Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology and Its Applications Worksheet Set B. Students and teachers of Class 12 Biology can get free printable Worksheets for Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Biotechnology and Its Application in PDF format prepared as per the latest syllabus and examination pattern in your schools. Class 12 students should practice questions and answers given here for Biology in Class 12 which will help them to improve your knowledge of all important chapters and its topics. Students should also download free pdf of Class 12 Biology Worksheets prepared by teachers as per the latest Biology books and syllabus issued this academic year and solve important problems with solutions on daily basis to get more score in school exams and tests
Worksheet for Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Biotechnology and Its Application
Class 12 Biology students should download to the following Chapter 10 Biotechnology and Its Application Class 12 worksheet in PDF. This test paper with questions and answers for Class 12 will be very useful for exams and help you to score good marks
Class 12 Biology Worksheet for Chapter 10 Biotechnology and Its Application
Important Questions for NCERT Class 12 Biology Biotechnology and Its Applications
Question. A transgenic food crop, which may help in solving the problem of night blindness in developing countries is :
(1) Bt soyabean
(2) Golden rice
(3) Flavr savr tomatoes
(4) Starlink maize
Answer : B
Question. GEAC stands for :
(1) Gene evaluation approval committee
(2) Genetic engineering approval committee
(3) Genetic engineering applied committee
(4) Gene enhancement approval committe
Answer : B
Question. Conventional methods to diagnose a disease are :
(1) Serum and urine analysis
(2) PCR
(3) ELISA
(4) All of the above
Answer : A
Question. Transgenic mice are being developed for use in :
(1) Testing the safety of polio vaccines before they are used on human
(2) Molecular diagnosis of diseases
(3) Production of human protein enriched milk
(4) Production of human insulin
Answer : A
Question. The first clinical gene therapy was given to a 4-year old girl with ADA deficiency in :
(1) 1984
(2) 1986
(3) 1992
(4) 1990
Answer : D
Question. The first transgenic cow, which produced human protein enriched milk was named :
(1) Andy
(2) Dolly
(3) Rosie
(4) Dumpy
Answer : C
Question. Two polypeptide chains of insulin are linked together by :
(1) disulphide bonds
(2) hydrogen bonds
(3) Phosphodiester bonds
(4) Glycosidic bonds
Answer : A
Question. 'Flavr Savr' is a transgenic variety of :
(1) Potato
(2) Tomato
(3) Soyabean
(4) Rice
Answer : B
Question. When cut by the restriction enzyme, the DNA fragments can be joined together using :
(1) DNA polymerase
(2) DNA ligase
(3) Alkaline phosphatase
(4) DNA gyrase
Answer : B
Question. Genetically engineered human insulin is made in
(1) Fungus
(2) Protista
(3) Plants
(4) Bacterium
Answer : D
Question. Toxin present in Bacillus thuringiensis does not kill the bacterium because it is inactive form what makes it active inside the insect ?
(1) the alkaline pH of the gut, which solubilises the crystals
(2) the acid pH of the gut
(3) the neutral pH of the gut
(4) All of the above
Answer : A
Question. Infection by pathogen can be detected by the presence of antigens or by detecting the antibodies synthesised against the pathogen, on this principle a test is based which is ?
(1) PCR
(2) ELISA
(3) Both (1) and (2)
(4) None of the above
Answer : B
Question. Indian parliament recently cleared, which amendment of the Indian patents bill,
(1) First amendment
(2) Second amendment
(3) Third amendment
(4) Fourth amendment
Answer : B
Question. The technique that serves the purpose of early diagnosis of disease or pathogen :
(1) Recombinant DNA technology
(2) Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
(3) Enzyme linked immuno sorbent assay (ELISA)
(4) All the above
Answer : D
Question. Transgenic tobacco which is developed through RNA interference, prevents the infection of :
(1) A nematode - Meloidegyne incognitia
(2) A bacterium - Pseudonomonas putida
(3) A fungi - Tricoderma
(4) An insect
Answer : A
Question. The organisation set up for making decisions regarding the validity of GM research and the safety of introducing GM organism for public services is :
(1) Genetic engineering approval committee
(2) Genetic engineering advanced company
(3) Genetic engineering applied committee
(4) None of these
Answer : A
Question. Use of bio-resources by multinational companies and other organisations without proper autorisation from the countries and people concerned without compensatory payment is called :
(1) Biotheft
(2) Biopatent
(3) Biopiracy
(4) None of the above
Answer : C
Question. Bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis is widely used in contemporary biology as
(1) Source of industrial enzyme
(2) Indicator of water pollution
(3) Insecticide
(4) Agent for production of dairy products.
Answer : C
Question. Bt toxin is produced by Bacillus thuringiensis which is :
(1) Bacterium
(2) Protozoa
(3) Fungus
(4) Virus
Answer : A
Very Short Answer Questions
Question. For which variety of Indian rice, patent was filed by a USA Company?
Answer : Indian Basmati was crossed with semi-dwarf variety and was claimed as a new variety for which the patent was filed by a USA company.
Question. What is Chakravarthy bug? Give its scientific name and its application?
Answer : Chakravarthy bug is a super bug of Pseudomonas with multiple plasmids. They are helpful in removing oil spills.
Question. Name a recombinant vaccine that is currently being used in vaccination program?
Answer : Hepatitis B recombinant vaccine, Engerix-B, is used for vaccination of hepatitis virus.
Question. Suggest any two possible treatments that can be given to a patient exhibiting adenosine deaminase deficiency.
Answer : (i) Enzymes replacement therapy (in which functional ADA is injected)
(ii) Bone marrow transplantation
(iii) Gene therapy/Culturing the lymphocytes followed by introduction of functional ADA cDNA into it and returning it into the patient’s body.
Question. Mention the chemical change that proinsulin undergoes, to be able to act as mature insulin.
Answer : An extra stretch called C-peptide is removed from pro-insulin during maturation.
Question. State the cause of adenosine deaminase enzyme deficiency.
Answer : Deletion of gene for adenosine deaminase.
Question. Can you suggest a method to remove oil (hydrocarbon) from seeds based on your understanding of rDNA technology and chemistry of oil ?
Answer : It is possible to remove gene for oil synthesis from seeds by recombinant DNA technology or genetic engineering.
Question. Mention two objectives of setting up GEAC by our government.
OR
GEAC is one of the organization set up by Indian Government. Write it’s full form. Give it’s two objectives.
Answer : Indian Government has set up organisations like GEAC (Genetic Engineering Approval Committee), which make decision about the validity of GM research and the safety of GM-organisms for public services.
Question. Name the Indian variety of rice patented by an American Company. R [Delhi Set, 2008]
Answer : The Indian variety of rice patented by American Company—Rice Tec inc. in 1997 was basmati rice.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Discuss briefly how a probe is used in molecular diagnostics.
Answer : Early detection of a disease is not possible by conventional diagnostic methods. So, some techniques have been implanted for early diagnosis like PCR, recombinant DNA technology and ELISA. In recombinant DNA technology, a probe is used. It is allowed to hybridise to its complementary DNA in the clone of cells. The cells are then detected by autoradiography. The cell with mutated gene will not be observed on the photographic film because, the probe will not have complementarity with the mutated gene.
Question. Who was the first patient to be treated with gene therapy? Why was the given treatment recurrent in nature?
Answer : Gene therapy is a collection of methods that allows the correction of gene defects diagnosed in a child or embryo. Correction of a genetic defect involves the delivery of a normal gene into the individual or embryo to take over the function of and compensate for the non-functional gene. The first clinical gene therapy was given in 1990 to a 4 yrs old girl with Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) deficiency. ADA deficiency is caused due to the deletion of gene for Adenosine Deaminase. It can be cured by bone marrow transplantation or by enzyme replacement therapy. In both the approaches, it is not completley curable. It may recurrent in nature because in the process of gene therapy, lymphocytes used are found to be mortal in nature and the patient requires periodic infusion of such genetically engineered lymphocytes. For permanent cure, gene isolated from the bone marrow cells producing ADA is introduced into the cells at early embryonic stages.
Question. Ignoring our traditional knowledge can be prove costly in the area of biological patenting. Justify.
Answer : Human communities have always generated, refined and passed on the knowledge from generation to generation. Such knowledge is called traditional knowledge and is often an important part of the cultural identities. A number of cases relating to traditional knowledge have attracted international attention. As a result, the issue of traditional knowledge has been brought to the general debate surrounding intellectual property. These cases involve, what is often referred to as ‘biopiracy’. The examples of turmeric and neem (Indian traditional herbal medicine) illustrates the issues that can arise when patent protection is granted to inventions relating to traditional knowledge which is already in the public domain. In these cases, invalid patents were issued because the patent examiners were not aware or the relevant traditional knowledge. e.g., India is one of the country possessing the richest diversity of rice (2000 varieties). Basmati rice is distinct for its unique aroma and flavour and 27 documented varieties of Basmati are grown in India. There is reference to Basmati in ancient texts, folklore and poetry, as it has been grown for centuries. In 1997, an American company Rice teen. Got patent rights on Basmati rice through the US patent and Trademark Office. This allowed the company to sell a ‘new’ variety of Basmati, in the US and abroad. This ‘new’ variety of Basmati had actually been derived from Indian farmer’s varieties. Indian Basmati was crossed with semi-dwarf varieties and claimed as an invention or a novelty. The patent extends to functional equivalents, implying that other people selling Basmati rice could be restricted by the patent. If we are not vigilant and we do not immediately counter these patent applications, other countries/individuals may encash on our rich legacy and we may not be able to do anything about it. However, India achieved success in contesting patent for Basmati, rice as on September 2000 Rice teen withdraw the claims contested by India. Therefore, ignoring our traditional knowledge, can be proved costly in the area of biological patenting.
Question. Highlight any four areas where genetic modification of plants has been useful.
Answer : Genetically Modified Plants (GMOs) are the plants, whose genes have been altered by manipulation. Genetic modification of plants is useful in different areas. Because of following reasons (a) It increases tolerance against abiotic stresses (cold, drought, salt, heat). (b) It reduces reliance on chemical pesticides (pest-resistant crops). (c) It reduces post-harvest losses. (d) It increases the efficiency of minerals used by plants (this prevents early exhaustion of fertility of soil). (e) It enhances nutritional value of food, e.g., vitamin-A enriched rice (golden rice). (f) It creates tailor-made plants to supply alternative resources such as starch fuels and pharmaceuticals to industries.
Question. What is a recombinant DNA vaccine? Give two examples.
Answer : Recombinant DNA vaccines are produced by using genetically engineered plasmids that have gene inserts possessing the surface proteins of a pathogen. After the binding of pathogens to these surface proteins, a weak immune response is elicited but it do not results in infection. These plasmids are inserted in bacteria or yeast cells that expresses the viral proteins, which are then injected into the human host as vaccine, where they are recognised as foreign and an immune response is elicited. Recombinant hepatitis-B vaccine and polio vaccine are the examples.
Question. Gene expression can be controlled with the help of RNA. Explain the method with an example.
Answer : RNAi technology is used to block the expression of certain genes and also referred to as gene silencing. During this process, a complementary RNA to the mRNA being produced by the gene is introduced into the cell. This RNA binds to the mRNA making it double stranded and therefore, stops the process of translation. e.g., a nematode Meloidegyne incognitia infects the roots of tobacco plants which reduces the production of tobacco. It can be prevented by using RNA interference (RNAi) process which is checked by silencing of specific mRNA due to a complementary dsRNA. dsRNA binds and prevents the translation of mRNA (silencing). By using Agrobacterium vectors, Nematode-specific genes were introduced into the host plants which produces both sense and anti-sense RNA in the host cells. These two RNAs are complementary to each other and form a double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) that initiates RNAi and hence, silence the specific mRNA of the nematode. The parasite cannot survive in transgenic host and so prevents the plants from pests.
Question. Why is it that the line of treatment for a genetic disease is different from infectious diseases?
Answer : The line of treatment for a genetic disease is different from infectious diseases because genetic diseases cannot be treated with any medication, only the signs and symptoms can be taken care of. The only way to treat them is by the manipulation of genes to correct or replace the faulty genes. On the other hand, infectious diseases are caused by pathogens and therefore, can be treated by substances that kill the pathogen or hamper its growth.
Question. Differentiate between gene therapy and gene cloning.
Answer : Difference between Gene Therapy and Gene Cloning
Gene therapy
The process of replacing defective gene responsible for hereditary disease by the normal gene is called gene therapy.
Gene cloning
The technique to produce identical copies of a particular segment of DNA or a gene.
Question. How is a mature, functional insulin hormone different from its pro-hormone form?
Answer : Mature functional insulin is obtained by processing of pro-hormone which contains extra peptide called C-peptide. This C-peptide is removed during maturation of pro-insulin to insulin.
Question. How have transgenic animals proved to be beneficial in:
(a) Production of biological products?
(b) chemical safety testing?
Answer : (a) Rosie–the transgenic cow, produced human proteins containing human a-lactalbumin.
Transgenic animals have been made to produce a-1-antitrypsin used to treat emphysema.
(b) Toxicity testing – Transgenic animals are more sensitive to toxic substances, so the results are obtained in less time.
Question. Explain how a hereditary disease can be corrected. Give an example of first successful attempt made towards correction of such diseases.
Answer : A hereditary disease can be corrected by gene therapy. In this method, normal genes are inserted into a person’s cells and tissues to treat a disease.
The first successful attempt for gene therapy was done for adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency.
Question. A person is born with a hereditary disease, suggest the possible corrective method for it.Illustrate by giving a specific example.
Answer : The possible corrective method is gene therapy.
For example, ADA (Adenosine deaminase) deficiency has been treated through gene therapy.
Lymphocytes from the blood of the patient are grown in a culture. A functional ADA cDNA is introduced into these lymphocytes, which are subsequently returned to the patient. The permanent cure is done by introducing ADA cDNA into cells at early embryonic stages.
Question. How did an American Company, Eli Lilly use the knowledge of rDNA technology to produce human insulin?
Answer : Two chains of DNA sequence corresponding to A and B chains of human insulin were prepared.
They introduced them into plasmids of E. coli to produce separate A and B chains. TheA and B chains extracted were then combined by creating disulphide bonds and form human insulin.
Question. (a) Mention the cause and the body system affected by ADA deficiency in humAnswer :
(b) Name the vector used for transferring ADA-DNA into the recipient cells in humAnswer : Name the recipient cells.
Answer : (a) The cause is the defective gene not producing ADA. The immune system is affected.
(b) A retroviral vector is used, recipient cells are lymphocytes.
Question. Why is the functional insulin thus produced considered better than the ones used earlier by diabetic patients?
Answer : The insulin prepared by rDNA technology does not produce sensitive allergic reactions and immunological reactions whereas those used earlier produced allergic reactions and other complications to the foreign protein as earlier they were extracted from pancreas of slaughtered cattle or pigs.
Question. How is ‘Rosie’ considered different from a normal cow? Explain.
Answer : Rosie is a transgenic cow.
Rosie produces human protein-enriched milk containing human a -lactalbumin.
Question. (a) Tobacco plants are damaged severely when infested with Meloidogyne incognita. Name and explain the strategy that is adopted to stop this infestation.
(b) Name the vector used for introducing the nematode specific gene in tobacco plant.
Answer : (a) Gene expression can be controlled by using RNA molecule and this technology is called RNA interference or RNAi or gene silencing. During this process nematode specific gene is introduced into host plant (using Agrobacterium) which produces dsRNA. This silences specific mRNA of the nematode and parasite dies.
(b) Agrobacterium tumifaciens.
Question. How is PCR used to detect gene mutation in case of suspected cancer patient?
Answer : A single stranded small DNA or RNA is tagged with radioactive molecule to be used as a probe.The probe is hybridised with DNA in cancer cells, to be followed by autoradiography. The clone with mutated gene will not appear in the autoradiography, because the probe will not have the complementary sequence with mutated gene.
Question. How is ‘Rosie’ considered different from a normal cow ? Explain.
Answer : Rosie is a transgenic cow.
Rosie produced human protein enriched milk, containing human alpha – lactalbumin.
Question. (a) While cloning vectors, which of the two will be preferred by biotechnologists – bacteriophages or plasmids. Justify with reason.
(b) Name the first transgenic cow developed and state the improvement in the quality of the product produced by it.
Answer : (a) Bacteriophages, because they have very high copy numbers of their genome within the bacterial cells whereas some plasmids may have only one or two copies per cell and others may have 15-100 copies per cell.
(b) Rosie, it produced human protein-enriched milk (2.4 gms per litre).
Question. What is Biopiracy ? State the initiative taken by the Indian Parliament towards it.
Answer : (i) Use of bio resources without authorisation, compensation.
(ii) The govt. has cleared patent terms, emergency provisions, research and development initiative.
Detailed Answer :
(i) Bio-piracy is defined as the illegal commercial utilization of biological material of a country by organisations or multinational companies without proper authorisation from the concerned countries.
Question. (a) What are transgenic animals ?
(b) Name the transgenic animal having the largest number amongst all the existing transgenic animals.
(c) Mention any three purposes for which these animals are produced.
Answer : (a) Animals that have had their DNA manipulated to possess and express an extra / foreign gene.
(b) Mice.
(c) (i) Normal physiology and development.
(ii) Study of disease.
(iii) Biological products.
(iv) Vaccine safety.
(v) Chemical safety testing. (Any three)
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. Define transgenic animals. Explain in detail any four areas where they can be utilised.
Answer : Animals that have had their DNA manipulated to possess and express an extra (foreign) gene are known as transgenic animals. Following are the four main areas where they can be utilised (i) To Study Normal Physiology and Development These animals can be used to study that which factor/gene products are needed at what time of development. By the expression of certain genes, they help scientists to understand the normal gene expression at various stages of growth and development. (ii) Study of Diseases Transgenic animals can be created to serve as models for various human diseases. They also help us to understand the involvement of various genes in diseases like cancer, Parkinson’ disease etc. (iii) Vaccine Safety Transgenic animals can be used to test vaccines like polio vaccine. Transgenic mice have shown promising results in this area and would replace the vaccine testing on monkeys in the years to come. (iv) Chemical Safety Testing Transgenic animals are created which are more sensitive to certain chemicals/drugs. These are used to study the toxicity or side effects of that chemical/drug. The advantage is that we get results faster.
Question. You have identified a useful gene in bacteria. Make a flow chart of the steps that you would follow to transfer this gene to a plant.
Answer : After identifying a useful gene in bacteria, following steps should be followed (i) Isolation of useful gene using restriction endonucleases ¯ (ii) Transferring the gene to a suitable vector to create a recombinant DNA molecule ¯ (iii) Transfer of these recombinant DNA molecules to the target cells. ¯ (iv) Screening of cells for transformation ¯ (v) Selection of transformed cells ¯ (vi) Regeneration of plants from the transformed cells to get transgenic plants.
Question. What is meant by the term biopesticide? Name and explain the mode of action of a popular biopesticide.
Answer : Biopesticide is a pesticide which is (i) Not chemical in nature. (ii) More specific in action against the pest. (iii) Safer for environment than chemical pesticides. A popularly known bio-pesticide is Bt toxin, which is produced by a bacterium called Bacillus thuringiensis. Bt toxin gene has been cloned from this bacterium and expressed in plants. Bt toxin protein when ingested by the insect, gets converted to its active form due to the alkaline pH of the gut. The activated toxin binds to the surface of midgut epithelial cells and create pores that causes swelling and lysis of the cell and eventually kills the insect.
Question. Name the five key tools for accomplishing the tasks of recombinant DNA technology. Also mention the functions of each tool.
Answer : The key tools for accomplishing the tasks of recombinant DNA technology with their functions are mentioned below (i) Restriction endonucleases for cutting the desired DNA at desired places. (ii) Gel electrophoresis for separating the desired DNA fragments. (iii) Ligase enzyme for creating recombinant DNA molecule. (iv) DNA delivery system like electroporation, microinjection, gene gun method, etc. (v) Competant host (usually bacteria/yeast) to take up the recombinant DNA.
Question. Highlight five areas where biotechnology has influenced our lives.
Answer : Biotechnology has influenced our lives in the following ways (i) It has provided us with genetically modified crops of better quality and high nutritive value. (ii) It has made better and safer recombinant vaccines available to the human. (iii) It has helped to develop transgenic animals that can produce human proteins. (iv) It has enabled the cure of genetic diseases using gene therapy. (v) Environment pollution has also been taken care of with the help of genetically engineered microbes.
Question. Name the process involved in the production of nematode-resistant tobacco plants, using genetic engineering. Explain the strategy adopted to develop such plants.
Answer : The process involved in the production of nematode-resistant plants is RNA interference or RNAi. Using Agrobacterium vectors, nematode-specific genes were introduced into the host plant. The introduction of DNA was such that it produced both sense and antisense RNA in the host cells. These two RNA’s being complementary to each other formed a double stranded RNA (dsRNA) that initiated RNAi and thus, silenced the specific mRNA of the nematode. The consequence was that the parasite could not survive in a transgenic host expressing specific interfering RNA. The transgenic plant, therefore, got itself protected from the parasite.
Question. How have biotechnologists effectively used Agrobacterium tumefaciens in plants and retroviruses in animals? Explain.
Answer : In plants the tumor inducing (Ti) plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens has been modified into a cloning vector, which is no more pathogenic to the plants, but is still able to use the mechanisms to deliver genes of our interest into a variety of plants. In animals retroviruses have been disarmed and are used to deliver desirable genes into animal cells. Once a gene or a DNA fragment has been ligated into a suitable vector it is transferred into a bacterial/plant or animal host (where it multiples).
Question. How has the use of Agrobacterium as vectors helped in controlling Meloidogyne incognitia infestation in tobacco plants? Explain in correct sequence.
Answer : By using Agrobacterium vectors, nematode-specific genes were introduced into the host plants which produce both sense and anti-sense RNA in the host cells.
These two RNAs are complementary to each other and form a double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) that initiates RNAi and hence silence the specific mRNA of the nematode.
The parasite cannot survive in the transgenic host, so protects the plants from pests.
Question. Gene expression can be controlled with the help of RNA molecule. Explain the method with an example.
Answer : Gene expression can be controlled by using RNA molecule and this technology is called RNA interference or RNAi. It is used to block the expression of certain genes and also referred to as gene silencing. During this process, RNA complementary to mRNA being produced by the gene, is introduced into the cell. This RNA binds to the mRNA making it double stranded and therefore stops its translation. Resistance to nematode Meloidogyne incognita in tobacco has been achieved by this method.
Question. Explain the synthesis of genetically engineered human insulin.
Answer : Genetically engineered insulin
- Insulin contains two short polypeptide chains—chain A and chain B linked by disulphide bridges.
- In mammals, insulin is synthesised as a pro-hormone (that needs to be processed to become mature and functional hormone). It contains an extra stretch called C peptide.
- C peptide is absent in mature insulin and is removed during maturation into insulin.
- Earlier, insulin was extracted from pancreas of slaughtered cattle and pigs but some patients began developing allergies.
- Disadvantages of extracting insulin from animals:
(i) Insulin being a hormone is produced in very little amounts in the body. Hence, a large number of animals need to be sacrificed for obtaining small quantities of insulin. Thismakes the cost of insulin very high, demand being manifold higher than supply.
(ii) Slaughtering of animal is not ethical.
(iii) There is potential of immune response in humans against the administered insulin which is derived from animals.
(iv) There is possibility of slaughtered animals being infested with some pathogen which may contaminate insulin.
Question. Recombinant DNA-technology is of great importance in the field of medicine. With the help of a flow chart, show how this technology has been used in preparing genetically engineered human insulin.
Answer :
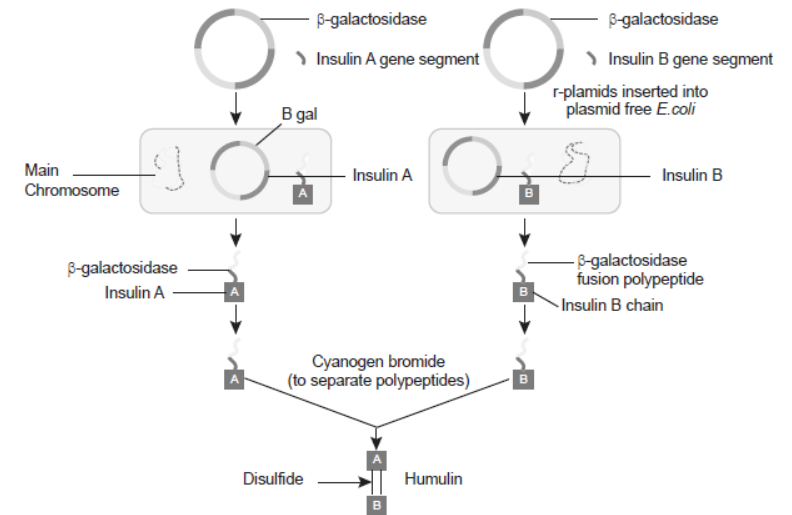
Question. How did Eli Lilly synthesise the human insulin? Mention one difference between this insulin and the one produced by the human pancreas.
Answer : Eli Lilly prepared two DNA sequences corresponding to A and B chains of human insulin and introduced them in plasmids of E. coli to produce insulin chains. Chains A and B were produced separately, extracted and combined by creating disulfide bonds to form human insulin. Insulin in human pancreas is synthesised as a pro-hormone containing the C peptide, which is removed to form mature hormone. The synthesised insulin did not contain C peptide and was directly prepared in mature form.
Question. A person is born with a hereditary disease with a weakened immune system due to deficiency of an enzyme. Suggest a technique for complete cure for this disease, identify the deficient enzyme and explain the technique used for cure.
Answer : Gene therapy can completely cure this disease.
The disease is due to ADA (Adenosine deaminase) deficiency.
Lymphocytes from the blood of the patient are grown in a culture. A functional ADA cDNA is introduced into these lymphocytes, which are subsequently returned to the patient. The permanent cure is done by introducing ADA cDNA into cells at early embryonic stages.
Question. (a) How do organic farmers control pests? Give two examples.
(b) State the difference in their approach from that of conventional pest control methods.
Answer : (a) By natural predation or biological control.
Examples: Lady bird used to kill aphids, dragon flies used to kill mosquitoes, Bacillus thuringiensis used to kill cotton bollworm.
| Conventional pest control | Organic farming based pest control |
| Use of chemical insecticides and pesticides. | No chemical used. |
| Harmful to non-target organisms. | Not harmful to non-target organisms. |
| Cause environmental pollution. | No adverse impact on environment. |
Question. (a) Why are transgenic animals so called?
(b) Explain the role of transgenic animals in (i) Vaccine safety and (ii) Biological products with the help of an example each.
Answer : (a) Transgenic animals are so called because these animals have their DNA manipulated.
(b) (i) Vaccine safety: Transgenic mice are developed to test safety of polio vaccine before being used on humAnswer :
(ii) Human protein (α-1-antitrypsin) is used to treat emphysema.
Question. List the three molecular diagnostic techniques that help detect pathogens from suspected patients. Mention one advantage of these techniques over conventional methods.
Answer : The three molecular diagnostic techniques that help to detect pathogens from suspected patients are:
(a) Recombinant DNA technology
(b) Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
(c) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
These techniques are better than the conventional methods because they help in early diagnosis of the disease even when the bacteria or virus concentration is very low & no symptoms are visible for the disease.
Question. (a) Name the source from which insulin was extracted earlier. Why is this insulin no more in use by diabetic people?
(b) Explain the process of synthesis of insulin by Eli Lilly Company. Name the technique used by the company.
(c) How is the insulin produced by human body different from the insulin produced by the above mentioned company?
Answer : (a) Earlier, insulin was extracted from pancreas of slaughtered cattle and pig. This insulin is not in use as some patients developed allergic reaction to this foreign protein.
(b) Eli Lilly used the following procedure for insulin synthesis:
(i) Two DNA sequences corresponding to A and B chains of insulin were prepared.
(ii) These sequences were then introduced in plasmids of E. coli.
(iii) The two insulin chains are produced separately.
(iv) The two chains are extracted and combined by creating disulphide bonds to form the assembled mature molecule of insulin.
(c) The pro-hormone produced in the human body has an extra stretch of C-peptide.
Question. (a) Why is Bacillus thuringiensis considered suitable for developing GM plants?
(b) Explain how it has been used to develop GM crops.
Answer : (a) Some strains of Bacillus thuringiensis produce proteins that kill some insects like lepidopterans (tobacco budworm, armyworm), coleopterans (beetles) and dipterans (flies, mosquitoes). Bt toxins are initially inactive protoxins but after ingestion by the insect their inactive toxin becomes active due to the alkaline pH of the gut which solublise the crystals. The activated toxin binds to the surface of midgut epithelial cells thus creating pores which causes cell swelling and lysis, further leading to death of the insects.
(b) Bacillus thuringiensis produces Cry protein. Cry protein producing gene is transferred to the plant to provide resistance against insect larvae. Man has developed several transgenic crops by introducing these genes from bacteria to crop plants such as Bt cotton, Bt corn, etc.
Question. Explain the different uses of biotechnology in medical field.
Answer : (i) The recombinant DNA technology is used for production of therapeutic drugs which are safe and effective.
(ii) About thirty recombinant therapeutics have been approved for human use in the world including India.
(iii) The genetically engineered insulin helps in maintaining the glucose–glycogen balance in the body.
(iv) Gene therapy treatment is used in the defective heredity by introduction of normal healthy and functional genes.
(v) It is used in the treatment of diseases like cystic fibrosis, haemophilia, AIDS, cancer, Parkinson’s, etc.
(vi) Due to advancement in the field of biotechnology, it is now possible to develop recombinant vaccines with specific actions and less side effects.
(vii) Also, monoclonal antibodies are produced with high specificity, for specific antigens and are ideal for diagnosis of specific diseases. One of the major role of these monoclonal antibodies is immune suppression for kidney transplantation.
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Organisms And Populations Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Organisms And Populations Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Worksheet Set C |
Worksheet for CBSE Biology Class 12 Chapter 10 Biotechnology and Its Application
We hope students liked the above worksheet for Chapter 10 Biotechnology and Its Application designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 12 Biology released by CBSE. Students of Class 12 should download in Pdf format and practice the questions and solutions given in the above worksheet for Class 12 Biology on a daily basis. All the latest worksheets with answers have been developed for Biology by referring to the most important and regularly asked topics that the students should learn and practice to get better scores in their class tests and examinations. Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to the NCERT book for Class 12 Biology to develop the Biology Class 12 worksheet. After solving the questions given in the worksheet which have been developed as per the latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 12 Biology designed by our teachers. We have also provided a lot of MCQ questions for Class 12 Biology in the worksheet so that you can solve questions relating to all topics given in each chapter.
You can download the CBSE Printable worksheets for Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Biotechnology and Its Application for latest session from StudiesToday.com
There is no charge for the Printable worksheets for Class 12 CBSE Biology Chapter 10 Biotechnology and Its Application you can download everything free
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all latest NCERT Chapter 10 Biotechnology and Its Application Class 12 Biology test sheets with answers based on the latest books for the current academic session
CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Biotechnology and Its Application worksheets cover all topics as per the latest syllabus for current academic year.
Regular practice with Class 12 Biology worksheets can help you understand all concepts better, you can identify weak areas, and improve your speed and accuracy.

