Class 9 Social Science India Size and Location Exam Notes. Please refer to the examination notes which you can use for preparing and revising for exams. These notes will help you to revise the concepts quickly and get good marks.
India occupies the central peninsula of southern Asia. It consists of the main land and the two group of the Islands. Andaman and Nicobar Island in the Bay of Bengal and Lakshadweep in the Arabian sea. The mainland of India lies at the head of the Indian Ocean between 8.4º and 37.6º North latitudes and 68.7º and 97.25º longitude.
India entirely lies to the north of the equator. The tropic of cancer 23.30º N passes nearly midway across India and divides it into two halves.
Standard Meridian Of India And Its Value
India lies to the east of the Prime Meridian between 68º7’ to 97º25’ East longitude. To follow one timings, India has accepted to 82º30’ E longitude as the Standard Meridian of India. The local time at this meridian has been accepted as the Indian Standard Time throughout India.
Implication Of The Tropic Of Cancer
1.Tropic of Cancer divides the country into almost two equal parts or two separate climatic zones.
2.Southern parts of India lie with in the tropic of cancer and are rationally hotter than northern parts, the latter belongs to the sub-tropical or the warm tropical zone of the northern hemisphere.
3.The areas lying to the north of the Tropic of Cancer will never have the mid day sun over head while in areas to the south of the tropic of cancer the sun will be exactly overhead at least twice in a year.
Size
1.India is a vast country which lies in the south of Asia.
2.It is the 7th largest country of the world after Russia, Canada, U.S.A., China, Brazil and Australia.
3.Its area is about 3.28 million sq. km and it is about 2.42% of the total area of the world.
4.India has a land boundary about 15200 km and the total length of the coast line of the main land including Andaman & Nicobar and Lakshadweep is 7,516.6 km.
5.India is bounded by young fold mountains in the northwest, north and north east.
6.South of about 22º north latitude, it begins to taper and extends towards the Indian Ocean, dividing it into two seas, the Arabian Sea on the west and Bay of Bengal on its east.
(a) India has a distinct physical and cultural identity :
Notwithstanding wide diversity, the Indian society has fostered unity and homogeneity. To a large extent this unity and homogeneity has been promoted by the geographical features of the country.
(i) On its north, India is bounded by lofty mountains. These mountains run east-west for thousands of kilometers. These provide a natural wall against all possible intrusions.
(ii) On the south, India is surrounded by the seas and the ocean from three sides. It means, the land is protected from outside intrusions.
These geographical features have ensured that :
(i) People from outside could come only through well-defined routes, whether by sea or through passes in mountains.
(ii) People who came from outside brought with them their cultural elements. These elements came to be assimilated in Indian culture.
(iii) Indian society adapted itself to the new norms.
(iv) Thus, by adopting new norms and values and accepting them as their own, unity and homogeneity came to be promoted.
(b) "The north-south extent of India is larger than its east-west extent even though the country's latitudinal and longitudinal extent in degrees is of the same value."
The north-south distance between two successive latitudes remains the same or constant; and it is 3214 km in this case. But the east-west distance between the two successive longitudes goes on progressively-decreasing from the equator to the poles. This is because all the meridians merge into a single point at the poles. In India the maximum east-west extent therefore is much less than 3200 km. It is 2933km only.
(c) Impact of the Longitudinal extent of India :
The earth takes 24 hours to complete one rotation (360º) about its axis. It means the earth rotates at the pace of 15 per hour(360º/24). As the longitudinal extent of India is about 30º longitude, the time lag between easternmost and westernmost points of India is of two hours. When it is 6.00 a.m at eastern extremity. India it is still 4.00 a.m. at the westernmost point of India. To avoid this time confusion, time along the Standard Meridian of India (82º 30ºE) passing through Mirzapur (in Uttar Pradesh) is taken as the standard time for the whole country. The latitude with an odd value of 82º30'E has been selected as the Standard Meridian of India as.
(i) It is well divisible by 7º30', a standard adopted by almost all the countries of the world.
(ii) It lies almost in the middle of India, and as such, it suits us the most.
(d) Impact of the Latitudinal extent of India :
Kanyakumari is situated near Equator. Here days and nights are almost equal, the maximum different is 45 minutes only. But as we move farther towards north or south of the Equator, the difference between the length of the day and night becomes progressively larger. In North Kashmir it is as much as 5 hours, as it is far away from the equator.
→ INDIA AND THE WORLD
The Indian landmass has a central location between the east and west Asia. India is a southward extension of the Asian continent. The Trans Indian Ocean routes which connect the countries of Europe in the west and the countries of East Asia provide a strategic central location to India Deccan Penninsula protrudes into the Indian Ocean, thus helping India to establish close contact with West Asia, Africa and Europe from the western coast and with south east and east Asia from the eastern coast. No other country has a long coast line on the Indian ocean as India. It is India’s eminent poisition in the Indian ocean which justifies the naming of an ocean after it.
→ MERITIS OF CENTRAL LOCATION OF INDIA
1. Because of its central location, India has the great advantage in establishing trade relation both with West Asia Africa and Europe on the eastern side.
2. India is situated in Asia which is the most populous continent of the world. Not only this it is situated in the middle of this largest continent as such India has vast and open market very near to it on both side.
3. India has sea on her three side so she can have direct trade relations through sea with all the countries of the world.
4. The Suez sea-route provides us the shortest route to industrial Europe and America.
5. The busy air-routes pass through India, connecting east. South East Asia and Australia on the one hand and Europe and America on the other.
6. The third largest ocean in the world came to be known as the Indian Ocean because the subcontinent of India stands at the head of this ocean. India was the favorite destination of the traders of the world
→TRADE REALTION
1. India’s relationships through the land routes are much older than her maritime contacts.
2. The various passes across the mountains in the north have provided passages to the ancient travellers, while the oceans restricted.
3. These routes have contributed in the exchange of ideas and commodities since ancient time.
4. The ideas of the Upanishads and the Ramayan, the stories of Panchtantra, the Indian numerals and the decimal system could reach many part of the world.
5. The spices, muslin and other merchandise were taken from India to different countries.
6. On the other hand, the influence of Greck sculpture, and architectural style of dome and minarets from West Asia can be seen in different parts of our country.
→ INDIA'S NEIGHBOURS
India’s occupies an important position in south Asia. India has 28 states and 7 union territories. India shares its land boundaries with Pakistan and Afghanistan in the north west, China (Tibet), Nepal and Bhutan in the north and Mayanmar and Bangaladesh in the east our sourthern neightbours across the sea are Srilanka and Mldives. Palak Strait separates India from Srilanka Maldives lie in the south of the Lakshdweep Island in the Indian ocean.
The Indian Subcontinent :
India is called a subcontinent because of its vastness and distinct physical and cultural identity. The countries that form the Indian subcontinent are Pakistan in the northwest, India at the core, Nepal in the north, Bhutan in the northeast and Bangladesh in the east.
GLOSSARY
1. Equator : It is an imaginary line which divides the earth into two equal hemisphere-Northern Hemisphere and Southern Hemisphere.
2. Prime Meridian : It is the main meridian which passes through Greenwich, near London. It is meridian from which longitude is measured.
3. Latitude : It is the distance of a place from the equator in the northern or the southern direction.
4. Longitude : It is the distance of place from the Prime Meridian in the eastern or the western direction.
5. Sub continent : A big geographical unit which stands out distinctly from the rest of the continent.
6. Tropic of Cancer : An imaginary line which runs parallel to the equator in the northern hemisphere of 23½ N Latitude.
7. Standard Meridian of India : The meridian of 82º30’ E whose local time serves as the standard time for the whole country.
8. Local Time : Time of a place determined by the mid day sun.
9. Standard Time : The local time taken as the time for the whole country.
10. Indian Union : Federation of India comprised of 28 states and 7 union Territories.
11. Indian mainland : The stretch of continuous landmass extending from Jammu and Kashmir to Kanyakumari and from Gujarat to Arunachal Pradesh.
12. Peninsula : A land mass bounded by the sea on three sides.
EXERCISE
A. VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1 What do you know about the location of the Indian subcontinent ?
Q.2 Where do you think the sun’s rays would be direct on the Great Nicobar Island or the Jammu & Kashmir state ?
Q.3 What is the latitudinal extent of India ?
Q.4 Why the difference between the duration of day and night is hardly felt at Kanyakumari but it is not so in Kashmir ?
Q.5 Which is the standard meridian of Indian ?
Q.6 What is the importance of standard meridian of India ?
Q.7 What do you know about Tropic of Cancer ?
Q.8 Define the following
(A) Latitude
(B) Longitude.
Q.9 Which island countries are our southernnei ghbours ?
Q.10 Latitudinal and longitudinal extent of India is about 30º. Why is North-South extent bigger than east west extent ?
Q.11 Name the longitude of our standard time meridian. Through which city of Uttar Pradesh does it cross ?
Q.12 Which two forces are responsible for shaping the present land form features of India ?
Q.13 In which hemisphere does India lie with reference to the Prime Meridian ? Mention the value of the Standard Meridian of India.
Q.14 List six countries of the world bigger than India. Compare the size of India with these countries.
Q.15 With reference to India, name the following surrounding it :
(i) Major islands
(ii) Seas, oceans and bays.
Q.16 Answer the following questions briefly.
(i) Name the group of islands lying in the Arabian sea.
(ii) Which island group of India lies to its south-east ?
(iii) Which island countries are our southern neighbors ?
B. SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1 The Tropic of Cancer runs almost half way through the country. What does this imply ?
Q.2 What is the longitudinal extent of our country ? State its significance.
Q.3 Account for the two hours time difference between the two eastern and western extremities of India.
Q.4 What are the implications of India’s longitudinal extent ?
Q.5 What is sub continent ? Name the countries which constitute the Indian sub continent ?
Q.6 Give an account of India’s location.
Q.7 The centre location of India at the head of the Indian ocean is considered of great significance. Why ?
Q.8 What are the implications of India’s latitudinal extent ?
Q.9 How far is Arunachal Pradesh befitting name for our easternmost state ?
Q.10 Give an account of India’s size ?
Q.11 Explain why Ahmedabad and Kolkata are able to see the noon sun exactly overhead in a year but not Delhi.
C. LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1 Why do we need a standard meridian for India ? Explain ?
Q.2 What do you know about the situation of India ? How has it helped her in attaining an important place in the world market.
Q.3 Give an account of India’s contact with the outside world.
Q.4 What are the implications of Tropic of Cancer ?
Q.5 Describe the trade relation of India in ancient time.
Q.6 Describe how geographical features of the country have fostered unity and homogeneity in the Indian society.
Q.7 Explain how the geographical location has helped India in attaining an important place in the world marker.
D. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
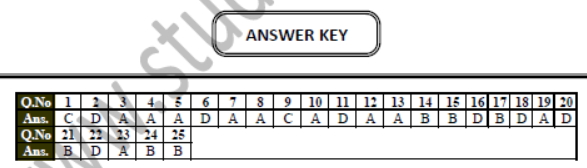
Q.1 Which of the following is the smallest state in India ?
(A) Sikkim
(B) Tripura
(C) Goa
(D) Uttaranchal
Q.2 The capital of Mizoram is -
(A) Imphal
(B) Kohima
(C) Agartala
(D) Aizwal
Q.3 The island groups of India lying in the Arabian Sea are -
(A) Lakshadweep
(B) Andaman & Nicobar
(C) Both
(D) None of these
Q.4 The state through which the Tropic of Cancer does not pass -
(A) Tamil Nadu
(B) Gujarat
(C) Madhya Pradesh
(D) West Bengal
Q.5 The southernmost tip of the Indian union and the main land -
(A) Indira Point
(B) Delhi
(C) Chennai
(D) All the above
Q.6 The southernmost latitude of the Indian mainland in degrees -
(A) 97.25º North
(B) 67.5º North
(C) 8.4º North
(D) 37.6º North
Q.7 The northern most latitude in degrees -
(A) 8.4º North
(B) 37.25º North
(C) 97.25º North
(D) All the above
Q.8 The strait separating Srilanka from India -
(A) Palk strait
(B) Kanyakumari
(C) Both of them
(D) None of these
Q.9 The place situated on three seas -
(A) Delhi
(B) Mumbai
(C) Kanyakumari
(D) All the above
Q.10 Prime Meridian of India is ................ longitude.
(A) 82.30’ E
(B) 72.25’ E
(C) 87.3’ E
(D) None of these
Q.11 North south extent of India is approx -
(A) 3600 km
(B) 3500 km
(C) 3000 km
(D) 3200 km
Q.12 East west extent of India is approx -
(A) 3000 km
(B) 3200 km
(C) 3600 km
(D) 4000 km
Q.13 Name the hemisphere in which India lies ?
(A) Northern hemisphere
(B) Southern hemisphere
(C) Western hemisphere
(D) Eastern hemisphere
Q.14 Which longitude divides India into two equal parts ?
(A) the Tropic of Capricorn
(B) The Tropic of Cancer
(C) Prime Meridian
(D) Standard Meridian
Q.15 Which country has the highest geographical area ?
(A) Canada
(B) Russia
(C) USA
(D) China
Q.16 What is India's position in the world with reference to geographical area ?
(A) 4
(B) 5
(C) 6
(D) 7
Q.17 Which island group of India lies to its South West –
(A) Andaman and Nicobar Island
(B) Lakshadweep Island
(C) Moor's Island
(D) Maldives Island
Q.18 How many states are there in India ?
(A) 25
(B) 26
(C) 27
(D) 28
Q.19 Which of the following is in the northwest of India ?
(A) Pakistan
(B) Bangladesh
(C) Sri Lanka
(D) China
Q.20 The Tropic of Cancer does not pass through ?
(A) Gujarat
(B) Madaya Pradesh
(C) Chhattisgarh
(D) Bihar
Q.21 Which one of the following water bodies separate Sir Lanka from India ?
(A) Palk Strait and Gulf of Khambat
(B) Palk Strait and Gulf of Mannar
(C) Gulf of Mannar and 10 Channel
(D) 10º Channel and Gulf Of Khambat
Q.22 Which of the following states does not share any international boundary ?
(A) Rajasthan
(B) West Bengal
(C) Uttarakhand
(D) Madhya Pradesh
Q.23 The Tropic of Cancer does not pass through –
(A) Rajasthan
(B) Tripura
(C) Jharkhand
(D) Bihar
Q.24 Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal and Sikkim have common frontiers with –
(A) China
(B) Nepal
(C) Bhutan
(D) Myanmar
Q.25 If you intend to visit Kavaratti during your summer vacations, which one of the following Union Territories of India, you will be going to –
(A) Pondicherry
(B) Lakshadweep
(C) Andaman and Nicobar
(D) Diu and Daman
Please click on below link to download pdf file for Class 9 Social Science India Size and Location Exam Notes.

