Class 9 Social Science The Story of Village Palampur Exam Notes. Please refer to the examination notes which you can use for preparing and revising for exams. These notes will help you to revise the concepts quickly and get good marks.
Case Study Of Palampur
It is an imaginary story of a village called Palampur. Palampur was a village near a river. All the elements of the environment such as land, soil, water, plants, animals, minerals etc. were there in the village.
Main occupation : The economic activities of the people were closely related to environment. The whole village was producting almost all its bare necessities of life. Its relationship with other village and outside were limited. Simple tools were used by farmers to cultivate fields. As different people had different occupations so people used to exchange goods with each other.
Organisation Of Production
Aim :
The aim of production is to produce the goods and services that we want. There are four requirements for production of goods and services.
1.Land and other natural resources.
2.Labour
3.Physical capital - (a) fixed Capital (b) Working Capital
4.Enterpreneur
1.Land : It is a factor of production that is used for cultivation or construction.
2.Labour : It is another important factor of production. It means human exertion. Some production activities require highly educated workers to perform the necessary task. Other require workers who can do manual work.
Physical Capital :
(a)Fixed capital : Tools, machines, building can be used in production over many years. These factors of production are called fixed capital.
(b)Working capital : These include the factors of production which are used up in production. Raw material and money in hand are called working capital.
Entrepreneur : One needs knowledge and enterprise to be able to combine or arrange all the factor of production to produce an output.
FARMING IN PALAMPUR
1. Land is fixed-features of land :
(A) Land is a fixed factor of production.
(B) It is a free gift of nature.
(C) It is a passive factor of production.
♦ Fixed land : Farming is the main production activity in Palampur. 75 per cent of the working people are dependent on farming for their livelihood. Since 1960 in Palampur, there has been no expansion in land area under cultivation. By then, some of the wastelands in the village had been converted to cultivable land. There exists no further scope to increase farm production by bringing new land under cultivation.
2. Is there a way one can grow more from the same land :
Ways to produce more from the same land :
All land is cultivated in Palampur. No land is left idle. During the rainy (Kharif) season, people grow jowar and bajra which are used as cattle feed. Between October to December they cultivate Potatoes. In the winter (or the Rabi) season they sow wheat. A part of the land area is also devoted to sugarcane which is harvested once every year. The main reasons why farmers are able to grow three different crops in a year are :
(i) As a result of the coming of electricity in the Palampur village, people have greatly improved the system of irrigation. They can now irrigate more lands quite effectively.
(ii) Tube wells were first installed by the government but soon people were able to set up their own tube wells.
(iii) By multiple cropping more than one crop is grown on a piece of land during the same year. All farmers in Palampur grow at least two main crops; many are growing potato as the third crop.
(iv) The other way is to use modern farming methods for higher yield. Higher yields are possible from a combination of HYV seeds, irrigation, chemical fertilizers, pesticides etc.
(A) Production from the same piece of land can be increased by using various modern techniques.
(B) To grow more than one crop on a piece of land during the year.
(C) Due to the uncertainty of monsoon use electric run tube wells to irrigated the field.
(D) Use of HYV seeds, chemical fertilizers and pesticides in farming to increase production.
♦ Green Revolution :
Large increase in crop yields, leading to record food production started, in our country from 1960 onwards and marked a turning point in Indian agriculture which has led to green revolution in our country. The great increase in the production of food-grain crops especially the wheat crop in our country during the last 30 years is called Green Revolution. This is because a sort of revolution has taken place in Indian agriculture leading to enormous food-grain production. The revolution is called green because it has led to unprecedented greenery of crops everywhere. The period from 1960 to 1980 is also called 'golden era' for the record food-grain production. It is because of the green revolution that our country has become self sufficient in food production and even buffer stocks of food-grains have been created for use in the times of natural calamities like drought and floods.
3. Will the land sustain ? Limitation of green Revolution :
(A) HYV seeds need plenty of water and also chemical fertilizers.
(B) Higher production is possible only from a combination of HYV seeds, irrigation, chemical fertilisers, pesticides etc.
(C) In many areas, Green Revolution is associated with the loss of soil fertility due to increased use of chemical ferticlisers.
(D) Also continuous use of ground water for tube well irrigation has reduced the water table below the ground.
4. Distribution of Land : The distribution of agricultural land is uneven in Indian village. About one third of farmers are land less with no land for cultivation. The top 20 % of farmers own about 64 % of cultivable land while the other medium and the small farmers own 36 % of arable land. Very few farmers are thus able to fulfill their family seeds.
5. Who will provide the labour ? Farming requires a great deal of hard work. Small farmers along with their families cultivate their own
fields. Thus, they provide the labour required for farming themselves. Medium and large farmers hire farm labourers to work on their field. Characteristics of rural labour :
1. Farm labourers come either from landless families cultivating small piece of land.
2. They are paid very low wages or sometime in kind.
3. Wages of workers very widely from region to region and from crop to crop.
4. There is a wide variation in the duration of employment.
6. The capital needed in farming :
1. Most of the small farmers borrow money from money lenders or traders to arrange capital.
2. The money lenders and traders to charge a high rate of interest from the farmers.
3. Medium and large farmers have their own savings from the farming.
4. They also get loan from the banks.
7. Sale of surplus from Products :
1. Medium and large farmers supply wheat to the market.
2. The traders at the market buy the wheat and sell it further to shopkeepers in the town and cities.
3. Farmers used the savings to arrange for the working capital for farming in the next season.
4. A part of the earning is saved and kept for buying capital for the next season.
5. Some farmers might also use the savings to buy cattle, trucks, or to setup shop.
→ NON FARM ACTIVITIES IN PALAMPUR
♦ Non farming activities : All the economic activities which require little land are known as non farming production activities. Dairy, cottage and small scale industry shop etc are some of the non farm production activities.
(i) Dairy : Dairy is a common activity in many families of Palampur. People feed their buffalos on various kinds of grass and the jowar and bajra that grow during the kharif season. The milk is sold in Raiganj, the nearby large village. Two traders from Shahpur town have set up collection cum chilling centers at Raiganj from where the milk is transported to far away towns and cities.
(ii) Small scale manufacturing in Palampur : Less than fifty people are engaged in manufacturing in Palampur. Unlike the manufacturing that takes place in the big factories in the towns and cities, manufacturing in Palampur involves very simple production methods and are done on a small scale. They are carried outmostly at home or in the fields with the help of family labour.
(iii) The Shopkeepers of Palampur : People involved in trade (exchange of goods) are not many in Palampur. The traders of Palampur are shopkeepers who buy various goods from wholesale markets in the cities and sell them in the village. There are a few small general stores in the village selling a wide range of items like
rice, wheat, sugar, tea, oil, biscuits, soap, toothpaste, batteries, candles, notebooks, pen pencil and even some cloth.
(iv) Transport : There are a variety of vehicles on the road connecting Palampur to Raiganj. Rickshawallahs, tongawallahs, jeep, tractor, truck drivers and people driving the traditional bullock cart and bogey are people in the transport services. They ferry people and goods from one place to another, and in return get paid for it.
♦ Importance :
1. They can become the source of income for the farmers.
2. They can provide employment to landless workers.
3. They can help in establishing a market in the village.
→ FEATURES OF LABOUR
1. Labour is an active factor of production.
2. Efficiency of the labour can be increased through training.
3. Farm labourers come either from landless families cultivating small plots of land.
4. Wages are paid to the labour in lieu of the services.
→ CHARACTERISTICS OF ENTREPRENEUR
1. It is a factor of production which combines or arranges all the factor of production to produce.
2. It is an active factor of production.
3. It produces goods and services for self consumption or to sell in the market.
4. It is the most important factor of production.
CHARACTERISTICS OF CAPITAL
1. It is a man made source of production.
2. Capital is of two types i.e. fixed capital and working capital.
3. It is a passive factor of production.
4. Capital has economic value.
→ REASON OUT WHY
(i) Why is it important to increase the area under irrigation ?
It is very important to increase the area under irrigation because it is not good to depend upon monsoon rains which are erratic and undependable.
(ii) Why small farmers have little surplus produce with them ?
1. Because their total production is small.
2. They keep a substantial share of their production for their own family need from village.
(iii) Why is it generally said that we should be very careful using our natural resources ?
There is no denying the fact that we should be very careful in using our natural resources. There are many reasons for the same :
1. Scientists are continuously warning us that we had been overusing the modern farming methods for the last so many years. Too much use of these methods is going to bring catastrophe for us.
2. Some point out that the Green Revolution has led to the loss of soil fertility due increasing use of chemical fertilizers.
3. The continuous use of ground water for tube well irrigation has reduced the water table below thegro und.
4. Minerals in the chemical fertilizers, when used for long, may escape from the soil and pollute the groundwater.
5. Chemical fertilizers have another disadvantage. They kill bacteria and other organisms which are quite necessary for the fertility of the soil.
→ COMPARATIVE STUDY
(i) Distinction between fixed capital and working capital :
♦ Fixed Capital : Tools, machines and building are called fixed capital because they can be used in production
over years.
♦ Working Capital : Raw material and money from the part of working capital because unlike tools, buildings and machines they are used up in production.
(ii) Difference between
(a) Multiple Cropping and
(b) Modern farming methods.
(a) Multiple Cropping : To grow more than one crop on a piece of land during the same years is called multiple cropping. With the improvement of irrigational facilities, as a result of the coming of electricity farmers are above to grow two main crops - kharif crops (like rice, millets, maize etc.) and rabi crops (wheat, barely, grain etc.). Many farmers are also able to grow potatoes as the third crop.
(b) Modern Farming Methods : Some other farmers, like in Punjab and Haryana, have increased their production by using latest scientific methods - like using fertilizers, improved varieties of seeds, use of latest machinery, improvement of irrigational facilities etc. As a result of these modern farming methods, the farmers of Punjab and Haryana heralded the Green Revolution and improved their production many folds.
(iii) How do the medium and large farmers obtain capital for farming ? How is it different from the small farmers ?
It is a fact that the small farmers with less than 2 hectares of land, have to face much more problems thanth e medium and large farmers. As compared to small farmers, medium and large farmers can quite easily obtain capital for farming.
1. Especially large farmers have their own savings from farming which they had accumulated year after year so they don’t have any need of taking any debt from any bank money lender or any other agency.
2. Mostly medium farmers also have their own savings to spend on the betterment of their farms. But if they stand in need of any borrowing, such an amount is not quite much because they have about 50 to 75 % of the amount already with them. Such farmers can go to the bank direct and get the loan at quite a reasonable rate. The bank shall be quite happy in advancing loan to such good pay-masters. There is no risk in advancing loans to medium farmers because of their better economic condition. As compared to him a small farmer is bound to face much questioning by the bank staff, any money lender or trader.
GLOSSARY
1. Land : It is a factor of production that is used for cultivation or construction.
2. Labour : Labour is another important factor of production. It means human exertion.
3. Capital : It is a wealth other than land which is used for production of wealth.
4. Production process : Organising and utilising the factors of production for the production of goods and services is known as production process.
5. Production : Production is the creation of value in a commodity e.g. manufacturing of a car from steel.
6. Working capital : These include the factors of production which are used up in a production. Raw material and money in hand are called working capital.
7. Fixed capital : Tools, machines, buildings can be used in production over many years. These factors of production are called fixed capital.
8. Factors of production : The essential elements which cooperate with one another in process of production. Following are the major factor of production.
I. Land II. Physical capital III. Labour IV. Human capital
9. Human capital : It is the most important factors of production which put together land labour and physical capital and produce an output either to use for self consumption or to sell in a market.
10. Multiple cropping : To grow more than one crop on a piece of land during the year in known as multiple cropping.
11. Yield : It is measured as crop produced on a given piece of land during a single season.
12. Non farm activity : It refers to the activities in a village other than farming. This includes activities like manufacturing, transportation, shop keeping etc.
13. Green Revolution : The large increase in agriculture production after 1976 due to adoption of new Agricultural strategy which implied a simultaneous use of better and modern agriculture inputs.
EXERCISE
A. VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1 What is climate ?
Q.2 What is production ? Give an example.
Q.3 What are the major economic activities of rural India?
Q.4 What are the factors of production ? Name any four factor of production ?
Q.5 What is fixed capital ?
Q.6 What is working capital ?
Q.7 What is human capital ?
Q.8 What is multiple cropping ?
Q.9 Name any four methods to increase production in agriculture.
Q.10 What is the importance of green Revolution for the Indian economy ?
Q.11 Name any four states which have benefitted from Green Revolution.
Q.12 Mention any four factors responsible for low yield of food grains in India.
Q.13 What is market ?
Q.14 “Scientific reports indicate that the modern farming methods have overused the land”. Explain by giving an example.
Q.15 What is Green Revolution ?
Q.16 “The yield of food grains per hectare is high in Punjab, Haryana and Uttar Pradesh”. Give four reasons.
B. SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1 How do farmers obtain capital for farming ?
Q.2 How have modern farming methods led to loss of soil fertility ?
Q.3 Modern farming methods require the farmer to start with more cash than before. Why ?
Q.4 Why do farmers engage in small scale manufacturing in villages ?
Q.5 What are the reasons for migration of rural population ?
Q.6 How does the spread of electricity help farmers ?
Q.7 What are the different ways of increasing production on a piece of land ?
Q.8 What are the differences between multiple cropping and modern farming methods ?
Q.9 It is generally said that we should be very careful in using our natural resources. Why ?
Q.10 The cost of cultivation is rising very fast in villages. Why ?
Q.11 Why was the initial impact of Green Revolution limited to wheat and only to a few regions?
Q.12 Write any four features of land as a factor of production.
Q.13 Write any four characteristics of labour as a factor of production.
Q.14 Write any four characteristics of capital as a factor of production.
Q.15 Mention any four characteristics of an entrepreneur as a factor of production.
Q.16 Mention any four characteristics of rural labour in India.
Q.17 'Capital is a basic need in agriculture.' How is it arranged by Indian farmers ? Explain.
Q.18 What are non-farm production activities ? Give a few examples. How can these lead to economic development in rural areas ?
Q.19 What is physical capital ? What are its different types ?
Q.20 Write any three differences between land and capital.
C. LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1 How is land distributed between farmers of Indian villages ?
Q.2 What are the different ways of increasing production on the same piece of land ?
Q.3 Modern farming methods require more inputs which are manufactured in Industry. Do you agree ?
Q.4 What can be done so that more non farming production activities can be started in villages?
Q.5 What are the advantages and disadvantages of Green Revolution ?
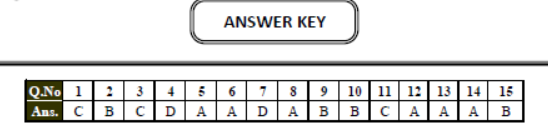
D. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Q.1 It is a place where goods and services sold -
(A) Industry
B) Office
(C) Market
(D) City
Q.2 .................... is the creation of value in commodity-
(A) Goods
(B) Production
(C) Transport
(D) Manufacturing
Q.3 ..................... is a working capital -
(A) Raw material
(B) Money
(C) Tools
(D) Labour
Q.4 .................... is a not fixed capital.
(A) Tools
(B) Machine
(C) Building
(D) Money
Q.5 The continuous use of ground water from tube well irrigation has ................... the water table -
(A) Reduced
(B) Increase
(C) Both of them
(D) None of these
Q.6 Factors responsible for low yield of food grains-
(A) Old technology
(B) Use of HYV seeds
(C) use of chemicals
(D) All the above
Q.7 The yield of food grains per hectare is high in Punjab because -
(A) Use of HYV seeds
(B) Use of modern machinery
(C) Use of tubewels for irrigation
(D) All of these
Q.8 Cultivated land area is -
(A) Fixed
(B) unlimited
(C) extend
(D) None of these
Q.9 Modern farming methods require a great deal of-
(A) Out put
(B) Input
(C) Both of them
(D) None of these
Q.10 Medium and large farmers have land more than-
(A) 1 hact.
(B) 2 hact
(C) 5 hact
(D) All the above
Q.11 Which of the following is part of working capital ?
(A) Raw material and land
(B) Raw material and building
(c) Money in hand and labour
Q.12 What is multiple cropping ?
(A) To grow more than one crop on a piece of land during the year.
(B) To grow more than one crop simultaneously
(C) To use HYV seeds to improve production
(D) None of the above
Q.13 What is the source of capital for the large farmers ?
(A) Banks and own savings
(B) Money lenders and relatives
(C) Banks and money lenders
(D) Poor farmers
Q.14 Which one of the following terms is used for measuring crop produced on a given piece of land during a single season ?
(A) Yield
(B) Productivity
(C) Cultivation
(D) Output
Q.15 'Bigha' and 'Guintha' are –
(A) The type of village house
(B) The type of hybrid seeds
(C) The measuring units of grain
(D) The measuring units of land area in village
Please click on below link to download pdf file for Class 9 Social Science The Story of Village Palampur Exam Notes.

