NCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science Chapter 9 Structured Query Language have been provided below and is also available in Pdf for free download. The NCERT solutions for Class 12 Computer Science have been prepared as per the latest syllabus, NCERT books and examination pattern suggested in Class 12 by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. Questions given in NCERT book for Class 12 Computer Science are an important part of exams for Class 12 Computer Science and if answered properly can help you to get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise answers for NCERT Class 12 Computer Science and also download more latest study material for all subjects. Chapter 9 Structured Query Language is an important topic in Class 12, please refer to answers provided below to help you score better in exams
Chapter 9 Structured Query Language Class 12 Computer Science NCERT Solutions
Class 12 Computer Science students should refer to the following NCERT questions with answers for Chapter 9 Structured Query Language in Class 12. These NCERT Solutions with answers for Class 12 Computer Science will come in exams and help you to score good marks
Chapter 9 Structured Query Language NCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science
Chapter - Structured Query Language
Question 1: Differentiate between delete and drop table command ?
Аnswer: DELETE command is used to remove information from a particular row or rows. If used without any condition, it will delete all row information but not the structure of the table. It is a DML command. DROP table command is used to remove the entire structure of the table and information. It is a DDL command.
Question 2: What is the use of wildcard ?
Аnswer: The wildcard operators are used with the LIKE operator to search a value similar to a specific pattern in a column. There are 2 wildcard operators. % – represents 0,1 or many characters – = represents a single number or character
Question 3: Write SQL query to add a column total price with datatype numeric and size 10, 2 in a table product.
Аnswer: ALTER TABLE product ADD total price number
Question 4: While creating table ‘customer’, Rahul a forgot to add column ‘price’. Which command is used to add new column in the table. Write the command to implement the same.
Аnswer: ALTER TABLE customer ADD price number(10,2)
Question 5: Deepika wants to remove all rows from the table BANK. But he needs to maintain the structure of the table. Which command is used to implement the same ?
Аnswer: DELETE FROM BANK
Question 6: Sonal needs to display name of teachers, who have “0” as the third character in their name.She wrote the following query. Select name from teacher where name = “$$0?”; But the query isn’t producing the result. Identify the problem.
Аnswer: The wildcards are incorrect. The corrected query is SELECT name FROM teacher
WHERE name LIKE’ _ _ 0%’
Question 7: Consider the following tables School and Admin and answer this question :
Give the output the following SQL queries :
1. Select Designation Count (*) From Admin Group By Designation Having Count (*) <2;
2. SELECT max (EXPERIENCE) FROM SCHOOL;
3. SELECT TEACHERNAME FROM SCHOOL WHERE EXPERIENCE >12 ORDER BY TEACHER NAME;
4. SELECT COUNT (*), GENDER FROM ADMIN GROUP BY GENDER
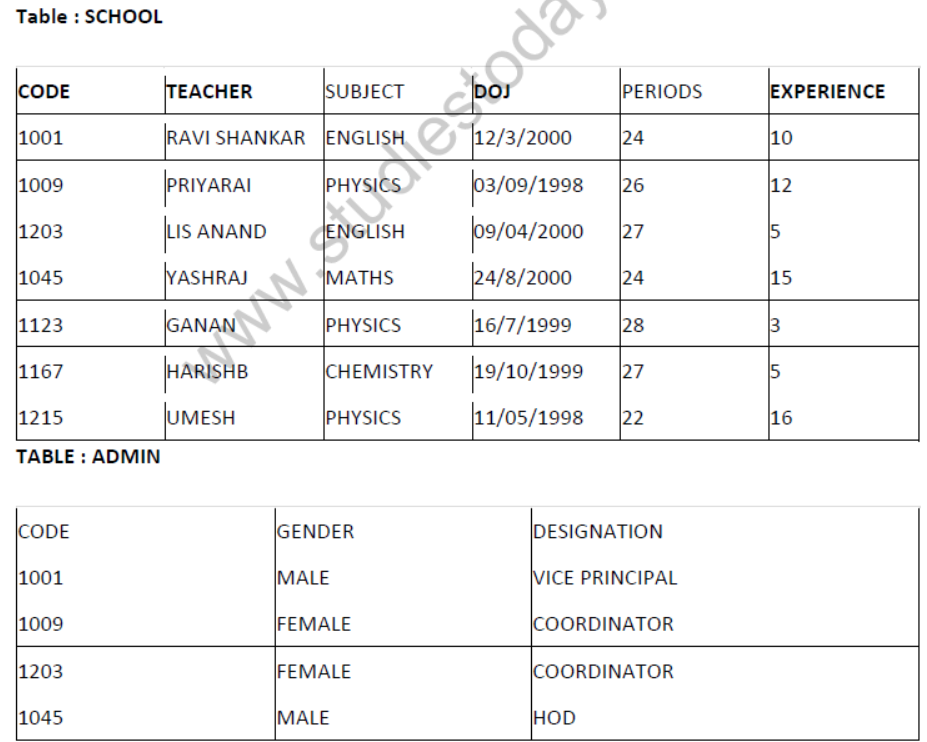
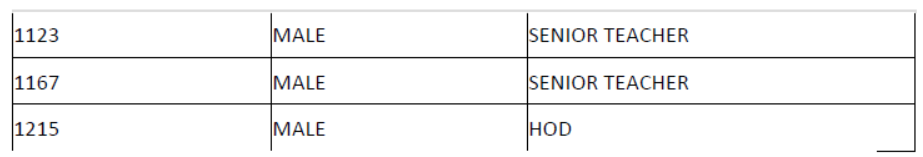
Аnswer:
(i) VICE PRINCIPAL 01
(ii) 16
(iii) UMESH
YASH RAJ
Short Answer Type Questions-II
Question 1: Write SQL queries for (i) to (iv) and find outputs for SQL queries (v) to (viii), which are based on the tables.
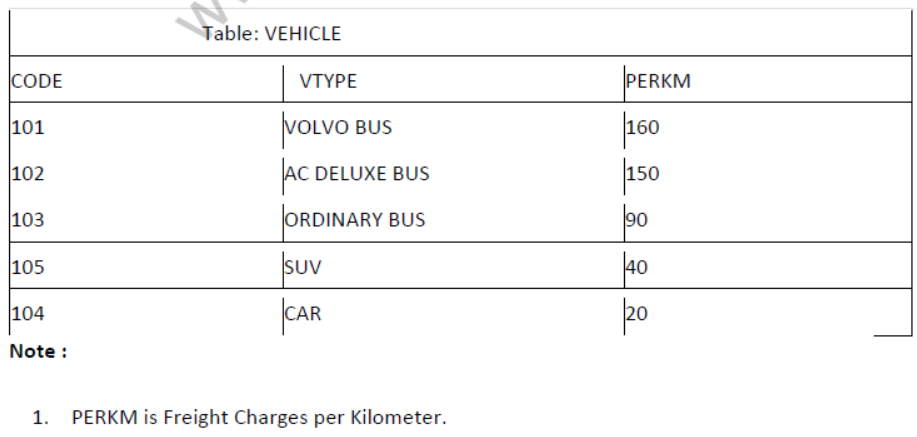
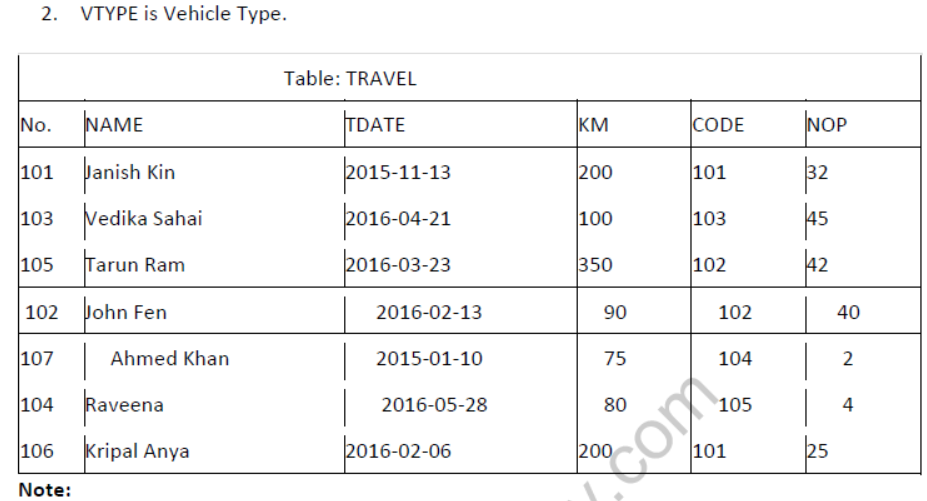
- NO is Traveller Number
- KM is Kilometer Travelled
- NOP is number of travellers travelled in vehicle.
- TDATE is Travel Date
1. To display NO, NAME, TDATE from the table TRAVEL in descending order of NO.
2. To display the NAME of all the travelers from the table TRAVEL who are travelling by vehicle with code 101 or 102.
3. To display the NO and NAME of those travelers from the table TRAVEL who travelled between ‘2015-1231’ and ‘2015-04-01’.
4. To display all the details from table TRAVEL for the travelers, who have travelled distance more than 100 KM in ascending order of NOP .
5. SELECT COUNT (*), CODE FROM TRAVEL GROUP BY CODE HAVING COUNT(*)>1;
6. SELECT DISTINCT CODE FROM TRAVEL;
7. SELECT A. CODE,NAME, VTYPE
FROM TRAVEL A,VEHICLE B
WHERE A.CODE=B.CODE AND ‘KM<90;
8.SELECT NAME, KM*PERKM
FROM TRAVEL A,VEHICLE B
WHERE A.CODE=B. CODE AND A.CODE=’105’;
Аnswer:
1. Select NO, Name, TDATE from TRAVEL order by NO desc
2. Select NAME from TRAVEL, where CODE in (101, 102)
3. Select NO, NAME from TRAVEL where TDATE between ’2015-12-31′ and ‘2015-04-01’.
4. Select * from TRAVEL where KM > 100 order by NOP.
5.
COUNT (*) CODE
2 101
2 102
6.
DISTANCE (CODE)
101
103
102
104
105
7. CODE NAME VTYPE
104 Ahmed khan CAR
105 Raveena SUV
8. NAME KM*PERKM
Tarun Ram 14000
Question 2: Write SQL queries for (i) to (iv) and find outputs for SQL queries (v) to (viii), which are based on the tables.
Table :VEHICLE
| VCODE | VEHICLETYPE | PERKM |
| VOl | VOLVO BUS | 150 |
| V02 V03 |
AC DELUXE BUS ORDINARY BUS |
125 80 |
| V0’5 | SUV | 30 |
| V04 | CAR | 18 |
Note:
PERKM is Freight Charges per kilometer.
Table : TRAVEL
| CNo 101 |
CNAME K.Niwal |
TRAVELDATE 2015-12-13 |
KM 200 |
VCODE VOl |
NOP 32 |
| 103 | Fredrick Sym | 2016-03-21 | 120 | VO3 | 45 |
| 105 102 |
Hitesh Jain Ravi Anish |
2016-04-23 2016-01-13 |
450 80 |
VO2 VO2 |
42 40 |
| 107 | John Malina | 2015-02-10 | 65 | VO4 | 2 |
| 104 | Sahanubhuti | 2016-01-28 | 90 | VO5 | 4 |
| 106 | Ramesh Jaya | 2016-04-06 | 100 | VOl | 25 |
- Km is Kilometers Travelled
- NOP is number of passengers travelled in vehicle.
1.To display CNO, CNAME, TRAVELDATE from the table TRAVEL in descending order of CNO.
2.To display the CNAME of all the customers from the table TRAVEL who are travelling by vehicle with code V01 or V02.
3.To display the CNO and CNAME of those customers from the table TRAVEL who travelled between ‘2015-12-31’ and ‘2015-05-01’.
4.To display all the details from table TRAVEL for the customers, who have travel distance more than 120 KM in ascending order of NOP.
5.SELECT COUNT (*) , VCODE FROM TRAVEL
GROUP BY VCODE HAVING COUNT(*)>1;
6. SELECT DISTINCT VCODE FROM TRAVEL;
7. SELECT A. VCODE, CNAME, VEHICLETYPE
FROM TRAVEL A,VEHICLE B
WHERE A.VCODE=B.VCODE AND KM<90;
8. SELECT CNAME, KM*PERKM FROM TRAVEL A,VEHICLE B
WHERE A.VCODE=B . VCODE AND A.VCODE= ‘V05 ‘ ;
Аnswer:
(i) Select CNO, CNAME, TRAVELDATE from TRAVEL order by CNO desc
(ii) Select CNAME from TRAVEL, where VCODE in (‘VOl’, ‘ V02 ‘)
(iii)Select CNO, CNAME from TRAVEL where TRAVELDATE between ‘2015-12-31’ and ‘2015-05-01 ‘
(iv) Select * from TRAVEL where KM > 120 order by NOP.
(v)
| COUNT (*) | VCODE |
| 2 2 |
V01 V02 |
DISTANCE (CODE)
V01
V03
V02
V04
V05
(vii)
| VCODE | CNAME | VEHICLETYPE |
| V04 | JOHN MALINI | CAR |
(viii)
CNAME KM*PERKM
Sahanubhuti 30
Note: PERKM is neither given in query nor in TABLE so no output is also acceptable.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1: Consider the following tables FACULTY and COURSES. Write SQL commands for the statements (i) to (v) and give outputs for SQL queries (vi) to (vii)
FACULTY
F_ID Fname Lname Hire_date Salary
102 Amit Mishra 12-10-1998 12000
103 Nitin Vyas 24-12-1994 8000
104 Rakshit Soni 18-5-2001 14000
105 Rashmi Malhotra 11-9-2004 11000
106 Sulekha Srivastava 5-6-2006 10000
COURSES
C_ID FJD Cname
C21 102 Grid Computing 40000
C22 106 System Design 16000
C23 104 Computer Security 8000
C24 106 Human Biology 15000
C25 102 Computer Network 20000
C26 105 Visual Basic 6000
(i) To display details of those Faculties whose salary is greater than 12000.
Аnswer:
Select * from faculty
where salry > 12000;
(ii) To display the details of courses whose fees is in th range of 15000 to 50000(both values included).
Аnswer:
Select * from Courses
where fees between 15000 and 50000;
(iii)To increase the fees of all courses by 500 of “System Design” Course.
<strong
Аnswer:
Update courses set fees = fees + 500
where Cname = “System Design”;
(iv)To display details of those courses which are taught by ‘Sulekha’ in descending order of courses.
Аnswer:
Select * from faculty fac, courses cour
where fac.f_id = cour.f_id and fac.fname = ‘Sulekha’ order by cname desc;
(v)Select COUNT (DISTINCT F_ID) from COURSES;
Аnswer: 4
(vi)Select MIN (Salary) from FACULTY, COURSES where COURSES.F_ID = FACULTY.FJD;
Аnswer: 6000
Question 2: Consider the following DEPT and WORKER tables. Write SQL queries for (i) to (iv) and find outputs for SQL queries (v) to (viii):
TABLE : DEPT
| DCODE | DEPARTMENT | CITY |
| D01 | MEDIA | DELHI |
| D02 | MARKETING | DELHI |
| D03 | INFRASTRUCTURE | MUMBAI |
| D05 | FINANCE | KOLKATA |
| D04 | HUMAN RESOURCE | MUMBAI |
TABLE : WORKER
| WNO | NAME . Y; | DOJ | DOB | GENDER | DCODE |
| 1001 | George K | 2013-09-02 | 1991-09-01 | MALE | D01 |
| 1002 | Ryma Sen | 2012-12-11 | 1990-12-15 | FEMALE | D03 |
| 1003 | Mohitesh | 2013-02-03 | 1987-09-04 | MALE | D05 |
| 1007 | Anil Jha | 2014-01-17 | 1984-10-19 | MALE | D04 |
| 1004 | Manila Sahai | 2012-12-09 | 1986-11-14 | FEMALE | D01 |
| 1005 | RSAHAY | 2013-11-18 | 1987-03-31 | MALE | D02 |
| 1006 | Jaya Priya | 2014-06-09 | 1985-06-23 | FEMALE | D05 |
Note : DOJ refers to date of joining and DOB refers to date of birth of workers.
(i)To display Wno. Name, Gender from the table WORKER in descending order of Wno. Ans.
Аnswer:
SELECT WNO, Name, Gender FROM Worker
ORDER BY Wno DESC;
(ii)To display the Name of all the FEMALE workers from the table WORKER.
Аnswer:
SELECT Name FROM Worker
WHERE gender = ‘FEMALE’;
(iii)To display the Wno and Name of those workers from the table WORKER who are born between
‘1987-01-01’ and ‘1991-12-01’.
Аnswer:
SELECT Wno, Name FROM Worker
WHERE DOB BETWEEN ‘1987-01-01’ AND ‘1991-12-01’;
OR
SELECT Wno, Name FROM worker
WHERE DOB > = 1987-01-01′ AND DOB < = ‘1991-12-01’;
WHERE DOB BETWEEN ‘1987-01-01’ AND ‘1991-12-01’;
OR
WHERE DOB > = ‘1987-01-01’ AND DOB < = ‘1991-12-01’;
(iv)To count and display MALE workers who have joined after ‘1986-01-01’.
Аnswer:
SELECT COUNT (*) FROM Worker
WHERE GENDER = ‘MALE’ AND DOJ > ‘198601-01’;
OR
SELECT * FROM Worker
WHERE GENDER = ‘MALE’ AND DOJ > ‘198601-01’;
(Any valid query for counting and/or displaying for male workers will be awarded 1 mark)
(v) SELECT COUNT (*), DCODE FROM WORKER GROUP BY DCODE HAVING COUNT (*) > 1;
Аnswer:
COUNT (*) DCODE
2 D01
2 D05
(vi)SELECT DISTINCT DEPARTMENT FROM DEPT;
Аnswer:
Department
MEDIA
MARKETING
INFRASTRUCTURE
FINANCE
HUMAN RESOURCE
(viii)SELECT NAME, DEPARTMENT, CITY FROM WORKER W, DEPT D WHERE W DCODE = D.
DCODE AND WNO < 1003;
Аnswer:
NAME DEPARTMENT CITY
George K MEDIA DELHI
Ryma Sen infrastructure MUMBAI
(viii) SELECT MAX (DOJ), MIN (DOB) FROM WORKER;
Аnswer: MAX (DOJ) MIN (DOB)
2014-06-09 1984-10-19
Note : In the output queries, please ignore the order of rows
Question 3: Consider the following DEPT and EMPLOYEE tables. Write SQL queries for (i) to (iv) and find outputs for SQL queries (v) to (viii).
TABLE : DEPT
| DCODE | DEPARTMENT | LOCATION |
| D01 | INFRASTRUCTURE | DELHI |
| D02 | MARKETING | DELHI |
| D03 | MEDIA | MUMBAI |
| D05 | FINANCE | KOLKATA |
| D04 | HUMAN RESOURCE | MUMBAI |
TABLE : EMPLOYE
| ENO | NAME | DOJ | DOB | GENDER | DCODE |
| 1001 | GEORGE K | 2013-09-02 | 1991-09-01 | MALE | D01 |
| 1002 | Ryma Sen | 2012-12-11 | 1990-12-15 | FEMALE | D03 |
| 1003 | Mohitesh | 2013-02-03 | 1987-09-04 | MALE | D05 |
| 1007 | Anil Jha | 2014-01-17 | 198410-19 | MALE | D04 |
| 1004 | Manila Sahai | 2012-12-09 | 1986-11-14 | FEMALE | D01 |
| 1005 | RSAHAY | 2013-11-18 | 1987-03-31 | MALE | D02 |
| 1006 | JAYA Priya | 2014-06-09 | 1985-06-23 | FEMALE | D05 |
Note :DOJ refers to date of joining and DOB refers to date of Birth of employees.
(i)To display Eno, Name, Gender from the table EMPLOYEE in ascending order of Eno.
Аnswer: SELECT Eno, Name, Gender FROM Employee ORDER BY Eno;
(ii)To display the Name of all the MALE employees from the table EMPLOYEE.
Аnswer: SELECT Name FROM EMPLOYEE WHERE
Gender = ‘MALE’;
(iii)To display the Eno and Name of those employees from the table EMPLOYEE who are born between ‘1987-01-01’ and ‘1991-12-01’.
Аnswer:
SELECT Eno, Name FROM Employee
WHERE DOB BETWEEN ‘1987-01-01’ AND ‘1991-12-01’;
OR
SELECT Eno, Name FROM Employee
WHERE DOB > = ‘1987-01-01′ AND DOB < =’1991-12-01’;
OR
SELECT Eno, Name FROM Employee WHERE DOB > ‘1987-01-01’ AND DOB < ‘199112-01’;
WHERE DOB BETWEEN ‘1987-01-01’ AND ‘1991-12-01’;
OR
WHERE DOB > = ‘1987-01-01’ AND DOB < = ‘1991-12-01’;
OR
WHERE DOB > ‘1987-01-01’ AND DOB < ‘199112-01’);
(iv)To count and display FEMALE employees who have joined after ‘1986-01-01’;
Аnswer: SELECT count (*) FROM Employee
WHERE GENDER = ‘FEMALE’ AND DOJ > ‘1986-01-01’;
OR
SELECT * FROM Employee
WHERE GENDER = ‘FEMALE’ AND DOJ > ‘1986-01-01’;
(Any valid query for counting and/or displaying for female employees will be awarded 1
mark)
(v)SELECT COUNT (*), DCODE FROM EMPLOYEE
GROUP BY DCODE HAVING COUNT (*) > 1;
Аnswer:
COUNT DCODE
2 D01
2 D05
(½Mark for correct output)
(vi)SELECT DISTINCT DEPARTMENT FROM DEPT
Аnswer: Department
INFRASTRUCTURE
MARKETING
MEDIA
FINANCE
HUMAN RESOURCE
(vii) SELECT NAME, DEPARTMENT FROM EMPLOYEE E, DEPT D WHERE E. DCODE = D.DCODE
AND ENO <1003;
NAME DEPARTMENT
George K MEDIA
Ryma Sen infrastructure
(viii) SELECT MAX (DOJ), MIN (DOB) FROM EMPLOYEE;
Аnswer:
MAX (DOJ) MIN (DOB)
2014-06-09 1984-10-19
Note : In the output queries, please ignore the order of rows.
Question 4: Write SQL commands for the queries (i) to (iv) and output for (v) & (viii) based on a table
COMPANY and CUSTOMER
CID NAME CITY PRODUCTNAME
111 SONY DELHI TV
222 NOKIA MUMBAI MOBILE
333 ONIDA DELHI TV
444 SONY MUMBAI MOBILE
555 BLACKBERRY MADRAS MOBILE
666 DELL DELHI LAPTOP
CUSTID NAME PRICE QTY CID
101 ROHAN SHARMA 70,000 20 222
102 DEEPAK KUMAR 50,000 10 666
103 MOHAN KUMAR 30,000 5 111
104 SAHIL BANSAL 35,000 3 333
105 NEHA SONI 25,000 7 444
106 SONAL AGGARWAL 20,000 5 333
107 ARUN SINGH 50,000 15 666
1. To display those company name which are having prize less than 30000.
2. To display the name of the companies in reverse alphabetical order.
3. To increase the prize by 1000 for those customer whose name starts with S?
4. To add one more column total price with decimal(10,2) to the table customer
5. SELECT COUNTO ,CITY FROM COMPANY GROUP BY CITY;
6. SELECT MIN(PRICE), MAX(PRICE) FROM CUSTOMER WHERE QTY>10;
7. SELECT AVG(QTY) FROM CUSTOMER WHERE NAME LIKE “%r%;
8. SELECT PRODUCTNAME,CITY, PRICE FROM COMPANY, CUSTOMER WHERE
COMPANY.CID=CUSTOMER.CID AND PRODU CTN AME=”MOBILE”;
Аnswer:
1. To display those company name which are having prize less than 30000.
SELECT NAME FROM COMPANY WHERE COMPANY.CID=CUSTOMER. CID AND PRICE < 30000
2.To display the name of the companies in reverse alphabetical order.
SELECT NAME FROM COMPANY
ORDER BY NAME DESC?;
3.To increase the prize by 1000 for those customer whose name starts with “S”
UPDATE CUSTOMER
SET PRICE = PRICE + 1000;
WHERE NAME LIKE ‘S%’;
4.To add one more column total price with decimal(10,2) to the table customer
ALTER TABLE CUSTOMER
ADD TOTALPRICE DECIMAL(10,2);
5.SELECT COUNT(*) ,CITY FROM COMPANY GROUP BY CITY;
3 DELHI
2 MUMBAI
1 MADRAS
6.SELECT MIN(PRICE), MAX(PRICE) FROM
CUSTOMER WHERE QTY> 10;
50000,70000
7.SELECT AVG(QTY) FROM CUSTOMER
WHERE NAME LIKE “%r%;
8.SELECT PRODUCTNAME, CITY, PRICE FROM COMPANY, CUSTOMER WHERE
COMPANY.CID=CUSTOMER.CID AND PRODUCTNAME=”MOBILE”;
MOBILE MUMBAI 70000
MOBILE MUMBAI 25000
Question 5: Consider the following tables SCHOOL and ADMIN and answer this question :
Table : SCHOOL
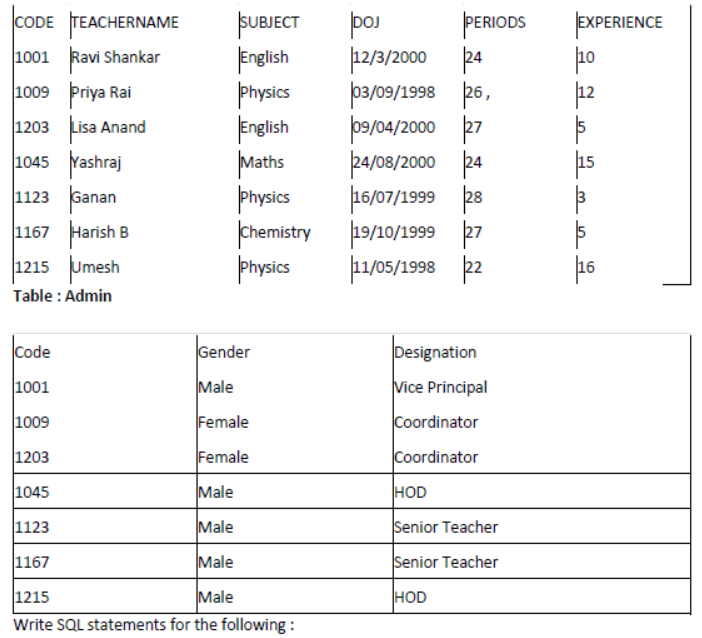
1. To display TEACHERNAME, PERIODS of all teachers whose periods are more than 25.
2. To display all the information from the table SCHOOL in descending order of experience.
3. To display DESIGNATION without duplicate entries from the table ADMIN.
4. To display TEACHERNAME, CODE and corresponding DESIGNATION from tables
SCHOOL and ADMIN of Male teachers.
Аnswer:
1. To display TEACHERNAME, PERIODS of all teachers whose periods are more than 25.
SELECT TEACHERNAME, PERIODS
FROM SCHOOL WHERE PERIODS >25.
2.To display all the information from the table SCHOOL in descending order of experience.
- SELECT * FROM SCHOOL;
3.To display DESIGNATION without duplicate entries from the table ADMIN.
SELECT DISTINCT DESIGNATION FROM ADMIN;
4.To display TEACHERNAME, CODE and corresponding DESIGNATION from tables SCHOOL
and ADMIN of Male teachers.
SELECT TEACHERNAME.CODE
DESIGNATION FROM SCHOOL.CODE = ADMIN.CODE
WHERE GENDER = MALE;
Question 6: Answer the questions (a) and (b) on the basis of the following tables SHOPPE and ACCESSORIES.
Аnswer:
Id SName Area
S001 ABC computronics CP
S002 All Infotech Media GKII
S003 Tech Shoppe CP
S004 Geeks Tecno Soft Nehru Place
S005 Hitech Tech Store Nehru Place
No Name Price Id
A01 Mother Board 12000 SOI
A02 Hard Disk 5000 SOI
A03 Keyboard 500 S02
A04 Mouse 300 SOI
A05 Mother Board 13000 S02
A06 Keyboard 400 S03
A07 LCD 6000 S04
T08 LCD 5500 S05
T09 Mouse 350 S05
T10 Hard Disk 4500 S03
1. To display Name and Price of all the Accessories in ascending order of their Price.
2. To display Id and SName of all Shoppe located in Nehru Place.
3. To display Minimum and Maximum Price of each Name of Accessories.
4. To display Name, Price of all Accessories and their respective SName where they are available.
(b)Write the output of the following SQL commands:
1. SELECT DISTINCT NAME FROM ACCESSORIES WHERE PRICE > =5000;
2. SELECT AREA, COUNT(*) FROM SHOPPE GROUP BY AREA;
3. SELECT COUNT (DISTINCT AREA) FROM SHOPPE;
4. SELECT NAME, PRICE*0.05 DISCOUNT FROM ACCESSORIES
Аnswer: (a) (i) SELECT Name, Price FROM ACCESSORIES ORDER BY Prices;
(ii)SELECT ID, SName FROM SHOPPE WHERE Area=”Nehru Place”;
(iii)SELECT Name, max (Price); min(Price) FROM ACCESSORIES, Group By Name;
(iv)SELECT Name, price, Sname FROM ACCESSORIES, SHOPPE WHERE
SHOPPE.ID=ACCESSORIES.ID
(b)(i) Name
Mother Board
Hard Disk
LCD
(ii)
Area Count
CP 2
GK II 1
Nehru Place 2
(iii) count(Distinct Area)
3
(iv) Name
Name DISCOUNT
600 600
Hard Disk 250
Key Board 20
Hard Disk 225
Question 7: Answer the questions (a) to (g) on the basics of the following tables APPLICANTS and COURSB.
1. To display name, fee, gender, join year about the applicants, who have joined before 2010.
2. To display names of applicants, who are paying fee more than 30000.
3. To display names of all applicants in ascending order of their join year.
4. To display the year and the total number of applicants joined in each YEAR from the table APPLICANTS.
C_ID Course
A01 Fashion Design
A02 Networking
A03 Hotel Management
A04 Event Management
A05 Office Management
5.To display the C_ID (i.e., CourselD) and the number of applicants registered in the course from the APPLICANTS and table.
6.To display the applicant’s name with their respective course’s name from the tables APPLICANTS and COURSES.
7.Give the output statements: of following SQL statements :
(i)SELECT Name, Join year FROM APPLICANTS
WHERE GENDER=’F’ and C_ID=’A02′;
(ii) SELECT MIN (Join year) FROM APPLICANTS
(iii)SELECT AVG (Fee) FROM APPLICANTS WHERE C_ID=’A01′ OR C_ID=’A05′;
(iv)SELECT SUM (Fee), C_ID FROM APPLICANTS
GROUP BY C_ID HAVING COUNT(*)=2;
Аnswer: (a) SELECT NAME,FEE,GENDERJOINYEAR FROM APPLICANTS
WHERE JOINYEAR<2000;
(b)SELECT NAME FROM APPLICANTS
WHERE FEE>30000;
(c)SELECT NAME FROM APPLICANTS
ORDERBY JOINYEAR ASC;
(d)SELECT YEAR, COUNTf) FROM APPLICANTS;
(e)SELECT C_ID, COUNT(*) FROM APPLICANTS, COURSES
WHERE APPLICANTS.C_ID=COURSES; C_ID;
(f)SELECT NAME,COURSE FROM
APPLICANTS, COURSES
WHERE APPLICANTS.C_ID=COURSES. C_ID;
(g)(i) Avisha 2009
(ii) 2009
(iii) 67
(iv)55000 A01
Question 8: Write SQL queries for (a) to (g) and write the output for the SQL queries mentioned shown in (hi) to (h4) parts on the basis of table ITEMS and TRADERS :
Table : ITEMS
- To display the details of all the items in ascending order of item names (i.e., INAME).
- To display item name and price of all those items, whose price is in the range of 10000 and 22000 (both values inclusive).
- To display the number of items, which are traded by each trader. The expected output of this query should be:
- To display the price, item name and quantity (i.e., qty) of those items which have quantity more than 150.
- To display the names of those traders, who are either from DELHI or from MUMBAI.
- To display the names of the companies and the names of the items in descending order of company names.
- Obtain the outputs, of the following SQL queries based on the data given in tables
ITEMS and TRADERS above.
(h1)SELECT MAX (PRICE), MIN (PRICE) FROM ITEMS;
(h2) SELECT PRICE*QTY
FROM ITEMS WHERE CODE-1004;
(h3) SELECT DISTINCT TCODE FROM ITEMS;
(h4) SELECT INAME, TNAME
FROM ITEMS I, TRADERS T WHERE I.TCODE=T.TCODE AND
QTY<100;
Аnswer:
(a) SELECT INAME FROM ITEMS ORDER BY INAME ASC;
(b)SELECT INAME, PRICE FROM ITEMS WHERE PRICE => 10000 AND PRICE =< 22000;
(c)SELECT TCODE, COUNT (CODE) FROM
ITEMS GROUP BY TCODE;
(d)SELECT PRICE, INAME, QTY FROM ITEMS
WHERE (QTY> 150);
(e)SELECT TNAME FROM TRADERS
WHERE (CITY = “DELHI”) OR (CITY = “MUMBAI”)
ORDER BY COMPANY DESC;
(g) (h1) 38000
1200
(h2) 1075000
(h3) T01
T02
T03
(h4) LED SCREEN 40 DISPHOUSE INC
CAR GPS SYSTEM ELECTRONICS
SALES
Question 9: Write SQL queries for (a) to (f) and write the outputs for the SQL queries mentioned shown in (hi) to (h4) parts on the basis of tables PRODUCTS and SUPPLIERS
Table : PRODUCTS
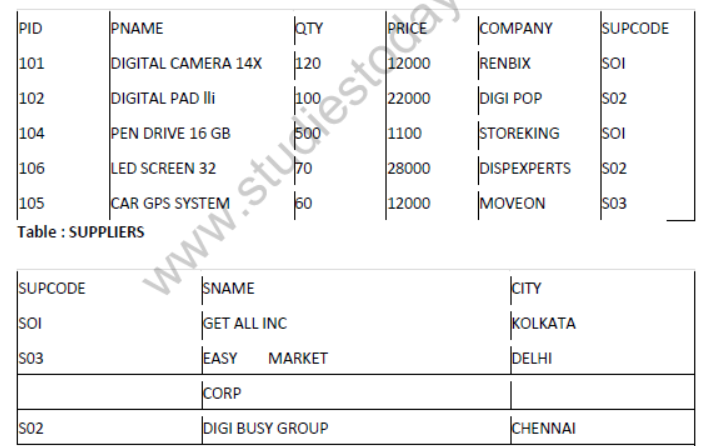
(a)To display the details of all the products in ascending order of product names (e., PNAME).
(b)To display product name and price of all those products, whose price is in the range of 10000 and 15000 (both values inclusive).
(c)To display the number of products, which are supplied by each supplier, i.e., the expected output should be;
2
2
1
(d)To display the price, product name and quantity (i.e., qty) of those products which have quantity more than 100.
(e)To display the names of those suppliers, who are either from DELHI or from CHENNAI.
(f)To display the name of the companies and the name of the products in descending order of company names.
(g)Obtain the outputs of the following SQL queries based on the data given in tables
PRODUCTS and SUPPLIERS above.
(gl) SELECT DISTINCT SUPCODE FROM PRODUCTS;
(g2) SELEC MAX (PRICE), MIN (PRICE) FROM PRODUCTS
(g3) SELECT PRICE*QTY
FROM PRODUCTS WHERE PID = 104;
(g4) SELECT PNAME, SNAME
FROM PRODUCTS P, SUPPLIERS S WHERE P SUPCODE = S. SUPCODE AND QTY>100;
Аnswer:
(a) SELECT * FROM PRODUCTS ORDER. BY PNAME ASC;
(b)SELECT PNAME, PRICE FROM PRODUCTS WHERE ((PRICE => 10000) AND (PRICE = < 15000));
(c)SELECT SUPCODE, COUNT (PID) [Yz] FROM PRODUCTS GROUP BY SUPCODE;
(d)SELECT PRICE, PNAME, QTY FROM PRODUCTS WHERE (QTY > 100);
(e)SELECT SNAME FROM SUPPLIERS WHERE ((CITY = “DELHI”) OR (CITY = “CHENNAI”));
(f)SELECT COMPANY, PNAME FROM PRODUCTS ORDER BY COMPANY DESC;
(g) SOI
(g1) S02
S03
(g2) 28000
1100
(g3) 550000
(g4) PNAME SNAME
DIGITAL CAMERA 14 X GET ALL INC
PENDRIVE 16 GB GET ALL INC
Question 10: Give a suitable example of a table with sample data and illustrate Primary and Alternate Keys in it. Consider the following tables CARDEN and CUSTOMER and answer (b) and (c) parts of this question :
Table : CARDEN
Ceode CarName Make Colour Capacity Charges
501 A-Star Suzuki RED 3Q 14
503 Indigo Tata SILVER 3 12
502 Innova Toyota WHITE 7 15
509 SX4 Suzuki SILVER 4 14
510 C Class Mercedes RED 4 35
Table : CUSTOMER
CCode Cname Ceode
1001 Hemant Sahu 501
1002 Raj Lai 509
1003 Feroza Shah 503
1004 Ketan Dhal 502
(b)Write SQL commands for the following statements:
1. To display the names of all the silver coloured cars.
2. Tp display names of car, make and capacity of cars in descending order of their sitting
capacity.
3. To display the highest charges at which a vehicle can be hired from CARDEN.
4. To display the customer name and the corresponding name of the cars hired by them.
(c)Give the output of the following SQL queries:
(i)SELECT COUNT(DlST!NCT Make) FROM CARDEN;
(ii)SELECT MAX(Charges), MIN (Charges) FROM CARDEN;
SELECT COUNTO, Make FROM CARDEN;
(iv) SELECT CarName FROM CARDEN WHERE Capacity=4;
Аnswer:
(a) Primary Key of CARDEN = Ceode of CARDEN
Alternate Key = CarName:
Primary key of Customer = Ceode
Alternate Key of Customer = Cname
(b) (i) SELECT CarName From CARDEN
WHERE Color = “SILVER”;
(ii)SELECT CarName, Make, Capacity
From CARDEN ORDER BY Capacity DESC;
(iii)SELECT MAX(Charges) From CARDEN;
(iv)SELECT Cname, CarName From
CUSTOMER, CARDEN WHERE CARDEN. Ccode = CUSTOMER. Ccode;
(c) (i) 4
(ii) MAX(Charges) MIN(Charges)
35 12
(iii)5
(iv)SX4
C Class
Question 11: (a) Give a suitable example of a table with sample data and illustrate Primary agd Candidate Keys in it. Consider the following tables CABHUB and CUSTOMER and answer (b) and (c) parts of this question :
Table : CABHUB
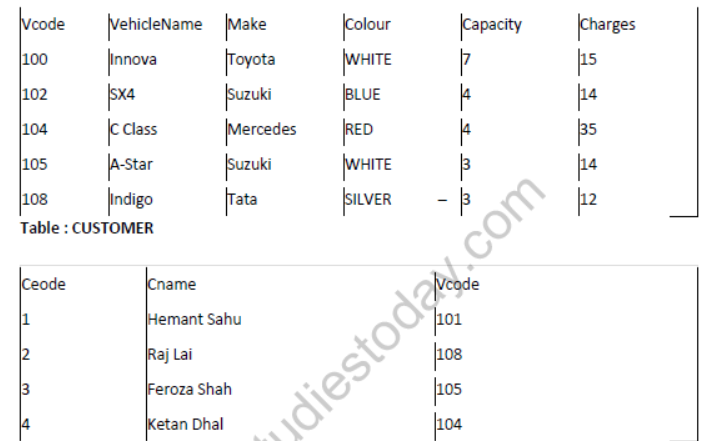
(b) Write SQL commands for the following statements:
1. To display the names of all the white coloured vehicles.
2. To display name of vehicle name and capacity of vehicles in ascending order of their sitting capacity.
3. To display the highest charges at which a vehicle can be hired from CABHUB.
4. To display the customer name and the corresponding name of the vehicle hired by them.
(c)Give the output of the following SQL queries :
1. SELECT COUNT (DISTINCT Make) FROMCABHUB;
2. SELECT MAX(Charges), MIN(Charges) FROM CABHUB;
3. SELECT COUNT (*) Make FROM CABHUB;
4. SELECT Vehicle FROM CABHUB WHERE Capacity=4;
Аnswer:
(a) Primary Key of CABHUB = Vcode
Alternate key of CABHUB = Vehicle Name.
Primary Key of Customer = Ccode
Alternate Key of CUSTOMER = Cname.
(b) (i) SELECT VehicleName FROM CABHUB WHERE Colour =”WHITE”;
(ii)SELECT VehicleName, Capacity From CABHUB ORDER BY Capacity ASC;
(iii)SELECT MAX(Charges) FROM CABHUB;
(iv)SELECT Cname,VehicleName FROM CABHUB, CUSTOMER WHERE CUSTOMER.
Vcode=CABHUB. Vcode;
(c)4
(ii)Max(Charges) Min(Charges)
35 12
(iii)5
(iv)SX4
C Class
Long Answer Type Question – II
Question 1:
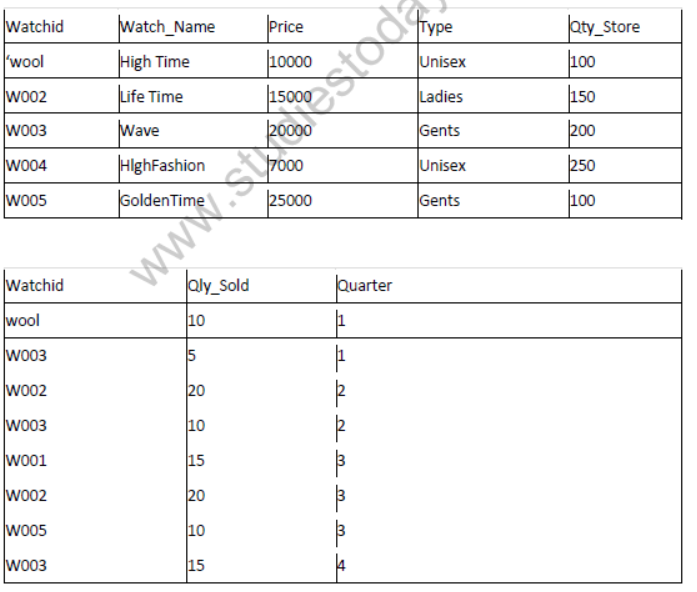
1. To display all the details of those watches whose name ends with ‘Time’
2. To display watch’s name and price of those watches which have price range in between 5000-15000.
3. To display total quantity in store of Unisex type watches.
4. To display watch name and their quantity sold in first quarter.
5. select max(price), min(qty_store) from watches;
6. select quarter, sum(qty_sold) from sale group by quarter;
7. select watch_name,price, type from watches w, sale s where w.watchid!=s.watchid;
8. select watch_name, qty_store, sum(qty_sold), qty_store-sum(qty_sold) “Stock” from watches w, sales where w. watchid=s. watchid group by s.watchid;
Аnswer:
(i) Select*from watches where watch_name like’Time’
(ii)select watchjname, price from watches where price between 5000 and 15000;
(iii)select sum(qty_store) from watches where type like ‘Unisex’;
(iv)select watch name, qty_sold from watches w,sale s where w.watchid=s.watchid and quarter=l;
(v)
max(price) min(qty_store)
25000 100
(vi)
quarter suxn(qty_sold)
1 15
2 30
3 45
4 15
(vii)
Watch_name price type
HighFashion 7000 Unisex
(viii)
Watch_name qty_store qty_sold Stock
HighTime 100 25 75
LifTime 150 40 110
Wave 200 30 170
GoldenTime 100 10 90
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science Chapter 3 Stack |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science Chapter 4 Queue |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science Chapter 8 Database Concepts |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science Chapter 9 Structured Query Language |
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science Chapter 9 Structured Query Language
The above provided NCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science Chapter 9 Structured Query Language is available on our website for free download in Pdf. You can read the solutions to all questions given in your Class 12 Computer Science textbook online or you can easily download them in pdf. The answers to each question in Chapter 9 Structured Query Language of Computer Science Class 12 has been designed based on the latest syllabus released for the current year. We have also provided detailed explanations for all difficult topics in Chapter 9 Structured Query Language Class 12 chapter of Computer Science so that it can be easier for students to understand all answers. These solutions of Chapter 9 Structured Query Language NCERT Questions given in your textbook for Class 12 Computer Science have been designed to help students understand the difficult topics of Computer Science in an easy manner. These will also help to build a strong foundation in the Computer Science. There is a combination of theoretical and practical questions relating to all chapters in Computer Science to check the overall learning of the students of Class 12.
You can download the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Computer Science Chapter 9 Structured Query Language for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the NCERT Solutions issued for Class 12 Computer Science Chapter 9 Structured Query Language have been made available here for latest academic session
Regular revision of NCERT Solutions given on studiestoday for Class 12 subject Computer Science Chapter 9 Structured Query Language can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all latest NCERT Chapter 9 Structured Query Language Class 12 Computer Science solutions based on the latest books for the current academic session
Yes, NCERT solutions for Class 12 Chapter 9 Structured Query Language Computer Science are available in multiple languages, including English, Hindi
All questions given in the end of the chapter Chapter 9 Structured Query Language have been answered by our teachers

