Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 12 Psychology Meeting Life Challenges Worksheet Set A. Students and teachers of Class 12 Psychology can get free printable Worksheets for Class 12 Psychology Chapter 3 Meeting Life Challenges in PDF format prepared as per the latest syllabus and examination pattern in your schools. Class 12 students should practice questions and answers given here for Psychology in Class 12 which will help them to improve your knowledge of all important chapters and its topics. Students should also download free pdf of Class 12 Psychology Worksheets prepared by teachers as per the latest Psychology books and syllabus issued this academic year and solve important problems with solutions on daily basis to get more score in school exams and tests
Worksheet for Class 12 Psychology Chapter 3 Meeting Life Challenges
Class 12 Psychology students should download to the following Chapter 3 Meeting Life Challenges Class 12 worksheet in PDF. This test paper with questions and answers for Class 12 will be very useful for exams and help you to score good marks
Class 12 Psychology Worksheet for Chapter 3 Meeting Life Challenges
Question. Individual’s reaction to external stressors is called:
(a) Strain
(b) Conflict
(c) Pressure
(d) Frustration
Answer. A
Question. Blocking of needs and motives that cause hindrance in achieving the goal result in:
(a) Stress
(b) Conflict
(c) Frustration
(d) Aggression
Answer. C
Question. Blocking of needs and motives by something or someone that hinders us from achieving desired goal leads to ______________.
(a) Internal pressures
(b) Social pressures
(c) Conflicts
(d) Frustration
Answer. D
Question. Frustration results from:
(a) incompatibility between two or more needs or motives.
(b) blocking of needs and motives
(c) expectations from oneself and others
(d) excessive demands
Answer. B
Question. Rajat is satisfied only if he does everything perfectly. This is an instance of
(a) Social pressure
(b) Internal pressure
(c) conflict
(d) Social stress
Answer. B
Question. The state of complete physical, emotional and psychological exhaustion is known as_____________.
(a) Resistance
(b) Stress
(c) Burnout
(d) Coping
Answer. C
Question. Making changes in oneself or surrounding like managing time better is an example of:
(a) Task-oriented strategy
(b) Avoidance-oriented strategy
(c) Emotion-oriented strategy
(d) None of the above
Answer. A
Question. _____________ are method for coping with stress.
(a) Relaxation training
(b) Meditation procedures
(c) Biofeedback
(d) All of the above
Answer. D
Question. Creative visualisation is a subjective experience that uses imagery and _____________.
Answer. Imagination
Question. _____________ results from blocking of anticipated desirable goal.
Answer. Frustration
Question. ____________ is the term to describe stress level that helps in achieving peak performance.
Answer. Eustress
Question. Psychoneuroimmunology focuses on the links between the mind, the brain and the________________.
Answer. Immune system
Question. The term ‘stress’ has been originated from the Latin word ____________ meaning ____________.
Answer. Strictus, tight or narrow
Question. Putting off what we know we need to do is called _____________.
Answer. Procrastination
Question. Frustration is one source of psychological stress. (True/False)
Answer. True/False Ambiguous statement, both are correct.
Question. State the symptoms and sources of stress.
Answer. Response to stress varies depending upon personality of an individual. Every person has his/her own pattern of stress response. Warning signs of stress vary from individual to individual depending upon intensity. Physical symptoms of stress can be palpitation or sweating, emotional symptoms can be confusion and irritability which are manifested in behavioural symptoms such as withdrawal or restlessness. If any of these symptoms is left unresolved, they may lead to suicide, burnout, a psychological disorder or a medical disease.
The various sources of stress are:
(i) Life Events: Changes due to life events such as moving into a new house, break-up of a long-term relationship cause stress.
(ii) Hassles: Happenings in our daily lives such as noisy surroundings, commuting, quarrelsome neighbours, electricity and water shortage, traffic snarls cause stress.
Attending to various emergencies are daily hassles experienced by a housewife.
(iii) Traumatic Events: Effects of extreme events such as fire, train or road accident, robbery, earthquake, tsunami persist as symptoms of anxiety, flashbacks, dreams and intrusive thoughts. Severe trauma can also strain relationships or can lead to disorders such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Question. Enumerate the different ways of coping with stress.
Answer. The three coping strategies given by Endler and Parker are:
(i) Task-oriented Strategy: This involves using alternate courses of action for coping.For example, scheduling your time better or using better methods to solve problems.
(ii) Emotion-oriented Strategy: This involves venting feelings of anger and frustration or deciding that nothing can be done to change things. For example, to stop worrying.
(iii) Avoidance-oriented strategy: This involves denying or minimizing the seriousness of the situation. It involves conscious suppression of stressful thoughts and their replacement by self-protective thoughts. Examples of this are watching TV, phone up a friend or try to be with other people.
According to Lazarus and Folkman the coping responses are of two types:
(i) Problem-focused strategies: These strategies attack the problem itself with behaviours designed to gain information, to alter the event and to alter belief and commitments.
For example, to make a plan of action.
(ii) Emotion-focused strategies: These call for psychological changes designed primarily to limit the degree of emotional disruption caused by an event, with minimal effort to alter the event itself. For example, to do things to let it out of your system.
Question. Discuss the factors that lead to positive health and well-being.
Answer. Positive health includes good physical, mental, social and spiritual well-being. This includes a healthy body free from disease, effective personal relationships, a sense of purpose in life, self-regard, and resilience to stress. This requires maintain of the following:
(i) Diet: A balanced diet can lift one’s mood, give more energy, feed muscles, improve circulation, prevent illness, strengthen the immune system and make one feel better to cope with stresses of life. The key to healthy living is to eat three main meals a day and eat a varied well-balanced diet.
(ii) Exercise: Regular exercise manages stress, reduces tension, anxiety and depression.It helps the individual to maintain good physical and mental health. Exercise requires changing one’s life-style. These produce a calming effect and may include yoga, aerobic exercises, jogging, swimming and cycling.
(iii) Positive Attitude: Some of the factors leading to a positive attitude are: having a fairly accurate perception of reality; a sense of purpose in life and responsibility; acceptance and tolerance for different viewpoints of others; and taking credit for success and accepting blame for failure. Finally, being open to new ideas and having a sense of humour with the ability to laugh at oneself help us to see things in a proper perspective.
(iv) Positive Thinking: This involves being an optimist and avoid having a pessimistic outlook towards life. Optimists use problem-focused strategies, seek help and advice from others.
(v) Social support: Availing social support leads to less medical and psychological complications such as observed in pregnant women who after getting social support and protection against stress cope life more successfully. The types of social support are tangible support, information support and emotional support. Tangible support involves assisting one with money, goods and services such as providing notes to a friend who has been absent. Information support is providing one with certain resources such as a student who has appeared in a board exam helps his friend in telling him how the board exams are conducted. Emotional support helps to overcome anxiety, loss of self-esteem by the ones who love and care for you. Social support reduces psychological distress, depression or anxiety during times of stress. It helps in providing psychological well-being.
Question. Give an example of a life event which is likely to be stressful. Suggest reasons why it is likely to cause different degrees of stress to the person experiencing it.
Answer. Life Events which are likely to be stressful are like moving into a new house, break-up of a long-term relationship cause stress. The stresses or the dimensions of stressors which people experience vary in terms of intensity (low intensity vs. high intensity), duration (short-term vs. long-term), complexity (less complex vs. more complex) and predictability (unexpected vs. predictable). The outcome of stress depends on the position of a particular stressful experience along these dimensions. Usually more intense, prolonged or chronic, complex and unanticipated stresses have more negative consequences than less intense, short-term, less complex and expected stresses. An individual’s experiences of stress depend on the physiological strength of that person. Thus, individuals with poor physical health and weak constitution would be more vulnerable than those who enjoy good health and strong constitution.
Question. Given what you know about coping strategies, what suggestions would you give to your friends to avoid stress in their everyday lives.
Answer. Stress can be avoided in everyday lives by using one or the other of the following strategies:
(i) Using alternate courses of action for coping. For example, scheduling your time better or using better methods to solve problems.
(ii) Venting feelings of anger and frustration or deciding that nothing can be done to change things. For example, to stop worrying.
(iii) Denying or minimizing the seriousness of the situation. It involves conscious suppression of stressful thoughts and their replacement by self-protective thoughts.Examples of this are watching TV, phone up a friend or try to be with other people.
(iv) Attacking the problem itself with behaviours designed to gain information, to alter the event and to alter belief and commitments. For example, to make a plan of action.
(v) Limiting the degree of emotional disruption caused by an event, with minimal effort to alter the event itself. For example, to do things to let it out of your system.
Question. We know that certain lifestyle factors can cause stress and may lead to diseases like cancer and coronary heart disease, yet we are unable to change our behaviour. Explain why?
Answer. Stress can lead to unhealthy lifestyle or health damaging behaviour. Lifestyle is the overall pattern of decisions and behaviours that determine a person’s health and quality of life. Stressed individuals may be more likely to expose themselves to pathogens, which are agents causing physical illness. People who are stressed have poor nutritional habits, sleep less and are likely to engage in other health risking behaviours like smoking and alcohol abuse. Such health impairing behaviours develop gradually and are accompanied by pleasant experiences temporarily.
CBSE Class 12 Psychology Chapter 3 Meeting Life Challenges Very Short Answer Questions
Question. Give the causes of environmental stress.
Answer. Environmental stresses are caused by air pollution, crowding, noise, heat of the summer, winter cold or disasters such as fire, earthquake, floods etc.
Question. Explain the term ‘frustration’.
Answer. Frustration results from blocking of needs and motives while achieving a desired goal.Causes of frustration are social discrimination, interpersonal hurt or low grades in school.
Question. Explain the term ‘conflict’.
Answer. Conflicts occur between two or more incompatible needs or motives, e.g. whether to learn dance or study psychology.
Question. What is task-oriented coping?
Answer. Task-oriented coping involves using alternate courses of action for coping. For example, scheduling your time better or using better methods to solve problems.
Question. Explain emotion-oriented coping strategy.
Answer. Emotion-oriented strategy involves venting feelings of anger and frustration or deciding that nothing can be done to change things. For example, to stop worrying.
Question. Discuss avoidance-oriented strategy of coping.
Answer. Avoidance-oriented strategy involves denying or minimizing the seriousness of the situation. It involves conscious suppression of stressful thoughts and their replacement by self-protective thoughts. Examples of this are watching TV, phone up a friend or try to be with other people.
Question. Explain biofeedback.
Answer. Biofeedback is a type of Stress Management Technique which involves three stages: developing an awareness of the particular physiological response, e.g. heart rate, learning ways of controlling that physiological response in quiet conditions; and transferring that control into the conditions of everyday life.
Question. What do you understand by Resilience ?
Answer. Resilience is a dynamic development process referring to the maintenance of positive adjustment under challenging life conditions. Resistance has been conceptualised as reflecting feelings of self-worth and self-confidence, autonomy and self-reliance, finding positive role models, feeling a close friend, cognitive skills such as problem-solving, creativity, resourcefulness and flexibility and a belief that one’s life has purpose and meaning effects of trance, stress and adversity and leave to live psychologically healthy and meaningful lives for a child to be resilient, s/he needs to have more than one of these strengths; social, interpersonal strengths, inner strengths, interpersonal and problem-solving skills.
Question. Explain the role of social support in promoting positive health and well-being.
Answer. Emotional support helps to overcome anxiety, loss of self-esteem by the availability of people on whom we can rely upon, those who love, care and value us. Social support reduces psychological distress, depression or anxiety during times of stress. It helps in promoting positive health and providing psychological well-being.
CBSE Class 12 Psychology Chapter 3 Meeting Life Challenges Short Answer Questions-I
Question. What are the signs and symptoms of stress?
Answer. Response to stress varies depending upon personality of an individual. Every person has his/ her own pattern of stress response. Warning signs of stress vary from individual to individual depending upon intensity. Physical symptoms of stress can be palpitation or sweating, emotional symptoms can be confusion and irritability which are manifested in behavioural symptoms such as withdrawal or restlessness. If any of these symptoms are left unresolved, they may lead to suicide, burnout, a psychological disorder or a medical disease.
Question. Explain the functioning of the Immune system.
Answer. The white blood cells (leucocytes) within the immune system identify and destroy foreign bodies (antigens) such as viruses. It also leads to the production of antibodies. There are several kinds of white blood cells or leucocytes within the immune system, including T cells, B cells and natural killer cells. T cells destroy invaders, and T-helper cells increase immunological activity. It is these T-helper cells that are attacked by the Human Immuno Deficiency Virus (HIV), the virus causing Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS). B cells produce antibodies. Natural killer cells are involved in the fight against both viruses and tumours.
Question. Explain the strategies to cope with stress. Give examples from daily life.
Answer. The three coping strategies given by Endler and Parker are:
(i) Task-oriented Strategy: This involves using alternate courses of action for coping.For example, scheduling your time better or using better methods to solve problems.
(ii) Emotion-oriented Strategy: This involves venting feelings of anger and frustration or deciding that nothing can be done to change things. For example, to stop worrying.
(iii) Avoidance-oriented strategy: This involves denying or minimizing the seriousness of the situation. It involves conscious suppression of stressful thoughts and their replacement by self-protective thoughts. Examples of this are watching TV, phone up a friend or try to be with other people.
According to Lazarus and Folkman the coping responses are of two types:
(a) Problem-focused Strategies: These strategies attack the problem itself with behaviours designed to gain information, to alter the event and to alter belief and commitments. E.g., to make a plan of action.
(b) Emotion-focused Strategies: These call for psychological changes designed primarily to limit the degree of emotional disruption caused by an event, with minimal effort to alter the event itself. E.g., to do things to let it out of your system.
Question. How social support can lead to positive health and well-being? Discuss.
Answer. Availing social support leads to less medical and psychological complications such as observed in pregnant women, who by getting social support and protection against stress cope life more successfully. The types of social support are tangible support, information support and emotional support. Tangible support involves assisting one with money, goods and services such as providing notes to a friend, who has been absent. Information support is providing one with certain resources such as a student who has appeared in a board exam helps his friend in telling him how the board exams are conducted. Emotional support helps to overcome anxiety, loss of self-esteem by the ones who love and care for you. Social support reduces psychological distress, depression or anxiety during times of stress. It helps in providing psychological well-being.
CBSE Class 12 Psychology Chapter 3 Meeting Life Challenges Short Answer Questions-II
Question. Describe the cognitive theory of stress (primary appraisal and secondary appraisal).
OR
Describe Lazarus general model of stress appraisal.
Answer. The perception of stress is dependent upon the individual’s cognitive appraisal which is of two types, primary and secondary. Primary appraisal refers to the perception of a new or changing environment as positive, neutral or negative in its consequences. Negative events are appraised for their possible harm, threat or challenge. Harm is the assessment of the damage that has already been done by the event. Threat is the assessment of the possible future damage that may be brought about by the event. Challenge is associated with expectations of the ability to cope with the stressful event. Secondary appraisal is the assessment of one’s coping abilities and resources and whether they will be sufficient to meet the harm, threat or challenge of the event.
Question. Explain the concept of stress giving examples from daily life.
Answer. Stress is described as the pattern of responses an organism makes to stimulus event that disturbs the equilibrium and exceeds a person’s ability to cope. Stressors like noise, crowding, a bad relationship, daily commuting to school or office are events that cause our body to give the stress response. Happenings in our daily lives such as noisy surroundings, commuting, quarrelsome neighbours, electricity and water shortage, traffic snarls cause stress. Attending to various emergencies are daily hassles experienced by a housewife.
Question. What are the effects of stress on the psychological functioning of an individual?
Answer. The effects of stress are described as follows:
(i) Emotional Effects: Those suffering from stress experience mood swings, show decreasing confidence, suffer from feelings of anxiety, depression or increased physical and psychological tension.(ii) Physiological Effects: Under stress there is an increased production of hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol. These hormones produce marked changes in heart rate, blood pressure levels, metabolism and physical activity. Changes such as release of epinephrine or nor-epinephrine, slowing down of the digestive system, expansion of air passages in the lungs and constriction of blood vessels also occur. (iii) Cognitive Effects: Cognitive effects of stress are poor concentration and reduced short-term memory capacity.
(iv) Behavioural Effects: These include disrupted sleep patterns, increased absenteeism and reduced work performance.
Question. What is GAS? How does Selye’s model relate prolong stress to bodily response. Explain.
OR
Explain the reaction of body to stress according to General Adaptation Syndrome.
OR
Describe the GAS model of stress.
OR
Explain stress according to General Adaptation Syndrome, (GAS) model, giving examples from everyday life.
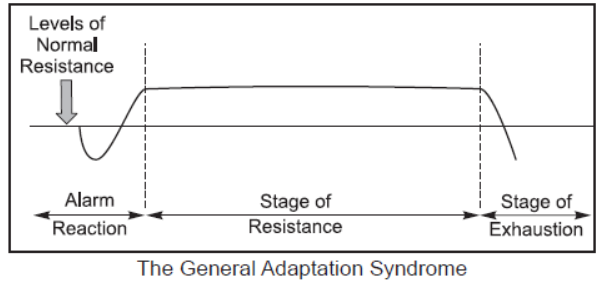
Answer. Selye observed that animals exposed to stressors show a similar pattern of bodily response. He called this pattern General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS).
According to him GAS involves three stages:
(i) Alarm reaction: The presence of a stressor leads to activation of the adrenal-pituitarycortex system. This triggers the release of hormones producing the stress response.
Now the individual is ready for fight or flight.
(ii) Resistance Stage: Under prolonged stress, the para-sympathetic nervous system calls for more cautious use of the body’s resources in which the organism makes efforts to cope with the threat.
(iii) Exhaustion stage: Continued exposure to the same stressor or additional stressors drains the body of its resources and leads to the third stage of exhaustion. The physiological systems involved in alarm reaction and resistance become ineffective and susceptibility to stress-related diseases increases.
Question. Differentiate between problem-focused and emotion-focused coping strategies with examples.
Answer. According to Lazarus and Folkman the coping responses are of two types:
(i) Problem-focused Strategies: These strategies attack the problem itself with behaviours designed to gain information, to alter the event and to alter belief and commitments. For example, to make a plan of action.
(ii) Emotion-focused Strategies: These call for psychological changes designed primarily to limit the degree of emotional disruption caused by an event, with minimal effort to alter the event itself. E.g., to do things to let it out of your system.
Question. Explain briefly four factors which facilitate developments of positive health.
OR
What is positive health? Describe stress buffers that facilitate positive health.
Answer. Positive health includes good physical, mental, social and spiritual well-being. This includes a healthy body free from disease, effective personal relationships, a sense of purpose in life, self-regard, and resilience to stress. This requires maintain of the following:
(i) Diet: A balanced diet can lift one’s mood, give more energy, feed muscles, improve circulation, prevent illness, strengthen the immune system and make one feel better to cope with stresses of life. The key to healthy living is to eat three main meals a day, and eat a varied well-balanced diet.
(ii) Exercise: Regular exercise manages stress, reduces tension, anxiety and depression.It helps the individual to maintain good physical and mental health. Exercise requires changing one’s life-style. These produce a calming effect and may include yoga, aerobic exercises, jogging, swimming and cycling.
(iii) Positive Attitude: Some of the factors leading to a positive attitude are: having a fairly accurate perception of reality; a sense of purpose in life and responsibility; acceptance and tolerance for different viewpoints of others; and taking credit for success and accepting blame for failure. Finally, being open to new ideas and having
a sense of humour with the ability to laugh at oneself help us to see things in a proper perspective.
(iv) Positive Thinking: This involves being an optimist and avoid having a pessimistic outlook towards life. Optimists use problem-focused strategies, seek help and advice from others.
(v) Social Support: Availing social support leads to less medical and psychological complications such as observed in pregnant women who by getting social support and protection against stress cope life more successfully. The types of social support are tangible support, information support and emotional support.Tangible support involves assisting one with money, goods and services such as providing notes to a friend who has been absent.
Information support is providing one with certain resources such as a student who has appeared in a board exam helps his friend in telling him how the board exams are conducted.
Emotional support helps to overcome anxiety, loss of self-esteem by the ones who love and care for you. Social support reduces psychological distress, depression or anxiety during times of stress. It helps in providing psychological well-being.
CBSE Class 12 Psychology Chapter 3 Meeting Life Challenges Long Answer Questions
Question. Explain the nature of stress giving examples. Discuss avoidance-oriented strategy of coping.
Answer. Nature of Stress:
The term ‘stress’ has been originated from the Latin word Strictus, meaning tight or narrow. Stress is described as the pattern of responses an organism makes to stimulus event that disturbs the equilibrium and exceeds a person’s ability to cope. Stressors like noise, crowding, a bad relationship, daily commuting to school or office are events that cause our body to give the stress response.
Eustress describes the level of stress that is good and positive and is one of a person’s best assets for achieving peak performance and managing minor crisis. Distress is the manifestation of stress that causes our body’s wear and tear. It produces unpleasant effects, hampers our productivity, emotionally upsets us and causes our performance to deteriorate.
Stress is often explained in terms of characteristics of the environment that are disruptive to the individual. Stressors are events that cause our body to give the stress response. Such events include noise, crowding, a bad relationship, or the daily commuting to school or office. The reaction to external stressors is called ‘strain’.
OR
Lazarus has distinguished between two types of appraisal, i.e. primary and secondary. The perception of stress is dependent upon the individual’s cognitive appraisal which is of two types, primary and secondary. Primary appraisal refers to the perception of a new or changing environment as positive, neutral or negative in its consequences. Negative events are appraised for their possible harm, threat or challenge. Harm is the assessment of the damage that has already been done by the event. Threat is the assessment of the possible future damage that may be brought about by the event. Challenge is associated with expectations of the ability to cope with the stressful event. Secondary appraisal is the assessment of one’s coping abilities and resources and whether they will be sufficient to meet the harm, threat or challenge of the event.
Selye observed that animals exposed to stressors show a similar pattern of bodily response. He called this pattern General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS). According to him GAS involves three stages Alarm reaction, Resistance Stage and Exhaustion stage. Coping is a dynamic situation-specific reaction to stress. E.g. watching TV, phone up a friend or try to be with other people.
Avoidance-oriented strategy: This involves denying or minimizing the seriousness of the situation. It involves conscious suppression of stressful thoughts and their replacement by self-protective thoughts. Examples of this are watching TV, phone up a friend or try to be with other people.
Question. Describe the techniques that can help manage stress in life.
Answer.
Some of the Stress Management Techniques are described as follows:
(i) Relaxation Techniques: Reduces symptoms of stress and incidence of illness such as high blood pressure and heart diseases. Deep breathing and muscle relaxation is used to relax the mind and body which starts from the lower part of the body and progresses up to the facial muscles.
(ii) Meditation Procedures: This technique refocuses the attention that brings about an altered state of consciousness. This is possible through concentration so that the mediator is unaware of any outside stimulation.
(iii) Biofeedback: This involves three stages: developing an awareness of the particular physiological response, e.g. heart rate, learning ways of controlling that physiological response in quiet conditions; and transferring that control into the conditions of everyday life.
(iv) Creative Visualisation: This involves imagery and imagination for keeping one’s mind quiet, body relaxed and eyes closed. This reduces the risk of interference from unhidden thoughts and provides the creative energy needed for turning an imagined scene into reality.
(v) Cognitive Behavioural Techniques: This approach involves replacing negative and irrational thoughts with positive and rational ones. It includes assessment, stress reduction techniques, and application and follow-through. Assessment involves discussing the nature of the problem and seeing it from the viewpoint of the client. Stress reduction involves learning the techniques of reducing stress such as relaxation and self-instruction.
(vi) Exercise: Regular exercise improves the efficiency of the heart, enhances the function of the lungs, maintains good circulation, lowers blood pressure, reduces fat in the blood and improves the body’s immune system. Swimming, walking, running, cycling, skipping help to reduce stress.
1. What is Eustress?
2. Define the term stress?
3. What is resilience and health?
4. What is positive health and what are the factors facilitating positive health?
5. What is Hardiness and explain the stress resistant personality?
6. What is Psychoneuroimmunology?
7. Define the word Burn-out?
8. Explain the cognitive theory of stress appraisal?
9. What are the coping strategies proposed by Lazarus?
10. What is positive heath and what are the factors affecting positive health?
11. Explain General adaptation syndrome of Hansseyle?
12. What are the various sources of stress?
13. What are the various stress coping strategies proposed by Endler and Parker?
14. What are the various life skills and how they will be helpful in overcoming stress?
15. What the various alternative strategies of stress coping?
16. Explain Post traumatic stress disorder?
17. What are the various observable physical features during stress Explain?
18. What are the various psychological effects of stress on Human beings?
Q1) “Stress is an integral part of our lives and has become a buzz word with every one living”. Define stress and Quote various examples that have created stressful situations in your life. (At least three)
Q2) How is Eustress different from Distress?
Q3) According to Lazarus, “An individual’s response to a stressful situation largely depends upon the perceived events and how they are interpreted”. Comment
Q4) What do you understand by the Burnout syndrome?
Q5) Her parents on having alcohol with her friends scolded Ashmita of 15yrs.She could not take it and ran away from home.
a) What is the coping strategy that Ashmita is using here?
b) Which strategy according to you is would be the best suited in dealing with such a situation?
c) What are the other strategies that Lazarus has given and how would these strategies help in such a situation?
Q6) How are social and psychological are related to each other? Give examples
b) what effects would it have on the psychological functioning of the person?
Q7) “Examination stress can cause test anxiety which can adversely affect stress performance”. Explain with help of examples.
Q8) Explain the techniques developed by Donald Meichenbaum in management of stress.
Q9) “While traveling in a train the passengers got to know that the engine has collapsed and the train is on fire. How does Selye’s theory of bodily responses apply to this situation?
Q10) “Stress is an integral part of individual’s living. Little bit of it is required to ignite an individual’s performance.” Comment.
Q11) Discuss the various factors that help in promoting positive health and well being.
Q12) “According to the various psychologists stress is generated by our own self in our minds. These are personal and unique to the person experiencing them.”
a) Which kind of stress is being discussed here?
b) What are the various sources of such kind of stress? Give a detailed explanations with examples
Q13) “Resilience” has become a buzzword in today’s life. Explain how it can be used to “bounce back” upon the stress one faces in daily life.
Q14) “Stress is a silent killer. It plays a significant role in deteriorating individual’s health.” Explain its adverse effects on the immune system with the help of a diagram.
Q15) With the help of a model, explain the various reactions that may take place due to stress?
| CBSE Class 12 Psychology Variations In Psychological Attributes Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Psychology Self And Personality Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Psychology Self And Personality Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Psychology Meeting Life Challenges Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Psychology Meeting Life Challenges Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Psychology Psychological Disorders Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Psychology Psychological Disorders Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Psychology Therapeutic Approaches Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 12 Psychology Therapeutic Approaches Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 12 Psychology Attitude And Social Cognition Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Psychology Social Influences And Group Processes Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Psychology Developing Psychological Skills Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 12 Psychology Psychology And Life Worksheet |
Worksheet for CBSE Psychology Class 12 Chapter 3 Meeting Life Challenges
We hope students liked the above worksheet for Chapter 3 Meeting Life Challenges designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 12 Psychology released by CBSE. Students of Class 12 should download in Pdf format and practice the questions and solutions given in the above worksheet for Class 12 Psychology on a daily basis. All the latest worksheets with answers have been developed for Psychology by referring to the most important and regularly asked topics that the students should learn and practice to get better scores in their class tests and examinations. Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to the NCERT book for Class 12 Psychology to develop the Psychology Class 12 worksheet. After solving the questions given in the worksheet which have been developed as per the latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 12 Psychology designed by our teachers. We have also provided a lot of MCQ questions for Class 12 Psychology in the worksheet so that you can solve questions relating to all topics given in each chapter.
You can download the CBSE Printable worksheets for Class 12 Psychology Chapter 3 Meeting Life Challenges for latest session from StudiesToday.com
There is no charge for the Printable worksheets for Class 12 CBSE Psychology Chapter 3 Meeting Life Challenges you can download everything free
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all latest NCERT Chapter 3 Meeting Life Challenges Class 12 Psychology test sheets with answers based on the latest books for the current academic session
CBSE Class 12 Psychology Chapter 3 Meeting Life Challenges worksheets cover all topics as per the latest syllabus for current academic year.
Regular practice with Class 12 Psychology worksheets can help you understand all concepts better, you can identify weak areas, and improve your speed and accuracy.

