CBSE Class 10 Social Science Agriculture VBQs read and download in pdf. Value Based Questions come in exams for Social Science in Class 10 and are easy to learn and helpful in scoring good marks. You can refer to more chapter wise VBQs for Class 10 Social Science and also get latest topic wise very useful study material as per latest NCERT book for Class 10 Social Science and all other subjects for free on Studiestoday designed as per latest Class 10 CBSE, NCERT and KVS syllabus and examination pattern
VBQ for Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India II Chapter 4 Agriculture
Class 10 Social Science students should refer to the following value based questions with answers for Contemporary India II Chapter 4 Agriculture in Class 10. These VBQ questions with answers for Class 10 Social Science will come in exams and help you to score good marks
Contemporary India II Chapter 4 Agriculture VBQ Questions Class 10 Social Science with Answers
MCQ Questions for Class 10 Social Science Agriculture
Question : Barley: Rabi crop, cotton: Kharif, _________ zaid crop.
(a) Wheat
(b) Mustard
(c) Soya bean
(d) Cucumber
Answer : D
Question : Rice is a commercial crop of which state ?
(a) Rajasthan
(b) Himachal Pradesh
(c) Punjab and Haryana
(d) Orissa
Answer : C
Question : Rabi crops are sown in :
(a) Summer
(b) Winter
(c) Monsoon
(d) Autumn
Answer : B
Question : Rank the following States in terms of wheat production :
i. Madhya Pradesh
ii. Uttar Pradesh
iii. Punjab
iv. Haryana
Options :
(a) (i)-(ii)-(iii)-(iv)
(b) (iii)-(ii)-(i)-(iv)
(c) (ii)-(iii)-(i)-(iv)
(d) (iv)-(ii)-(iii)-(i)
Answer : C
Question : Which is the most important plantation crop grown in Karnataka ?
(a) Tea
(b) Coffee
(c) Rice
(d) Banana
Answer : B
Question : Identify the crop with the help of the following
features:
l Arabica variety grown in India.
l Crop grown in Western Ghats.
Answer : Coffee.
Question : Identify the crop with the help of the following features:
l Staple food crop of India.
l Above 100 cm rainfall is required.
l It is a Kharif crop.
Answer : Wheat.
Question : Identify the crop with the help of the following features:
l It is a tropical as well as subtropical crop.
l It grows well in hot and humid climate.
l It required rainfall between 75 cm and 100 cm.
Answer : Sugarcane.
Answer : A
Explanation: This is the second most important cereal crop. It is the main food crop, in north and north-western part of the country. This rabi crop requires a cool growing season and a bright sunshine at the time of ripening. It requires 50 to 75 cm of annual rainfall evenly distributed over the growing season.
Explanation: Since the production is mainly for market, a well-developed network of transport and communication connecting the plantation areas, processing industries and markets plays an important role in the development of plantations.
True / False /Fill Up
Question : Some of the major rice growing areas are Assam, West Bengal, Coastal region of Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Kerala and Maharashtra along with Uttar Pradesh and Bihar.
Answer : True
Question : Wheat requires cool growing season and a bright sunshine at the time of ripening. (True/False)
Answer : True
Question : Cotton : __________, Tea : Plantation, Rice : Food.
Answer : Fiber.
Source/Extract Based Questions
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow:
We understand the physical diversities and plurality of cultures in India. These are also reflected in agricultural practices and cropping patterns in the country. Various types of food and fibre crops, vegetables and fruits, spices and condiments, etc. constitute some of the important crops grown in the country. India has three cropping seasons — rabi, kharif and zaid. A variety of food and non food crops are grown in different parts of the country depending upon the variations in soil, climate and cultivation practices. Major crops grown in India are rice, wheat, millets, pulses, tea, coffee, sugarcane, oil seeds, cotton and jute, etc. Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
Question : Millets come in the category of ________ crops(Food/ Non Food).
Answer : Food.
Question : Identify which cropping pattern the following crops belong to – Choose the correct option—
(a) a-2, b-1, c-3
(b) a-3, b-2, c-1
(c) a-1, b-3, c-1
(d) a-3, b-2, c-1
Answer : B
Question : Which one of the followings is not a physical feature that influence cropping pattern?
(a) Soil
(b) Terrain
(c) Dense population
(d) Air Moisture
Answer : C
Question : In order to increase the crop output, a farmer can control…………
(a) Cultivation Practices
(b) Sunlight
(c) Humidity
(d) Physiography
Answer : A
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow:
Primitive Subsistence Farming is still practised in few pockets of India. Primitive subsistence agriculture is practised on small patches of land with the help of primitive tools like hoe, dao and digging sticks, and family/ community labour. This type of farming depends upon monsoon, natural fertility of the soil and suitability of other environmental conditions to the crops grown. It is‘ Slash and Burn’ agriculture. Farmers clear a patch of land and produce cereals and other food crops to sustain their family. When the soil fertility decreases, the farmers shift and clear a fresh patch of land for cultivation. This type of shifting allows Nature to replenish the fertility of the soil through natural processes; land productivity in this type of agriculture is low as the farmer does not use fertilisers or other modern inputs. It is known by different names in different parts of the country.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option
Question : Primitive subsistence is commonly known as _______
Answer : Slash and Burn.
Question : Identify in which India state, the primitive subsistence is known by the following names:
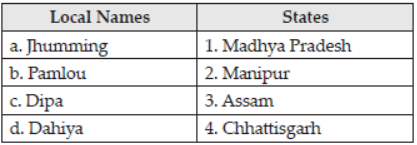
Choose the correct option—
(a) a-3, b-2, c-4, d-1
(b) a-2, b-1, c-4, d-3
(c) a-1, b-4, c-2, d-3
(d) a-4, b-2, c-1, d-3
Answer : A
Question : Which one of following is not a characteristic of ‘Slash and Burn’ Agriculture?
(a) Practiced by the Tribals.
(b) Discouraged by the government
(c) Healthy practice for the soil and environment
(d) Traditional tools are used.
Answer : C
Question : In order to regain the soil fertility, the farmer _______
(a) Leaves the farm vacant.
(b) Uses pesticides
(c) Irrigates through canals.
(d) Buys machinery like tractor and harvester.
Answer : A
Read the sources given below and answer the questions that follow:
Source A- Sugarcane
It is a tropical as well as a subtropical crop. It grows well in hot and humid climate with a temperature of 21°C to 27°C and an annual rainfall between 75 cm. and 100 cm. Irrigation is required in the regions of low rainfall. It can be grown on a variety of soils and needs manual labour from sowing to harvesting. India is the second largest producer of sugarcane only after Brazil. It is the main source of sugar, gur (jaggary), khandsari and molasses.
Source B- Oil seeds
In 2015, India was the second largest producer of groundnut in the world after china. In rapeseed production India was third largest producer in the world after Canada and China in 2015. Different oil– seeds are grown covering approximately 12 percent of the total cropped area of the country. Main oil seeds produced in India are groundnut, mustard, coconut, sesamum (til), soyabean, castor seeds, cotton seeds, linseed and sunflower. Most of these are edible and used as cooking mediums. However, some of these are also used as raw material in the production of soap, cosmetics and ointments.
Source C-Tea
Tea cultivation is an example of plantation agriculture. It is also an important beverage crop introduced in India initially by the British. Today, most of the tea plantations are owned by Indians. The tea plant grows well in tropical and sub-tropical climates endowed with deep and fertile well-drained climate all through the year. Frequent showers evenly distributed over the year ensure continuous growth of tender leaves. Tea is a labour-intensive industry.
Source A- Sugarcane
1. Name the major sugarcane producing states of India.
Answer : The major sugarcane-producing states are Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Bihar, Punjab and Haryana.
Source B- Oilseeds
2. What is the rank of India in producing groundnut and rapeseed?
Answer : In 2015 India was the second largest producer of groundnut in the world after china while In rapeseed production India was third largest producer in the world after Canada and China.
Source C-Tea
3. Write any two geographical conditions required for the growth of tea.
Answer : (i) Tea bushes require warm and moist frost-free climate through the year.
(ii) These require soil rich in humus and organic matter.
Read the extract and answer the questions that follows :
These are also reflected in agricultural partices and cropping patterns in the country. Various types of food and fibre crops, vegetables and fruits, spices and condiments, etc. constitute some of the important crops grown in the country. India has three cropping seasons—rabi, kharif and zaid. Rabi crops are sown in winter from October to December and harvested in summer from April to June. Some of the important rabi crops are wheat, barley, peas, gram and mustard.
Though, these crops are grown in large parts of India, states from the north and north-western parts such a Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Uttarakhand and Uttar Pradesh are important for the production of wheat and other rabi crops. Kharif crops are grown with the onset of monsoon in different parts of the country and these are harvested in September-October. Important crops grown during this reason are paddy, maize, jowar, bajra, tur (arhar), moong, urad, cotton, jute, groundnut and soyabean.
Some of the most important rice growing regions are Assam, West Bengal, coastal regions of Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Tamil Nadu, Kerala and Maharashtra, particularly the (Konkan cost) along with Uttar Pradesh and Bihar.
In between the rabi and the kharif seasons, there is a short season during the summer months known as the Zaid season. Some of the crops produced during ‘zaid‘ are watermelon, muskmelon, cucumber, vegetables and fodder crops. Sugarcane takes almost a year to grow.
1. Name the Rabi crops grown in India.
Answer : Wheat, barley, peas, gram and mustard.
2. Write any two geographical conditions required for the growth of rice.
Answer : (i) Rice is a kharif crop which grow with the onset of monsoon and harvested in September-October.
(ii) It requires high humidity and heavy rainfall.
3. What is Zaid season ? Name some crops grown during this season.
Answer : A short summer season between the rabi and kharif season is called as zaid season. The crops grown during this season are are watermelon, muskmelon, cucumber, vegetables and fodder crops.
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow:
We understand the physical diversities and plurality of cultures in India. These are also reflected in agricultural practices and cropping patterns in the country. Various types of food and fibre crops, vegetables and fruits, spices and condiments, etc. constitute some of the important crops grown in the country. India has three cropping seasons — rabi, kharif and zaid. A variety of food and non food crops are grown in different parts of the country depending upon the variations in soil, climate and cultivation practices. Major crops grown in India are rice, wheat, millets, pulses, tea, coffee, sugarcane, oil seeds, cotton and jute, etc.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option
1. Millets come in the category of ________ crops(Food/ Non Food).
Answer : Food.
2. Identify which cropping pattern the following crops belong to –
Choose the correct option—
(a) a-2, b-1, c-3
(b) a-3, b-2, c-1
(c) a-1, b-3, c-1
(d) a-3, b-2, c-1
Answer : B
3. Which one of the followings is not a physical feature that influence cropping pattern?
(a) Soil
(b) Terrain
(c) Dense population
(d) Air Moisture
Answer : C
4. In order to increase the crop output, a farmer can control…………
(a) Cultivation Practices
(b) Sunlight
(c) Humidity
(d) Physiography
Answer : A
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow:
Primitive Subsistence Farming is still practised in few pockets of India. Primitive subsistence agriculture is practised on small patches of land with the help of primitive tools like hoe, dao and digging sticks, and family/ community labour. This type of farming depends upon monsoon, natural fertility of the soil and suitability of other environmental conditions to the crops grown. It is‘ Slash and Burn’ agriculture. Farmers clear a patch of land and produce cereals and other food crops to sustain their family. When the soil fertility decreases, the farmers shift and clear a fresh patch of land for cultivation. This type of shifting allows Nature to replenish the fertility of the soil through natural processes; land productivity in this type of agriculture is low as the farmer does not use fertilisers or other modern inputs. It is known by different names in different parts of the country. Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option
1. Primitive subsistence is commonly known as _______
Answer : Slash and Burn.
2. Identify in which India state, the primitive subsistence is known by the following names:
Choose the correct option—
(a) a-3, b-2, c-4, d-1
(b) a-2, b-1, c-4, d-3
(c) a-1, b-4, c-2, d-3
(d) a-4, b-2, c-1, d-3
Answer : A
3. Which one of following is not a characteristic of ‘Slash and Burn’ Agriculture?
(a) Practiced by the Tribals.
(b) Discouraged by the government
(c) Healthy practice for the soil and environment
(d) Traditional tools are used.
Answer : C
4. In order to regain the soil fertility, the farmer _______
(a) Leaves the farm vacant.
(b) Uses pesticides
(c) Irrigates through canals.
(d) Buys machinery like tractor and harvester.
Answer : A
Assertion and Reasoning Based Questions
Mark the option which is most suitable :
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If both assertion and reason are false.
Question : Assertion : Staple food crop in India is rice and requires less rain.
Reason : Our country is the fourth largest producer of rice in the world.
Answer : (c) It is the staple food crop of a majority of the people in India. Our country is the second largest producer of rice in the world after China. Cultivation of rice requires annual rainfall above 100 cm . In the areas of less rainfall, it grows with the help of irrigation.
Question : Assertion : Pulses are not considered as a major source of protein in a vegetarian diet.
Reason : Rice is a rabi crop and requires lot of rain to grow.
Answer : (d) Rice is a kharif crop and requires about 100 cm of rainfall. However India is the largest producer as well as the consumer of pulses in the world. These are the major source of protein in a vegetarian diet.
Question : Assertion : Tea cultivation, is a labour – intensive industry.
Reason : Cultivation can be done throughout the year. Tea bushes require warm and moist frost-free climate.
Answer : (b) The tea plant grows well in tropical and subtropical climates endowed with deep and fertile well-drained soil, rich in humus and organic matter. It is consumed on large basis in India being an important beverage crop.
Question : Assertion : Organic farming is much in vogue.
Reason : In organic farming, crops are grown using high doses bio fertilizers to increase production.
Answer : (c) Organic farming is much in vogue today because it is practiced without factory made chemicals such as fertilizers and pesticides. Hence, it does not affect environment and human beings in a negative manner.
Mark the option which is most suitable :
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If both assertion and reason are false.
Question. Assertion : Staple food crop in India is rice and requires less rain.
Reason : Our country is the fourth largest producer of rice in the world.
Answer : (c) It is the staple food crop of a majority of the people in India. Our country is the second largest producer of rice in the world after China. Cultivation of rice requires annual rainfall above 100 cm. In the areas of less rainfall, it grows with the help of irrigation.
Question. Assertion : Biochemical inputs and irrigation are used for obtaining higher production.
Reason : Doses of biochemical input are used to grow crops rapidly.
Answer : (a) High doses of biochemical inputs and irrigation are used for obtaining higher production to meet the growing demands of the people. The farmers continue to take maximum output from the limited land.
Question. Assertion : Agriculture is not an old economic activity.
Reason : Farming varies from subsistence to commercial type.
Answer : (d) Cultivation methods have changed significantly depending upon the characteristics of physical, environmental and technological methods. Agriculture is definitely an old economic activity in India. Thus, both reason and assertion are false.
Question. Assertion : India’s primary activity is Agriculture.
Reason : Two–thirds of its population is engaged in agricultural activities.
Answer : (a) Agriculture is a primary activity, which produces most of the food that we consume. Two-third of India’s population is involved in agricultural activities and earns livelihood through it.
Question. Assertion : Tea cultivation, is a labour – intensive industry.
Reason : Cultivation can be done throughout the year.
Tea bushes require warm and moist frost-free climate.
Answer : (b) The tea plant grows well in tropical and subtropical climates endowed with deep and fertile well-drained soil, rich in humus and organic matter. It is consumed on large basis in India being an important beverage crop.
Question. Assertion : Crops are grown depending upon the variations in soil, climate and cultivation practices.
Reason : Crops are also grown according to availability of water.
Answer : (b) Variety of food and non food crops are grown in different parts of the country depending upon the variations in soil, climate and cultivation practices. Major crops grown in India are rice, wheat, millets, pulses, tea, coffee, sugarcane, oil seeds, cotton and jute, etc
Question. Assertion : Pulses are not considered as a major source of protein in a vegetarian diet.
Reason : Rice is a rabi crop and requires lot of rain to grow.
Answer : (d) Rice is a kharif crop and requires about 100 cm of rainfall. However India is the largest producer as well as the consumer of pulses in the world. These are the major source of protein in a vegetarian diet.
Question. Assertion : Plantation has an interface of agriculture and industry.
Reason : Plantation is a type of commercial farming, a single crop is grown on a large area.
Answer : (a) The plantation has an interface of agriculture and industry. Plantations cover large tracts of land, using capital intensive inputs, with the help of migrant labourer. All the produce is used as raw material in respective industries.
Question. Assertion : Organic farming is much in vogue.
Reason : In organic farming, crops are grown using high doses bio fertilizers to increase production.
Answer : (c) Organic farming is much in vogue today because it is practiced without factory made chemicals such as fertilizers and pesticides. Hence, it does not affect environment and human beings in a negative manner.
Very Short Questions for Class 10 Social Science Agriculture
Question : In India, there are different types of farming which involves.
Answer : Primitive subsistence farming, Intensive subsistence farming and commercial farming.
Question. List any two characteristics of Green Revolution.
Answer : (i) Increase in production of wheat and rice.
(ii) Use of high yielding varieties (HYV) of wheat and rice.
Question. What is Sericulture?
OR
Name two cotton producing states of India.
Answer : Rearing of silkworms for the production of silk fibre is known as Sericulture.
OR
Maharashtra and Gujarat.
Question. What is the position of India, in the world, in terms of sugarcane production ?
Answer : The position of India is second in the world, in terms of sugarcane production.
Question. Why pulses are grown as rotational crop ? Give two examples.
Answer : (i) Pulses are grown as a rotational crop because these have the capacity to fix atmospheric nitrogen in the soil into nitrogenous compound. These help to maintain or restore soil fertility.
(ii) These need less moisture and survive even in dry conditions.
Question. In which states ‘Jhumming’ is practiced ?
Answer : Jhumming is practiced in north-eastern states like Assam, Meghalaya, Mizoram and Nagaland.
Question. What are rabi crops ? Give four examples.
Answer : The crops which are grown in winter from October to December and are harvested in summer from April to June are called Rabi crops. Wheat, barley, peas and gram are some examples of such crops.
Question. What is Gross Cultivated Area ?
Answer : The net sown area and the land cultivated more than once, together make the ‘gross cultivated area’.
Question. What is agriculture ?
Answer : The art and science of cultivating soil, raising crops and rearing livestock including animal husbandry and forestry is called agriculture.
Question. Why Indian coffee is famous ?
Answer : India produces about four per cent of the world’s coffee. Indian coffee is known in the world for its good quality. The Arabica variety initially brought from Yemen is produced in the country which is in great demand all over the world.
Question. What is Dry Land Farming ?
Answer : It is a type of farming which is practised in scanty rainfall areas and where irrigation facilities are inadequate, e.g., cultivation of jowar and bajra.
Question. Name two schemes introduced by the Government of India for the benefit of the farmers.
Answer : (i) Kissan Credit Card (KCC), (ii) Personal Accident Insurance Scheme (PAIS).
Question. What is Wet Land Farming ?
Answer : It is a type of farming which is practised in high rainfall and irrigated areas, e.g., cultivation of rice and sugarcane.
Question. Mention any four plantation crops produced in India.
Answer : Tea, coffee, rubber and sugarcane.
Question. Write the temperature requirement of Maize crop.
Answer : 21–27 Degree Celsius.
Short Questions for Class 10 Social Science Agriculture
Question. How is ‘Slash and Burn’ agriculture done ?
Answer : ‘Slash and Burn’ agriculture which is also known as Primitive Subsistence farming. It is done on small patches of land. Farmers clear a patch of land and produce cereals and other food crops to sustain their family. When the soil fertility decreases, the farmers shift and clear a fresh patch of land for cultivation. This type of shifting allows nature to replenish the fertility of the soil through natural processes. Land fertility in this agriculture is low as farmers do not use fertilisers or other modern inputs.
Question. Which type of climate is required for the cotton industry ?
Answer : India is believed to be the original home of the cotton plant. Cotton is one of the main raw materials required for the cotton textile industry. India is the third largest producer of cotton in the world. Cotton grows well in drier parts of the black cotton soil of the Deccan plateau. It requires high temperature, light rainfall or irrigation, 210 frost free days and bright sunshine for its growth. It is a Kharif crop and requires 6 to 8 months to nature.
Question. Which steps were taken by the Government of India to modernize agriculture ?
Answer : Agriculture has been the backbone of Indian economy, though its share in the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) has registered a declining trend from 1951 onwards. Considering the importance of agriculture in India, the Government of India made efforts to modernize agriculture. Establishment of Indian Council of Agricultural Research, agricultural universities, veterinary services and animal breeding centers, horticulture development, research and development in the field of meteorology and weather forecast were some of the steps which were given priority for improving the Indian agriculture.
Question. Describe any three main features of ‘Rabi crop season.‘
Answer : Features of Rabi crop season :
(i) It begins with the withdrawl of monsoon in october. They are sown in winters from October to December.
(ii) At the time of ripening, it requires bright sunshine.
(iii) Crops depend on sub-soil moisture.
(iv) Requires less rainfall between 50-75 cm.
Availability of precipitation during winter months due to western temperate cyclones help in success of these crops.
Question. What is ‘Jhumming’ called in different parts of India and in foreign countries ?
Answer : The ‘slash and burn’ agriculture is known as ‘Milpa’ in Mexico and Central America, ‘Conuco’ in Venezuela, ‘Roca’ in Brazil, ‘Masole’ in Central Africa, ‘ladang’ in Indonesia, ‘Ray’ in Vietnam. In India, this primitive form of cultivation is called ‘Bewar’ or ‘Dahiya’ in Madhya Pradesh, ‘Podu’ or ‘Penda’ in Andhra Pradesh, ‘Pama Dabi’ or ‘Koman’ or ‘Bringa’ in Odisha, ‘Kumari’ in Western Ghats, ‘Valre’ or ‘Waltre’ in South eastern Rajasthan, ‘Khil’ in the Himalayan belt, ‘Kuruwa’ in Jharkhand and ‘Jhumming’ in the north eastern region.
Question. What do you understand by ‘Bhoodan’ and ‘Gramdan’ ?
Answer : Once when Vinoba Bhave was delivering a lecture at Pachampalli in Andhra Pradesh, some poor landless villagers demanded some land for their economic wellbeing.
Vinoba Bhave could not promise but assured them to talk to the Government of India regarding the provision of land for them. Suddenly, Shri Ram Chandra Reddy stood up and offered 80 acres of land to be distributed among 80 landless villagers.
This act was known as ‘Bhoodan’. In the same way, some zamindaars, owners of many villages offered to distribute some villages among the landless. It was known as ‘Gramdan’.
Question. Write a short note on rubber plantations in India.
Answer : It is a non-food crop and an equatorial crop, but under special conditions, it is also grown in tropical and subtropical areas. It requires moist and humid climate with rain fall of more than 200 cm and temperature above 25 degree Celsius. Rubber is an important raw material. It is mainly
grown in Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, and Garo hills of Meghalaya. India ranks fifth among the world’s natural rubber producers.
Question. Mention any four features of the Primitive Subsistence Farming.
Answer : (i) Primitive subsistence agriculture is practiced on small patches of land with the help of primitive tools like hoe, dao and digging sticks with the help of family/community labour.
(ii) This type of farming depends upon the monsoon, natural fertility of the soil and suitability of other environmental conditions for the crops to be grown.
(iii) Under this, farmers produce for self-consumption.
(iv) Per hectare availability of land is very low.
Long Questions for Class 10 Social Science Agriculture
Question. Name any four oilseeds produced in India. Explain the importance of oilseeds in our day to day life.
OR
Name any four oilseeds produced in India. What is their economic importance ?
Answer : Main oilseeds produced in India are :
(i) Groundnut (ii) Mustard
(iii) Coconut (iv) Sesam
Economic importance of oilseeds :
(i) Most of these are edible, and used as a cooking medium in the form of oil.
(ii) Extracted oil is also used as raw material for manufacturing a large number of items like paints, varnishes, hydrogenated oil, soaps, perfumes, lubricants, etc.
(iii) Oil cake which is the by product, obtained after the extraction of oil from oilseeds is an excellent cattle feed.
(iv) Oil cake is also used as a fertiliser.
Question. Name the two most important cereal crops grown in India. Describe the conditions required to grow these two crops.
Answer : Rice and wheat are the two most important cereal crops grown in India.
Rice is the staple food crop of most people in India especially in coastal regions.
The geographical condition required for growth of rice are as follow :
(i) It is a kharif crop and requires hot and humid climate for cultivation. Temperature above 25°C and high humidity with annual rainfall above 100 cm is favourable for growth of rice.
(ii) Rich alluvial soils of the flood plains, river basins and deltaic areas which are renewed every year are ideal for rice cultivation.
(iii) Rice requires abundant rainfall or good water supply through irrigation and flooded fields during the earlier part of its growing season in June-July. Ankle deep water in the field helps the crops.
(iv) Plenty of cheap labour is required as most of the farming involves manual labour. Wheat is the main food crop for the people residing in the North and North-western part of the country.
The geographical conditions favourable for growth of wheat are as follows :
(i) Wheat is a rabi crop and requires a cool growing season. Average temperature should be between
10°C to 5°C at the time of sowing, but higher temperatures and bright sunshine is required at the time of harvesting for proper ripening of arrains.
(ii) Wheat requires moderate rainfall of 50 to 75 cm annually, evenly distributed over the growing season. A little winter rain before ripening helps in increasing the yield.
(iii) Deep alluvial clayey soils of Northern Plains and even black soil of Deccan are suitable for growth of wheat.
There are two important wheat-growing zones in the country-the Ganga-Satluj plains in the Northwest and black soil region of the Deccan. Punjab,
Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Rajasthan and parts of Madhya Pradesh are the major wheat growing states.
Question. Describe the temperature and climatic conditions required for the cultivation of sugarcane. Name two leading producers.
OR
What geographical conditions are required for the cultivation of sugarcane ? Name the two largest producing states of sugarcane.
Answer : (i) Temperature : Sugarcane needs hot and humid climate with temperature ranging between 21°C to 27°C. Very high temperature is harmful for its growth, while low temperature slows its growth. It cannot withstand frost. Cool temperature is needed at the time of ripening.
(ii) Rainfall : It grows best in areas receiving 75 cms to 100 cms of rainfall. Too heavy rainfall results in low sugar content.
(iii) Soil : Sugarcane grows on well-drained fertile soil. It can grow on a variety of soils including black, alluvial, loamy and reddish loam. But the best soil is the alluvial soil of the Ganga plain and the black soil of southern India. Sugarcane exhausts the fertility of the soil. Hence, the use of manure is essential to ensure high yields.
(iv) Areas of production : Uttar Pradesh is the largest producer of sugarcane. The other states in the Ganga-plain are Bihar, Punjab and Haryana.
Question. Name the two major beverage crops grown in India.
Describe their growing areas.
Answer : Tea and Coffee are the two most important beverage crops of India. Assam is the major tea producing state in India along with West Bengal and Tamil Nadu. The cropping season in Assam begins as early as March and extends almost to mid-December. Besides, the popular black tea, Assam also produces small quantities of white and green tea. This state has favourable conditions for the growth of tea. The tea plant grows well in tropical and sub-tropical climates. It requires deep and fertile well-drained soil, rich in humus and organic matter. Tea bushes require moist, frost-free and warm climate all through the year with abundant skilled labour. Frequent evenly distributed showers over the year ensure continuous growth of tender tea leaves. The following are the conditions required for tea cultivation:
Temperature - 10 -30 degrees Celsius
Rainfall - average yearly rainfall of 200 cm
Altitude - ground level of between 600-2000 meters above sea level.
Coffee is a tropical plant which is also grown in semitropical climate.
The coffee tree requires heat, humidity and abundant rainfall. Karnataka, the largest coffee producing state has favourable conditions necessary for coffee cultivation.
The temperature of the place is 23°C to 28°C. Growth is most rapid during hot rainy season and during cool dry season, berries ripen and get ready for picking. Bright sunshine and warm weather are necessary for the harvesting. It needs rainfall between 60-85 inches. Water stagnation is very harmful for coffee plants; therefore, hill slopes are best suitable for growing it. Soil is the guiding factor in coffee plantation. The ideal soil is one with a good sub-surface drainage, and one that is easily workable. The presence of humus and other nitrogenous matter in the soil is an advantage.
Question. Describe three geographical requirements for maize cultivation – temperature, rainfall and soil. Name three maize producing states of India.
Answer : (i) Temperature : It grows well under temperature between 21°C and 27°C.
(ii) Rainfall : It grows well in areas of 50-100 cms of rain, and in areas of less rain if grown under irrigation.
(iii) Soil : It requires well drained alluvial fertile soil or red loams free from coarse materials. Important producers are Karnataka, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar and Andhra Pradesh.
Question. What are technological and institutional reforms which led to Green Revolution and White Revolution ?
Answer : In India, agriculture has been practiced for thousands of years. Sustained uses of land without compatible technological and institutional reforms have hindered the pace of agricultural development. Agriculture which provides livelihood for more than 60% of its population needs some serious technical and institutional reforms. Institutional reforms : Collectivisation, consolidation of holdings, cooperation and abolition of zamindari system were given priority to bring about institutional reforms in the country after independence. Land reform was the main focus of the first five year plan. The right of inheritance had already lead to fragmentation of land holdings necessitating consolidation of holdings. Kissan credit card, personal accident insurance scheme were also introduced by the government. Special weather bulletins and agricultural programs for farmers were introduced in the radio and television.
Technological reforms : The Green Revolution based on the use of packaged technology and the White Revolution were two of the strategies initiated to improve Indian agriculture. The government also announced minimum support price remunerative and
procurement prices for important crops to check the exploitation of farmers by speculators and middlemen.
Question. ”The declining share of agriculture in the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is a matter of serious concern in India.” Support the statement.
Answer : Agriculture has been the backbone of the Indian economy though its share in the Gross Domestic
Product (GDP) has registered a declining trend from 1951 onwards. The declining share of agriculture in the GDP is a matter
of serious concern because:
(i) Any decline and stagnation in agriculture will lead to decline in other spheres of the economy having wider implications on the society.
(ii) In 2010–11 about 52 per cent of the total workforce was employed by the agriculture sector, which makes more than half of the Indian population dependent on agriculture for sustenance. Analysing the importance of agriculture in India, the Government of India made concerte efforts to modernise agriculture through establishment of Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), agricultural universities, veterinary services and animal breeding,
horticulture development, research and development in weather forecast and field of meteorology, etc.
Question. Why an Indian farmer does not want his son to be a farmer ?
OR
Why farmers are withdrawing their investment from agriculture resulting in the downfall in the employment in agriculture ?
Answer : Though the GDP rate is increasing over the years, it is not generating sufficient employment opportunities in the country. The growth rate in agriculture is decelerating which is an alarming situation. Today, Indian farmers are facing a big challenge from international competition and our government is going ahead with reduction in the public investment in the agriculture sector, particularly, in irrigation, power, rural roads, market and mechanisation. Subsidy of fertilisers has decreased leading to an increase in the cost of production. Moreover, reduction in import duties on agricultural products has proved detrimental to agriculture in the country. Farmers are withdrawing their investment from agriculture causing a downfall in the agriculture. The farmers have started to face many problems and agricultural land is continuously decreasing. As a matter of fact, they do not want their children to become farmer.
Question. Explain the favourable climatic conditions required for the production of rubber. Also mention the states producing rubber.
Answer : (i) Temperature : It is a tree of the tropical forests, and requires a constant high temperature above 25°C. Thus, the rubber tree cannot be grown at high altitudes.
(ii) Rainfall : It needs heavy and well distributed rainfall throughout the year. The plant needs rainfall of more than 200 cms.
(iii) Soil : The plant requires alluvial or laterite soil areas of production.
India ranks fifth among the world’s natural rubber producers. The state of Kerala is the largest producer of rubber in India. Kerala accounts for about 91% of
the total area under rubber plantation. Tamil Nadu, Karnataka and the Andaman and Nicobar islands including the Garo Hills of the Himalayas are the other producers.
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Resources and Development VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Forest and Wildlife Resources VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Water Resources VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Agriculture VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Mineral and Energy Resources VBQs in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Minerals and Energy Resources VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Civics Manufacturing Industries VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Manufacturing industry VBQs in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Life Lines of National Economy VBQs in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Lifelines of National Economy VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Power Sharing VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Federalism VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Democracy and Diversity VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Gender Religion and caste VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Popular Struggles and Movements VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Popular Struggles and Movements VBQs in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Political Parties VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Political party VBQs in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Outcomes of Democracy VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Results of Democracy VBQs in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Civics Challenges To Democracy VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Challenges of Democracy VBQs in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science The Rise Of Nationalism In Europe VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science The Rise of Nationalism in Europe VBQs in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Nationalism in India VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Nationalism in India VBQs in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science The Making of a Global World VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science The Age of Industrialization VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Print Culture and the Modern World VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Development VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Sectors of the Indian Economy VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Economics Money And Credit VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Currency and credit VBQs in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Globalization and Indian Economy VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Globalization and Indian Economy VBQs in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Economics Consumer Rights VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science Consumer Rights VBQs in Hindi |
VBQs for Contemporary India II Chapter 4 Agriculture Class 10 Social Science
We hope students liked the above VBQs for Contemporary India II Chapter 4 Agriculture designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 10 Social Science released by CBSE. Students of Class 10 should download the Value Based Questions and Answers in Pdf format and practice the questions and solutions given in above Class 10 Social Science VBQs Questions on daily basis. All latest VBQs with answers have been developed for Social Science by referring to the most important and regularly asked topics which the students should learn and practice to get better score in school tests and examinations. Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to NCERT book for Class 10 Social Science to develop the Social Science Class 10 VBQs. After solving the questions given in the VBQs which have been developed as per latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 10 Social Science designed by our teachers. We have also provided a lot of other VBQs for Class 10 Social Science which you can use to further make yourself better in Social Science.
You can download the CBSE VBQs for Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India II Chapter 4 Agriculture for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the VBQs issued by CBSE for Contemporary India II Chapter 4 Agriculture Class 10 Social Science have been made available here for latest academic session
There is no charge for the VBQs and their answers for Class 10 CBSE Social Science Contemporary India II Chapter 4 Agriculture you can download everything free
Regular revision of VBQs given on studiestoday for Class 10 subject Social Science Contemporary India II Chapter 4 Agriculture can help you to score better marks in exams
Value Based Questions (VBQs) for Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India II Chapter 4 Agriculture help to test the ability of students to apply learnings to various situations in life.

