Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 10 Biology Heredity Worksheet Set C. Students and teachers of Class 10 Science can get free printable Worksheets for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Heredity in PDF format prepared as per the latest syllabus and examination pattern in your schools. Class 10 students should practice questions and answers given here for Science in Class 10 which will help them to improve your knowledge of all important chapters and its topics. Students should also download free pdf of Class 10 Science Worksheets prepared by teachers as per the latest Science books and syllabus issued this academic year and solve important problems with solutions on daily basis to get more score in school exams and tests
Worksheet for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Heredity
Class 10 Science students should download to the following Chapter 8 Heredity Class 10 worksheet in PDF. This test paper with questions and answers for Class 10 will be very useful for exams and help you to score good marks
Class 10 Science Worksheet for Chapter 8 Heredity
Objective Questions
Question : ___ is the observable set of characteristics of an organism
a. Phenotype
b. Genes
c. DNA
d. All of the above
Answer : A
Question : Which of the following statements is incorrect?
a. Gene is a sequence of nucleotides
b. During the process of gene expression, DNA is first copied into RNA
c. Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence
d. Genes cannot acquire mutations in their sequence
Answer : D
Question : The process where characteristics are transmitted from parent to offspring is called:
a. Variation
b. Heredity
c. Gene
d. Allele
Answer : B
Question : A zygote which has an X-chromosome inherited from the father will develop into a
a. boy
b. girl
c. X- chromosome does not determine the sex of a child
d. either boy or girl
Answer : B
Question : Two pea plants one with round green seeds (RRyy) and another with wrinkled yellow (rrYY) seeds produce F1 progeny that have round, yellow (RrYy) seeds. When F1 plants are selfed, the F2 progeny will have new combination of characters. Choose the new combination from the following: (i) Round, yellow, (ii) Round, green (iii) Wrinkled, yellow (iv) Wrinkled, green
a. (i) and (ii)
b. (i) and (iv)
c. (ii) and (iii)
d. (i) and (iii)
Answer : B
Question : In peas, a pure tall plant (TT) is crossed with a short plant (tt). The ratio of pure tall plants to short plants in F2 is
a. 1 : 3
b. 3 : 1
c. 1 : 1
d. 2 : 1
Answer : C
| (1) Plica semilunaris | (A) Giant reptiles |
| (2) Dinosaurs | (B) Philosophies Zoologique |
| (3) Kohlrabi | (C) Artificial selection |
| (4) Lamarck | (D) Vestigial |
a. 1-A, 2-C, 3-B, 4-D
b. 1-B, 2-D, 3-A, 4-C
c. 1-D, 2-A, 3-C, 4-B
d. 1-C, 2-B, 3-D, 4-A
Answer : C
Explanation:
Plica semilunaris is a crescent-shaped fold of conjunctiva located at the inner canthus lateral to the caruncle. It is a vestigial structure that represents the third eyelid or nictitating membrane of lower vertebrates.
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria that first appeared during the Triassic period.
Artificial selection is a process in which man selects a particular desired traits for breeding, in order to generate new plants/ animals with improved characters. For e.g. Early farmers cultivated wild cabbage or Brassica oleracea. This wild cabbage developed into many varieties such as cabbage, broccoli, kohlrabi, cauliflower, kale, and brussels. These varieties were artificially selected because of their characteristic traits. Philosophie Zoologique is an 1809 book by the French naturalist Jean- Baptiste Lamarck, in which he outlines his pre-Darwinian theory of evolution now known as Lamarckism.
Assertion a. and Reason (R) type questions.
Following questions consist of two statements – Assertion a. and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
a. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b. Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c. A is true but R is false.
d. A is false but R is true.
Question : Assertiona. : Variations are seen in offspring produced by sexual and asexual reproduction.
Reason (R) : DNA molecule generated by replication is not exactly identical to original DNA.
Answer : A
Question : Assertion : When pea plants (pure line) having round yellow seeds are crossed with pure line plants having wrinkled green seeds, then all pea plants obtained in F1, generation bear wrinkled green seeds.
Reason: Round and yellow seeds are dominant to wrinkled and green seeds.
Answer : D
Question : Assertion : Selfing of a plant for several generations helps plant breeders to obtain pure breeding varieties.
Reason: Pure breeding plants are heterozygous for many traits.
Answer : C
Very Short Answer
Question : Differentiate between dominant and recessive traits.
Answer : Dominant traits - The traits that express themselves in an organism in every possible combination and can be seen are called Dominant traits.
Recessive traits - A trait which is not expressed in the presence of a dominant allele is known as recessive
Question : What is meant by contrasting traits or characters?
Answer : A trait is generally represented by two forms. When these two forms are opposite to each other they are termed as contrasting trait. For example, contrasting trait for height is tall and dwarf.
Answer : Gregor Mendel
Answer : DNA in the nucleus of a cell is the information source for making proteins.
Question : Name the information source for making proteins in the cells.
Answer : Cellular DNA is the information source for making proteins in cells.
Question : Differentiate between dominant and recessive traits.
Answer : The character which gets expressed in the presence of its contrasting form is termed as dominant trait.
The trait which remains unexpressed in the presence of its contrasting form is called recessive trait.
Question : Who is known as father of genetics?
Answer : Gregor Johann Mendel .
Question : What is meant by contrasting traits or characters?
Answer : The characters which always appear in two opposing conditions are called contrasting characters. Tall and dwarf are two contrasting traits for the plant height.
Question : In evolutionary terms, we can say which among bacteria, spiders, fish and chimpanzees have a better body design? Why or why not?
Answer : Evolution shows that body design changed from simple to complex. Hence, bacteria has the simplest body design and chimpanzee has the most complex and better body design.
Question : Why are traits acquired during the life-time of an individual not inherited?
Answer : The traits can be inherited from one generation to the other only if there is a variation/change in DNA. The traits acquired during the life-time of an individual may not bring change in the genes of DNA.
Question : How does the creation of variations in a species promote survival?
Answer : Variations increases the adaptability of an organism to its changing environmental conditions.
Question : Why are the small numbers of surviving tigers a cause of worry from the point of view of genetics?
Answer : The small number of tigers are causing a worry for the genetics because if they become extinct then the genes of this species will be lost forever. There will be no scope of again getting this species back to life without their genes.
Question : If a trait A exists in 10% of a population of an asexually reproducing species and a trait B exists in 60% of the same population, which trait is likely to have arisen earlier?
Answer : Trait B is likely to have arisen earlier as it occurs in more number.
Question : Will geographical isolation be a major factor in the speciation of an organism that reproduces asexually? Why or why not?
Answer : No, because the asexually reproducing organisms does not depend on other organisms for their reproduction.
Question : How do Mendel’s experiments show that traits are inherited independently?
Answer : When Mendel crossed pure bred tall pea plants with pure bred short pea plants, he found that only tall plants were produced in F1 generation. Mendel, further crossed the tall pea plants obtained in F1 generation with dwarf plants and obtained the ratio of Tall: Short plant as 3 : 1 in F2 generation. This experiment proved that traits are inherited independently so other intermediate traits or new traits were formed.
Question : Can the wing of a butterfly and the wing of a bat be considered homologous organ? Why or why not?
Answer : The wing of butterfly and the wing of a bat cannot be considered homologous organs because both have different structures but same function. They have different basic structural design and developmental origin. They are analogous orgAnswer :
Question : What factors could lead to the rise of a new species?
Answer : The factors which can lead to the rise of a new species are gene flow, genetic drift, reproductive isolation and natural selection.
Question : Why are human beings who look so different from each other in terms of size, colour and looks said to belong to the same species?
Answer : Because irrespective differences in characters they have capacity of interbreeding.
Interbreeding is an important criteria to categorize them as one species.
Question : Give an example of characteristics being used to determine how close two species are in evolutionary terms.
Answer : Two organisms with similar characteristics have genes with similar DNA codes. Whereas the organisms with different characteristics will have different genes, different DNA structures.
Short Answer
Question : What are analogous organs? Explain with an example.
Answer : Analogous organs have the same function but have different structural design and origin. For example, wings of birds and insects have the same function but have different structural design and origin.
Question : Which is gene flow?
Answer : It is the exchange of genetic material by interbreeding between populations of the same species. Gene flow increases the variations in a population.
Question : How can we trace evolutionary relationships?
Answer : Evolutionary relationships can be traced by studying fossils, by studying homologous and analogous organs, by comparing the embryos of different animals and by comparing the DNA’s of different species.
Question : What is the significance of studying homologous and analogous organs?
Answer : Organisms that have homologous organs show relatedness and a common ancestory.
Question : Why evolution should not be equated with progress?
Answer : Evolution cannot be equated with progress because it seems to have just given rise to more complex body designs. For example bacteria still flourish in spite of a very simple body design while dinosaurs did not survive in spite of complex design. Thus evolution is simply the generation of diversity and shaping of diversity by environmental selection.
Question : How many pairs of chromosomes do human beings have, specify the types of chromosomes also?
Answer : Human beings have 23 pairs of chromosomes the first 22 pairs are called autosomes are similar in males and females. The 23rd pair is called the sex chromosome. In males it is XY and in females it is XX.
Question : How is the sex of the child determined in human beings?
Answer : Human beings have 23 pairs of chromosomes. 22 pairs are autosomes and the 23rd pair is the sex chromosome. The males have XY and the females have XX. All the gametes formed in the females are of one type i.e., X. In males there are two types of sperms that are formed –X and Y. If the sperms having X fertilizes with the egg the zygote formed is XX. This will form female child. If the sperm having Y fertilizes with the egg then the zygote formed is XY and the offspring will be male child. So basically it’s the male gametes that decide the sex of the unborn child.
Question : What is the effect of DNA copying which is not perfectly accurate on the reproduction process?
Answer : If DNA copying is not perfectly accurate then the variations occurs among the species of same organisms.
Question : What are homologous organs? Explain with an example.
Answer : Homologous organs are those organs in different plants or animals which have the same basic structural design and origin but may have different functions.
Example., hand of human and fore-limb of frog.
Question : What is classification?
Answer : It is the arrangement of organism into series of groups based on the similarity of characters on physiology, anatomy, morphology and other relationships.
Question : How do Mendel’s experiments show that traits may be dominant or recessive?
Answer : Mendel conducted a Monohybrid cross(crossed pure tall pea plants with pure dwarf pea plants) he observed only tall pea plants in the F1 generation, but on self crossing of the F1 progeny, both tall and dwarf pea plants were observed in F2 generation in the ratio 3: 1. Appearance of tall character in F1 and F2 generations shows tallness to be a dominant character. But absence of dwarf character in F1 and its reappearance in F2 confirms that dwarfness is recessive character.
Question : A man with blood group A marries a woman with blood group O and their daughter has blood group O. Is this information enough to tell you which of the traits − blood group A or O − is dominant? Why or why not?
Answer : The give information is not enough to tell us which of the traits – blood group A or O – is dominant. In blood heredity, blood Type A is always dominant and blood Type O is always recessive.
Here, father’s Blood group can be AA (homozygous) or AO (heterozygous) genotypically, where as that of mother can only be OO. For daughter to be born with blood group O, she must receive O type gene one each from father and mother. For this father must have heterozygous AO blood group and mother must have homozygous blood group OO.
Question : How do Mendel’s experiments show that traits are inherited independently?
Answer : Mendel performed an experiments in which he took a tall plant with round seeds and a short plant with wrinkled-seeds. In F1, They were all tall and had round seeds. Tallness and round seeds were thus dominant traits. When, he used these F1 progeny to generate F2 progeny by self-pollination, he found that some F2 progeny were tall plants with round seeds, and some were short plants with wrinkled seeds. At the same time there tall plants, but had wrinkled seeds, while others were short, but had round seeds. Thus,Mendel’s experiments show that the tall/short trait and the round seed/wrinkled seed trait are independently inherited.
Question : How is the equal genetic contribution of male and female parents ensured in the progeny? Explain
Answer :
During sexual reproduction, a female gamete or egg cell fuses with a male gamete or sperm cell which are haploid to form zygote. Zygote is diploid which contains 23 chromosomes from mother and 23 from father. In this way, an equal genetic contribution of male and female parents is ensured in the progeny.
Question : What are monohybrid and dihybrid cross? Give one example of each.
Answer : Monohybrid cross- This is the simplest cross in which only one character's inheritance is investigated. A cross is created by crossing two plants with one contrasting characteristic, such as tall or dwarf.
Dihybrid cross- A dihybrid cross is a cross between two plants with two sets of opposing characters. Round and green seed, for example, crossed with yellow and wrinkled seed.
Question : A study found that children with light-coloured eyes are likely to have parents with lightcoloured eyes. On this basis, can we say anything about whether the light eye colour trait is dominant or recessive? Why or why not?
Answer : Let us assume that children with light-coloured eyes can either have LL or Ll or ll genotype. If the children have LL genotype, then their parents will also be of LL
genotype.
LL × LL
↓
LL
If the children with light-coloured eyes have ll genotype, then their parents will also have ll genotype.
ll × ll
↓
ll
Therefore, it cannot be concluded whether light eye colour is dominant or recessive.
Question : In evolutionary terms, can we say which among bacteria, spiders, fish and chimpanzees have a ‘better’ body design? Why or why not?
Answer : Evolution cannot always be equated with progress or better body designs. Evolution simply creates more complex body designs. However, this does not mean that the simple body designs are inefficient. In fact, bacteria having a simple body design are still the most cosmopolitan organisms found on earth. They can survive hot springs, deep sea, and even freezing environment.Therefore, bacteria, spiders, fish, and chimpanzees are all different branches of evolution.
For example, in a family, a brother and sister are closely related and they have a recent common ancestor i.e., their parents. A brother and his cousin are also related but less than the sister and her brother. This is because the brother and his cousin have a common ancestor i.e., their grandparents in the second generation whereas the parents were from the first generation. With subsequent generations, the variations make organisms more different than their ancestors.
This discussion clearly proves that we classify organisms according to their resemblance which is similar to creating an evolutionary tree.
Question : Will geographical isolation be a major factor in the speciation of a self-pollinating plant species? Why or why not?
Answer : Geographical isolation can prevent the transfer of pollens among different plants. However, since the plants are self-pollinating, which means that the pollens are transferred from the anther of one flower to the stigma of the same flower or of another flower of the same plant, geographical isolation cannot prevent speciation in this case.
Question : Explain how sexual reproduction gives rise to more viable variations than asexual reproduction. How does this affect the evolution of those organisms that reproduce sexually?
Answer : In sexual reproduction, two individuals having different variations combine their DNA to give rise to a new individual. Therefore, sexual reproduction allows more variations, whereas in asexual reproduction, chance variations can only occur when the copying of DNA is not accurate.Additionally, asexual reproduction allows very less variations because if there are more variations, then the resultant DNA will not be able to survive inside the inherited cellular apparatus.
However, in sexual reproduction, more variations are allowed and the resultant DNA is also able to survive, thus making the variations viable.
Variation and Evolution: Variants help the species to survive in all the conditions.Environmental conditions such as heat, light, pests, and food availability can change suddenly at only one place. At that time, only those variants resistant to these conditions would be able to survive. This will slowly lead to the evolution of a better adapted species. Thus, variation helps in the evolution of sexually reproducing organisms.
Question : How does the creation of variations in a species promote survival?
Answer : Sometimes for a species, the environmental conditions change so drastically that their survival becomes difficult. For example, if the temperature of water increases suddenly, most of the bacteria living in that water would die. Only few variants resistant to heat would be able to survive. If these variants were not there, then the entire species of bacteria would have been destroyed. Thus, these variants help in the survival of the species.
However, not all variations are useful. Therefore, these are not necessarily beneficial for the individual organisms.
Question : A Mendelian experiment consisted of breeding tall pea plants bearing violet flowers with short pea plants bearing white flowers. The progeny all bore violet flowers, but almost half of them were short. This suggests that the genetic make-up of the tall parent can be depicted as
(a) TTWW
(b) TTww
(c) TtWW
(d) TtWw
Answer : (c) The genetic make-up of the tall parent can be depicted as TtWW Since all the progeny bore violet flowers, it means that the tall plant having violet flowers has WW genotype for violet flower colour. Since the progeny is both tall and short, the parent plant was not a pure tall plant. Its genotype must be Tt.
Therefore, the cross involved in the given question is
TtWw × ttww
↓
TtWw − ttww
Therefore, half the progeny is tall, but all of them have violet flowers.
Question : What are the different ways in which individuals with a particular trait may increase in a population?
Answer : Individuals with a particular trait may increase in a population as a result of the following:
(i) Natural selection: When that trait offers some survival advantage.
(ii) Genetic drift: When some genes governing that trait become common in a population.
(iii) When that trait gets acquired during the individual’s lifetime.
Question : What is natural selection?
Answer : According to Darwin, natural selection is the process which brings about evolution of new species of plants and animals.
It consists of the following processes:
(i) He noted that the size of population tends to remain constant despite the fact that more offsprings are produced than needed.
(ii) Variations provide adaptations.
(iii) The best adopted survive in the changing environment (survival of the fittest).
(iv) Nature selects the best organisms with better adaptations and after many generations new species are formed (natural selection).
Question : A man with blood group A marries a woman with blood group O and their daughter has blood group O. Is this information enough to tell you which of the traits – blood group A or O is dominant? Why or why not?
Answer : No. This information is not sufficient to determine which of the traits − blood group A or O is dominant. This is because we do not know about the blood group of all the progeny. Blood group A can be genotypically AA or AO.
Question : How is the sex of the child determined in human beings?
Answer : A male has XY sex chromosome and produces two types of sperms; 50% of them carrying X chromosomes and another 50% carrying the Y chromosomes. A female carries XX sex chromosomes and hence produces only X – carrying eggs. If X-carrying egg fuses with the X -carrying sperm, the child born will be a girl. If X – carrying egg fuses with the Y carrying sperm, the child born will be a boy.
Question : What is the effect of DNA copying which is not perfectly accurate on the reproduction process?
Answer : If DNA copying is not perfectly accurate then the variations occurs among the species of same organisms.
Question : ‘‘Variations that confer an advantage to an individual organism only will survive in population’’. Justify.
Answer : Variation is the difference in the characters or traits among the individuals of a species.
Sexual reproduction of organisms produces variation. The variations produced in organisms during successive generations gets accumulated in the organism. The significance of variations shows up only if it continues to be inherited by the offspring for several generation.
Question : Explain the terms analogous and homologous organs with examples.
Answer : Homologous organs are those organs of different organisms that have the identical basic structural style and origin, however have completely different functions. For example: The forelimbs of humans and also the wings of birds. Analogous organs are those organs of different organisms that have the different basic structural style and origin however have similar functions. For example: The wings of birds and insects.
Question : Explain the importance of fossils in deciding evolutionary relationships.
Answer : Fossils are the remains of organisms that once existed on earth. They represent the ancestors of plants and animals that are alive today. They provide evidences of evolution by revealing the characteristics of the past organism and the changes that have occurred in these organisms to give rise to the present organisms
Question : How do Mendel’s experiments show that traits are inherited independently?
Answer : Mendel crossed pea plants having round green seeds (RRyy) with pea plants having wrinkled yellow seeds (rrYY). Since the F1 plants are formed after crossing pea plants having green round seeds and pea plants having yellow wrinkled seeds, F1 generation will have both these characters in them. However, as we know that yellow seed colour and round seeds are dominant characters, therefore, the F1 plants will have yellow round seeds.
Then this F1 progeny was self-pollinated and the F2 progeny was found to have yellow round seeds, green round seeds, yellow wrinkled seeds, and green wrinkled seeds in the ratio of 9:3:3:1. In the above cross, more than two factors are involved, and these are independently inherited.
Question : Only variations that confer an advantage to an individual organism will survive in a population. Do you agree with this statement? Why or why not?
Answer : Yes, variations enable a species to adapt according to the changes and new needs and thus provide survival of species.
Question : How are the areas of study – evolution and classification – interlinked?
Answer : Classification of organisms into groups is based on the similarities and differences between them. The more characteristics two species or organisms will have in common, the more closely they are related and the more recently they will have had a common ancestor. Classification shows that how closely organisms are related with respect to evolution. It is in fact a reflection of their evolutionary relationship.
Question : What evidence do we have for the origin of life from inanimate matter?
Answer : In 1953, Miller and Urey assembled an early earth atmosphere which consisted gases like NH3, CH4 and H2S, etc. except oxygen, over water. They maintained it at the temperature just below the 100°C and passed electric sparks in the mixture of gases to stimulate lightning. This was continued about one week. After that they found that 15% carbon from CH4 had been converted to simple organic compound like sugar and amino acids which constitute into protein molecules. This experiment gives the evidence for origin of life from inanimate matter.
Question : How is the equal genetic contribution of male and female parents ensured in the progeny?
Answer : Individually both male and female parents possess 46 chromosomes. Both female and male gametes has 23 chromosomes each. When the female and the male gametes fuses, the zygote has 46 chromosomes again.
In this way, the equal genetic contribution of male and female parents is ensured in the progeny.
Question : Outline a project which aims to find the dominant coat color in dogs.
Answer : Suppose a black homozygous male is mated with a white homozygous female. If the progeny has all black dogs then the dominant coat colour is black.
Long Answer
Question : A green stemmed rose plant denoted by GG and a brown stemmed rose plant denoted by gg are allowed to undergo a cross with each other.
a. List your observations regarding:
(i) Colour of stem in their F1 progeny
(ii) Percentage of brown stemmed plants in F2 progeny if F1 plants are self pollinated.
(iii) Ratio of GG and Gg in the F2 progeny.
b. Based on the finding of this cross, what conclusion can be drawn?
Answer : a. (i) Colour of the stem in F1 progeny: All green
(ii) Percentage of brown stem: 25 %
((iii) GG: Gg is 1: 2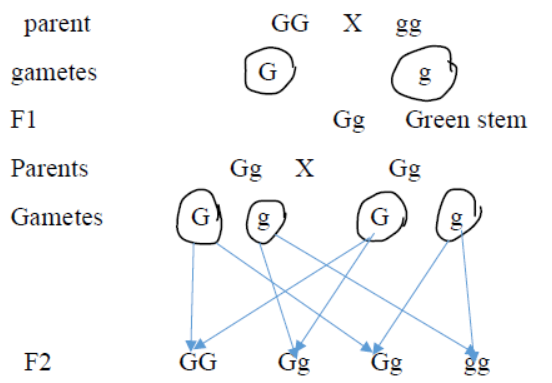
b. Based on the above cross, it can be concluded that
green colour is dominant and get expressed in F1
generation. The brown stem, which does not get
express itself in the F1 generation, is the recessive
character.
Question : A blue colour flower plant denoted by BB is cross bred with that of white colour flower plant denoted by bb.
a. State the colour of flower you would expect in their F1 generation plants.
b. What must be the percentage of white flower plants in F2 generation if flowers of F1 plants are self-pollinated?
c. State the expected ratio of the genotypes BB and Bb in the F2 progeny.
Answer : 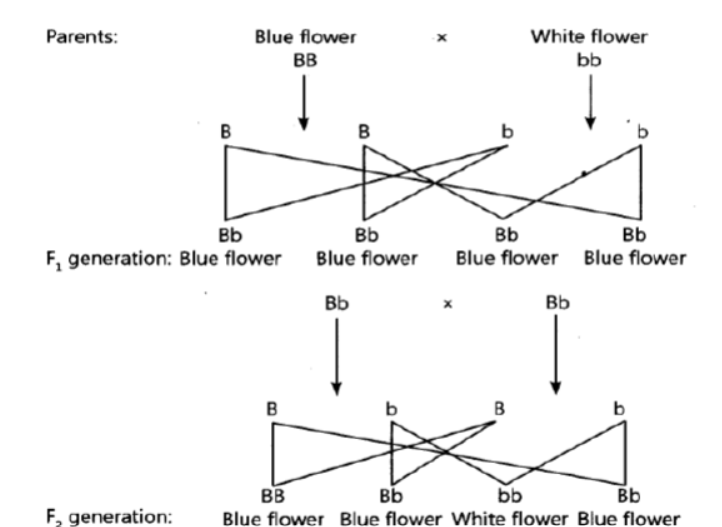
Question : With the help of a flow chart explain in brief how the sex of a newborn is genetically determined in human beings. Which of the two parents, the mother or the father, is responsible for determination of sex of a child?
Answer : In human beings, the sex of the individual is genetically determined. Sex chromosome of male is XY and of female is XX. Sex of a child depends on what happens at fertilisation.
The woman produces eggs having X chromosome while the man produces 50% sperms having X chromosome and 50% sperms having Y chromosome. Man therefore,actually determines the sex of the new born baby.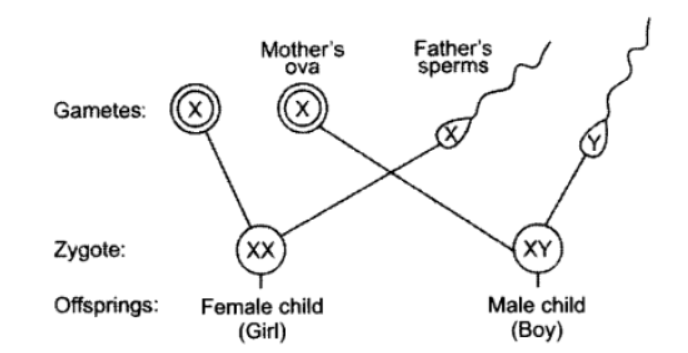
Question : What is variation? How is variation created in a population? What is the importance of variation for survival of a species?
Answer : The differences in the traits shown by the individuals of a species and also by the offsprings (siblings) of the same parents are referred to as variation.
New variation may arise during the process of DNA copying that already has variations accumulated from previous generations.Species having suitable variations have more chance of survival if there is change in environmental conditions.
Question : Define the following terms.
a.Heredity , b.Gene , c.Alleles
Answer : Heredity – Transmission of characters from one generation to another or from parents to offspring.
Gene – It is the basic unit of inheritance. It consists of a sequence of DNA,which is the genetic material. Genes can mutate and can take two or more alternative forms.
Alleles – The alternative forms of genes. They affect the same characteristics or traits in alternate forms. They are located on the same place of the chromosome.
Question : Define ‘evolution’. State Darwin’s theory of evolution.
Answer : Evolution is a change in the genetic composition of a population.
Darwin’s theory
1. The size of population remains the same, constant despite the fact that more off springs are produced than needed.
2. Variations provide adaptations.
3. The best adapted organism survive in the changing environment (survival of the fittest).
4. Nature selects the best organisms with better adaptations and after many generations new species are formed (natural selection).
Question : (i) What are traits?
(ii) Explain the inherited trait and acquired traits.
(iii) Define speciation. What are the factors which could lead to the rise of a new species?
Answer : (i) Traits: A characteristic feature is called trait.
(ii) Inherited and acquired trait (given in notes on page 112).
(iii) Speciation and factors (given in notes on page 112).
Question : State Mendel's Laws of inheritance.
Answer : i. Law of unit character: According to this law, all the characters of body are represented in the gametes by certain units called factors or determiners which always occur in pair. These genes are present on different chromosomes of homologous pairs at the same locus.
ii. Law of Dominance: Only one member of the contrasting pair of characters is capable of expressing itself while other remains hidden, is called principle of dominance.
iii. Law of Segregation: According to this law, in a hybrid, the two unlike factors of a character do not affect each other but keep their identity. During gamete formation, they are free to segregate or separate from one another and to be redistributed in the next generation. This law is also called the purity of gametes.
iv. Law of independent assortment: When two pairs of independent alleles are brought together, they show independent dominant effects. During the formation of gametes, the genes of different characters are independent of one another.
Question : Outline a project which aims to find a dominant coat colour in dogs.
High Order on Order Thinking Skills(HOTS)
Question : Dead remains of two species A and B were buried. Later only A’s body was found to be a fossil but not B’s given reason.
Answer : B’s body did not have hard tissues, like bones.
Question : After the death of two insects, one of the insect was burried in hot mud and the other in usually found mud. Which of the two is more likely to be preserved better and why?
Answer : The insect burried in hot mud. The body will not get decomposed in hot mud and the impression of the body will remain.
Question : With the help of an example explain how “Genes control characteristics or traits’’?
Answer : Tallness of a plant is a characteristic. Height of a plant depend on the amount of hormone secreted by the plant responsible for its tallness. The gene has the coding for the amount of hormone released. If the gene for that hormone has an alteration and makes its efficiency low, then the plant will be short.
Thus, this shows that traits are controlled by gene.
More Question
1) Give examples of animals where sex determination is not genetically determined?
2) If a trait A exists in 10% of a population of an asexually reproducing species and a trait B exists in 60% of the same population, which trait is likely to have arisen earlier?
3) Give example of characteristics being used to determine how close two species are in evolutionary terms.
4) What do fossils tell us about the process of evolution?
5) Why did Mendel choose garden pea for his experiments
6) Why do human beings who look so different from each other in terms of size, color, and looks are said to belong to the same species?
7) What is speciation?
8) How can we say that a child has two versions of a trait?
9) How do Mendel’s experiments show that traits may be dominant or recessive?
10) The genotype of purple flowered pea plants is denoted as WW and that of white flowered pea plant as ww. When these two are crossed
i) What color of flowers do you expect in their F1 progeny?
ii) What will be the percentage of white flowered plants produced if F1 plants are self pollinated?
| CBSE Class 10 Science Acids Bases And Salts Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Acids Bases And Salts Worksheet Set B |
Worksheet for CBSE Science Class 10 Chapter 8 Heredity
We hope students liked the above worksheet for Chapter 8 Heredity designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 10 Science released by CBSE. Students of Class 10 should download in Pdf format and practice the questions and solutions given in the above worksheet for Class 10 Science on a daily basis. All the latest worksheets with answers have been developed for Science by referring to the most important and regularly asked topics that the students should learn and practice to get better scores in their class tests and examinations. Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to the NCERT book for Class 10 Science to develop the Science Class 10 worksheet. After solving the questions given in the worksheet which have been developed as per the latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 10 Science designed by our teachers. We have also provided a lot of MCQ questions for Class 10 Science in the worksheet so that you can solve questions relating to all topics given in each chapter.
You can download the CBSE Printable worksheets for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Heredity for latest session from StudiesToday.com
There is no charge for the Printable worksheets for Class 10 CBSE Science Chapter 8 Heredity you can download everything free
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all latest NCERT Chapter 8 Heredity Class 10 Science test sheets with answers based on the latest books for the current academic session
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Heredity worksheets cover all topics as per the latest syllabus for current academic year.
Regular practice with Class 10 Science worksheets can help you understand all concepts better, you can identify weak areas, and improve your speed and accuracy.

