NCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science Chapter 8 Database Concepts have been provided below and is also available in Pdf for free download. The NCERT solutions for Class 12 Computer Science have been prepared as per the latest syllabus, NCERT books and examination pattern suggested in Class 12 by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. Questions given in NCERT book for Class 12 Computer Science are an important part of exams for Class 12 Computer Science and if answered properly can help you to get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise answers for NCERT Class 12 Computer Science and also download more latest study material for all subjects. Chapter 8 Database Concepts is an important topic in Class 12, please refer to answers provided below to help you score better in exams
Chapter 8 Database Concepts Class 12 Computer Science NCERT Solutions
Class 12 Computer Science students should refer to the following NCERT questions with answers for Chapter 8 Database Concepts in Class 12. These NCERT Solutions with answers for Class 12 Computer Science will come in exams and help you to score good marks
Chapter 8 Database Concepts NCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science
Chapter - Database Concepts
Question 1: What is relation? Define the relational data model.
Answer: A relation is a table having atomic values, unique row and unordered rows and columns. The relational mode represent data and relationship among data by a collection of tables known as relation, each of which has a number of columns with unique names.
Question 2: What are all the domain names possible in gender ?
Answer: Male and Female.
Question 3: Give a suitable example of a table with sample data and illustrate Primary and Candidate Keys in it.
Answer: A table may have more than one such attribute/ group of attribute that identifies a row/tuple uniquely, all such attribute(s) are known as Candidate Keys. Out of the Candidate keys, one is selected as Primary Key,
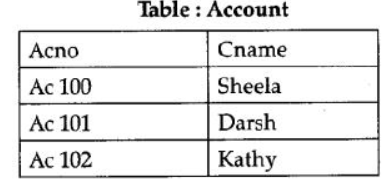
Question 4: Differentiate between cardinality and degree of a table with the help of an example.
Answer: Cardinality is defined as the number of rows in table. Degree is the number of columns in a table, eg: Consider the following tables
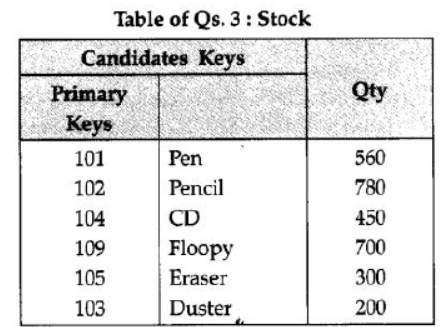
(1 Mark for writing suitable example/correct definition of a table)
(½ Mark for correct illustration/definition of Candidate Keys)
(½ Mark for correct illustration/definition of Primary Key)
Cardinality of Account table is : 3
Degree of Account table is : 2
[½ mark each for definition of cardinality and degree]
[1 mark for correct demonstration using example]
Question 5: Observe the following table carefully and write the names of the most appropriate columns, which can be considered as (i) candidate keys and (ii) primary key.
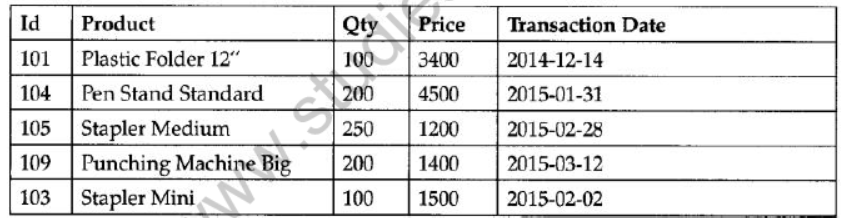
Answer:
Candidate keys : Id, Product
Primary keys: Id
(1 Mark for writing correct Candidate keys)
(1 Mark for writing correct Primary key)
Note : No marks to be deducted for mentioning Price and/or Transaction Date as additional candidate keys.
Question 6: Observe the following table carefully and write the names of the most appropriate columns,which can be considered as (i) candidate keys and (ii) primary key :
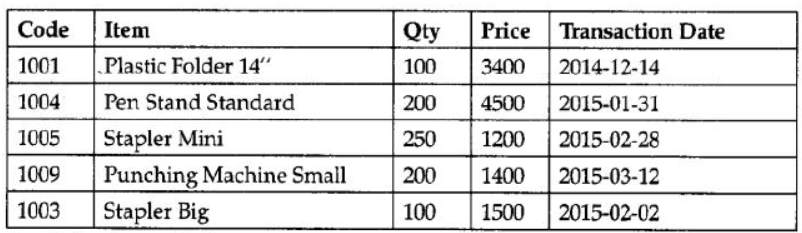
Answer:
Candidate keys : Code, Item Primary keys : Code
(1 Mark for writing correct Candidate keys)
(1 Mark for writing correct Primary key)
Note : No marks to be deducted for mentioning Price and/or Transaction Date as additional candidate keys.
Question 7: Define degree and cardinality. Based upon given table write degree and cardinality.
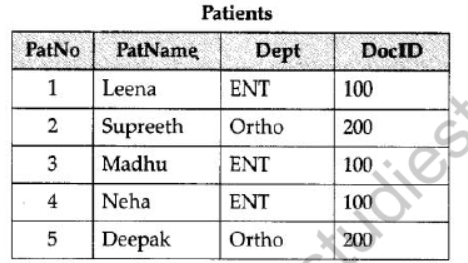
Answer:
Degree is the number of attributes or columns present in a table.
Cardinality is the number of tuples or rows present in a table.
Patients Degree = 4
[½ mark for each correct definition]
Cardinality = 5
[ ½ mark for each correct answer]
Question 8: Differentiate between the Primary key and Alternate key of a table with the help of an example.
Answer:
Primary Key – A primary key is a value that can be used to identify a unique row in a table .
Alternate Key – An alternate key is any candidate key which is not selected to be the primary key.
Example:
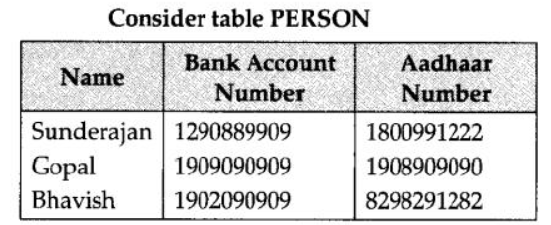
So, (Bank Account Number, Aadhaar Number) is a candidate key for the table.
Aadhaar Number ” Primary key
Bank Account Number ” Alternate Key
Question 9: Explain the concept of candidate keys with the help of an appropriate example.
Answer:
Candidate key is a column or set of columns that can help in identifying records uniquely.
Example, consider a Table STUDENT
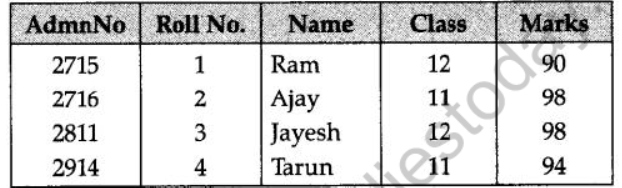
Here, AdminN0 & Roll N0 define Table uniquely.
Hence, they are candidate keys.
Question 10: A table ‘customer’ has 10 columns but no row. Later, 10 new rows are inserted and 3 rows are deleted in the table. What is the degree and cardinality of the table customer
Answer:
Degree = 10[no. of cols]
Cardinality = 10-3=7[no. of rows]
Question 11: A table ‘student’ has 3 columns and 10 rows and another table ‘student 2’ has the same number of columns and 15 rows. 5 rows are common in both the tables. If we take union,what is the degree and cardinality of the resultant table ?
Answer:
Degree-3
Cardinality – 30 = (20 + 15-5)
Question 12: A table ‘student’ has 4 columns and 10 rows and table ‘student 2’ has 5 columns and 5 rows.
If we take Cartesian product of these two tables, what is the degree and cardinally of the resultant table?
Answer:
Degree-4 ×5=20[no. of columns]
Cardinally – 10×5 = 50 [no. of rows]
Question 13: Observe the following table and answer the parts (i) and (ii) :
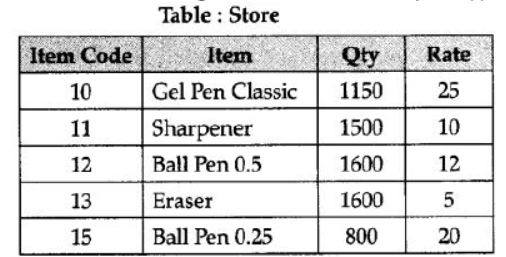
1. In the above table, can we have Qty as primary key.[Answer as yes/no]. Justify your answer.
2. What is the cardinality and degree of the above table ?
Answer:
1. We cannot use Qty as primary key because there is duplication of values and primary key value cannot be duplicate.
2. Degree = 4
[1/2 mark for each correct definition]
Cardinity = 5
[1/2 mark for each correct definition]
Question 14: What do you understand by Union & Cartesian product in the relational algebra ?
Answer:
Union of R and S : The Union of two relations is a relation that includes all the tuples that are either in R or in S or in both R and S. Duplicate tuples are eliminated.
Cartesian Product: The Cartesian Product is an operator which works on two sets. It combines the tuples of one relation with all the tuples of the other relation.
Example: Cartesian Product
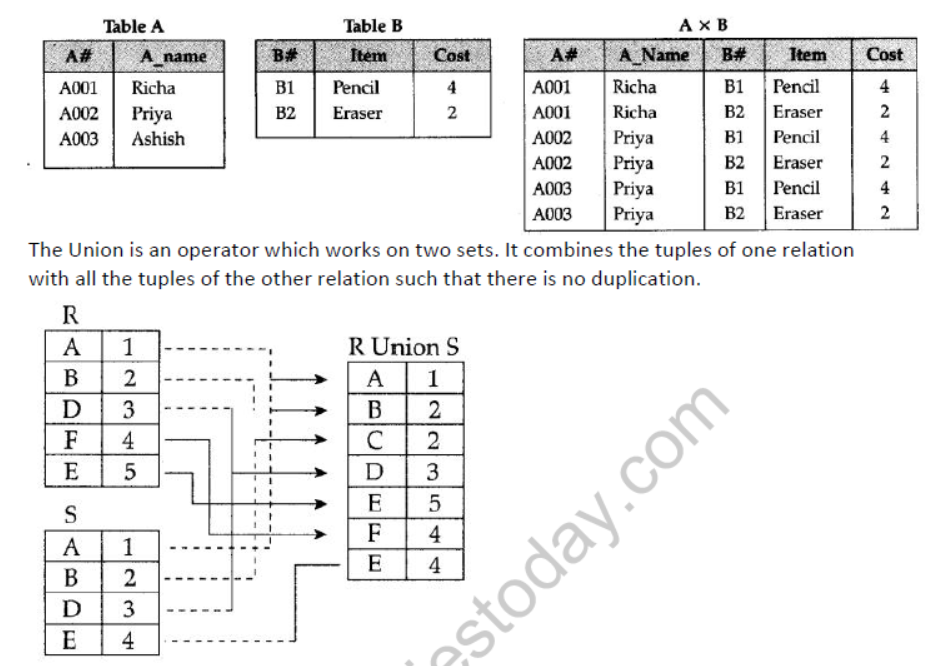
Question 15: Explain the concept of union between two tables, with the help of appropriate example.
Answer: The union operation denoted by ‘U’ combines two or more relations. The resultant of union operation contain tuples that are in either of the table or in both tables.
For example :
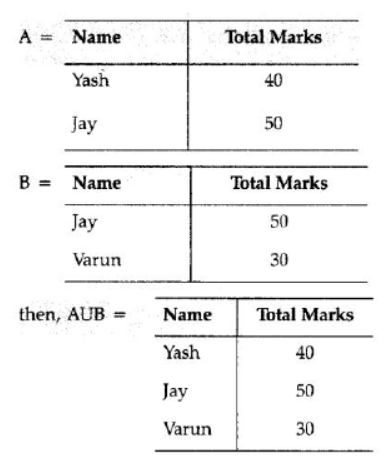
Question 16: In the following 2 tables, find the union value of Student 1 and Student 2.
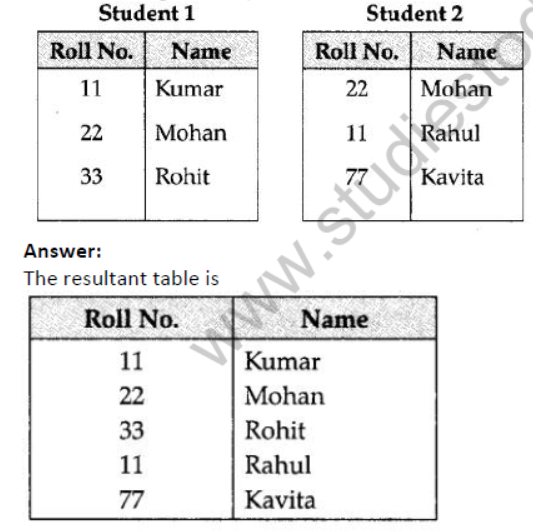
Question 17: Observe the table ‘Club’ given below :
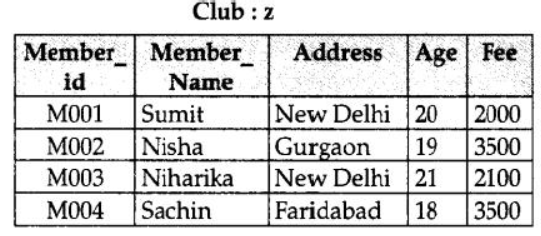
1. What is the cardinality and degree of the above given table ?
2. If a new column contact no has been added and three more members have joined the club then how these changes will affect the degree and cardinality of the above given table.
Answer:
cardinality: 4
Degree: 5
(1/2 Mark for each correct answer)
2. Cardinality: 7
Degree: 6
(1/2 Mark for each correct answer)
Question 18: In which situation can we apply union operation of two table ?
Answer:
Each table in the UNION
1. should have the same number of columns
2. similar data types
3. columns must be in the same order [2]
Short Answer Type Questions – II
Question 1: Observe the following STUDENTS and EVENTS tables carefully and write the name of the RDBMS operation which will be used to produce the output as shown in LIST. Also, find the Degree and Cardinality of the LIST.
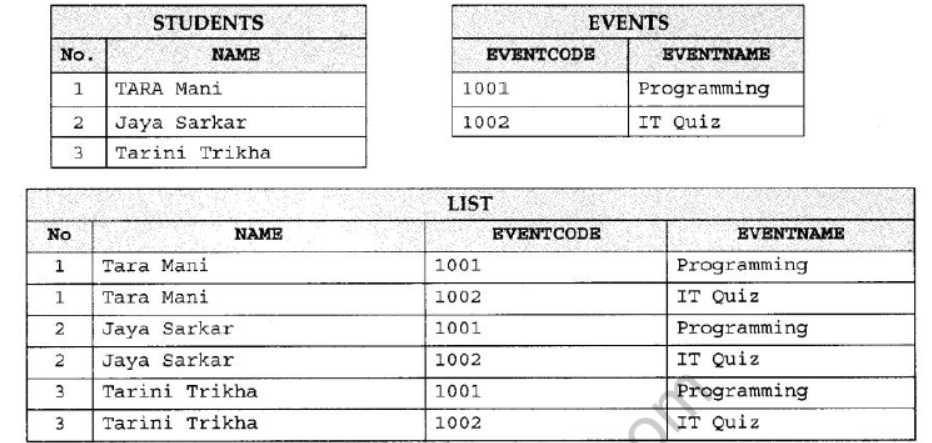
Answer:
Cartesian Product
Degree = 4
Cardinality = 6
Question 2: Observe the following PARTICIPANTS and EVENTS tables carefully and write the name of the RDBMS operation which will be used to produce the output as shown in RESULT. Also, find the Degree and Cardinality of the
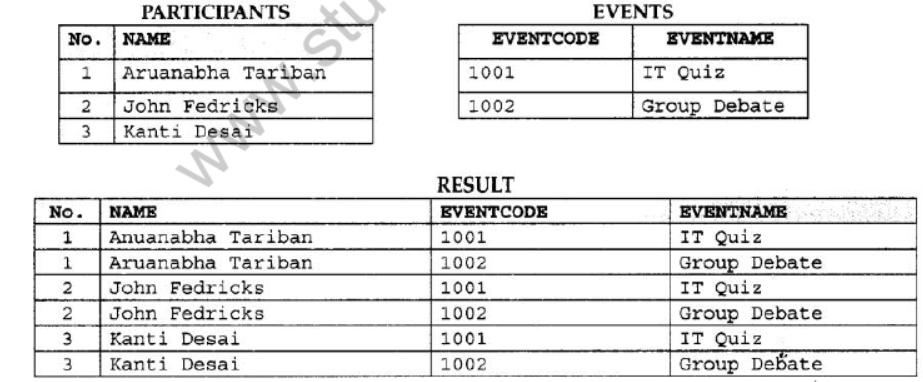
Answer:
Degree = no of columns = 4
Cartesian Product
Cardinality = no. of rows = 6
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science Chapter 3 Stack |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science Chapter 4 Queue |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science Chapter 8 Database Concepts |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science Chapter 9 Structured Query Language |
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science Chapter 8 Database Concepts
The above provided NCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science Chapter 8 Database Concepts is available on our website www.studiestoday.com for free download in Pdf. You can read the solutions to all questions given in your Class 12 Computer Science textbook online or you can easily download them in pdf. The answers to each question in Chapter 8 Database Concepts of Computer Science Class 12 has been designed based on the latest syllabus released for the current year. We have also provided detailed explanations for all difficult topics in Chapter 8 Database Concepts Class 12 chapter of Computer Science so that it can be easier for students to understand all answers. These solutions of Chapter 8 Database Concepts NCERT Questions given in your textbook for Class 12 Computer Science have been designed to help students understand the difficult topics of Computer Science in an easy manner. These will also help to build a strong foundation in the Computer Science. There is a combination of theoretical and practical questions relating to all chapters in Computer Science to check the overall learning of the students of Class 12.
You can download the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Computer Science Chapter 8 Database Concepts for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the NCERT Solutions issued for Class 12 Computer Science Chapter 8 Database Concepts have been made available here for latest academic session
Regular revision of NCERT Solutions given on studiestoday for Class 12 subject Computer Science Chapter 8 Database Concepts can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all latest NCERT Chapter 8 Database Concepts Class 12 Computer Science solutions based on the latest books for the current academic session
Yes, NCERT solutions for Class 12 Chapter 8 Database Concepts Computer Science are available in multiple languages, including English, Hindi
All questions given in the end of the chapter Chapter 8 Database Concepts have been answered by our teachers

