Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 12 Biology Microbes In Human Welfare Worksheet Set A. Students and teachers of Class 12 Biology can get free printable Worksheets for Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Microbes In Human Welfare in PDF format prepared as per the latest syllabus and examination pattern in your schools. Class 12 students should practice questions and answers given here for Biology in Class 12 which will help them to improve your knowledge of all important chapters and its topics. Students should also download free pdf of Class 12 Biology Worksheets prepared by teachers as per the latest Biology books and syllabus issued this academic year and solve important problems with solutions on daily basis to get more score in school exams and tests
Worksheet for Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Microbes In Human Welfare
Class 12 Biology students should download to the following Chapter 8 Microbes In Human Welfare Class 12 worksheet in PDF. This test paper with questions and answers for Class 12 will be very useful for exams and help you to score good marks
Class 12 Biology Worksheet for Chapter 8 Microbes In Human Welfare
Important Questions for NCERT Class 12 Biology Microbes in Human Welfare
Question. Nutritionally curd is more suitable then milk. Which of the following reason not supporting to this view
(a) It increasing vitamin B12
(b) It checks disease causing microbes
(c) LAB convert lactose into lactic curd
(d) It provide additional proteins
Answer: D
Question. Full potential of penicillin as an effective antibiotic was established by
(a) Alexander Flemming
(b) Ernest chain
(c) Howard florey
(d) Both 2 and 3
Answer: D
Question. Which of the following is "Clot buster"
(a) Citric acid
(b) Streptokinase
(c) Cyclosporin
(d) Statins
Answer: B
Question. Large holes in "Swiss cheese" are due to production of large amount of CO2 by ............... bacterium
(a) Leuconostoc mesenteroides
(b) Propionibacterium sharmanii
(c) Thermococcus proteus
(d) Staphylococcus thermophilus
Answer: B
Question. Functioning of statin is based on
(a) Competitive inhibition
(b) Endproduct inhibition
(c) Allosteric inhibition
(d) Negative feed back inhibition
Answer: A
Question. Methanogenic bacteria are not found in
(a) rumen of cattle
(b) gobar gas plant
(c) bottom of water-logged paddy fields
(d) activated sludge
Answer : D
Question. A nitrogen-fixing microbe associated with Azolla in rice fields is :
(a) Spirulina
(b) Anabaena
(c) Frankia
(d) Tolypothrix
Answer : B
Question. Which one of the following is not a nitrogenfixing organism?
(a) Anabaena
(b) Nostoc
(c) Azotobacter
(d) Pseudomonas
Answer : D
Question. Which gases are produced in anaerobic sludge digesters ?
(a) Methane and CO2 only
(b) Methane, hydrogen sulphide and CO2
(c) Methane, hydrogen sulphide and O2
(d) Hydrogen Sulphide and CO2
Answer : B
Question. The technology of biogas production from cow dung was developed in India largely due to the efforts of
(a) Gas Authority of India
(b) Oil and Natural Gas Commission
(c) Indian Agricultural Research Institute and Khadi and Village Industries Commission
(d) Indian Oil Corporation
Answer : C
Question. Bacillus thuringiensis is widely used as :
(a) Insecticide
(b) Weedicides
(c) Rodenticide
(d) All of the above
Answer : A
Question. BOD of waste water is estimated by measuring the amount of
(a) total organic matter
(b) biodegradable organic matter
(c) oxygen evolution
(d) oxygen consumption
Answer : D
Question. Which pigment gives a pinkish hue to rhizobium induced root nodules.
(a) Leghaemoglobin
(b) Carotenoid
(c) Mauveine
(d) None of the above
Answer : A
Question. Big holes in Swiss cheese are made by
(a) a machine
(b) a bacterium that produces methane gas
(c) a bacterium producing a large amount of carbon dioxide
(d) a fungus that releases a lot of gases during its metabolic activities.
Answer : C
Question. Conversion of milk to curd improves its nutritional value by increasing the amount of :
(a) Vitamin D
(b) Vitamin E
(c) Vitamin B12
(d) Vitamin A
Answer : C
Question. The technology of biogas production was developed in India mainly due to efforts of
(a) IARI
(b) KVIC
(c) IPM
(d) Both 1 and 2
Answer: D
Question. Which of the following bacteria was associated with discovery of penicillin
(a) Streptococus
(b) Staphylococcus
(c) Saccharomyces cerveisiae
(d) Propionobacterium
Answer: B
Question. Bacillus thuringiensis show their inhibitory effect on which part of the insect body
(a) Gut
(b) Respiratory tract
(c) Nervous system
(d) Circulatory system
Answer: A
Question. Which of the following biological agents are used for species specific, narrow spectrum insecticidal applications
(a) Adenoviruses
(b) Nucleopolyhedrosis viruses
(c) Retroviruses
(d) Trichoderma
Answer: B
Question. Members of which of the following fungal genus mainly participate in the mycorrhiza formation
(a) Azotobacter
(b) Fusarium
(c) Rhizopus
(d) Glomus
Answer: D
Question. A prokaryotic autotrophic nitrogen fixing symbiont is found in
(a) Alnus
(b) Cycas
(c) Cicer
(d) Pisum.
Answer: B
Question. Which one of the following helps in absorption of phosphorus from soil by plants?
(a) Glomus
(b) Rhizobium
(c) Frankia
(d) Anabaena
Answer: A
Question. Which one of the following is not a biofertiliser?
(a) Agrobacterium
(b) Rhizobium
(c) Nostoc
(d) Mycorrhiza
Answer: A
Question. An organism used as a biofertilizer for raising soybean crop is
(a) Azotobacter
(b) Azospirillum
(c) Rhizobium
(d) Nostoc.
Answer: C
Question. Consider the following statements (A–D) about organic farming.
(A) Utilizes genetically modified crops like Bt cotton
(B) Uses only naturally produced inputs like compost
(C) Does not use pesticides and urea
(D) Produces vegetables rich in vitamins and minerals
Which of the above statements are correct?
(a) B, C and D (b) C and D only
(c) B and C only (d) A and B only
Answer: C
Question. The common nitrogen-fixer in paddy fields is
(a) Rhizobium
(b) Azospirillum
(c) Oscillatoria
(d) Frankia.
Answer: B
Question. Which one of the following is not used in organic farming?
(a) Glomus
(b) Earthworm
(c) Oscillatoria
(d) Snail
Answer: D
Question. An example of endomycorrhiza is
(a) Nostoc
(b) Glomus
(c) Agaricus
(d) Rhizobium.
Answer: B
Question. Nitrogen fixation in root nodules of Alnus is brought about by
(a) Frankia
(b) Azorhizobium
(c) Bradyrhizobium
(d) Clostridium.
Answer: A
Question. Which one of the following pairs is not correctly matched?
(a) Streptomyces - Antibiotic
(b) Serratia - Drug addiction
(c) Spirulina - Single cell protein
(d) Rhizobium - Biofertilizer
Answer: B
Question. A free living nitrogen-fixing cyanobacterium which can also form symbiotic association with the water fern Azolla is
(a) Tolypothrix
(b) Chlorella
(c) Nostoc
(d) Anabaena.
Answer: D
Question. Which one of the following plants are used as green manure in crop fields and in sandy soils ?
(a) Crotalaria juncea and Alhagi camelorum
(b) Calotropis procera and Phyllanthus niruri
(c) Saccharum munja and Lantana camara
(d) Dichanthium annulatum and Azolla nilotica
Answer: A
Question. Which of the following is the pair of biofertilizers?
(a) Azolla and BGA
(b) Nostoc and legume
(c) Rhizobium and grasses
(d) Salmonella and E.coli
Answer: A
Question. Which aquatic fern is used to increase the yield in paddy crop?
(a) Azolla
(b) Salvinia
(c) Marsilea
(d) Isoetes
Answer: A
Question. Which of the following fern is an excellent biofertilizer?
(a) Marsilea
(b) Pteridium
(c) Azolla
(d) Salvinia
Answer: C
Question. Due to which of the following organism, yield of rice is increased?
(a) Sesbania
(b) Bacillus popilliae
(c) Anabaena
(d) Bacillus subtilis
Answer: C
Question. Which of the following is non-symbiotic biofertilizer?
(a) Anabaena
(b) Rhizobium
(c) VAM
(d) Azotobacter
Answer: D
Question. Farmers have reported over 50% higher yields of rice by using which of the following biofertilizer?
(a) Cyanobacteria
(b) legume-Rhizobium symbiosis
(c) Mycorrhiza
(d) Azolla pinnata
Answer: D
Question. The biofertilizers are
(a) Anabaena and Azolla
(b) cow dung, manure and farmyard waste
(c) quick growing crop ploughed under soil
(d) none of these.
Answer: A
Question. Which of the following species does not have the ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen?
(a) Azotobactor
(b) Anabaena
(c) Nostoc
(d) Spirogyra
Answer: D
Question. Which one of the following statements is correct?
(a) Legumes fix nitrogen only through the specialized bacteria that live in their roots.
(b) Legumes fix nitrogen independently of the specialized bacteria that live in their roots.
(c) Legumes fix nitrogen only through specialized bacteria that live in their leaves.
(d) Legumes are incapable of fixing nitrogen.
Answer: A
Question. Identify the organism which cannot fix atmospheric nitrogen.
(a) Nostoc
(b) Oscillatoria,
(c) Anabaena
(d) Spirogyra.
Answer: D
Question. Identify the process involved in making ― Toddy‖ .
(a) Lactic acid fermentation,
(b) Alcoholic fermentation
(c) Distillation,
(d) All the above
Answer: B
Question. Activated sludge formed in STP is used in :
(a) Aeration tank to serve as inoculums
(b) Anaerobic sludge digester p
(c) Used in aeration tank as well as anaerobic sludge digester
(d) Used in sedimentation tank.
Answer: C
Question. Which of the following is immediately given to a patient brought to a hospital with myocardial infarction?
(a) Streptokinase,
(b) Statin,
(c) Penicillin,
(d) Cyclosporin –A
Answer: A
Question. Big holes in Swiss cheese are made by ---------- .
(a) a fungus that releases carbondioxide.
(b) a bacterium that produces methane gas.
(c) Yeast
(d) a bacterium that produces large amount of carbondioxide.
Answer: D
Question. The use of biocontrol agents in farming will greatly reduce our dependence on….. .
(a) Fertilisers,
(b) manure,
(c) chemical pesticides
(d) weedicides.
Answer: C
Question. Which of the following is/are used in organic farming?
(a) Anabaena,
(b) Azospirillum,
(c) Trichoderma,
(d) All
Answer: D
Question. Baculoviruses are pathogens that :
(a) Attack viruses and bacteria,
(b) attack insect pests,
(c) kill useful insects,
(d) Kill nucleopolyhedrovirus.
Answer: B
Question. Identify the wrong pair:
(a) Statin : Monascus,
(b) Cyclosporin : Trichoderma
(c) Penicillin : Staphylococci,
(d) Ethanol : Yeast
Answer: C
Question. Match the following list of microbes and their commercially important products:
Microbe Product
A).Aspergillusniger i) Lactic acid
B).Lactobacillus ii) Citric acid
C).Acetobacteraceti iii) Butyric acid
D).Clostridium butylicum iv)Acetic acid
(a) A-ii, B-i, C-iii, D-iv
(b) A-ii, B-iii, C-i, D-iv,
(c) A-ii, B-iv, Ci, D-iii
(d) A-ii, B- i, C-iv, D-iii
Answer: D
Question. The vitamin whose content increases following the conversion of milk into curd by lactic acid bacteria is :
(a) Vitamin E,
(b) Vitamin B 12 ,
(c) Vitamin C ,
(d) Vitamin D
Answer: B
Question. The events of sewage treatment is given below
(a) Filtration
(b) Chlorination
(c) Biological treatment
(d) Sedimentation
Which one is the correct sequence of steps involved in sewage treatment?
(a) Steps A, B, C and D
(b) Step B C, A, and D
(c) Steps A, D, C and B
(d) Steps A, D, B and C
Answer: C
Question. Bottled juices are clarified by the use of ……… and ……… .
(a) Pectinase and lipase
(b) Protease and lipase
(c) Protease and amylase
(d) Protease and pectinase
Answer: D
Question. The spent slurry from the biogas plant is used as ………. .
(a) cooking fuel
(b) biofertiliser
(c) manure
(d) inoculum.
Answer: C
Question. Which of the following alcoholic drink is produced without distillation?
(a) Whisky
(b) Brandy
(c) Rum
(d) Wine
Answer: D
Assertion – Reason Type Questions:
Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below: -
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Question. Assertion (A) : Saccharomyces cerevisiae is used for making bread.
Reason (R) : Fermentation carried out by Yeast enzymes produces CO2 .
Answer: C
Question. Assertion (A) : Cyanobacteria like Nostoc and Anabaena are used as biofertilisers.
Reason (R) : Cyanobacteria absorb phosphorus from soil and passes it to crop.
Answer: C
Question. Assertion(A): Methanogens are present in the rumen of cattle.
Reason (R) : The break down of cellulosic materials in the rumen is carried out by methanogens.
Answer: C
Question. Assertion (A) : Azospirillum can enrich nitrogen content in the soil.
Reason (R) : Ammonia is converted into free nitrogen by Azospirillum .
Answer: A
Question. Assertion (A) : Dough used for making dosa and idli is fermented by bacteria.
Reason (R)) :The puffed-up appearance of dough is due to production of lactic acid.
Answer: C
Question. Assertion (A): Bacillus thuringiensis and Trichoderma are used as biocontrol agents by organic farmers.
Reason (R) : The use of biocontrol agents helps to reduce pollution caused by excessive use of fertilizers.
Answer: A
Question. Assertion(A) : Statins produced by Monascus is used for lowering blood cholesterol.
Reason (R) : Statins stimulate the enzyme responsible for synthesis of cholesterol.
Answer: A
Short Answer Type Questions:
Question. What are flocs in STP? Mention the role of flocs in STP.
Answer: Masses of bacteria associated with fungal filaments to form mesh like structures in aeration tank. These microbes consume the major part of the organic matter in the effluent and reduces the BOD.
Question. As a part of Swatch Vidyalaya programme, the Panchayath has donated a biogas plant and a single burner stove. The Panchayath authorities instructed to add 10 bags of cow dung initially in the biogas plant.
a. Mention the main constituents of biogas.
b. What is the use of spent slurry?
c. Give reason for adding cow dung in the biogas plant.
Answer: a) Methane, hydrogen sulphide, carbondioxide, hydrogen.
b) Used as manure.
c) Cow dung is rich in methanogens which help to produce biogas.
Question. How are the following microbes useful to us?
a. Trichodermapolysporum b.Monascuspurpureus
Answer: Trichoderma polysporum is the source of Cyclosporin which is used as immunosuppressive agent. Monascuspurpureus is the source of statins which is used for lowering cholesterol.
Question. An organic farmer added fungal genus Glomus in his crop field. How does it help in improving the yield?
Answer: Glomus forms mycorrhiza , It helps to absorb phosphorus from the soil and pass it to plant, resistant to root borne pathogen, tolerance to salinity and drought.
Question. Organ-transplant patients need a medicine called cyclosporine. How is it useful for the patient?
Answer: Cyclosporin is used as an immunosuppressant, It prevent the rejection of transplanted organ.
Question. a) What is activated sludge ?
b) Explain the fate of activated sludge in the sludge digester.
Answer: a)The effluent from aeration tank is passed into a settling tank where the bacterial flocs are allowed to sediment. This sediment is called activated sludge.
b) A small part of it is passed into aeration tank to serve as inoculums. The remaining part is pumped into anaerobic sludge digester.Here, the anaerobic bacteria digest bacteria and fungi in the sludge and forms methane, hydrogen sulphide and carbondioxide. These gases form biogas.
Question31. a) Name two photosynthetic biofertilisers. How do they improve soil fertility?
b) How is it different from mycorrhizae ?
Answer: a) Anabaena, Nostoc, Oscillatoria (Any two), Fix atmospheric nitrogen- also add organic material to the soil.
b) Mycorrhizae are symbiotic association between fungi and roots of higher plants.
Photosynthetic biofertilisers are free living or symbiotic.
Question. Alexander Fleming while working on Staphylococci bacteria, once observed a mould growing in one of his unwanted culture plate around which Staphylococci could not grow. Which was the mould that contaminated his culture plate. Mention the significance of this observation.
Answer: Penicillium notatum , The chemical produced by the mould (Penicillium) inhibited the growth of Staphylococci. This led to the discovery of antibiotic – penicillium.
Question. Suggest an eco-friendly and pollution free alternative source of energy for rural areas which is dependent on microbial activity. Name the microbe involved in the production of this cooking fuel and mention the chemical composition of it.
Answer: Biogas plant, Methanogens/ methanobacterium, Methane, carbondioxide, Hydrogen etc.
Question. The excessive use of chemical pesticides causes soil pollution and adversely affect human health. An alternative to pesticide is use of biocontrol agents. Name a bacterium and a virus which are used as biocontrol agents and mention their action.
Answer: Bacterium –Bacillus thuringiensis, Toxin released by his bacterium kill the pest larvae.
Virus _ Baculoviruses/Nucleopolyhedrovirus attack insects and other arthropods.
Long Answer Type Questions:
Question. a) Differentiate between biofertilisers and chemical fertilizers?
b) Explain the three types of biofertilisers.
Answer: a)Any two differences – biofertilisers are organisms/ but fertilizers are chemicals produced in factories, Use of biofertilisers do not cause pollution/ but excessive use of fertilizers causes pollution.
b) i.Bacteria – symbiotic (Rhizobium) fix atmospheric nitrogen.
Free living nitrogen fixers – Azospirillum and Azotobacter.
ii) Mycorrhizae –symbiotic association of fungi with roots of higher plants –any one role (absorb Phosphorus and pass it to plant, resistant to root borne pathogens, tolerance to salinity
and drought.
● Cyanobacteria – Nostoc,Anabaena, Oscillatoria –can fix atmospheric nitrogen.
Question.a) Secondary treatment of the sewage is also called 'Biological treatment‘. Justify the statement and explain the process.
Answer: Aerobic and anaerobic microbes used in secondary treatment.
Primary effluent is passed into aeration tank- constantly agitated mechanically and air is pumped into it-Flocs formation- these microbes consume major part of the organic matter in the effluent- reduces BOD – Effluent is passed into settling tank – forms activated sludge- small part is pumped back into aeration tank – major part is passed into anaerobic sludge digester – Anaerobic bacteria digest flocs into mixture of gases (methane, carbondioxide, hydrogen etc ) forms biogas –Effluent from the secondary treatment plant is released into natural water bodies.
Diagram Based / Case Based Questions:
Question. The given diagram shows the root system of a leguminous plant.
a. Name the microbe present inside the root nodule and mention the role of it.
b.How is this microbe differ from Nostoc?
c. The application of fertilizers and pesticides has improved our food production. But excessive use of these agrochemicals have adverse effect on environment and human health. So many farmers are moving away from the use of agrochemicals and started practicing organic farming.
Answer: a) Rhizobium, Can fix atmospheric nitrogen.
b) Rhizobium is symbiotic nitrogen fixer, But Nostoc is photosynthetic free living
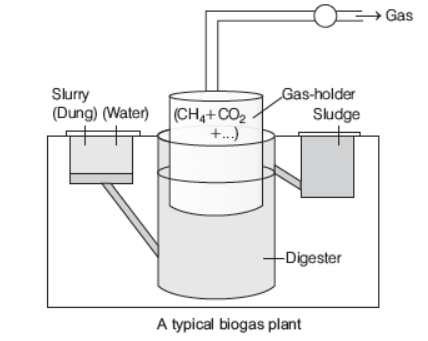
Question. Observe the given diagram and answer the questions :
a) What is a and how is it useful to us?
b) Name the main gases collected in b.
c) Name the microbes present in the digester part.
Answer: a) Spent slurry/ sludge, used as manure.
b) CH4 , CO2 , H2S , H2
c) Methanogens / Methanobacterium
Question. Organic farmers use a number of microbes for crop protection from pests.
a. Mention one benefit of microbial biocontrol method over pesticides.
b. Name a fungus and a bacteria which act as biocontrol agents.
Answer: a) No pesticide pollution, No impact on health
Fungus- Trichoderma , Bacterium: Bacillus thuringiensis
Sewage treatment plants are compulsory for all newly constructed residential apartments with many family accommodations. Sewage treatment aims to remove contaminants from sewage to produce an effluent that is suitable for discharge to the surrounding environment or can be reused for watering plants. Untreated sewage discharged into water bodies adversely affect the quality of water. The presence of high amount of organic matter in water increases the BOD. The two stages in sewage treatment are physical treatment and biological treatment. The secondary /biological treatment requires the action of aerobic and anaerobic microbes. The flocs formed in the aeration tank help to reduce the BOD. The biogas generation is also possible through STPs.
Question. Give reason for pumping a part of activated sludge in to aeration tank?
Answer: It acts as inoculums
Question. Where is activated sludge formed in STP?
Answer: In settling tank
Question. The effluent from the primary settling tank is taken to --------
i. Anaerobic sludge digester,
ii. Aeration tank ,
iii. Natural water bodies ,
iv.Biogas plant
Answer: Aeration tank
Question. Name two major categories of microbes which consume organic matter in the aeration tank.
Answer: Bacteria and fungi
1 Why does ‘Swiss cheese’ have big holes?
2 Why do we prefer to call secondary waste water treatment as biological treatment?
3 What for Nucleopolyhydro viruses are being used now a days?
4 Which species of Penicillium produces Roquefort cheese?
5 Match the following list of bacteria and their commercially important products: Bacterium Product
(i) Aspergillus niger (a) Lactic acid (ii) Acetobacter aceti (b) Butyric acid (iii) Clostridium butylicum (c) Acetic acid (iv) Lactobacillus (d) Citric acid
6 How do mycorrhizal fungi help the plants harbouring them?
7 What is the chemical nature of biogas. Name an organism which is involved in biogas production?
8 What are biofertilisers? Give two examples.
9 Explain the role of baculoviruses as biological control agents. Mention their importance in organic farming.
Microbes in Human Welfare Questions and Answers
Question. The immune system of a person is suppressed. In the ELISA test, he was found positive to a pathogen. Which cells of the body are affected by the pathogen?
Answer. Helper T lymphocytes
Question. What would happen to immune system, if thymus gland is removed from the body of a person?
Answer. Thymus is the primary lymphoid organ. In thymus gland, immature lymphocytes differentiate into antigen-sensitive lymphocytes. If thymus gland is removed from the body of a person, his immune system becomes weak. As a result the person's body becomes prone to infectious diseases.
Question. If a regular dose of drugs or alcohol is not provided to an addicted person, he shows some withdrawl symptoms. List any four such withdrawal symptoms.
Answer. The withdrawal symptoms are:
a. Anxiety b. Shakiness c. Nausea d. Sweating
Question. In the metropolitan cities of India, many children are suffering from allergy/asthma. What are the main causes of this problem. Give some symptoms of allergic reactions.
Answer. Allergy is the exaggerated response of the immune system of certain antigens present in the environment. In metropolitan cities life style is responsible in lowering of immunity and sensitivity to allergens. More polluted environment increases the chances of allergy in children. Some symptoms of allergic reactions are sneezing, watery eyes, running nose and difficulty in breathing.
Question. Life style diseases are increasing alarmingly in India. We are also dealing with large scale malnutrition in the population. Is there any method by which we can address both these problems?
Answer. The answer to address both these problems is called biofortification. This area looks at improving food quality with respect to protein, oil, vitamin, micro nutrient and mineral content. The oils need to be rich in omega 3 fatty acids which are good for heart. Similarly, proteins should have more of lysine and tryptophan (essential amino acids). Many varieties of maize, carrots and spinach have been released which fulfill the above criteria.
Biology in Human Welfare Questions and Answers
Question. Do you think we, human beings, are able to digest the cellulose present in our foods? Why or why not ?
Answer. We lack cellulase enzyme for digestion due to nonfunctioning of appendix.
Question. Baculoviruses are the pathogens that attack on plants and also are used for biocontrol. How both antagonistic functions are performed ?
Answer. Baculovirus like Nucleopolyhedral virus are- species specific, narrow spectrum, effective only against insects and arthropods.
Question. Three water samples namely river water, untreated sewage water and secondary effluent discharged from a sewage treatment plant were subjected to BOD test. The samples were labelled A, B and C; but the laboratory attendant did not note which was which. The BOD values of the three samples A, B and C were recorded as 20mg/L, 8mg/L and 400mg/L, respectively. Which sample of the water is most polluted? Can you assign the correct label to each assuming the river
water is relatively clean?
Answer. Most polluted water : 400 mg/L of secondary effluent (c). A (River water) : 08 mg/L; b (Untreated sewage water) : 20 mg/L.
Question. The Ministry of Environment and Forests has initiated Ganga Action Plan and Yamuna Action Plan to save these major rivers. How was the target fulfilled ?
Answer. Decreasing pollution, Sewage treatment and utilization of treated water.
Question. What are the negative impacts of biological control ?
Answer. May develop resistant insect varieties, may be lethal / harmful for human beings.
Important Notes for Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Microbes In Human Welfare
- Microbes are microscopic, single-celled, minute organisms that individually are too small to be seen with naked eyes, i.e. can be seen only under a microscope.
- Microbes constitute major groups of biological systems on the earth, which are present almost everywhere, i.e. in soil, air, water, plants and animals and also even inside our body. These can be found in extreme conditions of pH (alkaline and acidic soil) and temperature (thermal vents or geysers and below the several metre thick snow layers).
- Microbes are diverse group of organisms including protozoans, bacteria, fungi, microscopic plants, viruses, viroids and prions (proteinaceous infectious agents), etc.
- Some microbes cause infections and diseases in human beings, animals and plants. But several microbes are useful to man in diverse ways.
- The microbes like fungi and bacteria can be cultured in laboratory on nutritive media to form colonies that can be seen with the naked eyes.
Microbes in Household Products
Microbes and their products are used in everyday life, e.g. production of curd, formation of dough, cheese, toddy,etc.
Some products produced by microbes are given below
Curd
- Microorganisms like Lactobacillus and others commonly called Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB) grow in milk and convert it into curd. We have seen at home that a starter is added to milk which turns it into curd. This starter is known as inoculum, which contains millions of LAB.
- During growth, LAB produce acids that coagulate and partially digest the milk proteins. Thus, converting milk to curd. They also improve nutritional quality by increasing vitamin-B 12 content of the curd. A number of organic acids can also be found in curd.
- LAB also play a beneficial role in checking disease causing microbes in our stomach.
Dough
Microbes are used in making foods such as dosa and idli. The puffed up appearance of their dough is due to the production of CO2 gas through fermentation by bacteria. In bread making, dough is fermented using baker’s yeast, (Saccharomyces cerevisiae). It convertes the present sugar into CO2.
Toddy
It is a traditional drink of some parts of Southern India. It is made by fermenting sap from palm trees, coconut, etc. Microbes are also used to ferment fish, soybean, bamboo shoots, etc., to make food.
Cheese
It is formed by partial degradation of milk by different microorganisms. Different varieties of cheese are known by their texture, flavour and taste. This specificity comes from the microbes used. For example,
(i) Swiss cheese with large holes is produced by Propionibacterium shermanii. Holes are created due to the production of large amount of CO2 by this bacterium.
(ii) Roquefort cheese are ripened by growing a specific fungi, Penicillium roqueforti on them, which gives them a particular flavour.
Microbes in Industrial Products
In industry, microbes are used to make a number of products such as beverages, enzymes and antibiotics, etc., valuable to human beings. Industrial scale production requires growing microbes in very large vessels called fermentors.
Fermented Beverages
- Large scale production of beer, brandy, whisky, rum, etc., is done by fermenting malted cereals and fruit juices using unicellular fungi Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer’s yeast).
- Different types of alcoholic drink like wine and beer are produced without distillation. Whisky, brandy and rum are produced by distillation of the fermented broth.
Antibiotics
- These are the chemical substances which are produced by some microbes to kill or retard the growth of other disease causing microbes. Penicillin was the first antibiotic to be discovered by Alexander Fleming.
- Alexander Fleming observed that if a mould of Penicillium notatum grows on a nutrient medium, it does not let a bacterium, Staphylococcus grow around it. He then isolated the chemical produced by the mould and named it penicillin. However, its full potential as an effective antibiotic was established later on by Ernst Chain and Howard Florey. Penicillin was extensively used in treating American soldiers wounded in World War-II. For this discovery, Fleming, Chain and Florey were awarded the Nobel Prize in 1945.
- Antibiotics are widely used in treating human and animal bacterial diseases. Deadly diseases like plague, whooping cough (kali khansi), diphtheria, leprosy (kusht rog) are completely curable diseases now due to the use of antibiotics.
- One of the most productive sources of antibiotics has been the genus–Streptomyces from which many antibiotics have been derived. Some of them are streptomycin, tetracycline, erythromycin, terramycin, which are obtained from Streptomyces griseus, S. aureofaciens, S. erethreus and S. remosus, respectively.
Chemicals, Enzymes and Other Bioactive Molecules
Microbes are being used for commercial and industrial production of certain chemicals like alcohols, organic acids, enzymes and other bioactive molecules (which are functional in living systems or can interact with their components). Some of them are given below
Organic Acids Produced by Microbes
| Organic Acids Produced by Microbes |
| Organic acids | Microorganisms |
| Citric acid | Aspergillus niger (fungus) |
| Acetic acid | Acetobacter aceti (bacterium) |
| Butyric acid | Clostridium butylicum (bacterium) |
| Lactic acid | Lactobacillus (bacterium) |
| Enzymes and their Uses |
| Enzymes | Uses |
| Lipases | Used in detergent formulations. They are helpful in removing oily stains from the laundry. |
| Pectinases and proteases | Used in bottled juices, for clearing of juices. |
| Streptokinase | Obtained from genetically modified form of bacterium Streptococcus. It is used as a ‘clot buster’ for removing clots from the blood vessels of heart patients, who have undergone myocardial infarction leading to heart attack. |
| Bioactive Molecules and their Uses |
| Bioactive molecules (Products) | Microorganisms | Uses |
| Cyclosporin-A | Trichoderma polysporum (fungus) | As immunosuppressive agent in organ transplant patients. |
| Statins | Monascus purpureus (yeast) | As blood cholesterol lowering agents. It acts by competitively inhibiting enzyme responsible for cholesterol synthesis. |
Microbes in Sewage Treatment
- Sewage is the municipal wastewater generated everyday in cities and towns. It contains large amounts of organic matter and many pathogenic microbes. That is why before being disposed, in water bodies, it needs to be treated in Sewage Treatment Plants (STPs) to make it less polluting.
- Certain heterotrophic microbes naturally present in sewage are used in its treatment. This treatment is carried out in two stages, i.e. primary treatment and secondary treatment.
Primary Treatment
- In primary treatment, physical removal of particles, i.e. large and small, is done from the sewage through filtration and sedimentation. All solids that settle down, form the primary sludge and the supernatant forms the effluent, which is taken for secondary treatment.
Secondary Treatment
- In secondary treatment or biological treatment, the primary effluent is passed into large aeration tanks where it is constantly agitated mechanically. This allows the growth of the aerobic microbes into flocs (masses of bacteria associated with fungal filaments to form mesh-like structures) which consume the major part of the organic matter in the effluent that significantly reduces the BOD (Biochemical Oxygen Demand) of the effluent.
- BOD is the amount of oxygen that would be consumed, if all the organic matter in one litre of water were oxidised by bacteria. The sewage water is treated till the BOD is reduced. The greater is the BOD of wastewater, more is its polluting potential.
- The effluent is then passed into a settling tank where the bacterial flocs are allowed to sediment. This sediment is called activated sludge as it contains active microbes.
From here
– A small part of the activated sludge is pumped back into the aeration tank to serve as the inoculum.
– The remaining major part of the sludge is pumped into large tanks called anaerobic sludge digesters. Here, lack of oxygen kills the aerobic bacteria which are digested along with the other biomass by anaerobic bacteria and fungi.
– The effluent from the secondary treatment plant is generally released into natural water bodies like rivers and streams.
- During digestion of organic matter, bacteria produce a mixture of gases such as methane, hydrogen sulphide and carbon dioxide. These gases form biogas, which is inflammable and can be used as a fuel.
River Action Plan
- The ministry of environment and forests has initiated the Ganga Action Plan and Yamuna Action Plan to save these major rivers of our country from pollution. These plans propose to build a large number of sewage treatment plants, so that only treated sewage may be discharged into the rivers.
- The states involved in Ganga Action Plan are Uttarakhand,UP, Bihar, West Bengal and Jharkhand.
Microbes in Production of Biogas
- Biogas is a mixture of gases, but the major content is methane gas. It is produced by the anaerobic microbial activity during digestion of biomass with the help of certain bacteria. Biogas is used as fuel.
- The type of gas produced by microbes during their growth and metabolism depends upon the microbes and the organic substrates they utilise. Certain bacteria, which grow anaerobically on cellulosic material, produce large amount of methane along with CO2 and H 2. These bacteria are called methanogens and one such common bacterium is Methanobacterium. Methanogens produce large amount of biogas [CH4 (50-70%), CO2 (30-40%) and H2 (remaining)].
l Methanogens are also present in anaerobic sludge during sewage treatment. They are also present in rumen (a part of stomach) of cattle, where they help in breakdown of cellulosic material in the food and thus, play important role in nutrition of cattle.
Biogas Plant
- The excreta of cattle commonly called gobar, is rich in methanogenic bacteria. Thus, cattle dung can be used for generation of biogas, commonly called gobar gas.
- Cattle dung is available in large quantities in rural areas hence, biogas plants are mostly functional in rural areas.
- Biogas plant consists of a concrete tank (10-15 feet deep) in which biowastes are collected and slurry of dung is fed.
A floating cover is placed over the slurry, which keeps on rising, as the gas is produced in the tank due to the microbial activity.
- Methanobacterium in the dung acts on the biowaste to produce biogas. An outlet is also present which connects to a pipe that supply biogas to the nearby houses. The biogas thus produced is used for cooking and lighting.
- There is another outlet from which spent slurry is removed that can be used as fertiliser. Biogas production technology was developed in India mainly by Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC) and Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI).
Microbes as Biocontrol Agents
Biocontrol refers to the use of biological methods for controlling various plant diseases and pests. This method is employed because the long time use of chemical insecticides, pesticides and weedicides has been proved to be harmful for all living organisms and the environment (air, water, soil, etc).
Biological Control of Pests and Diseases
l The use of biocontrol measures has become more preferable since it greatly reduces our dependence on toxic chemicals. Here, pests can be controlled by making use of natural predation rather than chemicals.
l Biocontrol involves creation of a system where the insects/pests are not eradicated rather are kept at manageable levels by a system of check and balances within ecosystem. Various microbes can be used as biocontrol agents, e.g.
– Aphids and mosquitoes can be controlled by ladybird beetle and dragonflies, respectively.
– Butterfly caterpillars can be killed by using the bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt). Bt is available as dried spores which are mixed with water and sprayed on to plants such as brassicas and fruit trees, where these are eaten by the insect larvae. In the gut of the larvae, the toxin is released and the larvae get killed. This will kill the caterpillars, but leave other insects unharmed.
– Fungi (like Trichoderma sp., a free-living fungi that are common in root ecosystems) are effective against several fungal plant pathogens.
– Viruses (like baculoviruses belonging to genus- Nucleopolyhedrovirus) are excellent for species specific narrow spectrum insecticides. These do not have negative impact on non-target insects and have narrow
spectrum insecticidal applications.
l Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is an environmentally sensitive and effective approach of pest management that uses information on life cycles of organisms and their interaction with environment. The integrated pest management is done to control insects and pests of plants, animals and humans.
Microbes as Biofertilisers
- To cut down the pollution caused by chemical fertilisers, it is important to switch to organic farming (raising crops through the use of components of biological origin, e.g. biofertilisers).
- Biofertilisers are organisms, e.g. bacteria, fungi and cyanobacteria that enrich the nutrient quality of the soil.
The main sources of biofertilisers are as follows
Bacteria
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria fix atmospheric nitrogen into organic form, which is used by the plant as nutrient, e.g. Rhizobium is a symbiotic bacterium that lives in the root nodules of legumes and fixes atmospheric nitrogen into organic compounds.
Azotobacter and Azospirillum are free-living bacteria, which absorb free nitrogen from the soil, air and convert it into salts of nitrogen compounds.
Fungi
They also form symbiotic association with plants, i.e. mycorrhiza, which absorb phosphorus from soil and passes it to the plants. Many members of genus–Glomus form mycorrhiza. Plants with mycorrhizal association show other benefits also such as
(i) Resistance to root-borne pathogens.
(ii) Tolerance to salinity and drought.
(iii) Increase in plant growth and development.
Cyanobacteria
These are autotrophic microbes found in aquatic and terrestrial environments. Most of them fix atmospheric nitrogen, e.g. Anabaena, Nostoc, Oscillatoria, etc. In paddy fields, cyanobacteria serve as important biofertiliser. Blue-Green Algae (BGA) also add organic matter to the soil. Thus, increasing its fertility, but still BGA are not very popularly used.
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Human Reproduction Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Reproduction In Human Beings Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Reproductive Health Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Worksheet Set C |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Human Health And Disease Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Human Health And Diseases Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Microbes In Human Welfare Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Microbes In Human Welfare Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology Principles And Processes Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology Principles and Processes Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology and its Applications Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology and Its Applications Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Organisms And Populations Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biodiversity And Conservation Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biodiversity And Conservation Worksheet Set B |
Worksheet for CBSE Biology Class 12 Chapter 8 Microbes In Human Welfare
We hope students liked the above worksheet for Chapter 8 Microbes In Human Welfare designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 12 Biology released by CBSE. Students of Class 12 should download in Pdf format and practice the questions and solutions given in the above worksheet for Class 12 Biology on a daily basis. All the latest worksheets with answers have been developed for Biology by referring to the most important and regularly asked topics that the students should learn and practice to get better scores in their class tests and examinations. Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to the NCERT book for Class 12 Biology to develop the Biology Class 12 worksheet. After solving the questions given in the worksheet which have been developed as per the latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 12 Biology designed by our teachers. We have also provided a lot of MCQ questions for Class 12 Biology in the worksheet so that you can solve questions relating to all topics given in each chapter.
You can download the CBSE Printable worksheets for Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Microbes In Human Welfare for latest session from StudiesToday.com
There is no charge for the Printable worksheets for Class 12 CBSE Biology Chapter 8 Microbes In Human Welfare you can download everything free
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all latest NCERT Chapter 8 Microbes In Human Welfare Class 12 Biology test sheets with answers based on the latest books for the current academic session
CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Microbes In Human Welfare worksheets cover all topics as per the latest syllabus for current academic year.
Regular practice with Class 12 Biology worksheets can help you understand all concepts better, you can identify weak areas, and improve your speed and accuracy.

