NCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science Object Oriented Programming in C++ have been provided below and is also available in Pdf for free download. The NCERT solutions for Class 12 Computer Science have been prepared as per the latest syllabus, NCERT books and examination pattern suggested in Class 12 by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. Questions given in NCERT book for Class 12 Computer Science are an important part of exams for Class 12 Computer Science and if answered properly can help you to get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise answers for NCERT Class 12 Computer Science and also download more latest study material for all subjects. Object Oriented Programming in C++ is an important topic in Class 12, please refer to answers provided below to help you score better in exams
Object Oriented Programming in C++ Class 12 Computer Science NCERT Solutions
Class 12 Computer Science students should refer to the following NCERT questions with answers for Object Oriented Programming in C++ in Class 12. These NCERT Solutions with answers for Class 12 Computer Science will come in exams and help you to score good marks
Object Oriented Programming in C++ NCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science
Question 1: Differentiate between data abstraction and data hiding.
Answer: Data hiding can be defined as the mechanism of hiding the data of a class from the outside world. This is done to protect the data from any accidental or intentional access. Data hiding is achieved by making the members of the class private.
Data abstraction refers to, providing only essential information to’ the outside world and hiding their background details.
Members defined with a public label are accessible to all parts of the program. The data abstraction view of a type is defined by its public members.
Question 2: How encapsulation and abstraction are implemented in C++ language ? Explain with an example.
Answer: Abstraction refers to the act of representing essential features without including the background details or explanations.Encapsulation is wrapping up of data and function together in a single unit.We can say that encapsulation is way of achieving abstraction. Both these concepts are implemented in C++ in the form of a class. In a class data and function members are wrapped together. Only essential features are shown to the outside world in the form of member functions with public mode of accessibility. [1]
Example: [1]
class Rectangle
{
int L, B;
public: void Input()
{
cin>>L>>B;
}
void Output()
{
Cout<<L<<B;
}
};
In this example:
Data and member functions are together encapsulated
Only Input ( ) and Output ( ) functions are visible outside the class which can only can be accessed outside the class using objects of the same class – Abstraction
Question 3: Explain data hiding with an example.
Answer: Data Hiding
Data Hiding is the mechanism where the details of the class are hidden from the user.The user can perform only a restricted set of operations in the hidden member of the class
For example,
In order to make the design and maintenance of a car reasonable the complexity of equipment is divided into modules with particular interfaces hiding design decisions.
General Form:
class classname
{
private:
datatype data;
public:
Member functions,-'
};
main()
{
classname objectnamel, objectname2
.........;
{
Example :
class Square
{
private
int Num;
public:
void Get() {
cout<<"Enter Number:";
cin>>Num;
}
void Display!) { cout<<"Square Is:"<<Num*Num;
}
};
void main()
{
Square Obj;
Obj.Get();
Obj.Display (); [1]
getch()
}
Question 4: What do you understand by data encapsulation and Data hiding ?
Also, give a suitable C++ code to illustrate both.
Answer: Data hiding is a property of OOP by which the crucial data of an object is made hidden from the rest of the program or outside the world.
Encapsulation refers to the wrapping of data and associated functions together under a unit class.
// Program for hiding & Encapsulation
#include <iostream.h>
class Adder { // Encapsulation
public :
Adder (int i = 0)
{ total = i;}
void addNum (int Number)
{ total + = Number;
}
int getTotal ( )
{ return total;
}
private : int total ;
//Data Hiding
};
int main ( )
{
Adder a;
a . addNum (10);
a . addNum (20);
a . addNum (30);
cout << "Total :<<a.getTotal (
) < < endl;
return 0 ;
}
Question 5: Write the output of the following C++ program code:
class Eval
{
char Level;
int Point;
Public :
Eval () {
Level = 'E' ; Point = 0;
}
void Sink (int L)
{
Level - = L;
}
void Float (int L)
{
Level + = L;
Point ++;
}
void Show ( )
{
cout<<Level<<"#"<<Point<<endl;
}
};
void main ( )
{
Eval E;
E. Sink (3) ;
E. Show ( );
E. Float (7);
E. Show ( );
E. Sink (2) ;
E. Show ( );
}
Answer:
B#0
I#1
G#1
(1 Mark for each correct line of output)
Note:
• Deduct 1/2 Mark for not considering any or all end/(s) at proper place(s)
• Deduct 1/2 Mark for not writing any for all symbol(s)
Question 6: Observe the following program carefully and attempt the given questions :
#include<iostream.h>
#include<cono.h>
#include<stdlib,h>
void main()
clrscr();
randomize();
char courses![ ] [10]={“M.Tech”.”MCA”, “MBA”,”B.Tech”};
int ch;
for(int i= l;i<=3;i++)
{
ch=random(i)+1;
cout<<courses[ch]<<“\t;
}
getch () ;
}
(i) Out of all the four courses stored in the variable courses, which course will never be displayed in the output and which course will always be displayed at first in the output ?
(ii) Mention the minimum and the maximum value assigned to the variable ch ?
Answer:
(i) M. Tech will never be displayed in the output.
MCA will always be displayed at first in the output.
(ii) Minimum value of ch=l
Maximum value of ch=3
(1 Mark for each correct answer)
Note:
• Deduct 1/2 Mark for writing any additional option. [CBSE Marking Scheme 2016]
Question 7: Study the following program and select the possible output(s) from the options (i) to (iv) following it. Also, write the maximum and the minimum values that can be assigned to the variable VAL.
Note:
— Assume all required header files are already being included in the program.
— random(n) function generates an integer between 0 and n -1.
void main ()
{
randomize () ;
int VAL;
VAL = random (3) + 2;
chart GUESS [ ] = "ABCDEFGHIJK"
; for (int I = 1; I < = VAL;
I ++)
{
for (int J = VAL; J < = 7; J ++)
Cout<<GUESS [J] ;
cout<<endl;
}

Answer:
(ii) and (iii)
Min Value of VAL = 2
Max Value of VAL. = 4
(1/2 CA Mark for writing option (ii))
(1/2 Mark for writing option (iii))
Note:
• Deduct 1/2 mark for inviting each additional option along with both correct options:
(1/2 Mark for writing correct Minimum value of VAL)
(1/2 Mark for writing correct Maximum value of VAL)
Question 8: Rewrite the following program after removing the syntax errors (if any). Under line each correction.
#include <iostream.h>
Class Item
{
long IId, Qty;
public :
void Purchase {cin>>IId>>Qty;}
void sale ()
{
cout<<setw (5)<< IId<<" Old :"<Qty
<<endl;
cout<<"New :" <<Qty<<endl;
}
};
void main ()
{
Item I;
Purchase ();
I. Sale () ;
I. Sale ()
}
Answer:
#include<iostream.h>
#include<iomanip.h>
class Item
{
long IId, Qty;
public :
void purchase()
{cin>>IId>>Qty;}
void sale()
{
cout<<setw(5)<<IId<<"Old"<<Qty<<endl;
cout<< "New Qty<<endl;
}
};
void main( )
{
Item I ;
I. purchase( ); // Object missing
I. sale ( ) ;
I. sale( ); //; is missing
}
(1/4 mark for each correction)
Question 9: Rewrite the following program after removing the syntax errors (if any). Underline each correction.
# include <iostream.h>
class book {
long Bid, Qty;
public :
void purchase () {cin>>BID>>Qty;}
void sale ( )
{
cout<<setw<<BId<<"Old:"<<Qty<<en
dl;
cout<<"New; "<<—Qty<<endl;
}
};
void main ()
{
Book B;
B. Purchase();
sale ();
B. Sale ()
}
Answer:
#include<iomanip.h>
#include<iostream.h>
class Book
{
long Bid, Qty;
public:
void purchase()(cin>>Bld>>Qty;)
void sale( )
{
cout < < setw(5) < < Bld < < "0ld " < < Qty < < e n
dl;
cout<"New:"<<—Qty<<endl;
}
} ;
void main ()
{
Book B;
B. purchase ();
B. sale();
}
(1/2 mark for each correction) [CBSE Marking Scheme 2012]
Question 10: Answer the questions (i) and (ii) after going through the following class:
class Travel
{
int PlaceCode; char Place [20] ;
float Charges;
public :
Travel ( ) //Function 1
{
PlaceCode = 1; strcpy (Place,
"DELHI"); Charges =1000;
}
void TravelPlan (float C)
//Function 2
{
cout<<PlaceCode<< ":" <<Place<<
":" <<Charges<<endl;
}
- Travel ( ) //Function 3
{
cout<<"Travel Plan Cancelled"<<
endl;
}
Travel (int PC, char P [], float C)
// Function 4
{
PlaceCode = PC; strcpy (Place, P);
Charges = C;
}
} ;
(i) In Object Oriented Programming, what are Function 1 and Function 4 combinely referred to as?
(ii) In Object Oriented Programming which concept is illustrated by Function 3? When is this function called/invoked?
Answer:
The concept demonstrated is constructor over-loading:
(i) Function 1 and Function 4 are called overloaded Constructor of the Class Travel.
(ii) Function 3 is Destructor of Class Travel.
The destructors are called automatically when the objects are destroyed.
Short Answer Type Questions-II
Question 1: Write any four important characteristics of object Oriented Programming ? Give example of any one of the characteristics using C++.
Answer:
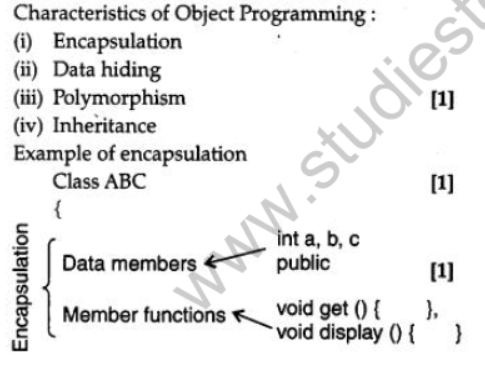
Question 2: Find the output of the following C++ program
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<ctype.h>
class Class
{
int Cno,total;
char section; public:
Class(int no=l)
{
Cno=no;
section='A';
total=30;
}
void admission(int c=20)
{
section++;
total+=c;
}
void ClassShow ()
{
cout<<Cno<<":"<<section<<":"<<total<
endl;
}
};
void main ()
{
Class C1 (5),C2;
Cl.admission(25)
Cl.ClassShow();
C2.admission() ;
Cl.admission(30)
C2.ClassShow();
Cl.ClassShow();
}
Answer:
5 : B : 55 [1]
1: B : 50 [1]
5 : C : 85 [1]
Question 3: Obtain the output of the following C+ + program, which will appear on the screen after its execution.
Important Note:
• All the desired header files are already included in the code, which are required to run the
code,
class Game
{
int Level, Score;
char Type;
public:
Game (char GType='p')
{Level=1; Score=0; Type= GType;}
void Play (int GS);
void Change ();
void Show()
{
cout<<Type<<"@"<<Level<<endl;
cout<<Score<<endl;
}
} ;
void main ()
{
Game A ('G'), B;
B. Show ();
A. Play (11);
A. Change ();
B. Play (25);
A. Show ();
B. Show ();
}
void Game: : Change()
{
Type=(Type== 'P')?'G' :'P';
}
void Game: :Play(int GS)
{
Score+=GS;
if(Score>=30)
Level=3;
else if (Score>=20)
Level=2;
else
Level=l;
}
Answer:
P@1
0
P@1
11
P@2
25
Question 4: Obtain the output of the following C+ + program, which will appear on the screen after its execution.
Important Note:
• All the desired header files are already included in the code, which are required to run the code,
class Player
{
int Score, Level;
char Game;
public:
Player (char GGame='A')
{Score=0; Level=1; Game =GGame;}
void Start (int SC);
void Next ();
void Disp ()
{
cout <<Game<<"@"<<Level <<endl;
cout <<Score<<endl;
}
};
void main ()
{
Player P,Q ('B');
P. Disp ();
Q. Start (75);
Q. Next ();
P. Start (120);
Q. DispO ;
P.Disp ();
}
void Player : : Next ()
{
Game = (Game =='A')?'B':'A' ;
}
void Player : : Start (int SC)
{
Score+=SC;
If (Score>=100)
Level=3;
else if (Score>=50)
Level=2;
else
Level=1;
}
Answer:
A@1 0
A@2
75
A@3
120 [3]
Question 5: Observe the following C++ code carefully and obtain the output, which will appear on the screen after execution of it.
#include <iostream.h>
class Mausam
{
int city, Temp, Humidity;
public :
Mausam (int C = 1) {City = C; Temp =
10; Humidity = 63;};
void Sun (int T) {Temp + = T;};
void Rain (int H) {Humidity +=H;};
void Checkout ( )
{
cout<<City<<":"<<Temp<< "&" <<Humidity
<<"%"<<endl;
}
} ;
void main ( )
{
Mausam M, N(2);
M. Sun (5);
M. Checkout ( );
N. Rain (10);
N.Sun (2) ;
N.Checkout ( );
M.Rain (15) ;
M.Checkout ( ) ;
}
Answer:
Output:
1:1:15% [1]
2:2:12% [1]
3:1:15% [1]
Question 6: Observe the following C++ code carefully and obtain the output, which will appear on the screen after execution of it.
# include <iostream.h>
class Aroundus
{
int Place, Humidity, Temp; public:
Aroundus(int p = 2) {
Place = P; Humidity = 60; Temp = 20;
}
void Hot (int T) {
Temp+=T ;
};
void Humid (int H) {
Humidity+=H ;
};
void JustSee ( )
{
cout<<Place<<":"<<Temp<<"&"<<Humidity <<"%"<<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Aroundus A, B (5) ;
A. Hot (10) ;
A. JustSee ( ) ;
B. Humid (15) ;
B. Hot (2) ;
B. JustSee ( ) ;
A. Humid (5) ;
A. Justsee ( ) ;
Answer:
Output:
2 : 30 & 60% [1]
5 : 22 & 75% [1]
2 : 30 & 65% [1]
Question 7: Find the output of the following program :
#include <iostream.h>
class METRO
{
int Mno, TripNo, PassengerCount;
public :
METRO (int Tmno=l)
{
Mno=Tmno;
TripNo=0;
PassengerCount=0;
}
void Trip (int PC = 20)
{ TripNo++; PassengerCount+=PC;}
void StatusShow ()
{cout<<Mno<<" : "<<TripNo<<":"
<<PassengerCount<<endl;}
} ;
int main ()
{
METRO M (5), T;
M.Trip () ;
T.Trip (50) ;
M.StatusShow ();
M.Trip (30) ;
T.StatusShow ();
M.StatusShow ();
}
Answer:
Output:
5 :1: 20
1 :1 : 50
5 : 2 : 50
Question 8: Find the output of the following program:
#include<iostream.h>
class TRAIN
{
int Tno, TripNo, PersonCount;
public :
TRAIN (int Tmno=l) {Tno=Tno; TripNo=0; PersonCount = 0;}
void Trip (int TC=100)
{TripNo++; PersonCount+=TC;}
void Show ()
{cout<<Tno<<" : "<<Trip’No<<" : "<<Person Count <<endl;}
};
void main ()
{
TRAIN T (10), N.
N. Trip () ;
T. Show () ;
T. Trip (70)
N. Trip (40)
N. Show () ;
T. Show () ;
}
Answer:
Output:
1202 : 0:0
950 : 2 :140
1202 :1: 70
Question 9: Write the output of the following C++ progam code:
Note : Assume all required header files are already being included in the program,
class seminar
{
char topic [30];
int charges;
public:
{
strcpy(topic,"Registration");
charges=5000;
}
seminar(char t [ ] )
{
strcpy (topic,t)
charges = 5000;
}
seminar (intc)
{
strcpy(topic,"Registration with
Discount") ;
charges=5000-c;
}
void regis(char t [ ], int c)
{
strcpy(topic, t);
charges=charges+c;
}
void regis(int c=2000)
{
charges=charges+c;
}
void subject(char t [ ],int c)
{
strcpy(topic,t);
charges=charges+c;
}
void show ( )
{
cout<<topic<<"@<<charges<<endl;
}
};
void main ( )
{
seminar s1,s2(1000),s3("Genetic Mutation") , s4;
s1.show ( );
s2.show ( );
s1.subject("ICT",2000) ;
s1.show ( );
s2.regis("Cyber Crime",2500);
s2.show ( );
s3.regis ( ) ;
s3.show();
s4=s2;
s4.show();
getch();
}
Answer:
Registration@5000
Registration with Discount@4000
ICT@7000
Cyber Crime@6500
Genetic Mutation@7000
Cyber Crime@6500
(1/2 mark for each correct output)
Note:
Question 10: Find and write the output of the following C+ + program code:
Note : Assume all required header files are already being included in the program,
class product
{
int PID'
float price;
int Qty;
public:
Product ( ) {PID=100;Price=20;Qty=100;}
void Add(int I, float p)
{
ID=I ;
Price=P;
}
void Alter(int Change,int TQ)
{
Price+=Change;
Qty+=TQ;
}
void Display ( )
{
cout<<"PID:"<<PID<<endl;
cout<<Qty<<"@"<<Price<<endl;
}
};
void main ( )
{
Product P,Q,R;
P. Add(104,50);
Q. Add(201,30) ;
R. Alter(-10,25) ;
P. Display();
Q. Display();
R. Display();
}
Answer:
PID: 100
104@150
PID:29 201
@130 PID:25
100@10
TOPIC-2
Function Overloading
Short Answer Type Questions-1
Question 1: Answer the questions (i) and (ii) after going through the following class :
class Motor
{
int MotorNo. Track;
public :
Motor ( ); //Function 1
Motor (int MN) ; //Function 2
Motor (Motor &M); //Function 3
void Allocate ( ) ///Function 4
void Move ( ); //Function 5
} ;
void main ( )
{
Motor M;
}
(i) Out of the following, which of the option is correct for calling Function 2?
Option 1 – Motor N (M);
Option 2 – Motor P (10);
(ii) Name the feature of Object Oriented
Programming, which is illustrated by Function 1, Function 2 and Function 3 combined together.
Answer:
(i) Option 2 is correct for calling Function 2. [1]
(ii) Function overloading, i.e., Polymorphism. [1]
Question 2: Answer the questions (i) and (ii) after going through the following class :
class Race
{
int CarNo, Track;
public:
Race ( ) ; //Function 1
Race (int CN) ; //Function 2
Race (Race &R); //Function 3
void Register ( ); //Function 4
void Drive ( ); //Function 5
};
void main ( )
{
Race R ;
:
}
(i) Out of the following, which of the option is correct for calling Function 2?
Option 1 – Race T (30);
Option 2 – Race U (R);
(ii) Name the feature of Object Oriented Programming, which is illustrated by Function 1, Function 2 and Function 3 combined together.
Answer:
(i) Option 1 – Race T (30); is correct since the parameter to T is integer.
(ii) When Functions – Function 1, Function 2 and Function 3 are combined together, it is referred as constructor overloading, i.e., Polymorphism.
Question 3: What is function overloading ? Write an example using C++ to illustrate the concept of function overloading.
Answer:
Function Overloading
In C++, we can declare different functions with same name. This property is called function overloading. Function overloading implements polymorphism.
Example:
# include <iostream.h >
#include < stdlib.h>
#include < conio.h>
#define pi 3.14
class fn [1]
{
public:
void area(int); //circle
void area(int,int); //rectangle
};
void fn : : area(int a)
{
cout <<"Area of Circle:"<<pi*a*a;
}
void fn::area (int a, int b)
{
cout <<"Area of rectangle:"<<a*b;
}
void main ( )
{
int ch;
int a, b, r;
fn obj;
cout<<''\nl.Area of Circle\
n2.Area of Rectangle\ n3.Exit\n:";
cout<<''Enter your Choice:";
cin>>ch;
switch(ch)
{
case 1:
cin>>r;
obj.area(r);
break; [1]
case 2:
'cin>>a>>b;
obj.area(a,b);
break;
case 3:
exit (0);
}
getch ( );
}
Question 4: Write the output of the following C++ code. Also, write the name of feature of Objects Oriented Programming used in the following program jointly illustrated by the functions [I]
to [IV]
include<iostream.h>
void Line ( ) //Function[I]
{
for(int L=1;L<=80;L++)
Cout<<"-";
cout<<endl;
}
void Line(int N) //Function[II]
{
for (int L=1;L<=N;L++)
Cout<<"*";
cout<<endl;
}
void Line (char C, Int N) //Function[III]
{
for(int L=1;L<=N;L++)
Cout<<C;
cout<<endl;
}
Void Line (int M, int, N) //Function [IV]
{
for (int L = 1;L<=N;L++)
cout<<M*L;
cout<<endl;
}
void main ( )
{
int A=9, B=4 C=3;
char K = "#" ;
Line (K, B);
Line (A,C);
}
Answer:
####
91827
Function Overloading
Question 5: Answer the question (i) and (ii) after going through the following class :
class Test
{
int Regno, Max, Min, Score;
public :
Test ( ) //Function 1
{
Regno =101; Max = 100; Min=40;
Score=75 ;
}
Test (int Pregno, int Pscore) //Function 2
{
Regno=Pregno;Max=100;Min=40;
Score=Pscore;
}
~Test() //Function 3
{
cout<<"Test Over"<<endl;
}
void Display ( ) //Function 4
{
cout<<Regno<<":"<<Max<<":"<<Min<< endl ;
cout<<" [Score]"<<Score<<endl ;
}
} ;
(i) As per object oriented programming which concept is illustrated by function 1 and function 2 together ?
Answer:
Polymorphism
OR
Function Overloading
OR
Constructor Overloading
(ii) What is Function 3 specially referred as ? When do you think, Function 3 will be invoked/called ?
Answer: Destructor is invoked or called when scope of an Object gets over.
Question 6: Answer the questions (i) and (ii) after going through the following class :
class Exam
{
int Rno, Maxmarks, MinMarks, marks;
pubic :
Exam () //Module 1
{
Rno=101;MaxMarks=100;MinMarks=40; Marks =75 ;
}
Exam (int Prno, int Pmarks) / / Module 2
{
Rno = Prno;MaxMarks = l0 0;MinMar ks=40;
Marks=Pmarks;
}
-Exam () //Module 3
{
cout<<"Exam Over" <<Endl ;
}
void show ( ) //module 4
{
cout<<Rno<<" : "< <MaxMarks < <":"<< MinMarks <<endl;
cout<<"[Marks Got]" <<Marks<<endl;
}
};
(i) As per Object Oriented Programming, which concept is illustrated by Module 1 and Module 2 together?
Answer:
Polymorphism
Or
Constructor Overloading
OR
Function Overloading
(ii) What is Module 3 referred as ? When do you think, Module 3 will be invoked/called?
Answer: Destructor. It is invoked as soon as the scope of the object gets over.
(1/2 Mark for indentifying it as Destructor)
(1/2 Mark for mentioning correctly when it be called/invoked)
Question 7: What do you understand by Function overloading or functional polymorphism? Explain with suitable example.
Answer: Function overloading is a method of using the same function or method to work using different sets of input. It is one of the example of polymorphism, where more than one
function carrying similar name behaves differently with different set of parameters passed to them,
void show ()
{
cout<<"\n Hello World!";
}
void show(char na [ ])
{
cout<<"\n Hello Word! Its"<<na;
{
(1 Mark for correct explanation of Function overloading)
(1 Mark for suitable example of Function overloading)
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science Chapter 3 Stack |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science Chapter 4 Queue |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science Chapter 8 Database Concepts |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science Chapter 9 Structured Query Language |
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science Object Oriented Programming in C++
The above provided NCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science Object Oriented Programming in C++ is available on our website for free download in Pdf. You can read the solutions to all questions given in your Class 12 Computer Science textbook online or you can easily download them in pdf. The answers to each question in Object Oriented Programming in C++ of Computer Science Class 12 has been designed based on the latest syllabus released for the current year. We have also provided detailed explanations for all difficult topics in Object Oriented Programming in C++ Class 12 chapter of Computer Science so that it can be easier for students to understand all answers. These solutions of Object Oriented Programming in C++ NCERT Questions given in your textbook for Class 12 Computer Science have been designed to help students understand the difficult topics of Computer Science in an easy manner. These will also help to build a strong foundation in the Computer Science. There is a combination of theoretical and practical questions relating to all chapters in Computer Science to check the overall learning of the students of Class 12.
You can download the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Computer Science Object Oriented Programming in C++ for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the NCERT Solutions issued for Class 12 Computer Science Object Oriented Programming in C++ have been made available here for latest academic session
Regular revision of NCERT Solutions given on studiestoday for Class 12 subject Computer Science Object Oriented Programming in C++ can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all latest NCERT Object Oriented Programming in C++ Class 12 Computer Science solutions based on the latest books for the current academic session
Yes, NCERT solutions for Class 12 Object Oriented Programming in C++ Computer Science are available in multiple languages, including English, Hindi
All questions given in the end of the chapter Object Oriented Programming in C++ have been answered by our teachers

