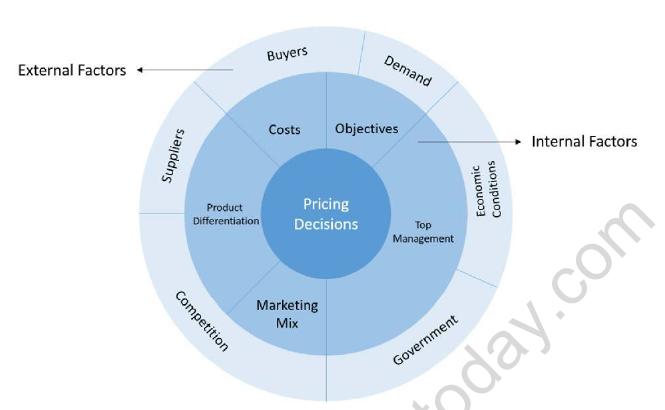
The decisions related to price and pricing policies of a firm are affected by several factors present in marketing environment. A firm plans production keeping in view the customers' needs, market characteristics, competing firms, behaviour of suppliers and distributors for its product and certain legislative factors. These factors give important inputs to the management for marketing-decisions. A firm also gives due consideration to these factors while determining price of the product. These are studied under two categories-
• Internal factors
• External factors
A. Internal factors
Internal factors are the forces which are within the control of a firm up to certain extent. The firm can regulate and change these factors as per requirement. For example all the P’s of marketing mix, procurement of raw material, employment of labour and cost of production etc. not only determine the success of firm’s operations, but also have great influence on product pricing.
The factors can be discussed as following-
(a) Objectives of the firm: A firm may have various objectives and pricing contributes in achieving them. Firms may pursue different objectives such as maximizing revenue, maximizing profit, maximizing market share or maximizing customer satisfaction. The Pricing policy should be established only after clear consideration of the firm’s objectives.
(b) Role of Top Management: Usually, it is the top management that takes a firm’s pricing decisions. But pricing activities are so crucial for future sales and profits that a marketing manager has to remain involved with the pricing. The role of the marketing manager is to assist the top management in price-determination and ensure that pricing takes place within the policies laid down by top-management.
(c) Cost of the Product: There is a direct relation between the cost of production and price of a product. If the cost of acquiring material and manufacturing cost of the product are high, the price of the product in the market will also be higher and vice versa. The firm should also fix prices that are realistic, considering current demand and competition in the market.
(d) Product Differentiation: The price of a product also depends upon its specifications. Generally, producers add more and more features to their products to attract customers, and the customers pay a price for them. Therefore, a highly differentiated product will have more features and attributes, and a higher price than one which is less-differentiated.
(e) Marketing Mix: Price being an important element of the marketing-mix must be coordinated with the other elements- product, place and promotion. The price should be such that it covers the expenses on the other elements of the marketing mix and corresponds to them ideally. For example- a high-priced branded electronic product should be sold in high-end urban showrooms instead of rural markets; the promotion technique should be TV-advertising and not personalselling, etc.
(f) Size of the organization: If the size of firm is big and the scale of production is large, it can afford to set lower product price and increase its sales. On the other hand small sized firm keep high price of its products.
(g) Location of the organization: Location of the organization is an important determinant of the price of a product. The price and product-size will vary depending upon whether the market is located in a rural or urban area. For
example, in the kirana stores in smaller towns and villages, one will find the ₹1 or ₹2 shampoo-sachets instead of a big 200ml or 250ml bottle found in departmental stores in a large city of the same shampoo.
(h) Nature of Goods: If product is necessity good, firm may set a moderate price keeping in view social welfare purpose; but if the product is luxury good in nature
and is being demanded by high end consumers; its price will be high.
(i) Promotional programs: The extent of promotional programs and advertisement expenditure also influence the price of a product. If it is huge , the product will have high price and vice-versa.
B. External Factors-
External factors are forces which are beyond control of the firm. A firm cannot alter or change these factors or forces for its advantage.
These factors can be discussed as following-
(a) Demand: The market demand for a product has a direct impact on its pricing. Since demand is affected by prospective buyers, their incomes, tastes and preferences etc., they should be taken into account while making decision of pricing. For an
instance if the demand for a product is inelastic, as in case of necessity goods, a high price may be fixed. But if the demand for a product is elastic, i.e., changeable in response to change in price, the firm should not fix higher prices; rather fix lower prices to grab major market share.
(b) Buyers’ behaviour: Buyers’ behavior also affects the pricing decisions. If they are habitual of the product the price may be fixed high. Similar pricing decisions are taken by the firm, if buyers have a particular perception of the product being a symbol of prestige/ status, or utility, e.g. luxury cars.
(c) Competition: Market-competition plays a crucial role in pricing. In a highlycompetitive market, a seller’s objective is to give maximum utility at minimumpossible price. Each firm tries to outsell others offering lesser price and better
quality products in the market. Therefore, prevailing information about what price the competitors are charging for similar products and what possibilities exist for increasing/decreasing price also affect pricing.
(d) Raw Material or Input suppliers: Pricing decisions take into consideration three parties-the supplier of raw material, the manufacturer, and the final consumer. If the supplier charges a high price for inputs, the manufacturer shifts this burden to the consumer by charging a higher price for the final product. On the other hand, if a manufacturer is making large profit on a particular product, suppliers will also try to cash in on these profits by charging a higher price for the raw material. When this happens, the manufacturer would only want to absorb the additional cost and not increase the prices further.
(e) Prevalent Economic Conditions: During a boom-period in the economy, when market-conditions are favourable due to ‘bullish attitude’ or inflationary trend, firms can afford to fix higher prices of their products. On the other hand, during slumpperiod when market-conditions are un-favourable due to ‘bearish attitude’, firms have to lower the prices of products to keep the business going and to clear off their old stocks.
(f) Government Regulations: If Government policies exert regulatory pressures, promote anti-price rise sentiment etc, then the companies cannot fix a higher price to capture the market. On the other hand, if government policies are supportive and promote businesses through healthy competition in the market, then firms can fix higher prices.
Knowledge Assessment – II
Fill in the blanks-
1. The decisions related to price and pricing policies of a firm are affected by --------------present in marketing environment.
2. Firms may pursue different objectives such as maximizing revenue, ------------------, maximizing market share or maximizing customer satisfaction.
3. If the cost of acquiring material and -------------- of the product is high, the price of the product in the market will also be higher.
4. The product price should be such that it covers the -------------on the other elements of the marketing mix.
5. If buyers are habitual of the product the price may be fixed ----------------
6. Favourable market-conditions due to ‘--------------- or inflationary trend, encourage firms to fix higher prices of their products.
7. If the supplier charges a high price for inputs, the manufacturer shifts this burden to the ------------- by charging a higher price for the final product
8. If the demand for a product is inelastic firms fix a -------------of the product.
9. Supportive government policies ------------ businesses through healthy competition.
10.Competitive firm tries to outsell others offering -------------- and better quality products in the market.
Answers: 1.several factors, 2. maximizing profit, 3. manufacturing cost, 4. expenses, 5. High 6. bullish attitude, 7. Consumer, 8.high price, 9. Promote, 10. lesser price
Please click on below link to download CBSE Class 12 Marketing Factors Affecting Pricing Notes

