Please refer to CBSE Class 12 Biology HOTs Human Health and Disease. Download HOTS questions and answers for Class 12 Biology. Read CBSE Class 12 Biology HOTs for Chapter 7 Human Health and Disease below and download in pdf. High Order Thinking Skills questions come in exams for Biology in Class 12 and if prepared properly can help you to score more marks. You can refer to more chapter wise Class 12 Biology HOTS Questions with solutions and also get latest topic wise important study material as per NCERT book for Class 12 Biology and all other subjects for free on Studiestoday designed as per latest CBSE, NCERT and KVS syllabus and pattern for Class 12
Chapter 7 Human Health and Disease Class 12 Biology HOTS
Class 12 Biology students should refer to the following high order thinking skills questions with answers for Chapter 7 Human Health and Disease in Class 12. These HOTS questions with answers for Class 12 Biology will come in exams and help you to score good marks
HOTS Questions Chapter 7 Human Health and Disease Class 12 Biology with Answers
Chapter-8. HUMAN HEALTH AND DISEASE
Question. Short-lived immunity acquired from mother to fetus across the placenta or through mother’s milk to the infant is categorised as
(a) active immunity
(b) passive immunity
(c) CMI
(d) autoimmunity.
Answer : B
Question. Which of the following immunoglobulins does constitute the largest percentage in human milk?
(a) IgA
(b) IgG
(c) IgD
(d) IgM
Answer : A
Question. Identify the correct pair representing the causative agent of typhoid fever and the confirmatory test for typhoid.
(a) Salmonella typhi / Widal test
(b) Plasmodium vivax / UTI test
(c) Streptococcus pneumoniae / Widal test
(d) Salmonella typhi / Anthrone test
Answer : A
Question. Which is the particular type of drug that is obtained from the plant whose one flowering branch is shown here?
(a) Hallucinogen
(b) Depressant
(c) Stimulant
(d) Painkiller
Answer : A
Question. At which stage of HIV infection does one usually show symptoms of AIDS?
(a) Within 15 days of sexual contact with an infected person.
(b) When the infected retrovirus enters host cells.
(c) When HIV damages large number of helper T - Lymphocytes.
(d) When the viral DNA is produced by reverse transcriptase.
Answer : C
Question. Which one of the following statements is correct with respect to AIDS?
(a) The HIV can be transmitted through eating food together with an infected person
(b) Drug addicts are least susceptible to HIV infection
(c) AIDS patients are fully cured with proper care and nutrition
(d) The causative HIV retrovirus enters helper T-lymphocytes thus reducing their numbers.
Answer : D
Question. The blood does not clot inside the body because of
(a) oxygenation of blood
(b) movement of blood
(c) presence of heparin in blood
(d) absence of fibrinogen in blood.
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following is correct regarding AIDS causative agent HIV?
(a) HIV is an enveloped virus containing one molecule of single-stranded RNA and one molecule of reverse transcriptase.
(b) HIV is an enveloped virus that contains two identical molecules of single-stranded RNA and two molecules of reverse transcriptase.
(c) HIV is an unenveloped retrovirus.
(d) HIV is an enveloped virus containing two identical molecules of single stranded RNA and one molecule of reverse transcriptase.
Answer : B
Question.
In the given figure, X is caused by
I. Wuchereria II. Microsporum
III. Haemophilus IV. Epidermophyton
(a) I and II
(b) II and III
(c) II and IV
(d) I and IV
Answer : C
Question. The cell-mediated immunity inside the human body is carried out by
(a) thrombocytes
(b) erythrocytes
(c) T-lymphocytes
(d) B-lymphocytes.
Answer : C
Question. In which one of the following options the two examples are correctly matched with their particular type of immunity?
Examples Type of immunity
(a) Polymorphonuclear leukocytes and monocytes Cellular barriers
(b) Anti-tetanus and anti-snake bite injections Active immunity
(c) Saliva in mouth and tears in eyes Physical barriers
(d) Mucus coating of epithelium lining the urinogenital tract and the HCI in stomach Physiological barriers
Answer : A
Question. Internal bleeding, muscular pain, blockage of the intestinal passage and anaemia are some of the symptoms caused due to infection by
(a) Ascaris
(b) Wuchereria
(c) Plasmodium
(d) Trichophyton.
Answer : A
Question. Select the correct statement with respect to diseases and immunisation.
(a) If due to some reason B and T lymphocytes are damaged, the body will not produce antibodies against a pathogen.
(b) Injection of dead/inactivated pathogens causes passive immunity.
(c) Certain protozoans have been used in mass production of hepatitis B vaccine.
(d) Injection of snake antivenom against snake bite is an example of active immunisation.
Answer : A
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Name the drugs obtained from hemp plant.
Answer : Bhang, ganja, charas marijuana and datura.
Question. How do neutrophils acts as a cellular barrier to pathogens in humans?
Answer : Cellular barrier is a type of innate immunity. Neutrophil is a type of leucocyte (WBC) in the blood which phagocytose and destroy microbes, thus act as cellular barrier to pathogens in human.
Question. How does nicotine affect human body?
Answer : Nicotine stimulates the release of adrenaline leading to high blood pressure and heartbeat rate.
Question. A person`s nails and lips turn grey to bluish. Find out the disease he is suffering from. Name the pathogen.
Answer : i) Pneumonia ii) Streptococcus pneumonia
Question. A group of viruses infect only nose and the respiratory passage but not the lungs.
Answer : Common cold
Rhino virus
Question. The health department would like to control malaria without using chemicals in any form. Being a student of Biology what method would you suggest?
Answer : By the introduction of the mosquito larvae feeding fish Gambusia
Question. Only Female Anopheles mosquito acts as a vector? Why?
Answer : Because they require human blood protein for the production of egg.
Question. Name the missing organisms/ diseases in the table given below.
Answer : A. Ring worm
B. Wuchereria sps.
C.Entamoeba histolytica
D.Malignant malaria
Question. Why do children of metro cities of India suffer from allergies and asthma?
Answer : Because of the protected environment provided early in life and due to exposure to high level of pollution.
Question. A doctor injects preformed antibodies against a snake bite. What type of immunity does it develop in the patient?
Answer : Passive immunity
Question. A person has developed allergic reactions like sneezing, watery eyes, running nose and difficulty in breathing. What could be the reason for these symptoms?
Answer : Secretion of Histamine & Serotonin by mast cells
Antihistamine, Adrenalin, steroid
Question. A patient has lost his immunity.
(i) Name the disease associated with it.
(ii) Name the confirmatory test to diagnose the disease.
(iii) Why did he lose his immunity?
Answer : i) AIDS
II) ELISA
III) His T-Lymphocytes were destroyed
Question. A person claimed that he has seen sounds, heard colours and smelt light.
(i) What could be the possible reason?
(ii) Name two chemicals responsible for this condition.
(iii) Mention any one source for these chemicals.
Answer : i) Hallucination
ii) LSD, cocaine
iii) Erythroxylum coca/Atropa belladona/Datura sps.
Question. Complete the following flow chart showing replication of retrovirus.
Answer : a)Viral RNA enters macrophages
b) Reverse transcriptase
c) HIV viral particles
d) T-Lymphocytes.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. What category of pathogens causes poliomyelitis? How is crippling caused in the victim of this disease? How this disease can be mprevented?
Answer : Poliomyelitis is caused by poliovirus - one of a small group of RNA - containing viruses. They are included within the picornavirus group. It affects the central nervous system resulting in crippling. The disease can be prevented by avoiding contaminated food and water. Immunization using the Sabin vaccine (taken orally) or the Salk vaccine (injected) is highly effective.
Question. (a) Name the infective stage of Plasmodium which Anopheles mosquito takes in along with the blood meal from an infected human.
(b) Why does the infection cause fever in human?
(c) Give a flow chart of the part of the life cycle of this parasite passed in the insect.
Answer : (a) The infective stage of Plasmodium which Anopheles mosquito takes in along with the blood meal from an infected human is gametocyte.
(b) Malaria is characterised by fever at intervals, sudden acute chillness (cold rigor stage) accompanied by shivering followed by rise in temperature. Peak fever (hot or febrile stage) is 41.1°C or 106°F which persists for 3-6 hours. After 2-4 hours of fever, there is profuse sweating (sweating or defervescence stage) which lowers the body temperature to near normal.
(c) Life cycle of Plasmodium vivax showing stages in insect
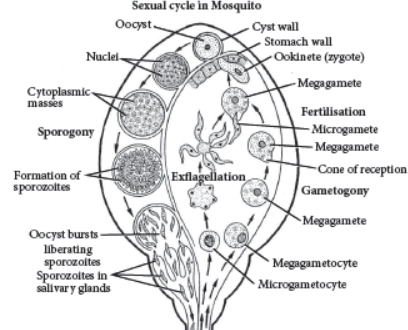
Question. How does the skin serve as the first line of defence?
Answer : The oil and sweat (chemical barriers) secreted by sebaceous and sudoriferous glands of skin contains fatty acids and lactic acid, which make the skin surface acidic. These have antibacterial and antifungal activity. Lysozyme present in sweat, also kills many bacteria. Thus it provides first line of defence.
Question. What is meant by contact inhibition? How does this phenomenon operate in cancer cells?
Answer : The normal cells are characterised by contact inhibition i.e. they form monolayers. Further, they cannot move away from each other. However in cancer cells they form multilayer due to loss of contact inhibition. As a result, they freely move, and get deposited in any part of the body, a property referred to as metastasis.
Question. A young boy when brought a pet dog home started to complain of watery eyes and running nose. The symptoms disappeared when the boywas kept away from the pet.
(a) Name the type of antibody and the chemicals responsible for such a response in the boy.
(b) Mention the name of any one drug that could be given to the boy for immediate relief from such a response.
Answer : (a) Such a response in the boy is called allergy which occurs due to production of IgE antibodies and chemicals like histamine and serotonin from the mast cells.
(b) Anti-histamine could be given to the boy for immediate relief from such a response.
Question. Differentiate between benign and malignant tumours.
Answer : Benign tumour does not invade and destroy the tissues in which it originates or spread to distant sites in the body, i.e., a tumour that is not cancerous. Benign tumour may nonetheless cause serious morbidity or mortality by compressing or obstructing vital structures. Malignant tumour invades and destroys the tissue in which it originates and has the potential to spread to other sites in the body via the blood stream and lymphatic system.
Question. Name one plant and the addictive drug extracted from its latex. How does this drug affect the human body?
Answer : Heroin commonly called smack is chemically diacetylmorphine obtained by acetylation of morphine which is extracted from the latex of poppy plant Papaver somniferum. It is a depressant and slows down body functions. It induces drowsiness and lethargy. Its after effects include indigestion, reduced vision, decreased weight, sterility and total loss of interest in work.
Question. How does moderate fever help a person in combating infections? What is to be done to bring down very high body temperature?
Answer : Moderate fever strengthens the defence mechanism by activating the phagocytes and by inhibiting the growth of microbes. A very high temperature may prove dangerous. It must be quickly brought down by giving antipyretics (fever reducing drugs e.g., aspirin) and by applying cold packs.
Question. Which of the given sets include the primary lymphoid organs?
(a) Thymus, lymph nodes and spleen
(b) Bone marrow and thymus
(c) Bone marrow, Peyer’s patches and thymus
(d) Thymus, liver and tonsils
Answer : D
Question. Surgical removal of thymus of a newborn shall result in the failure to produce
(a) Allergens
(b) Interferons
(c) B-lymphocyte
(d) T-lymphocytes
Answer : A
Question. T-lymphocytes mature in the ........... while B-lymphocyte mature in the ........ .
Most appropriate combination of words to fill the blanks is
(a) thymus; bone marrow
(b) bone marrow; thymus
(c) thyroid; bone marrow
(d) yellow bone marrow; red bone marrow
Answer : A
Question. Full form of MALT is
(a) Mucosal Associated Lymphoid Tissue
(b) Memory Associated Lymphoid Tissue
(c) Memory Associated Lymphocyte Tissue
(d) Mucosa Associated Lymphocyte Tissue
Answer : A
Question. MALT constitutes about ...…… per cent of the lymphoid tissue in human body.
(a) 50%
(b) 20%
(c) 70%
(d) 10%
Answer : A
Question. Which of the following is not an autoimmune disease?
(a) Alzheimer’s disease
(b) Rheumatoid arthritis
(c) Psoriasis
(d) Vitiligo
Answer : A
Question. AIDS virus contains
(a) RNA with protein
(b) DNA with protein
(c) RNA without protein
(d) Only DNA
Answer : A
Question. Which of the following properties is possessed by malignant tumours?
(a) Metastasis
(b) Uncontrolled cell division
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Controlled cell division
Answer : C
Question. Which one of the following is not a property of cancerous cells, whereas the remaining three are?
(a) They compete with normal cells for vital nutrients
(b) They do not remain confined in the area of formation
(c) They divide in an uncontrolled manner
(d) They show contact inhibition
Answer : D
Question. Transmission of HIV infection from infected mother to her child occurs through
(a) liver
(b) placenta
(c) skin
(d) None of these
Answer : B
Question. In the given flow chart, the replication of retrovirus in a host cell is shown. Observe it carefully and fill up the blank A, B and C. (Image 109)
(a) A–Bacteriophage, B–Viral DNA is produced, C–New viral RNA is produced
(b) A–Transcriptase, B–Bacterial RNA is produced, C–New viral DNA is produced by the infected cell
(c) A–Bacteriophage, B–Viral DNA is produced, C–New viral RNA is produced by the infected cell
(d) A–Retrovirus, B–Viral DNA is produced by reverse transcriptase, C–New viral RNA is produced by the infected cell
Answer : D
Question. HIV is a ....A...... and has genetic material composed of ...B...., HIV replicates inside the host cells. It is considered a retrovirus because it uses an enzyme, ....C.... , to convert ...... D...... into .......E...... . Here A to E refers to
(a) A–retrovirus, B–RNA, C–reverse transcriptase, D–RNA, E–DNA
(b) A–retroviral, B–DNA, C–reverse transcriptase, D–DNA, E–RNA
(c) A–rhinovirus, B–DNA, C–reverse transcriptase, D–DNA, E–RNA
(d) A–adenovirus, B–RNA, C–reverse transcriptase, D–RNA, E–DNA
Answer : A
Question. In an infected human body the ‘HIV factory’ is
(a) sperm
(b) ova
(c) macrophages
(d) spleen cells
Answer : C
Question. Cannabinoids are obtained from
(a) inflorescence of the plant Cannabis sativa
(b) fruits of the plant Papaver somniferum
(c) latex of the plant Cannabis sativa
(d) plant Papaver somniferum inflorescence
Answer : A
Question. The flower tops, leaves and the resin of Cannabis sativa are used to produce
(a) marijuana
(b) hashish
(c) charas
(d) All of these
Answer : D
Question. The drug that produces profound cardiovascular effects in human beings is
(a) cocaine
(b) ganja
(c) benzodiazepine
(d) insulin
Answer : B
Question. At which stage of HIV infection does one usually show symptoms of AIDS?
(a) Within 15 days of sexual contact with an infected person
(b) When the infected retrovirus enters host cells
(c) When HIV damages large number of helper T-lymphocytes
(d) When the viral DNA is produced by reverse transcriptase
Answer : C
Question. A patient is suspected to be suffering from Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS). Which diagnostic technique will you recommend for its detection?
(a) ELISA
(b) MRT
(c) Ultrasound
(d) WIDAL
Answer : A
Question. Cell division or mitosis is a normal process in living cells but sudden and abnormal mitosis in an organ will frequently result in
(a) zygote
(b) cancer
(c) new organ
(d) gastrula
Answer : B
Question. Thymus is a lobed organ located near the...... A .....and beneath the ....B.... . The most appropriate combination for A and B is
(a) A–heart; B–breast bone
(b) A–liver; B–ribs
(c) A–heart; B–ribs
(d) A–intestine; B–ribs
Answer : A
Question. A drug called heroin is obtained from
(a) Rauwolfia serpentina
(b) Cannabis sativa
(c) Cajanus cajan
(d) Papaver somniferum
Answer : D
Question. Cannabinoid are the group of chemicals, which interact with cannabinoid receptors present principally in
(a) brain
(b) neuron
(c) nephron
(d) dendron
Answer : A
Question. The site where immature lymphocytes differentiate into antigen sensitive lymphocytes are
(a) primary lymphoid organs
(b) secondary lymphoid organs
(c) lymph nodes
(d) tonsils
Answer : B
Question. Given below the diagrammatic representation of lymph nodes. (Image 104)
Label A, B and C.
(a) A–Lymph nodes, B–Thymus, C–Lymphatic vessels
(b) A–Lymphatic vessels, B–Thyroid, C–Lymph nodes
(c) A–Tonsils, B–Peyer’s patchs, C–Lymphatic vessels
(d) A–Tonsils, B–Thymus, C–Peyer’s patches
Answer : A
Question. What is the main lymphoid organ where all blood cells including lymphocytes are produced?
(a) Bone marrow
(b) Tonsils
(c) Liver
(d) Spleen
Answer : A
Question. Which part of poppy plant is used to obtain the drug “smack”?
(a) Flowers
(b) Latex
(c) Roots
(d) Leaves
Answer : B
Question. Identify the wrongly matched pair.
(a) Ringworm – Trichophyton
(b) Plague – Varicella zoster virus
(c) Malignant malaria – Plasmodium falciparum
(d) Common cold – Rhinovirus
Answer : B
Question. In the immune system, interferons are a part of
(a) physiological barriers
(b) cellular barriers
(c) physical barriers
(d) cytokine barriers
Answer : D
Question. Find out the wrong match.
(a) Eosinophils – Allergic response
(b) Basophils – Secrete histamine and serotonin
(c) Neutrophils – Phagocytic and destroy foreign organisms
(d) Monocytes – Secrete heparin
Answer : D
Question. Which one of the following options gives the correct matching of a disease with its causative organism and mode of infection?
Disease Causative Mode of organism infection
(a) Typhoid Salmonella With inspired typhi air
(b) Pneumonia Streptococcus Droplet pneumoniae infection
(c) Elephantiasis Wuchereria With infected bancrofti water and food
(d) Malaria Plasmodium Bite of male vivax Anopheles mosquito
Answer : B
Question. Match the causative organisms with their diseases.
(A) Haemophilus (1) Malignant influenzae malaria
(B) Entamoeba (2) Elephantiasis histolytica
(C) Plasmodium (3) Pneumonia falciparum
(D) Wuchereria (4) Typhoid bancrofti
(E) Salmonella typhi (5) Amoebiasis
(a) A – 1, B – 5, C – 3, D – 2, E – 4
(b) A – 3, B – 5, C – 1, D – 2, E – 4
(c) A – 5, B –1, C – 3, D – 4, E – 2
(d) A – 1, B – 3, C – 2, D – 5, E – 4
Answer : B
Question. Which one of the following is incorrect about cancer cells?
(a) They exhibit mass proliferation.
(b) They exhibit the property of contact inhibition.
(c) They are produced when cellular oncogenes of normal cells are activated.
(d) They are metastatic.
Answer : B
Question. Which immunoglobulin can pass through placenta?
(a) IgA
(b) IgD
(c) IgG
(d) IgE
Answer : C
Question. Consider the following four statements
(i - iv) regarding kidney transplant and select the two correct ones out of these.
(i) Even if a kidney transplant is proper, the recipient may need to take immuno-suppresants for a long time.
(ii) The cell-mediated immune response is responsible for the graft rejection.
(iii) The B-lymphocytes are responsible for rejection of the graft.
(iv) The acceptance or rejection of a kidney transplant depends on specific interferons.
The two correct statements are
(a) (ii) and (iii)
(b) (iii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (ii)
Answer : D
Question. Which of the following sets of diseases is caused by bacteria?
(a) Cholera and tetanus
(b) Typhoid and smallpox
(c) Tetanus and mumps
(d) Herpes and influenza
Answer : A
Question. A doctor identifies symptoms of nasal congestion, headache, sore throat, hoarseness, cough in a patient. The conclusion is that, the patient is infected by a pathogen
(a) Plasmodium
(b) Adenovirus
(c) Salmonella
(d) Rhinovirus.
Answer : D
Question. The figure given below shows mode of action of AIDS virus. Which step shows formation of viral DNA from RNA by reverse transcription? 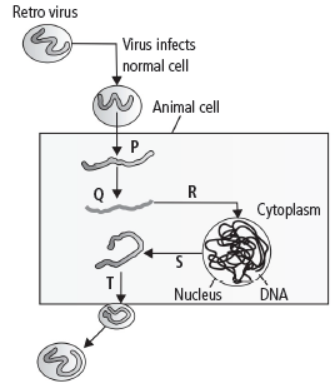
(a) P
(b) Q
(c) R and S
(d) T
Answer : B
Question. Which one of the following statements is correct with respect to immunity?
(a) Preformed antibodies need to be injected to treat the bite by a viper snake.
(b) The antibodies against small pox pathogen are produced by T-lymphocytes.
(c) Antibodies are protein molecules, each of which has four light chains.
(d) Rejection of a kidney graft is the function of B-lymphocytes.
Answer : A
Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false but reason is true.
Question. Assertion : Some diseases that occurred in childhood do not attack again.
Reason : Memory cells plays an important role.
Answer : D
Question. Assertion : Inflammatory response is produced in the body after some infections.
Reason : This is one of the ways of defence mechanism.
Answer : A
Question. Assertion : Smack is a by-product of heroin synthesis.
Reason : Heroin is an opium alkaloid.
Answer : B
Question. Assertion : Spleen produces all type of blood cells in fetus but produces only lymphocytes in adults.
Reason : Macrophages of spleen are phagocytic.
Answer : B
Question. Assertion : Immunity is the ability of the body to protect-against all type of foreign bodies that enters the body.
Reason : Spleen is the only organ involved in immunity.
Answer : D
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. How does saliva act in body defence?
Answer : Saliva contains lysozyme which kills the microorganisms that come with food and drink, thus act in body defence.
Question. Name any two infectious diseases that are transmitted through fecal-oral route.
Answer : Poliomyelitis and Shigellosis
Question. What does the enzyme reverse transcriptase catalyze?
Answer : Reverse transcriptase is an enzyme, found mainly in retroviruses, that catalyses the synthesis of DNA from RNA.
Question. How does colostrum provide initial protection against diseases to new born infants?
Answer : Colostrum provides protection against disease to new born babies because it is rich in antibodies, e.g. IgA.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. 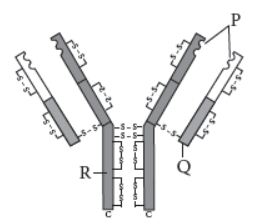
Identify P, Q and R in the schematic diagram of an antibody given above and answer the questions.
(a) Write the chemical nature of an antibody.
(b) Name the cells that produce antibodies in humans.
(c) Mention the type of immune response provided by an antibody.
Answer : In the given structure of an antibody molecule, ‘P’ is the antigen binding site, ‘Q’ is constant region of light chain and ‘R’ is constant region of heavy chain.
(a) Antibodies are immunoglobulins which are protein in nature.
(b) B-cells produce antibodies.
(c) Humoral immune response is an antibody mediated immune response.
Question. (a) What happens to a normal cell in a body when oncogenes get activated under certain conditions?
(b) Which techniques are useful to detect cancer of internal organs?
(c) Why are cancer patients often given a-interferon during their treatment?
Answer : (a) When cellular oncogenes or proto-oncogenes are activated under certain conditions in normal cells in a body, they could lead to oncogenic transformation of the cells. Transformation of normal cells into cancerous neoplastic cells may be induced by physical, chemical or biological agents also.
(b) Techniques like radiography (use of X-rays), CT (computed tomography) and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) are very useful to detect cancers of the internal organs. Computed tomography uses X-rays to generate a three-dimensional image of the internal organ. MRI uses strong magnetic fields and non-ionising radiations to accurately detect pathological and physiological changes in the living tissue.
(c) Cancer patients are often given a-interferon during their treatment, because these biological response modifiers activate the immune system and help in destroying the tumour.
Question. (a) What is meant by addictive disorder?
(b) Name any two opiate narcotics.
(c) How does amphetamines affect human body?
Answer : (a) Addictive disorder is a state in which a person has a strong desire to take the addictive substance (drugs, alcohol, tobacco etc.).
(b) The two opiate narcotics are morphine and heroin.
(c) Amphetamines are called antisleep drugs as they are CNS stimulants. They cause alertness, self-confidence, talkativeness and increased work capacity. They suppress hunger. High doses produce euphoria, depression and insomnia. After effects include nausea and vomiting.
Question. (a) List any two situations when a medical doctor could recommend injection of preformed antibodies into the body of a patient. Name this kind of immunization and mention its advantages.
(b) Name the kind of immunity attained when instead of antibodies, weakened antigens are introduced into the body.
Answer : (a) If a person is infected with some deadly microbes to which quick immune response is required as in tetanus, we need to directly inject the preformed antibodies or antitoxin. Even in the cases of snakes bites the injection which is given to the patients, contain preformed antibodies against the snake venom. This type of immunisation is called passive immunisation. It provides immediate relief.
(b) In vaccination, a preparation of antigenic proteins of pathogens or inactivated weakened pathogens are introduced into the body. This produces immune response and the type of immunity is called active immunity.
Question. What is the role of each of the following in the body defences.
(i) Antihistamine (ii) Plasma cells
(iii) Helper T cells
Answer : (i) Antihistamine is a drug that inhibits the action of histamine in the body by blocking either of two types of receptors for histamine, H1 or H2. When stimulated by histamine, H1 receptors may produce such allergic reactions as hay fever, pruritus (itching), and urticaria (nettle rash). Antihistamines that block H1 receptors (H1-receptor antagonists) are used to relieve these conditions.
(ii) Plasma cells are antibody-producing cells found in blood forming tissues and also in the epithelium of the lungs and gut. They develop in the bone marrow, lymph nodes, and spleen when antigens stimulate B-lymphocytes to produce the precursor cells that give rise to them.
(iii) Helper T cell is a type of T-lymphocyte that plays a key role in cell-mediated immunity by recognizing foreign antigen on the surface of antigen-presenting cells when associated with the individual’s MHC antigens, which is further processed by antigen-presenting cells. Helper T-cell stimulates the production of cytotoxic T-cell, which destroys the target cells.
Question. Which pathogen causes diphtheria? Why is it dreaded as fatal disease? How can it be prevented?
Answer : Diphtheria is caused by Corynebacterium diphtheriae. This disease is dreaded because at later stage, a soft grey membrane forms across the throat, constricting the air passage causing difficulty in breathing and swallowing. Bacteria multiply at the site of infection and release a toxin into the bloodstream which damages heart and nerves. Death from heart failure or general collapse can follow within four days. The disease is spread by direct contact with a patient or carrier or by contaminated milk. It can be prevented by taking DPT vaccine.
Question. What is metastasis? List any four danger signals of cancer.
Answer : Metastasis is the phenomenon in which cancer cells spread to distant sites through body fluids to develop secondary tumour. This occur by three main routes :
(i) through the blood stream (haematogenous),
(ii) through the lymphatic system,
(iii) across body cavities.
The four danger signals of cancer are :
– A lump or hard area in the breast.
– Unexplained loss of weight and low-grade fever
– An uncurable ulcer.
– Non-injury bleeding from the surface of skin, mouth or any other opening of the body.
Question. Differentiate between active immunity and passive immunity. Give any one example where passive immunisation is needed.
Answer : The given table shows differences between active and passive immunity. (Table 22)
In case of snake bites, injection containing preformed antibodies against the snake venom is given to the patient.
Question. Some of the events occur during life cycle of Plasmodium are given below. Identify the correct statement.
(a) Female mosquito take up sporozoites with blood meal.
(b) The sporozoites reproduce sexually in liver cells.
(c) When mosquito bites a man, gametocytes are injected.
(d) The gametocytes develop in RBCs.
Answer : D
Question. Which of the following diseases is caused by a protozoan?
(a) Amoebiasis
(b) Ascariasis
(c) Syphilis
(d) Influenza
Answer : A
Question. Which of the following is an opioid drug ?
(a) Heroin
(b) Cocaine
(c) Marijuana
(d) Hashish
Answer : A
Question. Transplantation of tissues/organs fails often due to non-acceptance by the patient’s body.
Which type of immune response is responsible for such rejections?
(a) Cell-mediated immune response
(b) Hormonal immune response
(c) Physiological immune response
(d) Autoimmune response
Answer : A
Question. Select incorrect option regarding the lymphoid organs labelled as P, Q, R and S in the diagram of human lymphatic system. (Image 11)
(a) T cells mature in Q.
(b) B and T cells undergo maturation in R.
(c) B and T cells undergo proliferation and differentiation in P.
(d) B cells mature in S.
Answer : B
Question. Read the statements.
(i) IgE antibodies are produced in an allergic reaction.
(ii) B-lymphocytes mediate cell mediated immunity.
(iii) The yellowish fluid colostrum has abundant IgE antibodies.
(iv) Spleen is a secondary lymphoid organ Of the above statements.
(a) (i) and (iv) are correct
(b) (i) and (ii) are correct
(c) (ii) and (iii) are correct
(d) (iii) and (iv) are correct.
Answer : A
Question. In higher vertebrates, the immune system can distinguish self-cells and non-self. If this property is lost due to genetic abnormality and it attacks self-cells, then it leads to
(a) autoimmune disease
(b) active immunity
(c) allergic response
(d) graft rejection.
Answer : A
Question. The mature infective stages of malarial parasite which are transferred from mosquito to man are
(a) trophozoites
(b) sporozoites
(c) gametocytes
(d) merozoites.
Answer : B
Question. Infection of Ascaris usually occurs by
(a) Tse-tse fly
(b) mosquito bite
(c) drinking water containing eggs of Ascaris
(d) eating imperfectly cooked pork.
Answer : C
Question. Identify the molecules (A) and (B) shown below and select the right option giving their source and use. (Image 10)
Molecule Source Use
(a) A-Cocaine Erythroxylum Accelerates the coca transport of dopamine
(b) B - Heroin Cannabis Depressant and sativa slows down body functions
(c) B-Cannabinoid Atropa Produces belladonna hallucinations
(d) A - Morphine Papaver Sedative and somniferum pain killer
Answer : D
Question. Common cold differs from pneumonia in that
(a) pneumonia is a communicable disease whereas the common cold is a nutritional deficiency disease.
(b) pneumonia can be prevented by a live attenuated bacterial vaccine whereas the common cold has no effective vaccine
(c) pneumonia is caused by a virus while the common cold is caused by the bacterium Haemophilus influenzae
(d) pneumonia pathogen infects alveoli whereas the common cold affects nose and respiratory passage but not the lungs.
Answer : D
Question. A person suffering from a disease caused by Plasmodium, experiences recurring chill and fever at the time when
(a) the sporozoites released from RBCs are being rapidly killed and broken down inside spleen
(b) the trophozoites reach maximum growth and give out certain toxins
(c) the parasite after its rapid multiplication inside RBCs ruptures them, releasing haemozoin.
(d) the microgametocytes and megagametocytes are being destroyed by the WBCs.
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following body parts is majorly affected in the disease A? (Image 10)
(a) Muscles of the legs
(b) Blood vessels of the thigh region
(c) Skin between the fingers
(d) Lymphatic vessels of the lower limbs
Answer : D
Question. Select the correct statement from the ones given below.
(a) Barbiturates when given to criminals make them tell the truth.
(b) Morphine is often given to persons who have undergone surgery as a pain killer.
(c) Chewing tobacco lowers blood pressure and heart rate.
(d) Cocaine is given to patients after surgery as it stimulates recovery.
Answer : B
Assertion & Reasoning Based MCQs
For question numbers 51-60, two statements are given-one labelled Assertion and the other labelled Reason.
Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false but reason is true.
Question. Assertion : Allergy is an autoimmune disorder.
Reason : Allergy involves IgE antibodies and chemicals like histamine and serotonin from mast cells.
Answer : B
Question. Assertion : Cancer patients are given chemotherapeutic treatments.
Reason : Chemotherapeutic agents are used to destroy malignant cells.
Answer : C
Question. Assertion : Tranquilizers are used to treat schizophrenia.
Reason : Tranquilizers are psychedelic drugs.
Answer : D
Question. Assertion : Mucous membrane are physiological barriers.
Reason : Microorganisms and dust particles entering the respiratory tract are trapped in the mucus.
Answer : B
Question. Assertion : Smoking causes oxygen deficiency in the body.
Reason : Carbon monoxide when inhaled while smoking, combines with haemoglobin to form chemically stable compound.
Answer : B
Case Based MCQs
Case I : Read the following passage and answer questions from 41 to 45 given below:
X and Y are communicable diseases whereas W and Z are non-communicable diseases. X is transmitted through vectors whereas Y is transmitted through droplet infection. W is
caused due to a hormone deficiency whereas Z is a degenerative disease.
Based on the above information, answer the following questions.
Question. Identify W, X, Y and Z.
(image) 13
Answer : B
Question. Select the correct statement.
(a) If X is sleeping sickness then its vector is Leishmania.
(b) If Y is diphtheria then it is caused by Bacillus anthracis.
(c) If W is hypothyroidism then it is caused by deficiency of thyroxine hormone.
(d) If Z is myocardial infarction then patient develops acute rheumatic fever, joint pain and throat infection.
Answer : C
Question. If X and Y both are usual diseases then which of the following holds true?
(a) X could be dengue caused by flavivirus and Y could be AIDS caused by HIV.
(b) X could be chikungunya whereas Y could be rhinitis.
(c) X could be hepatitis whereas Y could be rabies.
(d) X could be chicken pox caused by Varicella zoster virus whereas Y could be yellow fever caused by flavivirus.
Answer : B
Question. If X and Y both are bacterial diseases then select the correct match from the following.
(a) X- Bubonic plague – Yersinia pestis
(b) Y - Gonorrhea – Neisseria gonorrhoeae
(c) X - Whooping cough – Bordetella pertussis
(d) Y - Botulism – Clostridium botulinum
Answer : A
Question. Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement A : Communicable diseases could be contagious or non-contagious.
Statement B : Diseases that spread through vectors are non-contagious disease.
(a) Both statements A and B are true.
(b) Statement A is true but statement B is false.
(c) Statement A is false but statement B is true.
(d) Both statements A and B are false.
Answer : A
Case II : Read the following passage and answer questions from 46 to 50 given below:
In a study to test a new vaccine against a viral disease, mouse model testing is done. In this process, mice are vaccinated and their blood samples were tested. Mice developed mild disease symptom. After few days those mice were again infected with the virus. This time they do not show any disease symptoms. Their blood samples were tested. Two graphs show antibody concentration for the first and second infection in mice blood. (Image 13)
Based on the above information, answer the following questions.
Question. P and Q in the given graphs indicate
(a) IgM and IgG respectively
(b) IgG and IgM respectively
(c) IgG and IgE respectively
(d) IgM and IgA respectively.
Answer : B
Question. Which form of pathogen is used in vaccination?
(a) Activated and strong pathogenic antigens
(b) Inactivated and weakened pathogenic antigens
(c) Hyperactive and strong pathogen
(d) Preformed antibodies
Answer : B
Question. Which of the following is incorrect for P?
(a) It is the most abundant class of Ig.
(b) It is found in blood, lymph and intestine.
(c) It is unable to cross the placental barrier.
(d) It is a monomer.
Answer : C
Question. How does vaccination work?
(a) The immune system produces antibodies which stay in the blood.
(b) Memory lymphocytes remain in the body to fight off any future infection with the same pathogen.
(c) Antigenic proteins of pathogens generate primary immune response and the memory B and T cells.
(d) All of these.
Answer : D
Question. Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement A : Mice do not show any disease symptoms during second exposure to the pathogenic virus.
Statement B : The antibody production is accelerated and more intense during secondary immune response.
(a) Both statements A and B are true.
(b) Statement A is false but statement B is true.
(c) Statement A is true but statement B is false.
(d) Both statements A and B are false.
Answer : A
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. When is tumour referred to as malignant?
Answer : Tumour is called malignant when it invades and destroys the tissue in which it originates and has the potential to spread to other sites in the body via the bloodstream and lymphatic system.
Question. Which disease is associated with the following symptoms : Sudden onset of profuse watery stool followed by vomiting, rapid dehydration, and muscular cramps?
Answer : Cholera
Question. A boy of ten years had chicken-pox. He is not expected to have the same disease for the rest of his life. Mention how it is possible.
Answer : A body when encounters a pathogen for first time produces antibodies, that result in memory of the first encounter to protect the body in future.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. List the specific symptoms of typhoid. Name its causative agent.
Answer : Typhoid is caused by Salmonella typhii. Its specific symptoms are :
(i) constant high fever but low pulse rate
(ii) weakness and
(iii) abdominal pain and passes frequent stools.
Question. Why is using tobacco in any form injurious to health?
Answer : Tobacco is used for smoking, chewing and snuffing. Its main stimulating component is a poisonous, volatile alkaloid nicotine, which causes addiction. Besides the poisonous nicotine, it also contains carbon monoxide and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. It leads to various diseases such as cancer, high and low blood pressure, smoker’s cough and bronchitis.
Question. The diagram below illustrates the attack of a virus on a host cell. (Image 15)
(i) Name the parts numbered 1 and 2.
(ii) Describe the functions performed by the part labelled number 1 on its entry into host cell.
(iii) What are such viruses called?
(iv) Name any two human diseases caused by such viruses.
Answer : (i) 1 is viral RNA and 2 is provirus.
(ii) Viral RNA initiates the formation of viral DNA in the host.
(iii) Retroviruses.
(iv) Cancer, AIDS.
Question. (a) Name a drug used
(i) as an effective sedative and painkiller
(ii) for helping patients to cope with mental illnesses like depression, but often misused.
(b) How does the moderate and high dosage of cocaine affect the human body?
Answer : (a) (i) Morphine (ii) Barbiturates (b) Cocaine taken in low dose induces sense of well being and pleasure and delays fatigue, but in high dosage, it causes hallucinations.
Question. Name the type of cell the AIDS virus first enters into after getting inside the human body.
Explain the sequence of events that the virus undergoes within these cells to increase their progeny.
Answer : The AIDS virus first enters into macrophages after getting inside the human body.
Sequence of events are as follows: (Image 21)
Question. Describe the structure of immunoglobulin (Ig). Draw diagram showing the formation of antigen-antibody complex and label the parts.
Answer : Immunoglobulins are glycoproteins made up of four polypeptide chains (linked by disulphide bonds), two heavy and two light chains. Light and heavy chains are subdivided into variable and constant region. Variable portion is used for binding to antigen and a constant portion determines its adherence and diffusivity. (Image 22)
Question. Name the pathogen that causes amoebiasisin hu mans. Give the symptoms and the mode of transmission of the disease.
Answer : Amoebiasis is caused by monogenetic protozoan Entamoeba histolytica. It is characterised by abdominal pain, mild diarrhoea alternating with constipation, passing out of mucus, pieces of necrotic mucous membrane and blood in faeces, and faeces with cysts. The infection occurs by the cysts of Entamoeba present in the stool of infected person, cat, dog, monkey, rat, rabbit etc. through the agency of house flies, manure, air currents, a number of other physical contacts and unsafe drinking water.
Question. Why does a doctor administer tetanus antitoxin and not a tetanus vaccine to a child injured in a roadside accident with a bleeding wound? Explain.
Answer : A child injured in a roadside accident with a bleeding wound has chances of getting infected from tetanus so quick immune response is required, therefore, preformed antibodies, or antitoxin (a preparation containing antibodies to the toxin) is directly injected. In vaccination, a preparation of antigenic proteins of pathogen or inactivated/weakened pathogen (vaccine) are introduced into the body. The antibodies produced in the body against these antigens would neutralise the pathogenic agents during actual infection. Therefore, vaccine administration would not give quick relief and thus not considered effective.
Question. How is the fetus with Rh-positive blood affected if the mother is Rh-negative?
Answer : An Rh-ve person, if exposed to Rh+ve blood, will form specific antibodies against the Rh antigens. This is observed in case of Rh-ve blood of a pregnant mother with Rh+ve blood of the foetus. Rh antigens of the foetus do not get exposed to the Rh-ve blood of the mother in the first pregnancy as the two bloods are well separated by the placenta. However, during the delivery of the first child, there is a possibility of exposure of the maternal blood to small amounts of the Rh+ve blood from the foetus. In such cases, the mother starts preparing antibodies against Rh antigen in her blood. In case of her subsequent pregnancies, the Rh antibodies from the mother (Rh-ve) can leak into the blood of the foetus (Rh+ve) and destroy the foetal RBCs. This could be fatal to the foetus or could cause severe anaemia and jaundice to the baby. This condition is called erythroblastosis foetalis. This can be avoided by administering anti-Rh antibodies to the mother immediately after the delivery of the first child.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. (a) Name and explain any four lymphoid organs present in humans.
(b) Categorise the named lymphoid organs as primary or secondary lymphoid organs, giving reasons.
Answer : (a) Four lymphoid organs present in humans are :
(i) Bone marrow : It is the main lymphoid organ where all blood cells including lymphocytes are formed. Maturation of B-lymphocytes occurs here.
(ii) Thymus : It is the site of T-lymphocyte maturation.
Thymus is situated near the heart and is quite large in size at the time of birth but keeps reducing with age.
(iii) Lymph nodes: These are small solid structures found at intervals along the lymphatic system. They are composed of lymphoid tissue and act as filters for the lymph, preventing
foreign particles from entering the bloodstream. Lymph nodes also produce lymphocytes and plasma cells.
(iv) Spleen: It is a bean shaped organ which is the largest single mass of lymphoid tissue in the body. In fetus the spleen produces all types of blood cells but in adult it only produces
lymphocytes. Macrophages of spleen are phagocytic.
(b) Bone marrow and thymus are primary lymphoid organs where T-lymphocytes and B-lymphocytes mature and acquire their antigen-specific receptors. Lymph nodes and spleen
are secondary lymphoid organs where B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes after maturation migrate via blood vascular and lymphatic system to the secondary lymphoid organs
where they undergo poliferation and differentiation.
Question. Give the scientific name of the organism that causes whooping cough. Give two main symptoms of this disease. What vaccine gives protection from this disease?
Answer : Whooping cough or pertussis is caused by Bordetella pertussis and is common childhood disease. It causes constant cough leaving the child breathless, tired and red in face. Later the voice becomes hoarse and the cough gives a whoop or a loud crowing sound while inhaling. The child usually vomits and there is frothy discharge from his mouth and nose. Immunisation of the disease is done by DPT vaccination within six weeks of birth.
Question. Describe the asexual and sexual phases of life cycle of Plasmodium that causes malaria in humans.
Answer : Malaria is caused by the toxins produced in the human body by malarial parasite Plasmodium. Life cycle of Plasmodium requires two hosts for completion. Life cycle of Plasmodium in man (asexual phase): The infective stage of Plasmodium is sporozoite. When the mosquito bites man, sporozoites present in the salivary gland of female Anopheles mosquito are injected into the blood of the man. The parasites initially multiply within the liver cells and then attack the red blood cells (RBCs) resulting in their rupture. The rupture of RBCs is associated with release of a toxic substance, haemozoin, which is responsible for the chill and high fever recurring every three to four days. The released parasites from the ruptured RBCs infect new RBCs and develop into gametocytes (male and female). When a female Anopheles mosquito sucks the blood of an infected human host, it receives RBCs containing gametocytes. Life cycle of Plasmodium in mosquito: The gametocytes come out of the RBCs into the lumen (cavity) of the stomach of the mosquito. Inside the stomach of the mosquito, the male and female gametocytes fuse (fertilize) to form zygote called oocyst. The nucleus of oocyst divides first by meiosis and subsequently by mitosis, forming large number of small haploid nuclei. At the same time, spindle shaped bodies called sporozoites are formed. When mature oocysts rupture, the sporozoites are liberated into the haemocoel (body cavity filled with blood) of the mosquito. Being motile, the sporozoites move to different organs in the body cavity of the mosquito, but many of them penetrate the salivary glands. The mosquito now becomes infective. When the female Anopheles mosquito bites a healthy person, the sporozoites are injected in his/her blood along with saliva. These sporozoites start the cycle again in human body.
| CBSE Class 12 Biology HOTs Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology HOTs Human Reproduction |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology HOTs Reproductive Health |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology HOTs Principles Of Inheritance And Variation |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology HOTs Molecular Basis of Inheritance |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology HOTs Evolution |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology HOTs Human Health and Disease |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology HOTs Microbes In Human Welfare |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology HOTs Biotechnology Principles and Processes |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology HOTs Biotechnology And Its Applications |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology HOTs Organism And Population |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology HOTs Ecosystem |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology HOTs Biodiversity And Conservation |
HOTS for Chapter 7 Human Health and Disease Biology Class 12
Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to NCERT book for Class 12 Biology to develop the Biology Class 12 HOTS. If you download HOTS with answers for the above chapter you will get higher and better marks in Class 12 test and exams in the current year as you will be able to have stronger understanding of all concepts. High Order Thinking Skills questions practice of Biology and its study material will help students to have stronger understanding of all concepts and also make them expert on all critical topics. You can easily download and save all HOTS for Class 12 Biology also from www.studiestoday.com without paying anything in Pdf format. After solving the questions given in the HOTS which have been developed as per latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 12 Biology designed by our teachers. We have also provided lot of MCQ questions for Class 12 Biology in the HOTS so that you can solve questions relating to all topics given in each chapter. After solving these you should also refer to Class 12 Biology MCQ Test for the same chapter
You can download the CBSE HOTS for Class 12 Biology Chapter 7 Human Health and Disease for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the HOTS issued by CBSE for Class 12 Biology Chapter 7 Human Health and Disease have been made available here for latest academic session
HOTS stands for "Higher Order Thinking Skills" in Chapter 7 Human Health and Disease Class 12 Biology. It refers to questions that require critical thinking, analysis, and application of knowledge
Regular revision of HOTS given on studiestoday for Class 12 subject Biology Chapter 7 Human Health and Disease can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, HOTS questions are important for Chapter 7 Human Health and Disease Class 12 Biology exams as it helps to assess your ability to think critically, apply concepts, and display understanding of the subject.

