Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 10 Chemistry Periodic Classification Of Elements Worksheet Set C. Students and teachers of Class 10 Science can get free printable Worksheets for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements in PDF format prepared as per the latest syllabus and examination pattern in your schools. Class 10 students should practice questions and answers given here for Science in Class 10 which will help them to improve your knowledge of all important chapters and its topics. Students should also download free pdf of Class 10 Science Worksheets prepared by teachers as per the latest Science books and syllabus issued this academic year and solve important problems with solutions on daily basis to get more score in school exams and tests
Worksheet for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements
Class 10 Science students should download to the following Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements Class 10 worksheet in PDF. This test paper with questions and answers for Class 10 will be very useful for exams and help you to score good marks
Class 10 Science Worksheet for Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements
Multiple choice questions
Question. According to Mendeleev’s Periodic Law, the elements were arranged in the periodic table in the order of
(a) increasing atomic number
(b) decreasing atomic number
(c) increasing atomic masses
(d) decreasing atomic masses
Answer. C
Question. Which of the following statement(s) about the Modern Periodic Table are incorrect
(i) The elements in the Modern Periodic Table are arranged on the basis of their decreasing atomic number
(ii) The elements in the Modern Periodic Table are arranged on the basis of their increasing atomic masses
(iii) Isotopes are placed in adjoining group (s) in the Periodic Table
(iv) The elements in the Modern Periodic Table are arranged on the basis of their increasing atomic number
(a) (i) only
(b) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(d) (iv) only
Answer. B
Question. On the basis of electronic configuration of 5X, the group number and period of the element ‘X’ is:
(a) Group 15 period 2
(b) Group 13 period 2
(c) Group 19 period 5
(d) Group 13 period 5
Answer. B
Question. An element ‘X’ is forming an acidic oxide. Its position in modern periodic table will be
(a) Group 1 and Period 3
(b) Group 2 and Period 3
(c) Group 13 and Period 3
(d) Group 16 and Period 3
Answer. D
Question. Elements P, Q, R and S have atomic numbers 11, 15, 17 and 18 respectively. Which of them are reactive non-metals?
(a) P and Q
(b) P and R
(c) Q and R
(d) R and S
Answer. B
Question. Which of the following elements has 2 shells and both are completely filled?
(a) Helium
(b) Neon
(c) Calcium
(d) Boron
Answer. D
Question. Which of the following are the characteristics of isotopes of an element?
(i) Isotopes of an element have same atomic masses
(ii) Isotopes of an element have same atomic number
(iii) Isotopes of an element show same physical properties
(iv) Isotopes of an element show same chemical properties
(a) (i), (iii) and (iv)
(b) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Answer. C
Question. Three elements B, Si and Ge are
(a) metals
(b) non-metals
(c) metalloids
(d) metal, non-metal and metalloid respectively
Answer. C
Question. Which of the given elements A, B, C, D and E with atomic number 2, 3, 7, 10 and 30 respectively belong to the same period?
(a) A, B, C
(b) B, C, D
(c) A, D, E
(d) B, D, E
Answer. B
Question. Where would you locate the element with electronic configuration 2, 8 in the Modern Periodic Table?
(a) Group 8
(b) Group 2
(c) Group 18
(d) Group 10
Answer. C
Question. Newlands relation is called
(a) Musical Law
(b) Law of Octaves
(c) Periodic Law
(d) Atomic Mass Law
Answer. B
Today, 118 elements are known, the first 94 of which occur in nature. Of the 94 natural elements, eighty are stable.The periodic table is a graphic description of the periodic law, which states that the properties and atomic structures of the chemical elements are a periodic function of their atomic number.
Elements are placed in the periodic table by their electron configurations, which exhibit periodic recurrences that explain the trends of properties across the periodic table. As we go across a period from left to right, we add a proton to the nucleus and an electron to the valence shell with each successive element. As we go down the elements in a group, the number of electrons in the valence shell remains constant, but the principal quantum number increases by one each time.
An understanding of the electronic structure of the elements allows us to examine some of the properties that govern their chemical behavior. These properties vary periodically as the electronic structure of the elements changes.
They are
(1) size (radius) of atoms and ions,
(2) ionization energies, and
(3) electron affinities.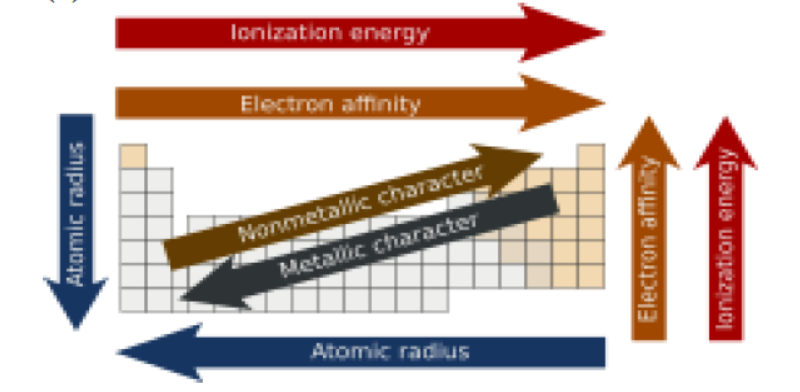
Question. Which of the following set of elements is written in order of their increasing metallic character?
(a) Na, Li, K
(b) C, O, N
(c) Mg, Al, Si
(d) Be, Mg, Ca
Answer. D
Question. Which of the following is the correct order of the atomic radii of the elements oxygen, fluorine and nitrogen?
(a) O < F < N
(b) N < F < O
(c) O < N < F
(d) F < O < N
Answer. D
Question. The positions of four elements A, B, C and D in the modern periodic table are shown below. Which element is most likely to form an acidic oxide?
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following elements would lose an electron easily?
(a) Mg
(b) Na
(c) K
(d) Ca
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following elements does not lose an electron easily?
(a) Na
(b) F
(c) Mg
(d) Al
Answer : B
Question. Which among the following elements has the largest atomic radii?
(a) Na
(b) Mg
(c) K
(d) Ca
Answer : C
Question. Elements P, Q, R and S have atomic numbers 11, 15, 17 and 18 respectively. Which of them are reactive non-metals?
(a) P and Q
(b) P and R
(c) Q and R
(d) R and S
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following gives the correct increasing order of the atomic radii of O, F and N?
(a) O < F < N
(b) N < F < O
(c) O < N < F
(d) F < O < N
Answer : D
Question. What happens to tendency to gain electron in a period?
(a) Increases,
(b) Decreases,
(c) Remaining same,
(d) First increases then decreases.
Answer. A
Question. Which of the following elements would lose an electron easily?
(a) Mg
(b) Na
(c) K
(d) Ca
Answer. C
Question. Atomic size decreases from left to right in a period because
(a) Effective nuclear charge increases
(b) Number of shells remains the same
(c) Force of attraction between the nucleus and valence electrons increases
(d) All of these
Answer. D
Assertion-Reason Type Questions
For question numbers 1 to 2 two statements are given-one labeled as Assertion (A) and the other labeled
Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below:
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false.
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true.
Question. Assertion: X with atomic number 13 is a metal.
Reason: It belongs to group 13 and 3rd period.
Answer : B
Question. Assertion: Carbon is a metalloid.
Reason: Carbon forms CO2 which is acidic oxide whereas CO is neutral oxide.
Answer : D
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. If Lithium, sodium and potassium form a Dobereiner’s triad, and if the atomic masses of Li and K are 7 and 39, respectively, Predict the atomic mass of sodium?
Answer : Sum of atomic masses of extreme elements=7+39=46. Average at mass =46/2 =23.So sodium will have atomic mass =23
Question. Name the two elements for which temporary names were given as Eka-aluminium and Eka-silicon and spaces were left by Mendeleev in his table even before their discovery.
Answer : Gallium and Germanium
Question. Write the formulae of chlorides of Eka-silicon and Eka-aluminium, the elements predicted by Mendeleev.
Answer : Formula of Chloride of Eka Silicon is GeCl4 and that of Eka Aluminium is GaCl3
Question. State Mendeleev periodic law
Answer : Properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic masses.
Question. How does atomic size vary from left to right in a period?
Answer : Atomic size decreases from left to right in a period.
Question. Which has smaller size: K(19) or Na(11); B(5) or C(6)?
Answer : Na(11) is smaller in size than K(19), C(6) is smaller in size than B(5).
Question. On moving from left to right in the second period, what happens to the number of valence electrons?
Answer : Valence electrons keeps on increasing from left to right in the second period.
Question. Write the number of valence electrons present in a nitrogen atom (714N)
Answer : It has 5 valence electrons.
Question. How does atomic size vary from left to right in a periodic table?
Answer : Atomic size decreases along a period from left to right in the periodic table.
Question. How does metallic character (electropositive character) varies down the group?
Answer : It increases down the group.
Question. Give any one difference in the electronic configuration of Group 1 and Group 2 elements.
Answer : Group 1 elements have 1 valence electron and are more reactive than Group 2 elements which have two valence electrons.
Question. The formula of magnesium oxide is MgO. State the formula of barium nitrate and barium sulphate, if barium belongs to the same group.
Answer : Ba(NO3)2, BaSO4
Question. “Fluorine is more electronegative than iodine”. Give reason in support of this.
Answer : ‘F’ is smaller in size than I, therefore the tendency to gain electrons is more due to more effective nuclear charge.
Question. What would be nature of oxides formed by the elements on the right hand side of periodic table?
Answer : Acidic
Question. The electronic configuration of two elements ‘A’ and ‘B’ are 2, 8, 7 and 2, 8, 8, 2, respectively. Write the atomic number of these elements. What will be the formula of the compound formed and the nature of bond between them, when these elements chemically combine together?
Answer : A has atomic number ‘17’, ‘B’ has atomic number ‘20’.
BA2 is the formula of the compound. The bond formed between A and B will be ionic bond
Question. Which has larger atomic radius, K(19) or Ca(20)?
Answer : K(19) is larger than Ca(20).
Question. How does reactivity of metals vary down the group?
Answer : It increases down the group.
Question. Define electropositivity.
Answer : It is defined as measure of tendency to lose electrons. The greater the tendency to lose electrons, more will be electropositivity.
Question. Which is smaller: (i) Na+ or Na, (ii) Cl or Cl– ?
Answer : (i) Na+, (ii) Cl
Question. Arrange the following metals in decreasing order of atomic size: Ca, Mg, Ba, Be
Answer : Ba > Ca > Mg > Be
Question. List any two properties of the elements belonging to the first group of modern periodic table.
Answer : (i) They should have valency equal to 1 and form monovalent positive ions.
(ii) They are highly reactive soft metals
Question. How does valency of an element vary across a period?
Answer :The valency of an element first increases and then decreases across a period.
Question. Out of Li and K, which one have stronger metallic character and why?
Answer :K’, because it can lose electrons easily due to larger size and less effective nuclear charge.
Question. The atomic radii of first group elements are given below:
Group-1 element Atomic Radii (pm)
Na 86
K 231
Rb 244
Cs 282
State the reason behind the observed trend in the above elements.
Answer : Atomic radii increases down the group because number of shells go on increasing, effective nuclear charge decreases, distance between nucleus and valence shell increases
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. The electronic configuration of an element is 2, 8, 4. State its:
(A) group and period in the Modern Periodic Table.
(B) name and write its one physical property.
Answer : (A) As the number of valence electrons in the given element is 4, it belongs to Group 14 of the Modern Periodic Table.
As the number of occupied shells is 3 (since electrons are filled in K, L and M shells), the element belongs to third period.
(b) The given element is Silicon (atomic symbol: Si). It’s physical property is:
(i) Silicon is a solid
(ii) It is a semi-conductor
(iii) It exhibits allotropy
(iv) It has a metallic luster
Question. Can the following groups of elements be classified as Dobereiner s'triad?
(A) Na, Si, Cl
(B) Be, Mg, Ca
Atomic mass of Be 9; Na 23; Mg 24; Si 28; Cl 35; Ca 40.
Explain by giving reason.
Answer : For a group to be Dobereiner’s triad, the atomic mass of the middle element must be average of the atomic masses of the first and the third elements.
(A) No, Na, Si, Cl cannot be classified as Dobereiner’s triad because all these elements do not have similar properties, although the atomic mass of silicon is the average of the atomic masses of sodium (Na) and chlorine (Cl).
Atomic mass of Si = 23 +35 /2
= 58 /2 =29
(B) Yes, Be, Mg, Ca can be classified as Dobereiner’s triad because they have similar properties and the mass of magnesium (Mg) is roughly the average of the atomic mass of Be and Ca.
Atomic mass of Mg = 9+40 /2
= 49 /2 =24.5
Question. State the Modern Periodic Law. What is the number of groups and periods in the Modern Periodic Table?
Answer : The Modern Periodic Law states that ‘properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic number.’
The number of groups in the Modern Periodic Table are 18 and the number of periods are 7.
Question. Write the formulae of chlorides of Eka-silicon and Eka-aluminium, the elements predicted by Mendeleev. [NCERT]
Answer : Eka-silicon is identified as germanium (Ge),which is placed in group 4 of Mendeleev’s periodic table. The valency of germanium is 4,so the chemical formula of its chloride must be
GeCl4.
Eka-aluminium was later identified as gallium (Ga). It is placed in group 3 of Mendeleev’s periodic table. Hence, the valence of gallium is 3 and the formula of chloride would be GaCl3.
Question. Two elements X and Y have atomic numbers 12 and 16 respectively. To which period of the modern periodic table do these two elements belong? What type of bond will be formed between them and why? Also give the chemical formula of the compound formed.
Answer : Electronic configuration of X: 2,8,2, Y: 2,8,6 Both X and Y belong to 3rd period.
Ionic bond will be formed.
Reason: X will lose 2 electrons and Y will gain 2 electrons to complete their octet and become stable.
Formula is XY.
Question. Give reason: The system of classification into triads was not found to be useful.
Answer : The system of classification into Dobereiner’s triads was not found to be useful as he failed to arrange all the then-known elements in the form of triads of elements having similar chemical properties. He could identify only three triads.
Question. Consider the following : 20Ca, 8O, 16S, 4Be Which of the above elements would you expect to be in group 2 of the Modern Periodic table?
Answer : Consider the electronic configuration of elements:
Ca: 2, 8, 8, 2
O: 2, 6
S: 2, 8, 6
Be: 2, 2
As Ca and Be all have the same number of valence electrons (2), they belong to Group 2 of the Modern Periodic Table.
Question. Name the group number of the following elements, halogens, alkali metals, inert gases, hydrogen, in the Modern Periodic Table.
Answer : Halogens — group No. 17
Alkali metals — group No. 1
Inert gases — group No. 18
Hydrogen — group No. 1
Question. What happens to the valency of elements as we move from left to right in a Periodic Table?
Answer : As we move from left to right in a Periodic Table the valency first increases till 4 and then again decreases.
L → R Valency in a period → 1 2 3 4 3 2 1 0
Question. What happens to the metallic character as we move from top to bottom in a group?
Answer : The metallic character increases as we move from top to bottom as the tendency to lose electrons increases.
Question. The atomic number of ‘X’ is 17. Predict its
(a) valency, (b) formula of halide, (c) type of ion formed, (d) reactivity with respect to the other members of same group.
Answer : ‘X’ has atomic number 17
∴ Electronic configuration → 2, 8, 7
(a) Valency = 1
(b) Formula of halide = HX
(c) Type of ion formed = Negative ion (Anion).
(d) Reactivity = Most reactive among those elements which lie below X in a group.
Question. What are the merits of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table?
Answer : Merits of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table are:
(i) Mendeleev left some gaps in his table. Predicted the chemical properties of these 3 elements which were discovered later and had same properties as predicted by Mendeleev, they were gallium, germanium and scandium.
(ii) He arranged the elements very systematically in periods and groups.
Question. Carbon with atomic number 6 and silicon with atomic number 14 belong to same group although carbon is non-metal and silicon is semi-metal.
Answer : Carbon with atomic number 6, shows electronic configuration 2, 4. Silicon with atomic number 14 shows electronic configuration 2, 8, 4.
Both the elements have same valence electrons, hence they are placed in same group.
Question. How does the valency of an element be determined, if its electronic configuration is known? What will be the valency of an element with atomic number 9?
Answer : Valency is equal to the number of valence electrons when valence electrons are from 1 to 4 or 8 – no. of
valence electrons when valence electrons are from 5 to 8.
F(9): 2, 7; It can gain 1 electron to become stable, so its valency = 1.
Question. Three elements ‘X’, ‘Y’ and ‘Z’ having atomic numbers 11, 7 and 6 respectively react with oxygen to form their oxides.
(a) Arrange these oxides in increasing order of their basic nature.
(b) Give reason for your answer.
Answer : X(11): 2, 8, 1; Y(7): 2, 5; Z(6): 2, 4
(a) Y < Z < X
(b) ‘X’ is metallic in nature, therefore it will form basic oxide. ‘Y’ and ‘Z’ are non-metals will form acidic oxides. ‘Y’ will form more acidic oxide than ‘Z’ because it is more non-metallic in nature
Question. How does electronegativity of an element change as we go down a group and across a period? Give reason.
Answer : Electronegativity decreases down the group due to increase in atomic size and decrease in effective nuclear charge.
Electronegativity increases along a period due to decrease in atomic size and increase in effective nuclear charge.
Question. Given below are four elements with their atomic numbers:
Element Atomic Number
A 16
B 11
C 3
D 14
(a) Identify the element which belong to same group of Modern Periodic Table.
(b) Arrange the given elements in decreasing order of atomic size.
(c) Write the formula of the oxide of ‘B’.
(d) Which of the above element is a metalloid?
Answer : a) ‘B’ and ‘C’ belong to same group. (b) B > D > A > C
(c) B2O (d) ‘D’ is a metalloid.
Question. Which is bigger (i) O or F, (ii) N or P and why?
Answer : O is bigger in size than F due to less effective nuclear charge.
P is bigger in size than N due to more number of shells.
Question. Two elements ‘M’ and ‘N’ belong to Group I and II respectively and are in the same period of the periodic table. How do the following properties of M and N vary:
(a) size of their atoms (b) their metallic characters
(c) their valencies in forming oxides (d) formulae of their chlorides
Answer : (a) Size of ‘N’ is smaller than ‘M’.
(b) ‘M’ is more metallic than ‘N’.
(c) Valency of ‘M’ is 1 and valency of ‘N’ is 2.
(d) MCl and NCl2 are the formulae of their chlorides.
Question. Calcium is an element with atomic number 20
(i) Will it be a metal/non-metal? (ii) What will be its valency?
(iii) What would be formula of its chloride?
(iv) Will it be larger/smaller than K?
Answer : (i) It is a metal. (ii) Its valency is equal to 2.
(iii) CaCl2 is the formula of its chloride. (iv) It will be smaller than K.
Question. How does the metallic character of elements changes along a period of the periodic table from left to right and why?
Answer : It decreases due to decrease in atomic size and decrease in tendency to lose electrons.
Question. What is meant by periodicity of properties of elements? Why are the properties of elements placed in the same group of periodic table similar?
Answer : The repetition of similar properties of elements after a certain interval of elements is called periodicity of properties.
Elements of the same group have same number of valence electrons, same valency and therefore posses similar chemical properties.
Question. Give reasons for the following:
(a) Lithium atom is smaller than sodium atom.
(b) Chlorine (Atomic number 17) is more electronegative than sulphur (Atomic number 16).
Answer : (a) It is because Li(2, 1) has two shells whereas Na(2, 8, 1) has three shells.
(b) Chlorine is smaller in size and has more effective nuclear charge than sulphur, therefore it is more electronegative.
Question. In the periodic table, how does the tendency of an atom to lose electrons changes on moving from (i) left to right across a period?, (ii) top to bottom in a group?
Answer : (i) It decreases due to increase in effective nuclear charge.
(ii) It increases due to decrease in effective nuclear charge.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. Two elements A and B belong to group 1 and 2 respectively in the same period. Compare them with respect to:
(a) Valency (b) Size of atom (c) Formula of oxide
(d) Nature of oxide (e) Metallic character
Answer : Group 1 2
Elements A B
(a) Valency A → 1, B → 2
(b) Size of atom → A is bigger atom than B.
(c) Formula of oxide → A2O, BO
(d) Nature → Basic
(e) Metallic character → A is more metallic than B.
Question. Give the characteristics of a period.
Answer : In a period as we go from left to right:
(a) Valence electrons → Goes on increasing
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8.
(b) Valency → Valency first increases and then decreases
1, 2, 3, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0.
(c) Size of atom → Size of atom goes on decreasing
(d) Metallic character → Decreases
(e) Non-metallic character → Increases
Question. Name the following elements
(a) Two shells, both of which are completely filled.
(b) Three shells with 2 valence electrons.
(c) Group 1, two shells.
(d) Group 17, period 3.
(e) Metal, with valency 3 group number 13 period 3.
Answer : (a) Two shells → K L
Filled → 2, 8
Atomic number → 10
∴ Element — Neon.
(b) Three shells → K, L, M
2 Valence electron → 2, 8, 2
Atomic number →12 ∴ Element = Magnesium
(c) Group 1
2 shells → K L
Electronic configuration → 2, 1
Atomic number → 3 ∴ Element = Lithium
(d) Group 17
Period → 3, K L M
Electronic configuration → 2, 8, 7
Atomic number → 17, ∴ Element = Chlorine
(e) Group → 13
Valency → 3
Period → 3 K L M
Electronic configuration → 2, 8, 3
∴ Atomic number → 13, ∴ Element = Aluminium.
Question. On the baiss of the table of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
(a) Name the element which is in
(i) I group and 3rd period. (ii) VII group and 2nd period.
(b) Suggest the formula for the following:
(i) Oxide of nitrogen (ii) Hydride of oxygen
(c) In group VIII of Periodic Table, why does cobalt with atomic mass 58.93 appear before nickel having atomic mass 58.71?
(d) Besides gallium, which two other elements have since been discovered for which Mendeleev had left gaps in his Periodic Table?
(e) Using atomic masses of Li, Na and K, find the average atomic mass of Li, and K and compare it with the atomic mass of Na. State the conclusion drawn from this activity.
Answer : (a) (i) Sodium (ii) Fluorine
(b) (i) N2O5 (ii)H2O
(c) Co resembles with Rh and Ir whereas ‘Ni’ resembles with Pd and Pt.
(d) Germanium and scandium
Question. (a) Which 2 criteria did Mendeleev use to classify the elements in his table.
(b) State Mendeleev’s Periodic law.
(c) Why could no fixed position be given to hydrogen in Mendeleev’s Periodic Table.
(d) How and why does the atomic size vary as you go:
(i) From left to right along a period
(ii) Down a group?
Answer : (a) (i) Increasing order of atomic mass and similarities in chemical properties of elements.
(ii) The formula of oxides and hydrides formed by elements.
(b) Mendeleev’s Periodic Law → Properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic masses.
(c) Hydrogen had no fixed position in Mendeleev’s Periodic table because it resembles alkali metal by forming positive ions and resembles halogens by forming diatomic molecule.
(d) (i) Atomic size decreases from left to right, as the valence electrons are attracted by the nucleus due to increase in the nuclear force.
(ii) The atomic size increases from top to bottom in a group because the number of shells keep on increasing therefore distance between nucleus and valence electrons increases.
Question. Mendeleev ′ predicted the existence of certain elements not known at that time and named two of them as Eka-silicon and Eka-aluminum.
(a) Name the elements which have taken the place of these elements
(b) Mention the group and the period of these elements in the Modern Periodic Table.
(c) Classify these elements as metals, non-metals or metalloids
(d) How many valence electrons are present in each one of them?
Answer : (a) Eka- silicon is Germanium (Ge)
Eka- aluminium is Gallium (Ga)
(b) Eka- silicon – group 14 & period 3
Eka- aluminium – Group 13 & period 3
(c) Eka- silicon - metalloid
Eka- aluminium – metal
(d) Valence electron present in Eka- silicon is 4
Valence electron present in Eka- aluminium is 3
Question. (a) Electropositive nature of the element(s) increases down the group and decreases across the period
(b) Electronegativity of the element decreases down the group and increases across the period
(c) Atomic size increases down the group and decreases across a period (left to right)
(d) Metallic character increases down the group and decreases across a period.
On the basis of the above trends of the Periodic Table, answer the following about the elements with atomic numbers 3 to 9.
(a) Name the most electropositive element among them
(b) Name the most electronegative element
(c) Name the element with smallest atomic size
(d) Name the element which is a metalloid
(e) Name the element which shows maximum valency
Answer : (a) Lithium (3) (b) Fluorine (9) (c) Fluorine (9)
(d) Boron (5) (e) Carbon (6). Its valency is 4.
Question.29. An element X which is a yellow solid at room temperature shows catenation and allotropy. X forms two oxides which are also formed during the thermal decomposition of Ferrous sulphate crystals and are the major air pollutants.
(a) Identify the element X
(b) Write the electronic configuration of X
(c) Write the balanced chemical equation for the thermal decomposition of Ferrous sulphate crystals?
(d) What would be the nature (acidic/ basic) of oxides formed?
(e) Locate the position of the element in the Modern Periodic Table.
Answer :
Question. An element X of group 15 exists as diatomic molecule and combines with hydrogen at 773 K in presence of the catalyst to form a compound, ammonia which has a characteristic pungent smell.
(a) Identify the element X. How many valence electrons does it have?
(b) Draw the electron dot structure of the diatomic molecule of X. What type of bond is formed in it?
(c) Draw the electron dot structure for ammonia and what type of bond is formed in it?
Answer : 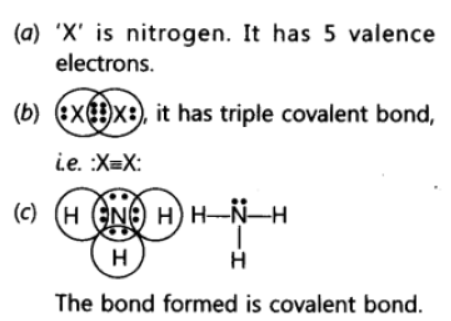
Question. a) In this ladder (Figure 5.2) symbols of elements are jumbled up. Rearrange these symbols of elements in the increasing order of their atomic number in the Periodic Table.
(b) Arrange them in the order of their group also.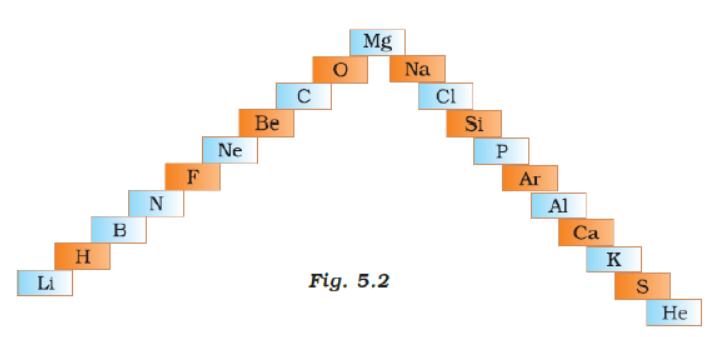
Answer : (a) H, He, Li, Be, B, C, N, O, F, Ne, Mg, Al, Si, P, S, Cl, Ar, K, Ca
(b) Group 1:H, Li, Na, K
Group 2: Be, Mg, Ca
Group 13: B. Al
Group 14: C, Si
Group 15: N. P
Group 16: 0, S
Group 17: F. U
Group 18: He, Ne, Ar
1. How many elements are known to us presently?
2. Why did the scientists feel the need to classify elements?
3. What was the basis of ‘triads’ formed by Dobereiner? Give an example.
4. What was Newlands ‘Law of Octaves’?
5. Describe in brief the classification made by Mendeleyev.
6. Why did Mendeleyev leave some gaps in his periodic table?
7. Give 2 examples of such elements which could fit into gaps left by Mendeleyev.
8. Besides Gallium, which other elements have since been discovered to fill the gaps left by Mendeleyev in his periodic table?
9. What is the basis of the Modern classification?
10. Why have Mg, Ca and Sr been kept in the same group of the periodic table? Which group is it?
11. An element has electronic configuration 2, 8, 7.
(a) What is its atomic number?
(b) Name another element to which it has similar properties.
(c) Is it smaller or bigger than another element with atomic no. 16?
12. Why has hydrogen been placed in the first group of the periodic table although it is a non-metal?
13. How does the atomic radius change in a period and a group?
14. What change is observed across a period and down a group in the following:
(a) Electron affinity (b) Ionization energy What is the unit of each?
15. Why are cations smaller than their corresponding atoms?
16. Why is the 18th gp of the periodic table called the zero group?
| CBSE Class 10 Chemistry Chemical Reactions And Equations Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 10 Chemistry Chemical Reactions And Equations Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Acids Bases And Salts Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Acids Bases And Salts Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 10 Chemistry Metals And Non Metals Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 10 Chemistry Metals And Non Metals Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 10 Physics Electricity Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Sources Of Energy Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Sustainable Management of Natural Resources Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Chemistry Revision Worksheet Set D |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Collection Of Important Questions Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Physics Worksheet Set A |
Worksheet for CBSE Science Class 10 Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements
We hope students liked the above worksheet for Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 10 Science released by CBSE. Students of Class 10 should download in Pdf format and practice the questions and solutions given in the above worksheet for Class 10 Science on a daily basis. All the latest worksheets with answers have been developed for Science by referring to the most important and regularly asked topics that the students should learn and practice to get better scores in their class tests and examinations. Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to the NCERT book for Class 10 Science to develop the Science Class 10 worksheet. After solving the questions given in the worksheet which have been developed as per the latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 10 Science designed by our teachers. We have also provided a lot of MCQ questions for Class 10 Science in the worksheet so that you can solve questions relating to all topics given in each chapter.
You can download the CBSE Printable worksheets for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements for latest session from StudiesToday.com
There is no charge for the Printable worksheets for Class 10 CBSE Science Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements you can download everything free
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all latest NCERT Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements Class 10 Science test sheets with answers based on the latest books for the current academic session
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements worksheets cover all topics as per the latest syllabus for current academic year.
Regular practice with Class 10 Science worksheets can help you understand all concepts better, you can identify weak areas, and improve your speed and accuracy.

