at that stage would not have allowed these industries to develop.
(c) Therefore, India allowed the imports of only essential items like machinery, fertilizers, petroleum etc.
Question. Explain how globalisation can be made fairer.
Answer : Globalisation can be made fairer in the following ways:
• Policies should be made in such a way that they protect the interests of not only the rich and prosperous producers but also the workers.
• The government can negotiate with World Trade Organisation for fairer rules and can align with developing countries to stand against the domination of developed countries.
• Equal space should be provided to both developed and developing economies to explore the market and compete.
Question. “Foreign trade integrates the markets in different countries.” Support the statement with arguments.
Answer : Foreign trade integrates the markets of different countries as:
(a) It provides an opportunity for both producers and consumers to reach beyond the markets of their own country.
(b) Producers now compete with markets located in other countries.
(c) There is an expansion of choice of goods beyond the domestic market.
(d) For example, during the Diwali season, buyers in India have the option of buying either Indian or Chinese decorative lights and bulbs. The Chinese manufacturers get the opportunity to expand their business.
Question. Explain the role of government in- making globalisation fair.
Answer : Government can play an important role in making globalisation fair in the following ways:
• Policies should be made in such a way that they protect the interests of not only the rich and prosperous producers but also the workers.
• Labour laws should be properly implemented favouring the workers so that their basic rights like sustainable wages, better working conditions, health etc. are not hampered.
• Efforts should be made to protect the small producers from international competition and prepare a stage for their survival.
Question. What is a trade barrier? Wliy did the Indian government put trade barriers after Independence? Explain.
Answer : Trade barriers are the restrictions that are imposed by the government on free import and export activities so as to protect its producers and entrepreneurs.
The Indian government put barriers on foreign trade and foreign investment after independence because:
• It was considered necessary to protect the producers within the country from foreign competition.
• In 1950s and 1960s, the industries were in nascent stage and competition from imports at that stage would not have allowed these industries to develop.
• Therefore, India allowed the imports of only essential items like machinery, fertilizers, petroleum etc.
Question. How has foreign trade been integrating markets of different countries in the world? Explain with examples.
Answer : Foreign trade integrates the markets of different countries as:
• It provides an opportunity for both producers and consumers to reach beyond the markets of their own country.
• Producers now compete with markets located in other countries.
• There is an expansion of choice of goods beyond the domestic market.
For example, during the Diwali season, buyers in India have the option of buying either Indian or Chinese decorative lights and bulbs. The Chinese manufacturers get the opportunity to expand their business.
Question. What are the harmful effects of MNCs to a host country? Give three examples.
Answer : The harmful impacts of MNCs to a host country are:
• They can hamper the growth of local industries by giving them tough competition.
• They generally use capital intensive techniques which may not be suitable for a developing country like India, where unemployment is a big problem.
• They may misuse the environment of the host country by over exploiting its natural resources.
Question. “Technology has stimulated the globalisation process.” Support the statement with examples.
Answer : Technology has stimulated the process of globalisation in the following ways:
• Transportation technology has witnessed several improvements in past fifty years. This has made much faster delivery of goods across long distances possible at lower costs, such as use of containers have led to huge reduction in port handling costs and increased the speed with
which exports can reach markets. Also, the cost of air transport has fallen. Ultimately, it has
stimulated the globalisation process.
• Telecommunication has also shown remarkable development. Computers, internet, e-mail, voice-mail, etc. are used intensively to contact one another around the world.
• There has been a remarkable development in information and communication technology. It has enabled to access information instantly and communicate even in the remotest areas. Call centres use this to satisfy their customers abroad or provide outsourcing services from anywhere.
Question. What is the meaning of SEZ? Mention any two features of SEZ.
Answer : Special Economic Zones. These are designated areas in a region set up by the government to attract foreign companies to invest in their countries.
The features of Special Economic Zones are:
• The companies who set up production units in these areas are exempted from paying taxes for an initial period of five years.
These areas are provided with best infrastructural facilities like roads, water, transportation, communication, markets etc.
Question. How did ‘Cargill Foods’ become the largest producer of edible oils in India? Explain.
Answer : Cargill Foods, a very large American MNC, bought Parakh foods, which had a large marketing network in many parts of India. It was a well reputed company. It had four oil refineries, whose control passed to Cargill Foods. Cargill Foods is, now, the largest producer of edible oil in India, with a capacity of making 5 million pouches daily.
Question. What would happen if Government of India puts heavy tax on import of Chinese toys?
Explain any three points.
Answer : If Government of India puts heavy tax on import of Chinese toys, then
(a) the Chinese toys will become expensive and may be people will not buy them and, thus, the Chinese toys will loose their market in India.
(b) people in India, will buy local made goods (toys) and the local industries will get a boost and their sale will also go up.
(c) as there would be greater demand of Indian goods, the Indian, manufacturers, then, will earn more profits and workers will get more employment.
Question. What is a tariff? Why is it imposed on goods?
Answer : A tariff is a tax imposed on goods when they are moved across a political boundary. Mostly, they are imposed on imported commodities.
Tariffs are imposed on goods
(i) To protect infant industries of the home country.
(ii) To prevent the dumping of foreign countries.
(iii) A source of revenue.
Question. What role can the government play in order to ensure a fair globalisation?
Or
Explain how globalisation can be made fairer.
Answer : The government can play a major role in ensuring a fair globalisation in India:
(i) Its policies must protect the interests, not only of the rich and the powerful, but all the people in the country.
(ii) The government can ensure that labour laws are properly implemented and workers get their rights.
(iii) It can support small producers to improve their performance till the time they become strong enough to compete.
(iv) If necessary, the government can use trade and investment barriers. (v) It can negotiate at the WTO for ‘fairer rules’.
(vi) It can also align with other developing countries with similar interests to fight against the domination of developed countries in the WTO.
Question. Why do developed countries want developing countries to liberalise their trade and investment? What do you think should the developing countries demand in return?
Answer : Developed countries want developing countries to liberalise their trade and investment because then the MNCs belonging to the developed countries can set up factories in less expensive developing nations, and thereby increase profits, with lower manufacturing costs and high sale price.
In my opinion, the developing countries should demand, in return, for some manner of protection of domestic producers against competition from imports. Also, charges should be levied on MNCs looking to set base in developing nations.
Question. How is information technology connected with globalisation?
Answer : Information and communication technology is closely connected with globalisation. In recent times, technology in the areas of telecommunications, computers, internet has been changing rapidly.
(i) Telecommunications facilities such as telegraph, telephone including mobiles, fax have brought the world closer. Now people can contact around the world easily. These developments are used to access the information instantly and communicate in the remote areas.
(ii) Computer and internet have entered in almost all the fields. Internet allows one to share information on almost everything. We can send instant e-mail and talk through voice-mail across the world at almost negligible cost.
Question. What would happen of Government of India parts heavy tax on import of Chinese toys? Explain any three points.
Answer : (i) Those who wish to import Chinese toys would have to pay tax on this.
(ii) Because of the tax, buyers will have to pay a higher price on imported toys.
(iii) Chinese toys would no longer be so cheap in the Indian markets and imports from China will automatically reduce.
(iv) Indian toy makers will prosper.
Question. How has liberalisation of trade and investment policies helped the globalisation process?
Answer : (i) Liberalisation of trade and investment policies has helped the globalisation process by making foreign trade and foreign investment easier.
(ii) This has led to a deeper integration of national economies into one conglomerate whole.
(iii) Now goods could be imported and exported easily. Foreign companies could set up factories and offices in India.
Question. Explain how the developing countries which are members of the WTO suffer due to trade barriers.
Answer : The developing countries suffer due to trade barriers. WTO is supposed to allow free trade for all in practice. But the developed countries have unfairly retained trade barriers.
(i) WTO rules have forced the developing countries to remove trade barriers.
(ii) Farmers in most developed countries receive money from their respective government for production. Due to this massive money, they are able to sell their farm products at abnormally low prices.
(iii) Developed countries are asking governments of developing countries to stop supporting their farmers, but they are doing it themselves.
Question. Globalisation will continue in the future. Can you imagine what the world would be like twenty years from now? Give reasons for your answer.
Answer : Globalisation will continue in the future. Twenty years from now, the world will be more globally connected and integrated into one international economy, if this process continues on a fair and equitable basis. Trade and capital flows will increase alongside the mobility of labour. This will occur because liberalisation will get augmented and MNCs will converge with other companies producing the same goods.
Question. “Information and communication technology has played a major role in spreading out products and services across countries.” Support the statement.
Answer : (i) In recent times, technology in the areas of telecommunications, computers, internet has been changing rapidly
(ii) Telecommunication facilities are used to contact one another around the areas. This has been facilitated by satellite communication devices.
(iii) Computers have now entered almost every field of activity. Through the use of internet, one can communicate across the world at negligible costs.
(iv) These devices help us in various ways, transfer of money across the countries has become easy. We can place order for a variety of things through the phone or the internet, and goods are delivered at our home.
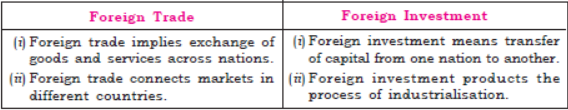
Question. Differentiate between foreign trade and foreign investment.
Answer :
Question. Analyse one good and one bad effect of globalisation on India.
Answer : One good effect of globalisation on India:
Globalisation has resulted in greater competition among producers—both local and foreign. As a result, quality of the products has been improved. At the same time prices of goods have been lowered.
One bad effect of globalisation on India:
For a large number of small producers and workers globalisation has posed a great problem. The small producers failed to compete and got perished. Several units have shut down rendering many workers jobless.
Question. Explain any three steps taken by the Indian Government to attract foreign investment.
Answer : In the recent years, the Indian Government has taken special steps to attract foreign companies to invest in India:
(i) The government has set up industrial zones called special Economic Zones (SEZs). SEZs provide world class facilities – electricity, water, roads, transport, storage recreational and educational facilities.
(ii) Companies who set up production units in the SEZs do not have to pay taxes for an initial period of five years.
(iii) The government has also allowed flexibility in the labour laws to attract foreign investment. The companies can now lower workers ‘flexibly’ for short period when there is intense pressure of work. This is done to reduce the cost of labour for the companies.
Question. What is the impact of flexible labour laws on workers?
Answer : Flexibility in labour laws has badly affected the workers. MNCs employ them on a temporary basis in order to cut costs. They do not pay throughout the year. During peak seasons, workers are made to work for long hours and in night shifts. They are also not given fair wages. This forces them to lead a very hard and highly insecured life.
Question. What are the benefits of foreign trade?
Answer : Benefits of foreign trade are:
(i) With the opening of trade, goods travel from one market to another.
(ii) Choice of goods in markets rises.
(iii) Prices of similar goods in two markets tend to become equal.
(iv) Producers in the two countries now closely compete against each other even though they are separated by thousands of miles.
Question. Describe the major problems created by the globalisation for a larger number of small producers and workers.
Or
Describe the effects of globalisation on small producers and workers.
Answer : Small producers such as producing batteries, capacitors, toys have been hit hard due to competition with the MNCs. They could not compete on the issue of price and quality. As a result of it, their production decreased and many units were closed. Many workers became jobless. Many employers prefer to employ workers on temporary basis which means workers’ jobs are no longer secure. Women are denied their fair share of benefits. Workers have to put in very long working hours without any overtime.
Question. What is the impact of globalisation on the consumers of India?
Answer : (i) Globalisation and greater competition among producers—both local and foreign have been of advantage to consumers, particularly the well-off sections in the urban areas.
(ii) There is a greater choice before these consumers who now enjoy improved quality and lower prices for several products.
(iii) As a result, these people today enjoy much higher standards of living than was possible earlier.
Question. What do you mean by liberalisation of foreign trade?
Answer : (i) Removing barriers or restrictions set by the government is known as liberalisation.
(ii) With the liberalisation of trade, businesses are allowed to make decisions freely about what they wish to import or export.
(iii) The government imposes lesser restrictions than before and is therefore, said to be more liberal.
Question. “Globalisation and competition among producers has been of advantage to the consumers.”
Answer : Give arguments in support of this statement. Globalisation and competition among producers has been of advantage to the consumers in the ways as mentioned below :
• Now there is more choice for the consumers in the markets. For example in the field of toys, the markets are flooded with Chinese toys which are cheaper and of better quality than Indian toys. People now have a choice between Indian toys and Chinese toys.
• The consumers now have products of better quality.
• The prices of various products have come down due to competition among the producers/manufacturers.
• Globalisation has led to improvement in the standard of living of people.
Question. What is the role of WTO in international trade?
Answer : (i) WTO’s aim is to liberalise international trade.
(ii) It establishes rules regarding international trade and sees that these rules are obeyed.
(iii) 164 countries of the world are its members currently.
(iv) It is seen that the developed countries have unfairly retained trade barriers. On the other hand, WTO rules have forced developing countries to remove trade barriers.
Question. Describe the steps that may be taken make globalisation more ‘fair’.
Answer : • Labour laws should be implemented properly to avoid exploitation of the workers.
• The government should protect the interest of the small producers by using trade and investment barriers till they are in a position to compete with large producers or MNCs.
• The government should negotiate at the WTO for “fairer rules”.
• The government should align with other developing countries to fight against the domination of developed countries.
Question. Chinese toys have taken over the Indian toy market due to globalization and promotion of International trade leading to huge losses to Indian toy manufacturers. Why?
Answer : We cannot deny the fact that Chinese toys have taken over the Indian toy market due to promotion of international trade and globalisation leading to huge losses to the Indian toy manufactures.
(a) With lifting of trade barriers, import and export of foreign goods have become easier and markets of native countries are flooded with foreign products.
(b) Prices of foreign products especially the Chinese items like toys are cheap and have a great variety to attract customers.
(c) Technology has made its mark. Foreign goods increase the revenue for the native countries. Moreover, free trade and marketing needs to be accepted for country’s economic growth.
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. What are the various ways in which MNCs set up or control production in other countries?
Answer : Various ways in which MNCs control production in other countries:
(i) By setting up partnerships with local companies — At Times MNCS set up production jointly with some of the local companies. The benefit to the local company of such joint production is two bold. First MNCS can provide φ money for additional investments, the like buying new machines for faster production. Second, MNCS might bring with them the latest technology for production.
(ii) By closely competing with local companies or buying them up. The most common route for MNC investments is to buy up local companies and to expand production. With their huge wealth they can easily do so.
(iii) By using local companies for supply—Large MNCs in developed countries place orders for production with small producers. E.g. garments, footwear, sports item etc. The products are supplied to MNCs which then sell these under their own brand names to the customers. These large MNCs have great power to determine price, quality, delivery and labour conditions for these distant producers.
Question. What values worked behind the restrictions on foreign trade in India after independence?
Answer : After India became independent, the Indian government put barriers to foreign trade and foreign investment. The values that worked behind this are:
(i) It was essential at that time to protect the producers within the country from foreign competition. Industries were just coming up in the 1950s and 1960s, and competition from imports at that stage would not have allowed these industries to emerge.
(ii) Since industries were newly born during that period, it was necessary to make their foundation strong by providing them opportunities to flourish first within the country, then across the country.
(iii) The restrictions on foreign trade for a certain period proved to be a boon for domestic producers in the sense that they became self-sufficient. This self- sufficiency made them able to face competitions.
Question. Describe with an example the role of multinational corporations in the process of globalisation.
Answer : MNCs have played a major role in the process of globalisation.
(i) MNCs are in search for locations around the world that are favourable for their production activities.
(ii) Foreign investment and foreign trade has increased.
(iii) A large part of the foreign trade is controlled by the MNCs.
(iv) MNCs are engaged in translocating capital, technology, people, goods and services across different nations of the world. This is how globalisation is promoted.
It can be further illustrated with the help of an example – Production of cars by Ford Motors in India would lead to interlinking of production. Ford Motors will produce various car components in India. Some other components may be produced elsewhere on the globe. Components produced in India will be shipped to Ford factories outside India. Components and other resources will be shipped to India for automobiles to be produced in India. All these processes will result in the interlinking of production.
Question. ‘Rapid improvement in technology has been one major factor that has stimulated the globalisation process. Explain.
Or
Explain the role of technology in stimulating globalisation process.
Answer : Rapid improvement in technology has been one major factor that has stimulated the globalisation process. For instance, the past fifty years have seen several improvements in transportation technology. This has made much faster delivery of goods across long distances possible at lower costs.
Even more remarkable have been the developments in information and communication technology. In the recent times, technology in the areas of tele- communication, computers, Internet has been changing rapidly. Telecommunication facilities (Telegraph, telephone including mobile phones, fax) are used to contact one another around the world, to access information instantly, and to communicate from remote areas. This has been facilitated by satellite communication devices. Computers have now entered almost every field of activity. Internet allows us to send instant electronic mail (e-mail) and talk (voice- mail) across the world at negligible costs.
Question. What is liberalisation? What steps were taken by the government to liberate the Indian economy?
Answer : Removing barriers or restrictions set by the government is known as liberalisation:
(i) The Indian government, after Independence, had put barriers to foreign trade and foreign investment. This was considered necessary to protect the producers within the country from foreign competition. Industries were just coming up in the 1950s and 1960s and competition from imports at that stage would not have allowed these industries to come up. Thus, India allowed imports of only essential items.
(ii) In 1991, the government decided that the time had come for Indian producers to compete with producers around the globe. It felt that competition would improve the performance of producers within the country. Since they would have to improve their quality.
(iii) Barriers on foreign trade and foreign investment were removed to a large extent. Now, goods could be imported and exported easily and also foreign companies could set up factories and officers here.
(iv) With libralisations of trade, businesses are allowed to make decisions freely about what they wish to import or export.
Question. Information and communication technology or IT has stimulated the globalisation process. How would it influence the country like India where people still depend on agriculture and believe in their customs and traditions?
Answer : Rapid improvement in technology has been one major factor that has stimulated the globalisation process. For instances, the past fifty years have seen several improvements in transportation technology. This has made much faster delivery of goods across long distances possible at lower costs.
Even more remarkable have been the developments in information and communica-tion technology. In the recent times, technology in the areas of telecommunication, computers, Internet has been changing rapidly. Telecommunication facilities (Telegraph, telephone including mobile phones, fax) are used to contact one another around the world, to access information instantly, and to communicate from remote areas. This has been facilitated by satellite communication devices. Computers have now entered almost every field of activity. Internet allows us to send instant electronic mail (e-mail) and talk (voice-mail) across the world at negligible costs.
Question. Supposing you find two people arguing: One is saying globalisation has hurt our country’s development. The other is telling, globalisation is helping India develop. How would you respond to these arguments?
Answer : Both the arguments are right to some extent. Globalisation has hurt our country’s development as well as helped our country develop. In other words, we can say that globalisation has positive as well as negative impact on our country’s development.
Positive impact of the globalisation on India
(i) Availability of variety of products which enabled the consumers to have greater choice and enjoy improved quality and lower prices for several products.
(ii) This led to higher standard of living.
(iii) Increase in foreign direct investment.
(iv) Creation of new jobs in certain industries.
(v) Top Indian companies have been benefited by investing in new technology and production methods along with successful collaborations with foreign companies.
(vi) Globalisation has enabled some large Indian company to emerge as multinationals themselves. For example, Tata Motors, Infosys, Ranbaxy etc.
(vii) Enabled some large Indian companies to emerge as multinationals.
(viii) Created new opportunities for companies providing services, particularly those involving IT.
Negative impact of the globalisation on India
(i) Small producers failed to compete and got perished. Rising competition has led to shutting down of many units. Many workers became jobless. For instance, batteries, capacitors, plastics, toys, dairy products and vegetable oil are the examples of the industries which have been hit hard due to hard competition.
(ii) Globalisation and pressure of competition have substantially changed the lives of workers. Faced with growing competition most employers these days prefer to employ workers ‘flexibly’. This means that workers’ jobs are no longer secure.
Question. What were the reasons for putting barriers to foreign trade and foreign investment by the Indian government? Why did it wish to remove these barriers?
Answer : Reasons for putting barriers to foreign trade and foreign investment by the Indian Government:
(a) To protect the domestic producers within the country from foreign competition.
(b) The competition from importers would have crippled the new-born industries of India. In such a situation, imports of only such commodities were allowed which were quite necessary such as machinery, fertilisers, petroleum etc.
(c) During 1950s and 1960s, competition from imports was giving a death blow to growing industries in India. Hence, India allowed imports of only essential goods.
Later in the 1990s, the government wished to remove these barriers because it felt that domestic producers were ready to compete with foreign industries. It felt that foreign competition would in fact improve the quality of goods produced by Indian industries. This decision was also supported by powerful international organisations. Thus, the government decided that the time had come for Indian producers to compete with producers around the globe.
Question. How are multinational corporations (MNCs) controlling and spreading their productions across the world? Explain.
Answer : Multinational Corporations (MNCs) usually set up production where it is close to the markets, where there is skilled and unskilled labour available at low costs and where the availability of other factors of production is assured. MNCs also might look for government policies that look after their interests.
Having assured themselves of these conditions, MNCs set up factories and offices for production. At times they set up production jointly with some of the local companies of these countries. They provide money to these local companies for additional investments like buying new machines for faster production. They also buy up local companies and then expand production. MNCs with huge wealth can quite easily do so.
There is another way in which MNCs control production. Large MNCs in developed countries place orders for production with small producers. The products are supplied to MNCs, which then, sell these under their own brand names to the customers. Thus, we see that there are a variety of ways in which the MNCs are spreading their production and interacting with local producers in various countries across the globe.
Question. Explain the meaning of the term ‘globalisation’. State any two factors that have helped in the process of globalisation.
Answer : Globalisation refers to the integration between countries through foreign trade and foreign investments by multinational companies.
• It means integrating our economy with world economy.
• Under globalisation a country becomes economically interdependent at the global or international level.
• This happens at various levels.
• Producers from other countries can come and sell their goods and services in India.
• Similarly, Indian goods and services can be sold in other countries.
Two factors that have enabled Globalisation:
(i) Information Technology — Telecommunication facilities like mobile, internet fax have helped us at negligible cost. Now a new magazine published for London readers can be designed and printed in Delhi.
(ii) Liberalisation of foreign trade and foreign investment – In India, trade barriers that were imposed after independence to protect producers’ interests in the country from foreign competition were removed after 1991. Businessmen were allowed to import or export freely.
Question. How does foreign trade lead to integration of markets across countries? Explain with an example other than those given here.
Answer : (i) Foreign trade gives opportunity to producers to sell their goods in other countries of the world. Producers can sell their produce not only in markets located within the country but can also compete in markets located in other countries of the world.
(ii) For the ordinary consumers, the foreign trade proves very useful because the best brands of different articles are produced all over the world. Their choice of goods expands manifolds.
(iii) For the buyers, import of goods produced in another country is one way of expanding the choice of goods beyond what is domestically produced.
(iv) Foreign trade gives opportunity to producers in the two countries closely compete against each other even though they are far away from each other. This is how markets are integrated through foreign trade. For example, Japanese electronic items are imported to India, and have proved to be a tough competition for less-technologically-advanced companies here.
Question. What is SEZ? The setting of SEZ has been opposed by some people in India. Why? Explain.
Answer : In recent years, central and state governments in India are taking special steps to attract foreign companies to invest in India. So Special Industrial Zones are being set up. They are also called Special Economic Zones. They have world class facilities – like electricity, water, transport, recreational and educational facilities. Companies that set up production units SEZs do not have to pay taxes for an initial period of five years.
SEZs work against the economic interest of certain sections of society, hence, they are opposed by some people:–
(i) SEZs can be set up only after acquiring land from the farmers and they are not left with any source of livelihood.
(ii) Labour does not get the protections of labour law in SEZs.
Question. What are the factors that multinational companies take into account before setting up a factory in different countries?
Answer : Before setting up a company or a factory an MNC takes into account the following things.
(i) Availability of cheap labour and other resources: MNC’s set up offices and factories for production in various regions of the world where cheap labour and other resources are available in order to earn greater profit. For example: MNC may spread its production activities to the following countries – USA for designing a product, China for manufacturing components etc. By doing so it is able to reduce the cost of production.
(ii) Favourable government policy: If the government policies are favourable it helps MNCs. For example: Flexibility of labour laws will reduce cost of production. MNCs are able to hire worker on casual and contractual wages for a short period instead of a regular basis. This reduces the cost of labour for the company and increases its margin of profit.
Question. Why is ‘tax’ on imports known as trade barrier? Why did the Indian government impose barriers to foreign trade and foreign investments after independence? Give three reasons.
Answer : Trade barrier means restrictions imposed on import and export of goods. It is called so because some restrictions have been set up. The trade barriers provide protection to domestic goods from foreign competition. The government can use barriers to increase or decrease (regulate) foreign trade and to decide what kind of goods and services and how much of each should come into the country.
Reasons for putting barriers to foreign trade and foreign investment by the Indian Government were:
(i) To protect the domestic producers within the country from foreign competition.
(ii) The competition from importers would have crippled the new-born industries of India. In such a situation, imports of only such commodities were allowed which were quite necessary such as machinery, fertilisers, petroleum etc.
(iii) During 1950s and 1960s, competition from imports was giving a death blow to growing industries in India. Hence, India allowed imports of only essential goods.
Question. “The impact of globalisation has not been uniform.” Explain this statement.
Answer : (i) Globalisation has been proved beneficial for the top Indian companies but so far workers are concerned, globalisation has perished them.
(ii) The top Indian companies have invested in newer technology and production methods and raised their production standards. Some have gained from successful collaborations with foreign companies. Globalisation has enabled some large Indian companies to emerge as multinationals themselves. For examples: Tata Motors (Automobiles), Infosys (IT), etc.
(iii) But for a large number of small producers and workers globalisation has posed great problems. They have been hit hard due to competition. Several units have shut down rendering many workers jobless.
Thus, we can say that the impact of globalisation has not been uniform.
Question. What is globalisation? Describe the role of Multinational Corporations (MNCs) in promoting globalisation process.
Answer: Globalisation means: integrating the economy of a country with the economies of other countries under conditions of free flow of trade and capital and movement of persons across borders.
MNCs play an important role in promoting globalisation process in the following ways:
• They serve as agents for the transfer of superior technology. They have provided advanced technology, manufacturing process and improved skills to underdeveloped countries.
• They help in the transfer of capital from countries where it is abundant to where it is scarce.
• They help in building up knowledge base and development of human resources. They help in creating large scale employment opportunities by setting up their branches and subsidiaries.
• The operations of MNCs have a favorable effect on the balance of payments account of the host country.
Question. What is trade? Explain the importance of international trade.
Answer: The exchange of goods among people, states and countries is referred to as trade.
The international trade is important because:
• It helps in exchange of surplus goods with those of deficit countries through foreign trade.
• It helps in improving the quality of domestic goods.
• It contributes to the economic growth of the country by raising income level of the people and increasing foreign exchange reserves.
• It enables a country to import advanced technology of other countries to improve its own production.
Question. Describe any five factors that promote the Multinational Corporations (MNCs) to set up their production units in a particular place.
Answer: The factors that MNCs take into consideration to set up their production units in a particular place are:
• Where it is close to the markets.
• Where the skilled and unskilled labour at low costs is available.
• Where the favourable government policies looking after their interest are , present.
• Where the other factors of production such as raw materials, water, electricity and transport are available.
• Where there are standard safety measures for assured production.
Question. Describe the major problems created by the globalisation for a large number of small producers and workers.
Answer: The major problems created by the globalisation for a large number of small producers and workers are:
• The small producers or workers either have to compete or perish.
• Small scale industries like batteries, capacitors, plastic toys etc. have been hit hard due to global products and have suffered great losses in their businesses.
• Several small factory units are forced to shut down.
• Millions of workers have gone jobless and jobs are no longer secure.
• It has increased income inequalities among various countries.
• Unorganised sector has expanded. {any five)
Question. How are Multinational Corporations (MNCs) controlling and spreading their productions across the world? Explain.
Answer: The ways in which MNCs controlling and spreading their productions across the world are:
• By directly setting up factories and offices for production.
• By setting up production jointly with some of the local companies of other countries.
• By buying up local companies and then expand production.
• By placing orders for production with small producers of the countries such as garments, footwear.
• By buying mass produced goods of domestic industries and, then sell it under their own brand name at much higher rates in foreign countries.
Question. Explain the role of information technology in globalisation.
Answer: Information and communication technology has stimulated the globalisation process as:
• In recent years, technology in the areas of computers, telecommunication and internet has been changed rapidly.
• Telecommunication facilitates including telegraph, telephone, mobile phone, fax are used to contact one another around the world and to get information instantly and to communicate from remote areas.
• All this has been facilitated by satellite communication devices.
• Computers and internet have enabled people to obtain and share information on any subject.
Question. What has been the impact of globalisation on India? Explain.
Answer: The impact of globalisation on Indian economy is as follows:
• It has created competition among producers, both local and foreign, which is advantageous to the consumers, particularly the well off. Now, there is a greater choice of goods before the consumers.
• It has enabled many Indian companies to become multi-national companies such as Tate Motors, Infosys and Ranbaxy.
• It has created new employment opportunities for companies providing services specially information technology. A lot of services such as data entry, accounting, and administrative tasks are done cheaply in India and exported to other countries.
• New jobs are created in industries such as electronics, cell phones, automobiles and fast food.
• It had a negative impact on small manufacturers. Due to competition, some industries has been hit hard such as batteries, capacitors, plastic toys, vegetable oil etc. A number of units have shut down and a lot of workers have become jobless.
Question. Explain with three examples how top Indian companies have benefitted from globalisation.
Answer: The top Indian companies have benefitted from globalisation in the following ways:
• They have been able to survive in the international competition.
• They have invested in newer technology and production methods and raised their production standards.
• They also have gained from successful collaborations with foreign companies.
• Many of them have emerged as multinationals themselves such as Tata Motors and Asian Paints.
• It has provided them new opportunities for expansion and value addition of their services. (any three)
Question. How do large companies often manipulate the markets? Explain with an example.
Answer: The large companies manipulate the market in the following ways:
• Sometimes false information is passed on through media and other sources to attract consumers.
For example, a company selling powder milk for babies as the most scientific product claiming it to be better than mother’s milk which although was a false claim.
• Some food items were consumed in India for many years although it is very harmful for the health of people. But through attractive and convincing advertisements in media, it was able to control the market such as Maggie noddles manufactured by Nestle was found harmful after testing in India in May 2015.
• They may also hide the essential information about the product like expiry date, contents, terms and conditions etc. to keep the consumers in dark.
• Sometimes, the expired products are packed in a new packing and again released in the market.
• It has also been evident that artificial scarcity is created by the producers and the product is hoarded for sale in future at a high price.
Question. How have Indian markets been transformed in recent years? Explain with examples.
(What changes do you notice in the markets in India recently?)
Answer :
i. We have a wide choice of goods and services before us in the Indian markets now. The latest models of digital cameras, mobile phones and televisions made by the leading manufacturers of the world are within our reach. Electronics goods became cheaper. Every season, new models of automobiles can be seen on Indian roads.
ii. A similar explosion of brands can be seen for many other goods: from shirts to televisions to processed fruit juices. Many international food-processing companies like Coco Cola entered Indian markets.
Question. How do MNCs control production all over world?
Or State the ways by which MNCs expand production all over the world?
Answer :
i. The most common route for MNC investments is to buy up local companies and then expand production. To take an example, Cargill Foods, a very large American MNC, has bought over smaller Indian companies such as Parakh Foods.
ii. There’s another way in which MNCs control production. Large MNCs place orders for production with small producers. They purchase goods like garments and footwear from these small companies and then sell these under their own brand names to the customers.
iii. These large MNCs have tremendous power to determine price, quality, delivery, and labour conditions for these distant producers.
iv. They set up partnerships with local companies and expand production in some cases. Thus MNCs are exerting a strong influence on production at distant locations.
Question. Why is foreign trade necessary?
Or What are the functions of foreign trade?
Or What are the advantages of foreign trade?
Answer :
i. Foreign trade creates an opportunity for the producers to reach beyond the domestic markets, and reach international markets.
ii. Producers can sell their produce not only in markets located within the country but can also compete in markets located in other countries of the world.
iii. Similarly, for the buyers, import of goods produced in another country is one way of expanding the choice of goods beyond what is domestically produced. Foreign trade thus results in connecting the markets or integration of markets in different countries.
iv. Foreign trade promote international understanding and economic inter dependence between countries.
Question. What are the factors that have enabled globalization?
Answer :
i. Rapid improvement in transportation technology has made much faster delivery of goods across long distances possible at lower costs.
ii. Even the developments in information and communication technology helped a lot. In recent times, technology in the areas of telecommunications, computers and Internet has been changing rapidly. Telecommunication facilities (telegraph, telephone including mobile phones, fax) are used to contact one another around the world, to access information instantly, and to communicate from remote areas. This has been facilitated by satellite communication devices.
iii. Liberalization of foreign trade and foreign investment policy and the removal of trade barriers by many countries helped globalization.
iv. Establishment of World Trade Organization played an important role in encouraging globalization.
Question. What is trade barrier? Why did India Government put barrier to foreign trade?
Answer :
i. Restricting foreign trade by imposing tax on imports is called trade barrier. Governments can use trade barriers to increase or decrease (regulate) foreign trade and to decide what kind of goods and how much of each, should come into the country.
ii. The Indian government, after Independence, had put barriers to foreign trade and foreign investment. This was considered necessary to protect the producers within the country from foreign competition.
iii. Industries were just coming up in the 1950s and 1960s, and competition from imports at that stage would not have allowed these industries to come up. Thus, India allowed imports of only essential items such as machinery, fertilizers, petroleum etc.
iv. All developed countries, during the early stages of development, have given protection to domestic producers through a variety of meAnswer :
Question. Examine the impact of globalization in India.
Or Impact on producers, consumers and workers.
Or How do we feel the direct impact of globalization on our daily life?
Answer :
i. Firstly, Multinational Companies have increased their investments in India over the past 15 years,MNCs have been interested in industries such as cell phones, automobiles, electronics, soft drinks, fast food or services such as banking in urban areas.
ii. In these industries and services, new jobs have been created. Also, local companies supplying raw materials, etc. to these industries have prospered.
iii. Secondly, several of the top Indian companies have been able to benefit from the increased competition. They have invested in newer technology and production methods and raised their production standards. Some have gained from successful collaborations with foreign companies.
iv. Moreover, globalization has enabled some large Indian companies to emerge as multinationals themselves! Tata Motors (automobiles), Infosys (IT), Ranbaxy (medicines), Asian Paints (paints),Sundaram Fasteners (nuts and bolts) are some Indian companies which are spreading their operations worldwide.
v. Globalization has also created new opportunities for companies providing services, particularly those involving IT. The Indian company producing a magazine for the London based company is an example.
vi. Besides, a host of services such as data entry, accounting, administrative tasks, engineering are now being done cheaply in countries such as India and are exported to the developed countries.
vii. For a large number of small producers and workers globalization has posed major challenges.Batteries, capacitors, plastics, toys, tyres, dairy products, and vegetable oil are some examples of small manufacturers, who have been hit hard due to competition.
viii. There is a greater choice before the consumers who now enjoyed improved quality and lower prices for several products. As a result, these people today enjoy higher standards of living than before.
Question. What are the negative effects of globalization? (Impact of globalization on small producers and workers)
Answer :
i. Globalization and the pressure of competition have changed the lives of workers. To stand in the global competition many companies cut down the benefits given to workers, reduced their salaries and treated as temporary workers.
ii. Jobs are no longer secure to them. Working conditions in organized sector resemble the unorganized sector.
iii. For a large number of small producers and workers globalization has posed major challenges.Batteries, capacitors, plastics, toys, tyres, dairy products, and vegetable oil are some examples of small manufacturers, who have been hit hard due to competition.
iv. Several of the units have shut down rendering many workers jobless.
Question. What is meant by SEZ?
Answer :
i. It is the short form of Special Economic Zone. Such industrial zones are set up by the government to attract foreign companies to invest in India.
ii. SEZs are to have world-class facilities: electricity, water, roads, transport, storage, recreational and educational facilities. Companies who set up production units in the SEZs do not have to pay taxes for an initial period of five years.
iii. Government has also allowed flexibility in the labour laws to attract foreign investment.
Question. What is fair globalization? What role can the Government play to have a fair globalization?
Or Describe any 3 ways in which the flexibility of labour laws help companies.
Answer :
i. Fair globalization is a measure to eliminate the negative effect of globalization. It would create opportunities for all, and ensure that the benefits of globalization are shared better by all countries.
ii. The government policies must protect the interests, not only of the rich and the powerful, but all the people in the country.
iii. The government can ensure that labour laws are properly implemented and the workers get their rights. It can support small producers to improve their performance until the time they become strong enough to compete.
iv. If necessary, the government can use trade and investment barriers. It can negotiate at the WTO for ‘fairer rules’.
v. It can also align with other developing countries with similar interests to fight against the domination of developed countries in the WTO.
CASE BASED STUDY QUESTIONS
Ford Motors, an American company, is one of the world’s largest automobile manufacturers with production spread over 26 countries of the world. Ford Motors came to India in 1995 and spent Rs. 1700 crore to set up a large plant near Chennai. This was done in collaboration with Mahindra and Mahindra, a major Indian manufacturer of jeeps and trucks. By the year 2004, Ford Motors was selling 27,000 cars in the Indian markets, while 24,000 cars were exported from India to South Africa, Mexico and Brazil. The company wants to develop Ford India as a component supplying base for its other plants across the globe.
Question. Would you say Ford Motors is a MNC? Why?
Answer: Ford Motors has production facilities spread over 26 countries of the world. Hence, it can be termed an MNC.
Question. What is foreign investment? How much did Ford Motors invest in India?
Answer: The investment which comes from abroad is called foreign investment. Ford Motors had invested Rs. 1700 crore.
Question. By setting up their production plants in India, MNCs such as Ford Motors tap the advantage not only of the large markets that countries such as India provide, but also the lower costs of production. Explain the statement.
Answer: The cost of labour is cheaper in India; compared to the developed countries. This means that an MNC can save lot of money on wages and salaries by setting up production plants in India. This helps in lowering the cost of production. India itself is a large market with sizeable population of middle class and upper class and hence provides a big market for many products.
Question. Why do you think the company wants to develop India as a base for manufacturing car components for its global operations? Discuss the following factors:
(a) Cost of labour and other resources in India
Answer: Wages and salaries are much lower in India compared to in developed countries. Moreover, raw materials and power is also cheaper. This is a definite advantage which India offers as a production base.
(b) The presence of several local manufacturers who supply autoparts to Ford Motors
Answer: There are many companies which manufacture various auto-parts; like Sundaram Fasteners.Because of their lower cost of operation, these companies supply various parts at less price than price in the developed countries.
(c) Closeness to a large number of buyers in India and China
Answer: India and China together comprise about 30% of the world population and thus they provide a huge market for various companies. Making a production base in India provides easy access to these two markets.
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Resources and Development VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Forest and Wildlife Resources VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Water Resources VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Agriculture VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Mineral and Energy Resources VBQs in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Minerals and Energy Resources VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Civics Manufacturing Industries VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Manufacturing industry VBQs in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Life Lines of National Economy VBQs in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Lifelines of National Economy VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Power Sharing VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Federalism VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Democracy and Diversity VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Gender Religion and caste VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Popular Struggles and Movements VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Popular Struggles and Movements VBQs in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Political Parties VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Political party VBQs in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Outcomes of Democracy VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Results of Democracy VBQs in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Civics Challenges To Democracy VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Challenges of Democracy VBQs in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science The Rise Of Nationalism In Europe VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science The Rise of Nationalism in Europe VBQs in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Nationalism in India VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Nationalism in India VBQs in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science The Making of a Global World VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science The Age of Industrialization VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Print Culture and the Modern World VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Development VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Sectors of the Indian Economy VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Economics Money And Credit VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Currency and credit VBQs in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Globalization and Indian Economy VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Globalization and Indian Economy VBQs in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Economics Consumer Rights VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Consumer Rights VBQs in Hindi |
VBQs for Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy Class 10 Social Science
We hope students liked the above VBQs for Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 10 Social Science released by CBSE. Students of Class 10 should download the Value Based Questions and Answers in Pdf format and practice the questions and solutions given in above Class 10 Social Science VBQs Questions on daily basis. All latest VBQs with answers have been developed for Social Science by referring to the most important and regularly asked topics which the students should learn and practice to get better score in school tests and examinations. Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to NCERT book for Class 10 Social Science to develop the Social Science Class 10 VBQs. After solving the questions given in the VBQs which have been developed as per latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 10 Social Science designed by our teachers. We have also provided a lot of other VBQs for Class 10 Social Science which you can use to further make yourself better in Social Science.
You can download the CBSE VBQs for Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the VBQs issued by CBSE for Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy Class 10 Social Science have been made available here for latest academic session
There is no charge for the VBQs and their answers for Class 10 CBSE Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy you can download everything free
Regular revision of VBQs given on studiestoday for Class 10 subject Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy can help you to score better marks in exams
Value Based Questions (VBQs) for Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy help to test the ability of students to apply learnings to various situations in life.

