Please refer to CBSE Class 10 Science HOTs How Do Organisms Reproduce. Download HOTS questions and answers for Class 10 Science. Read CBSE Class 10 Science HOTs for Chapter 7 How do Organisms Reproduce below and download in pdf. High Order Thinking Skills questions come in exams for Science in Class 10 and if prepared properly can help you to score more marks. You can refer to more chapter wise Class 10 Science HOTS Questions with solutions and also get latest topic wise important study material as per NCERT book for Class 10 Science and all other subjects for free on Studiestoday designed as per latest CBSE, NCERT and KVS syllabus and pattern for Class 10
Chapter 7 How do Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Science HOTS
Class 10 Science students should refer to the following high order thinking skills questions with answers for Chapter 7 How do Organisms Reproduce in Class 10. These HOTS questions with answers for Class 10 Science will come in exams and help you to score good marks
HOTS Questions Chapter 7 How do Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Science with Answers
Question. Which of the following sequence of events do not represent the correct sequence of sexual reproduction in higher plants?
(a) Pollination → Embryo formation→ Fertilization
(b) Embryo formation → Pollination → Fertilization
(c) Embryo Formation → Fertilization → Pollination
(d) Pollination → Fertilization→ Embryo formation
Answer : A , B
Question. Which of the following statements are correct?
(a) Bisexual flowers contain either stamen or pistil.
(b) Unisexual flowers contain either stamen or pistil.
(c) Bisexual flowers possess both stamen and pistil.
(d) Unisexual flowers exhibit cross-pollination.
Answer : B , C
Question. Choose the correct statements among the following.
(a) Flowers always have both the sex organs.
(b) Flowers are the reproductive organs of the plants.
(c) All plants bear flowers.
(d) Flowers give rise to fruit after fertilization.
Answer : B
Question. Sperms are produced in
(a) the penis
(b) the vas deferens
(c) the prostate gland
(d) none of the above
Answer : D
Question. An event that represents the onset of reproductive phase in human females is called
(a) adolescence
(b) menstruation
(c) implantation
(d) fertilization
Answer : B
Question. Which of the following structures is responsible for transmission of characters from parents to offspring?
(a) Centrosome
(b) Ribosome
(c) Cytoplasm
(d) Genes
Answer : D
Question. Which of the following do not represent the correct sequence of reproductive stages?
(a) Zygote → Gametes → Embryo → Seedling
(b) Gametes → Zygote → Embryo → Seedling
(c) Gametes → Zygote → Seedling → Embryo
(d) Gametes → Embryo → Seedling → Zygote
Answer : A , C , D
Question. Fragmentation (breaking up of filaments into smaller pieces) is the common method of asexual reproduction in
(a) yeast
(b) Spirogyra
(c) Amoeba
(d) Plasmodium
Answer : B
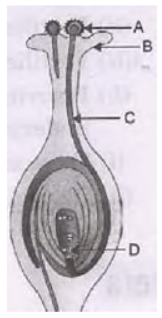
Question. In the following figure the parts A, B, C and D are sequentially (Image 159)
(a) stigma, anther, petal and pistil
(b) anther, pistil, petal and stigma
(c) anther, petal, pistil and stigma
(d) stigma, anther, pistil and petal
Answer : B
Question. The characters that are transmitted from parents to offspring exhibit
(a) only variations
(b) only similarities
(c) both variations and similarities with parents
(d) mixed and independent characters
Answer : C
Question. Which one is due to bacterial infection?
(a) AIDS
(b) Gonorrhoea
(c) Cancer in cervix
(d) Tumour in ovary
Answer : B
Question. Rhizopus and Mucor reproduce mainly by
(a) producing spores
(b) producing buds
(c) fragmentation
(d) multiple fission
Answer : A
Question. The chromosome number in parents and offspring of a particular species remains constant due to
(a) halving of chromosome number during gamete formation
(b) doubling of chromosome number during gamete formation
(c) doubling of chromosome number after gamete formation
(d) multiplication of chromosomes during gamete formation
Answer : A
Question. The tubular threadlike structures bearing sporangia at their tips in Rhizopus are called
(a) roots
(b) rhizoids
(c) hyphae
(d) filaments
Answer : C
Question. Where does cervix lie in the female?
(a) Above the vagina
(b) Above the uterus
(c) Below the Fallopian tube
(d) Behind the ovary
Answer : A
Question. Which of the following factors is/are responsible for rapid spread of Rhizopus (bread mould) on bread?
(a) Presence of round-shaped sporangia
(b) Formation of numerous spores
(c) Availability of moisture in bread
(d) Availability of nutrients in bread
Answer : B , C ,D
Question. In vegetative propagation, new plants are produced from
(a) root, stem and flowers
(b) root, stem and seeds
(c) root, stem and leaves
(d) root, leaves and flowers
Answer : C
Question. Why is reproduction essential for living organisms?
(a) To maintain growth
(b) To maintain number
(c) To continue the species from generation to generation
(d) To provide variations
Answer : C
Question. Why do offspring formed by asexual reproduction look very similar among themselves?
(a) Because asexual reproduction is a common method of reproduction
(b) Because asexual reproduction takes place after maturing of individuals
(c) Because asexual reproduction involves one parent and does not involve gametes
(d) Because asexual reproduction takes place in all the conditions
Answer : C
Question. What is contraception?
(a) Promotion of conception
(b) Promotion of sterility
(c) Prevention of conception
(d) None of the above
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following functions are not related to testes?
(a) Formation of placenta
(b) Secretion of male hormone
(c) Formation of male gametes
(d) Secretion of oestrogen
Answer : A ,D
Question. Sexual reproduction results in more variations in the offspring because
(a) genetic material comes from many parents
(b) genetic material is brought from two different species
(c) genetic material comes from two parents of the same species
(d) it is a long process involving two parents
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following statements is common for Hydra, yeast, Spirogyra and Amoeba?
(a) They are unicellular.
(b) They are multicellular.
(c) They reproduce asexually.
(d) They cannot multiply.
Answer : C
Question. The male and female gamete-producing organs of a flower is called
(a) ovary and ovule
(b) stamen and anther
(c) stigma and stamen
(d) anther and ovary
Answer : D
Question. The example of multiple fission (ability of a cell to divide into many daughter cells) is seen in
(a) Hydra
(b) Plasmodium
(c) Paramoecium
(d) Spirogyra
Answer : B
Mark the statements true (T) or false (F).
Question. Binary fission is the simplest method of sexual reproduction.
Answer : false
Question. Surgical methods are safe contraceptive methods.
Answer : true
Question. If Planaria is cut into pieces, each piece can regenerate into an entire individual.
Answer : true
Question. Surgery can be used for removal of unwanted pregnancies.
Answer : true
Question. Buds may be unicellular or multicellular.
Answer : true
Question. Implantation of embryo occurs in uterus.
Answer : true
Question. AIDS is a bacterial infection.
Answer : false
Question. Vasectomised male will not ejaculate.
Answer : false
Match the columns
A B
(i) Budding (a) Mechanical barrier
(ii) Rhizopus (b) Fruit
(iii) Pistil (c) Binary fission
(iv) Sexual reproduction (d) Cross-pollination
(v) Copper-T (e) Regeneration
(vi) Ovary of a flower (f) Vegetative reproduction
(vii) Fertilized egg (g) Multiple fission
(viii) Amoeba (h) Spore formation
(ix) Grafting (i) Hydra
(x) Planaria (j) Zygote
(xi) Unisexual flower (k) Gametes
(xii) Plasmodium (l) Female reproductive part of a flower
Answer : 1. (i)(i) (ii)(h) (iii)(l) (iv)(k) (v)(a) (vi)(b)
(vii)(j) (viii)(c) (ix)(f) (x)(e) (xi)(d) (xii)(g)
Match the columns
A B
(i) Testis (a) Sperm duct
(ii) Vas deferens (b) Scrotal sac
(iii) Condom (c) Contraception
(iv) IUCD (d) Lower part of vagina
(v) Cervix (e) Prevention of STD
Answer : (i)(b) (ii)(a) (iii)(e) (iv)(c) (v)(d)
HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE?
HOTS: (High Order Thinking Skill) Questions with Answers:
Very Short Answer Type Questions :
Question. Why is variation beneficial to the species but not necessary for the individual?
Ans. Variation is beneficial to the species as it enables a species for its survival. A favourable variation makes an organism to live better in a changed environment and an unfavourable variation will not. So it is not necessarily true that a variation is beneficial to the individual always.
Question. What is the advantage of reproduction through spores in the case of Rhizopus?
Ans. The spores are covered by thick walls that protect them until they come into contact with aother moist surface and can begin to grow.
Question. What are those organisms called which bear both the sex organs in the same individual? Give one example of such organism.
Answer: Organisms having both the sex organs in the same individual are called Hermaphrodite. E.g., Earthworm.
Question. In a bisexual flower inspite of the young stamens being removed artificially the flower produces fruit. Provide a suitable explanation for the above situation.
Ans. Though the stamens are removed but pistils are present so cross pollination might have taken place which leads to fertilisation and finally to the formation of fruits.
Question. What is termed as the blue print of life and why?
Ans. DNA is termed as the blue print of life because it carries all the information for the organisms to grow, survive and reproduce.
Proteins which are the structural and functional unit of cells are synthesized according to the information stored in DNA.
Question. How does the chemical method help in preventing pregnancy?
Ans. Chemical methods prevent the ovaries from releasing the egg hence no fertilisation can occur thus preventing pregnancy.
Question. Name the plant that reproduces vegetatively by leaf?
Ans. Bryophyllum reproduces vegetatively by leaf.
Question. Name the method by which Hydra reproduces? Is this method sexual or asexual?
Ans. Hydra can reproduce by budding and regeneration. Both are asexual method, of reproduction.
Question. Expand: (a) IUCD (b) STDs.
Ans. (a) IUCD: Intra Uterine Contraceptive Devices.
(b) STDs: Sexually Transmitted Diseases.
Question. Name the life process of an organism that helps in the growth of its population.
Ans. Reproduction.
Question. If a woman is using copper-T, will it help her in protecting from sexually transmitted diseases?
Ans. No, copper-T will not help her in protecting from sexually transmitted diseases. It only prevents the implantation of embryo inside uterus.
Question. What are the benefits of using mechanical barriers during sexual act?
Ans. Mechanical barriers like condoms prevent unwanted pregnancies and transmission of sexually transmitted diseases like AIDS, syphilis etc.
Question. Explain the vegetative reproduction in Bryophyllum.
Ans. Bryophyllum has a special case of vegetative propagation. The buds are generated from the margins of the leaves. These buds grow up to be new saplings on the leaf itself and fall off to the ground to be rooted and matured. These buds are formed from mitosis of meristematic type tissues in the phylloclade of the plant. They are called epiphyllous buds since they are present on top of the leaves. Buds in Bryophyllum are known as epiphyllous buds.
Question. Which among the following organism is capable of reproducing through spores?
(i) Amoeba
(ii) Plasmodium
(iii) Hydra
(iv) Rhizopus
Ans. (iv) Rhizopus
Question. Name the agents which bring about cross pollination.
Ans. Insects, wind, water, animals etc., are the agents which bring about cross pollination.
Question. How many gametes are produced after germination of angiosphermous pollen grains over the stigma of carpel ?
Ans. Two male gametes are produced after germination of angiosphermous pollen grains over the stigma of carpel.
Question. The simple animals such as planaria can be cut into number of pieces and each piece grows into a complex organism. What is this process known as?
Ans. Regeneration
Question. Name the unicellular organism which caused the disease known as kala-azar.
Ans. Leishmania
Question. Which process taking place in the nucleus of a cell leads to variation in the offspring during reproduction?
Ans. DNA copying
Question. What causes joining up of stock and scion in grafting technique of vegetative propagation in plants? Define the terms stock and scion. Name one positive trait each of the plant contributing scion and stock should have.
Ans. The stock and scion unite due to cambial cavity. Stock is the portion on which grafting is done and it provides the roots. Scion is the portion of the plant which is grafted on the other plant and it contributes the stem. The plant contributing scion should have large sized fruits and the plant contributing stock should have deep root system.
Question. Which type of layering is done in Jasmine?
Ans. Air Layering (Gootee)
Question. Where does fertilization takes place in human female?
Ans. Oviduct (fallopian tube)
Question. Why is it said that “sexual reproduction promotes diversity of characters in the offsprings”?
Ans. It is because sexual reproduction results from the fusion of two gametes coming from two different and sexually distinct individuals. This leads to variation, is necessary for evolution.
Question. What happens if the fallopian tubes are partially blocked and the ovulated eggs are prevented from reaching the uterus?
Ans. Fertilization may take place but the zygote may develop in the tube instead of uterus.
Question. Name the causative organism of syphilis and gonorrhoea.
Ans. Treponema pallidum and Nisseria gonorrhoeae.
Question. Why are variation possible in progeny of sexually reproductive individuals?
Ans. Treponema pallidum and Nisseria gonorrhoeae.
Question. Differentiate between pollen grain and ovule.
Ans. Pollen grains contain male gametes and ovules contains female gametes in plants.
Question. Give the respective scientific terms used for studying:
a. The mechanism by which variations are created and inherited and
b. The development of new type of organisms from the existing ones.
Ans. a. Heredity
b. Fission.
Question. Name the method by which Spirogyra reproduce under favourable conditions. Is this method sexual or asexual?
Ans. Fragmentation. Asexual
Question. Name the method by which Planaria reproduce under favourable conditions. Is this method sexual or asexual?
Ans. Regeneration. Asexual
Question. a. What is the location of the following:
(i) DNA in a cell (ii) Gene
b. Expand DNA.
Ans. a. (i) Nucleus. (ii) Located on the chromosomes.
b. Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid.
QUESTION BANK FOR PRACTICE
Q1) Name those parts of the flower which serve the same function as the following do in the animals
(1) Testes (2) Ovary (3) Eggs (4) Sperms
Q2) ‘Malarial parasite’ divides into many daughter individuals simultaneously by multiple fission state an advantage the parasite gets because of this type of reproduction.
Q3) Is copy of DNA formed identical to original cell? If yes or no, how is it beneficial to a species?
Q4) An individual may have a good health even when the whole of reproductive system is removed. What is the function of the reproduction system then?
Q5) Grafting is a common method of obtaining a superior plant from two different plants.
Explain.
Q6) The buds produced in the notches along the leaf margins of Bryophyllum plant fall on the soil and develop into new plants. Which type of reproduction is this?
Q7) What is the name of the yellow powdery substance present in the anther of a flower.
Q8) What substances are contained in oral pills used as contraceptives.
Q9) Which life process ensures that a plant or animal species will not disappear from the earth?
Q10) Fertilization is possible if ovulation has taken place during middle of the menstrual cycle. Give reasons.
Q11) Why is the female reproductive system more complex than the male reproduction system?
Q12) A potato is cut into a number of small pieces, these potato pieces are placed on wet cotton kept in a tray. After a few days, green shoots and roots appear only from some potato pieces and not from all potato pieces why?
Q13) What is the significance of human testis being located in the scrotum?
Q14) How the surgery methods are misused by people to prevent pregnancy?
Q15) Why is the number of sperms produced always more than the number of eggs produced?
Q16) DNA copies generated will be similar but may not be identical to the original. Explain.
Q17) After fertilization, name the part in each case which develops into
(a) the fruit (b) the seeds.
Q18) What is meant by implantation in human reproductive system.
Q19) Justify why the male reproductive system is called “urinogenital system”.
Q20) Justify that parthenogensis is not the same as asexual reproduction.
Q21) State the advantages of tissue culture in growing plants.
Q22) What is meant by internal fertilization and external fertilization? Explain with examples.
Q23) Mention any two functions of human ovary.
Q24) What is the significance of syngamy and triple fusion?
Q25) (a) Draw the diagram showing the germination of pollen on the stigma. Label style, male germ cell, ovule and female germ cell.
(b) What happens to the following parts of a flower after fertilization:
(i) Ovule
(ii) Zygote
(iii) Ovary
Q26) Name the following structures:
a. Primary sex organs in man and women.
b. Reproductive parts of a flower.
c. A barrier method of birth control used by human.
(Q27) What is proliferative phase during menstrual cycle?
Short Answer Type Questions :
Question. Explain how do organisms create an exact copy of themselves.
Ans. To build the copies of DNA or the genetic material, the cells use biochemical reactions. Additional cellular apparatus along with the DNA copies are separated and so a cell divides to give rise to two almost identical cells.
Question. State the importance of chromosomal difference between sperms and eggs of humAns
Ans. Eggs always contain same type of sex chromosomes (both X). Sperms contain X or Y sex chromosomes. Thus, sperm containing X chromosome when combines with X chromosome of egg results in a female child. Whereas sperm containing Y chromosome when combines with X chromosome of egg results in a male child.
Question. Write one main difference between asexual and sexual mode of reproduction. Which species is likely to have comparatively better chances of survival–the one reproducing asexually or the one reproducing sexually? Give reasons to justify your answer.
Ans. Asexual reproduction involves only one parent and the offsprings produced are clone and similar copies of their parents where as sexual reproduction involves two parents and
the offsprings produced are different from their parents. Offsprings produced by sexual reproduction have better chances of survival. Sexual reproduction leads to variation
because it leads to the formation of offspring by the combination of DNA from both the parents, so the species will have better adaptability and better survival rate.
Question. How does the embryo gets nourishment inside the mother’s body?
Ans. The embryo gets nourishment inside the mother’s body through a disc shaped structure called placenta. It connects embryo with mother’s blood. It supplies nutrients, oxygen to the growing embryo and removes carbon dioxide, wastes from embryo. Through this structure the blood of embryo comes in close contact with mother’s blood and by diffusion process exchange of nutrients occurs. The placenta is formed by interlocking of two sets of villi, which provides maximum surface area for absorption of nutrients and oxygen gas.
Question. List six specific characteristics of sexual reproduction.
Ans. Characteristics of sexual reproduction are:
(a) In sexual reproduction, two parents are involved (male and female).
(b) The new organism produced is genetically different from both parents.
(b) During gamete formation meiosis occurs. After fertilization all divisions are mitotic.
(d) Sexual reproduction helps in evolution.
(e) Fertilization of gametes leads to zygote formation. This zygote grows and develops to form a new organism.
(f) Humans, fish, dogs, hens, cats, cows, horses, deer, rabbit; lions and tigers all reproduce by the method of sexual reproduction. Most of the flowering plants also reproduce by sexual reproduction.
Question. What is carpel? Write the function of its various parts.
Ans. The flask-shaped organ in the centre of a flower is called carpel. It is also called as female reproductive organ of the plant.
It is made up of three parts:
1. Stigma
2. Style
3. Ovary
(a) Stigma is the top part of carpel and is sticky. So, it receives the pollen from the anther of stamen.
(b) Style connects stigma to ovary.
(b) Ovary contains female gametes of the plant and helps in reproduction.
Question. How does reproduction help in providing stability to population of species?
Ans. There is a natural cycle of born and death, through reproduction the lost species can be replenished. Stability of a particular species is maintained by equalizing birth and death ratios which is possible through reproduction. It ensures the survival of a particular species which might extinct if there is no reproduction process.
Question. Reproduction is essentially a phenomenon that is not for survival of an individual but for the stability of a species. Justify?
Ans. For an organism to survive it has to perform various life processes like nutrition, respiration, circulation, excretion etc.
Reproduction is not required for survival of an organism.
During reproduction there is replication of DNA and only genetic material is transferred from one generation to the next producing certain variations in the offsprings. This process
helps in maintaining the continuity of a species.
Question. Answer the following questions:
(i) Budding, fragmentation and regeneration, all are considered as asexual mode of reproduction. Why?
(ii) With the help of neat diagrams, explain the process of regeneration in Planaria.
Ans. (i) Budding, fragmentation and regeneration are considered as asexual mode of reproduction because only one parent is involved no sex cells are involved.
(ii) Regeneration in planaria.
The process of getting back a full organism from its body parts is called regeneration. Planaria reproduces by this method in which if the body of Planaria somehow gets cut into a number of pieces, then each body piece can regenerate into a complete Planaria by growing all the missing parts.
Question. Mohan was watching his mother cutting some potatoes into small pieces, each with one or two buds. These buds have started sprouting. She planted them in kitchen garden and started watering them daily. Mohan asked his mother why she planted them as they have no seeds.
(i) What is this method of propagation called?
(ii) Which part of plant is used in this case?
(iii) Is it sexual or asexual mode of reproduction?
Ans. (i) It is called vegetative propagation.
(ii) The stem tuber is used.
(iii) It is asexual mode of reproduction as there is no involvement of gametes and it involves single parent.
Question. How is the process of binary fission different in Amoeba and Leishmania?
Ans. In amoeba, the process of binary fission occurs in any plane but in Leishmania binary fission occurs in a definite orientation.
Leishmania has a whip like structure at one end of the cell. The division occurs longitudinally in relation to this whip like structure.
Question. Answer the following questions:
(i) Trace the path of the sperms from where they are produced in the human body to the exterior?
(ii) Write the functions of seminal vesicles and prostate glands in human male reproductive system?
Ans. (i) Seminiferous tubules → Epididymis → Sperm duct →Urethra
(ii) Seminal vesicles secretion serves as a medium for transportation of sperms and also they activate and nourish the sperms. The secretion of prostate gland makes the medium alkaline and neutralises the acidic medium of female vagina.
Question. What are stamen and carpel in a flower ? What is the name of yellow powdery substance present in the anther of a flower ?
Ans. Stamen is the male reproductive part of a flower whereas carpel is a female reproductive part of a flower. The yellow powdery substance present in the anther of a flower is pollen grains.
Question. How will an organism be benefited if it reproduces through spores?
Ans. An organism can be benefited if it reproduces through spores by following ways:
(a) Spores are covered with thick walls which protect them from adverse environmental conditions like drought, high temperature etc. So, they can survive even in these conditions.
(b) They are very light, small and can be easily dispersed through wind, water, animals and on getting favourable conditions they germinate and give rise to new individuals.
(b) This mode of reproduction is simple and faster.
(d) Large numbers of spores are produced at one time within a sporangium.
Question. Mention the functions of (a) placenta (b) fallopian tube in the human female , reproductive system.
Ans. a. Placenta:
(i) Helps in transporting glucose and oxygen from the mother to the embryo.
(ii) Waste generated by the embryo is removed by transferring it to the mother’s blood.
b. Fallopian tube:
(i) Helps in carrying the egg from the ovary to the uterus.
(ii) Fertilization occurs here.
Question. Give one example each of a unisexual and bisexual flower.
or
Differentiate between unisexual and bisexual flower.
or
Distinguish between unisexual and bisexual flowers giving one example of each.
Ans. Unisexual flower have only one type of sex organ, either carpels or stamen, hence they are either male or female flower. For example: Cucurbit and maize. Bisexual flower have both carpels and stamens. For example: Marigold and rose.
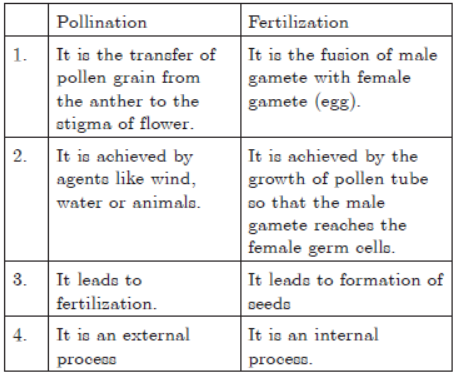
Question. List any two differences between pollination and fertilization.
Ans.
Question. List three techniques to prevent pregnancy. Which of them is not meant for males? How does the use of such techniques have an impact on health and prosperity of a family?
or
List any four methods of contraception used by humAns How does their use have a direct effect on the health and prosperity of a family?
Ans. Three techniques to prevent pregnancy:
a. Mechanical barrier — male or female.
b. Taking oral pills/i-pill/saheli - changing the hormonal balance of the body so that eggs are not released.
c. Use of the loop or the Copper-T.
d. Surgical method - tubectomy / vasectomy Use of hormonal preparations is not meant for males.
Effect on Health and Prosperity:
a. Health of women is maintained
b. Parents can give more attention to children
c. More resources can be made available.
Question. (a) List any four reasons for adopting contraceptive methods.
(b) If a woman is using Copper-T, will it help in protecting her from sexually transmitted diseases? Why?
Ans. (a) Four reasons for adopting contra¬ceptive methods are:
(i) To increase the gap between, two children.
(ii)To prevent unwanted preg¬nancy.
(iii)To prevent transmission of STDs.
(iv)To control population growth.
(b) If a woman is using a copper-T, it will not help in protecting her from sexually transmitted diseases. Copper-T prevents only implantation in the uterus.
Question. Draw a longitudinal section of a flower and label the following parts:
(i) Part that produces pollen grain.
(ii)Part that transfers male gametes to the female gametes.
(iii) Part that is sticky to trap the pollen grain.
(iv) Part that develops into a fruit.
Ans.
Question. Explain the following methods of contraception giving one example of each:
(i) Barrier method
(ii) Hormonal imbalance method
(iii) Surgical method.
Ans. (i) Barrier Method: In this method, physical devices such as condoms, diaphragm and cervical caps are used. These devices prevent the entry of sperm in the female genital tract during copulation, thus acting ‘ as a barrier between them.
(ii) Hormonal Imbalance Method: In this method, specific drugs are used by females, which are of two types: oral pills and vaginal pills. Oral pills contain hormones which stop the ovaries from releasing ovum into the fallopian tube. These pills are also called oral contraceptives (OCs) which act by changing the hormonal balance of the body so that eggs are not released and fertilisation cannot occur. The use of Intrauterine Contraceptive Devices (IUCDs) prevents implantation in the uterus. This device is copper-T placed safely inside the uterus by a doctor or nurse.
(iii) Surgical Method: In this method, a small portion of vas deferens in male and the fallopian tube in ‘ female is surgically removed or tied. It is called vasectomy in males and tubectomy in females. In this case, if the vas deferens in male is blocked, sperm transfer will be prevented and if the fallopian tube in the female is blocked, the egg will not be able to reach the uterus, thus fertilisation will not take place.
Question. What is AIDS? Which microbe is responsible for AIDS infection? State one mode of transmission of this disease. Explain in brief one measure for the prevention of AIDS.
Ans. AIDS is the Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome. It is caused by a virus called Human Immunodeficiency Virus. AIDS is transmitted by sexual contact with an infected person.
AIDS can be prevented by avoiding sexual contact with infected person or by using condom during sex.
Question. State in brief the changes that take place in a fertilised egg (zygote) till birth of the child in the human female reproductive system. What happens to the egg when it is not fertilised?
Ans. The egg gets fertilised in the oviduct. The fertilised egg, the zygote gets implanted in the lining of the uterus and starts dividing. The uterus prepares itself every month to receive and nurture the growing embryo. The lining thickens and is richly supplied with blood to nourish the growing embryo.
The embryo gets nutrition from the mother’s blood with the help of a special tissue called placenta. The development of the child inside the mother’s body takes approximately nine months. On completion of 9 months, the child is born as a result of rhythmic contractions of the muscles in the uterus.
If the egg is not fertilised, the thick and nourishing lining of the uterus breaks and comes out through vagina as blood and mucous.
Question. List and explain in brief three methods of contraception.
Ans.Methods of contraception are:
1. Use of condom for penis or for vagina as a mechanical barrier for the sperms to reach the egg.
2. Use of oral pills which change the hormonal balance so that eggs are not released.
3. Surgical method where either the vas deferens of male is blocked or the fallopian tube of female is blocked.
Question. Illustrate the following with the help of suitable diagrams:
(i) Spore formation in Rhizopus.
(ii)Multiple fission in Plasmodium.
Ans.
Question. (a) Draw a diagram showing germination of pollen on stigma of a flower.
(b) Label pollen grain, male germ- cells, pollen tube and female germ-cell in the above diagram.
(c) How is zygote formed?
Ans. (a) and (b)
(c) Zygote is formed when male gamete, Le. sperm fuses with female gamete, i.e. ovum.
Long Answer Type Questions :
Question. Compare the following:
a. Unisexual and bisexual flower.
b. Self-pollination and cross pollination.
c. Style and filament.
Ans. a. Unisexual flowers have either stamens or carpels, e.g., Papaya and Watermelon. Bisexual Flowers have both stamens and carpels, e.g., Mustard and Hibiscus.
b. Self-Pollination is transfer of pollen grains from the stamen to the stigma of same flower. Cross Pollination is transfer of pollen grains to another flower by agents like wind, water or animals.
c. Style is the middle elongated part of the carpel. It acts as a passage for pollen to reach ovary for the fertilization. Filaments is the elongated part of stamen.
Question. List six specific characteristics of sexual reproduction.
Ans. Characteristics of sexual reproduction:
a. Two parents are involved.
b. Two dissimilar gametes are formed by meiosis.
c. Variations are produced.
d. Occurs in all the higher and some of the lower organisms.
e. Fertilization / fusion of gametes leading to zygote formation.
Question. List four points of significance of reproductive health in a society. Name any two areas related to reproductive health which have improved over the past 50 years in our country.
Ans. Significance:
a. Prevent STDs.
b. Advantage of small family.
c. Less mortality among new-borns.
d. Reduces the cases of maternal mortality.
Areas which have improved:
a. Family Planning.
b. Decrease in STD cases.
Question. In the diagram of human male reproductive system given below:
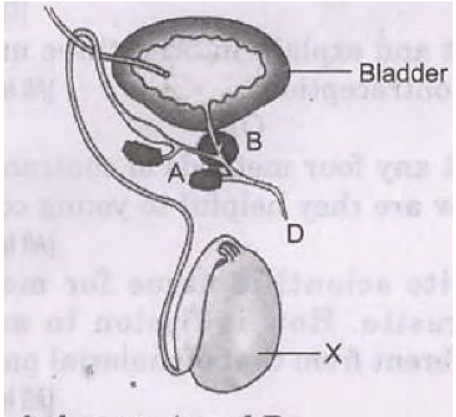
a. Label parts A and B.
b. Name the hormone produced by organ “X’. What is the role of this hormone in human male?
c. Mention the name of substances that are transported by tubes (i) C and (ii) D.
Ans. a. A - seminal vesicle, B - prostate gland.
b. Testosterone: It controls gamete formation/secondary sex organs/ accessory glands.
c. C - sperms, D - sperms/semen and urine.
Question. Answer the following related to AIDS.
(i) Expand AIDS, HIV.
(ii) Is AIDS an infectious disease?
(iii) State few methods of transmission of this disease.
(iv) Give some preventive measures for control of AIDS.
(v) When is World AIDS day celebrated?
Ans. (i) AIDS – Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome HIV – Human Immuno deficiency Virus
(ii) Yes, AIDS is an infectious disease.
(iii) Few methods of transmission of this disease are:
(a) Sexual contact with an infected person.
(b) Transfusion of blood from an infected person.
(b) From mother to child through placenta during pregnancy.
(d) Sharing of infected needles for injection of drugs or vaccines.
(iv) Some preventive measures for control of AIDS are:
(a) Using disposable syringes.
(b) Using condoms for sex.
(b) Before blood transfusion, blood should be tested for AIDS.
(d) Educating people about transmission and prevention of AIDS.
(v) World AIDS day is celebrated on December 1 every year.
Question. Answer the following questions:
(i) Draw the female reproductive part of a flower and label:
(a) The part which is sticky and receptors of pollen grains.
(b) The part that transfers male gametes.
(c) The part that contains the female gametes.
(ii) How do the pollen grains reach to the female reproductive part in a flower?
(iii) Describe how male and female gametes unite in a flowering plant with suitable diagrams.
Ans.
(i) (a) Stigma is sticky in nature and receptors of pollen grains.
(b) Pollen tube which arises from pollen grains transfers male gametes by passing through style into ovary.
(c) Ovary contains ovules that carry an embryo sac which contains the female gametes.
(ii) Pollen grains reach the stigma of carpel through pollination process by various pollinating agents like wind, insects, water etc.
(iii)
The process of mixing of male and female gametes to form a zygote is called fertilisation. By pollination process pollen grains gets deposited on stigma of carpel. Under suitable conditions they germinate. A long pollen tube containing two male gametes arises and it passes through style to reach the ovary. The ovary contains ovule which has a embryo sac. Female gamete is present inside embryo sac. The pollen tube enters the ovule through micropyle and penetrates through the embryo sac. One male gamete fuses with female gamete to produce zygote whereas the second male gamete fuses with polar nuclei to form endosperm. This process is called double fertilisation.
Question. Given below are few questions based on analogy. Fill in the blanks with appropriate answer in each.
(i) Diaphragm: Barrier methods: : Copper-T : _______.
(ii) Removal of vas deferens surgically: Vasectomy: : ______ : Tubectomy
(iii) HIV : AIDS : : _________ : Gonorrhoea
(iv) Ovary: Oestrogen: : Testis : __________
(v) Propagation by tissue culture: _________ : : Development of new plants from adventitious buds in Bryophyllum : Natural Methods of vegetative propagation.
Ans. (i) Intrauterine Contraceptive Device (IUCD)
(ii) Removal of oviduct surgically
(iii) Nisseria gonorrhoeae
(iv) Testosterone
(v) Artificial Methods of vegetative propagation
Question. We hear and read about female foeticide, which is really a wrong practice. In some families, be it rural or urban, females are tortured for giving birth to a girl child. They do not seem to understand the scientific reason behind the birth of a boy or a girl.
In your opinion, the approach of the society towards mother in this regard is correct or not? Explain the scientific reason.
Ans. No, it is not correct. Mother should not be blamed for this.
There is no difference between a male and female child, both are equal. A female is born if it receives the X bearing sperms from father as father carries both X and Y chromosomes and
mother carries only X chromosomes.
Question. A student is observing a permanent slide showing sequentially the different stages of asexual reproduction taking place in yeast.
Name this process and draw diagrams of what he observes in a proper sequence.
Ans. This process is called budding.
Question. Rajeev, a sales executive in a MNC was not keeping well for a long time. He underwent a complete medical check-up and was diagnosed as HIV+. He was terminated on account of this condition.
(i) To which category of disease does AIDS belong to? Give its causative organism.
(ii) Do you think it was a right decision by the head of the company? Justify?
(iii) What concern should the society show towards HIV+ individuals?
Ans. (i) AIDS is a sexually transmitted disease. Its causative organism is HIV.
(ii) No it was not a right decision by the head of the company because HIV is not spread by shaking hands, mixing with HIV infected individuals. Instead he should be given equal rights,
justice and freedom so that he should feel happy and should not get depressed.
(iii) The society should show positive attitude towards HIV positive persons. They should be given proper care and treatment. Everybody should support them so that they can
lead a healthy life without getting mental depression. We should not isolate them but we should provide proper education and create awareness among people about HIV and AIDS.
Question. Study the diagram and answer the following:
(i) What does the figure represents?
(ii) Give an example of organism which shows this process.
(iii) Describe the process shown in the picture.
Ans. (i) The figure represents binary fission which is an asexual mode of reproduction.
(ii) Amoeba and Paramecium show this mode of reproduction.
(iii) The genetic material first duplicates through mitosis leading to duplication of nucleus through karyokinesis and a constriction appears in the cell membrane which deepens
and finally a single parent cell divides into two daughter cells.
The division of cytoplasm is called cytokinesis. This mode of asexual reproduction is called binary fission.
Question. Draw and label the diagram of embryo of a gram seed. Give the functions of each parts labeled by you ?
Ans. Cotyledons store food for the growth of embryo.
Radicle becomes root in future plant.
Plumule becomes shoot in future plant.
Question. Answer the following by carefully studying the figure:
(i) Identify the image shown below.
(ii) Label in the figure the ovary, oviduct, uterus, vagina.
(iii) State the functions of the labeled parts in part b. 206
Ans. (a) The figure represents female reproductive system.
(b) The figure is as shown.
Question. (i) Observe a permanent slide of Amoeba under a microscope.
(ii) Similarly observe another permanent slide of Amoeba showing binary fission.
Now, compare the observations of both the slides.
Ans. One slide shows an amoeba containing a nucleus and cytoplasm whereas the second slide shows amoeba undergoing binary fission i.e., nucleus to be dividing,
constriction appearing on the cytoplasm, a single amoeba divides to produce two daughter amoeba.
Question. In the process of reproduction as used by Spirogyra, the organism splits itself into small pieces.
a. What is this process of reproduction called?
b. Is this type of reproduction sexual or asexual? Answer with reason.
c. Is this process same as regeneration?
Ans. a. Fragmentation.
b. Asexual as only one parent is involved,
c. In fragmentation, the body of a simple multicellular organism breaks down into many ‘fragments’. All cells undergo division and the organism develops from each fragment.
In regeneration, body of a multicellular organism get broken into many pieces, each piece is capable of re-growing into a complete individual.
Important Questions for NCERT Class 10 Science How Do Organisms Reproduce
Question. In vegetative reproduction, the new individuals are genetically –
a) Similar
b) Dissimilar
c) Abnormal
d) None of these
Ans. a) Similar
Question. When an organism breaks into a number of parts and each part develop into an individual, it is called –
a) Budding
b) Binary fission
c) Regeneration
d) Spore formation
Ans. c) Regeneration
Question. In man, fertilization of ovum takes place in
a) Vagina
b) ovary
c) uterus
d) Fallopian tubes
Ans. d) Fallopian tubes
Question. Define parthenogenesis.
Ans. Development of organism from an unfertilized egg.
Question. How may male gametes are produced by pollen grains?
Ans. Two
Question6. During grafting, the portion of plant that is grafted is called –
a) Stock
b) Scion
c) stalk
d) stem
Ans. b) Scion
Question. Which part of the flower forms the fruit?
a) Whole flower
b) Only stamens and carpel
c) Only ovary
d) Only carpel
Ans. c) Only ovary
Question. Anemophily is the pollination by –
a) Birds
b) Rain
c) insects
d) Wind
Ans. d) Wind
Question. What is syngamy?
Ans. Fusion of male gamete with the egg cell is called syngamy.
Question. Name the structure through which pollen tubes enters the ovule.
Ans. Stigma
Question. A common feature of reproduction in Amoeba, spirogyra and yeast is that
a) Asexual reproduction occurs after sexual reproduction
b) Asexual reproduction occurs before sexual reproduction
c) Asexual reproduction does not involve gametes
d) Asexual reproduction involves only one parent
Ans. (d) Asexual reproduction involves only one parent.
Question. The normal duration of menstrual cycle is
a) 7 – 8 days
b) 13 – 15 days
c) 3 – 4 days
d) 28 days
Ans. d) 28 days
Question. Which of the following is an IUCD?
a) copper – T
b) diaphragm
c) oral pills
d) tubectomy
Ans. a) copper – T
Question. What is parturition?
Ans. Parturition – The birth of fully developed foetus in completion of gestation.
Question. What is puberty?
Ans. Puberty – Age when reproductive system functionally active or starts producing ova or sperm is called puberty.
Question. Fertilization in plants occurs in the –
a) Embryo sac
b) Style
c) Pollen tube
d) Stigma
Ans. a) Embryo sac
Question. Characters that are transmitted from parents to offspring during reproduction show
a) only similarities with parents
b) only variations with parents
c) neither similarities nor variations
d) both similarities and variations with parents
Ans. d) both similarities and variations with parents
Question. Which among the following diseases is not sexually transmitted?
a) syphilis
b) Gonorrhoea
c) HIV – AIDS
d) Hepatitis
Ans. d) Hepatitis
Question. What is tubectomy?
Ans. Removal of a section of fallopian tube.
Question. Name the causative organism, of AIDS?
Ans. HIV – Human Immunodeficiency virus.
Question. A common feature of reproduction in Amoeba, spirogyra and yeast is that
a) They reproduce only sexually
b) They are all unicellular
c) they reproduce asexually
d) They are all multicellular
Ans. They reproduce asexually
Question. Which of this is seminal fluid?
a) Prostate gland
b) Cowper’s gland
c) Seminal vesicle
d) all of these
Ans. c) Seminal vesicle
Question. At the time of entering into ovule, pollen tube has
a) three male nuclei
b) two mole nuclei
c) one gamete nucleus
d) four male gametes
Ans. Two male nuclei
Question. How many follicles mature every month during the reproductive phase of human female?
Ans. One egg is produced every month by one of the ovaries
Question. What is the product of fertilization?
Ans. Zygote
Question. Asexual reproduction takes place through budding in
(a) Amoeba
(b) Yeast
(c) Plasmodium
(d) Leishmania.
Ans. (b) Yeast
Question. Which of the following is not a part of female reproductive system in human beings?
(a) Ovary
(b) Uterus
(c) Vas deferens
(d) Fallopian tube
Ans. (c) Vas deferens
Question. The anther contains
(a) Sepals
(b) Ovules
(c) Carpel
(d) Pollen grains.
Ans. (d) Pollen grains.
Very Short Answer Type Questions :
Question. The simple animals such as planaria can be cut into number of pieces and each piece grows into a complex organism. What is this process known as?
Ans.. Regeneration
Question. Name the unicellular organism which caused the disease known as kala-azar.
Ans. Leishmania
Question. Which process taking place in the nucleus of a cell leads to variation in the offspring during reproduction?
Ans. DNA copying
Question. Which type of layering is done in Jasmine?
Ans. Air Layering (Gootee)
Question. Where does fertilization takes place in human female?
Ans. Oviduct (fallopian tube)
Question. Give an advantage of vegetative propagation.
Ans. Vegetative propagation can be practised for growing such plants which usually do not produce seeds or produce non-viable seeds.
Question. Organisms have a varied body design. Name the property which gives the basic difference in body design.
Ans. Errors in DNA copying (variations).
Question. When a cell reproduces, what happens to its DNA?
Ans. Its DNA first doubles up followed by its equal and accurate division between two daughter cells.
Question. Define variation in relation to a species. Why is variation beneficial to the species?
Ans. Variation means certain changes which occur in sexually reproducing organisms because of errors in DNA copying. Variations are beneficial for species because they given survival advantage even in the adverse environmental conditions.
Short Answer Type Questions :
Question. a. List any two methods of asexual reproduction.
b. Explain how Spirogyra reproduces.
Ans. a. (i) Budding in Hydra and Yeast.
(ii) Spore formation in Fungi.
b. Spirogyra breaks up into smaller pieces upon maturation. These fragments grow into new individuals
Question. Reproduction is one of the most important characteristics of the living beings. Give three reasons in support of your answer.
or
Define reproduction. How does it help in providing stability to the population of species?
Ans. a. Reproduction is the process of producing individuals of its own kind. Through reproduction, the continuity is maintained.
b. Members of population are eliminated due to old age, disease, accidents and other reason. They have to be replaced by new members in order to maintain a stable population.
c. Reproduction brings variation so that population may adapt better and evolution in species takes place. Ultimately new species originate from preexisting ones.
d. Reproduction is not essential for an individual as its survival is not dependent upon it but is essential for a species for its survival.
Question. Mention the total number of chromosome along with sex chromosome. Explain how in a sexually reproducing organism chromosome number of parents and their offsprings is the same.
Ans. Total number chromosomes is 23 pairs. The last pair is called sex chromosome. If they are similar, they are termed as XX chromosome. They are present in the females. If they are dissimilar, they are called XY. They are present in the males. DNA doubling is always followed by cell division. But multicellular organisms have special linkages of cells in specialised organs which have only half the number of chromosomes and half the amount of DNA. Thus, when these germcells from two individuals combine during sexual reproduction to form a new individual, it results in re-establishment of number of chromosome and DNA content.
Question. List any four modes of asexual reproduction.
Ans. a. Four modes of asexual reproduction:
b. Fission
c. Budding
d. Spore formation
e. Fragmentation
f. Regenerations
Question. What is placenta? Explain its function in human female.
or
State the role of placenta in the development of embryo.
or
What is placenta? Describe its structure. State its functions in case of a pregnant human female.
Ans. Placenta is a specialized tissue embedded in the uterine wall. It contains villi on the embryo’s side and blood spaces on the mother’s side.
Function:
a. Helps in passing of nutrients from mother to foetus.
b. Exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide gases.
c. Passing of waste materials from embryo to the mother.
Question. (a) Explain the role of placenta in the development of human embryo.
(b) Give example of two bacterial and two viral sexually transmitted diseases. Name the most effective contraceptive which prevents spread of such diseases.
Ans. (a) Role of placenta in the development of human embryo: A special tissue develops between the uterine wall and the embryo (foetus) called placenta, where exchange of nutrients, glucose and oxygen takes place. The developing embryo will also generate waste substances which can be removed by transferring them into the mother’s blood through the placenta. The development of the child inside the mother’s blood takes approximately nine months.
(b) Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) transmitted by bacteria are:
(i) Gonorrhoea (ii) Syphilis
STDs transmitted by virus:
(i) AIDS (ii) Genital warts
The most effective contraceptive which prevents the spread of these diseases is by the use of mechanical barriers such as physical devices like condoms.
Question. Expand AIDS. List any four methods of prevention (control) of AIDS.
Ans. AIDS stands for Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome.
Four methods of prevention or control of AIDS are as follows:
(i) Use condom during sex.
(ii) Avoid sharing of needles.
(iii) Test blood for AIDS before transfusion.
(iv) Avoid sexual contact with unknown person.
Question. What are sexually transmitted diseases? Name four such diseases. Which one of them damages the immune system of human body?
Ans. Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) are the diseases which are spread by sexual contact from an infected person to a healthy person. They are caused by various microorganisms that live in warm and moist environments of the vagina, urethra, anus and mouth.
The four sexually transmitted diseases are:
(i) Gonorrhoea
(ii) Syphilis
(iii) Trichomoniasis
(iv) AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome). AIDS damages the immune system of human body.
Question. (a) Name the parts labelled A, B, C, D and E.
(b) Where do the following functions occur?
(i) Production of an egg
(ii) Fertilisation
(iii) Implantation of zygote.
(c) What happens to the lining of uterus:
(i) before release of a fertilised egg?
(ii) if no fertilisation occurs?
Ans. (a) A – Oviduct or Fallopian tube;
B – Ovary;
C – Uterus;
D – Cervix;
E – Vagina.
(b) (i) Ovaries;
(ii) Fallopian tube;
(iii) Lining of the uterus.
(c) (i) The lining of uterus becomes
(ii) The lining of uterus slowly breaks and comes out through the vagina as blood and mucous, if no fertilisation occurs.
Question. “Regeneration is not same as reproduction”.
a. Justify the statement.
b. What is meant by regeneration?
c. How is this process different from fragmentation?
Ans. a. Regeneration is not the same as reproduction, since most organisms would not normally depend on being cut up to be able to reproduce.
b. The ability to give rise to new individuals from the body parts of the parent individual is called regeneration.
c. In fragmentation, the body of a simple multicellular organism breaks down onto many ‘fragments’. All cells undergo division and the organism develops from each fragment. Regeneration occurs only through some specialised cells.
Question. Explain the process of regeneration in Planaria. How is this process different from reproduction?
Ans. Regeneration is the ability to give rise to new individuals from the body parts of the parent individual e.g., Hydra and Planaria, if their bodies get broken into many pieces, each piece is capable of re-growing into a complete individual.
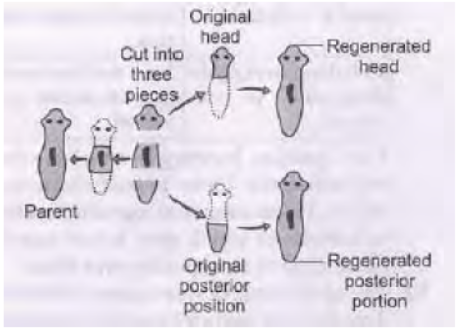
In some organism regeneration occurs but only to regain lost body parts like in tail of lizard, arm of a star fish. In the case of Planaria, it is a way of reproduction that is producing organisms of its own kind.
Question. a. Give the functions of: (i) Stigma (ii) Ovary
b. State in brief the formation of seed in a flower.
Ans. a. (i) The sticky terminal part of the carpel is called stigma. It receives pollen.
(ii) The swollen bottom part of the carpel is called ovary. It contains female germ cells which form seed after fertilization.
b. After fertilization, the zygote divides several times to form an embryo within the ovule. The ovule develops a tough coat and is gradually converted into a seed.
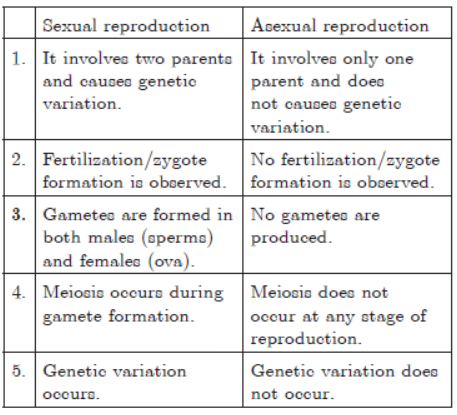
Question. List five distinguishing features between sexual and asexual types of reproductions in tabular form.
Ans.
Question. a. Identify the organisms A, B and the mode of asexual reproduction exhibited by them.

b. How will an organism be benefitted if it reproduces through spores?
c. Mention the two asexual methods by which hydra can reproduce. Explain briefly any one such method.
Ans. a. (i) Bryophyllum - vegetative propagation. (ii) Plasmodium - multiple fission.
b. Spores are covered with thick walls that protect them until they come into contact with a moist surface.
c. Budding and Regeneration.
Budding : A bud develops as an outgrowth due to repeated cell division at a specific site, these buds develop into tiny individuals, mature and detach from the parent to become new individuals.
Regeneration: Specialized cells divide to form large number of cells and undergo changes to become various cell types and tissues.
Question. Name the type of asexual reproduction demonstrated by the following organisms:
a. Amoeba
b. Rhizopus
c. Planaria
d. Plasmodium
e. Bryophyllum
Ans. a. Binary fission
b. Spore formation
c. Fragmentation
d. Multiple fission
e. Vegetative propagation
Question. a. Identify A,B,C and D in the given diagram and write their names.
b. What is pollination? Explain its significance.
c. Explain the process of fertilization in flowers.
Name the parts of flower that develop after fertilization into (i) seed (ii) fruit
Ans. a. A - pollen grain; B - stigma; C - Pollen tube, D - Female germ cell/Egg cell.
b. Pollination - Transfer of pollen grains from anther to the stigma of a flower.
Significance of pollination - Process of pollination leads to fertilization as it brings the male and female gametes together for fusion.
c. After a pollen falls on a suitable stigma, the pollen tube grows out of the pollen grain and travels through the style to reach the ovule in the ovary. Here the male germ cell (carried by the pollen tube) fuses with the female germ cell to form a zygote.
Long Answer Type Questions :
Question. What is the difference between albuminous seed and exalbuminous seed?
Ans.
Question. Answer the following questions:
(i) Write the function of following parts in human female reproductive system:
(a) Ovary
(b) Oviduct
(c) Uterus
(ii) Describe in brief the structure and function of placenta.
Ans. (i) (a) Ovary: It produces egg for fertilisation. It secretes estrogen and progesterone. Estrogen regulates secondary sexual characters and progesterone controls the thickness of the lining of uterus.
(b) Oviduct: It is the site of fertilisation and carries egg or fertilised ovum (zygote) to the uterus.
(c) Uterus: It helps to nourish the fertilised ovum that will develop into foetus. It holds the baby till it is ready for birth.
(ii) Placenta is a disc shaped structure on uterine wall before implantation of embyro. It provides oxygen and nutrients to the foetus. It helps to remove waste also. The placenta is
composed of both material tissues and tissue derived from the embryo. The chorion is the embryonic derived portion of the placenta. It is composed of foetal blood vessels and
trophoblasts which are organised into finger-like structures called chorionic villi.
Question. Draw in sequence (showing the four stages), the process of binary fission in amoeba.
Ans. Binary fission is an asexual mode of reproduction in amoeba where a single parent cell divides into two daughter cells and each daughter cell receives a copy of genetic material.
Question. Apotato is cut in to a number of small pieces, these pot at opieces are place donw etc otton kept in a tray. After a few days, green shoot sandroot sappear only froms omepota topi ecesandnot from all potato pieces,why?
Ans. In those potato pieces which possess the buds on getting moisture, light, oxygen new plants develop from them which is an example of natural methods of vegetative propagation and those potato pieces which do not have buds, from them new plants do not grow.
Question. Answer the following questions:
(i) Identify the process depicted in the diagram given below:
(ii) The spores have a covering of thick walls around it. What is its advantage?
(iii) What are hyphae?
Ans. (i) The process is known as spore formation in rhizopus.
(ii) Spores are covered by a thick structure to withstand unfavourable conditions like drought, high temperature etc.,
so that they can survive for a long time.
(iii) Hyphae are long, thread, branched filaments of fungus which release enzymes to absorb nutrients from food sources.
Question. Study the below diagram and answer the following:
(i) Label the parts A, B, C and D.
(ii) Which parts represent the male and female reproductive part respectively.
(iii) What is the function of the parts labeled A and D ?
(iv) What do you mean by pollination and explain the different types of pollination?
Ans. (i) A – Petals; B – Stamens; C – Pistil; D – Sepals
(ii) Part B [Stamens] represent male reproductive part and part C [Pistil] represent female reproductive part of a flower.
(iii) The main function of petal is to attract insects for pollination so they are large, showy and brightly coloured. The main function of sepal is to protect the stamens and pistils.
(iv) Pollination is the process of transfer of pollen grains from anther to the stigma of the carpel by various pollinating agents like wind, insects etc. There are two types of pollination :
(a) Self-pollination : The transfer of pollen grains from anther of a flower to stigma of the same flower or different flower but in same plant is called self pollination.
(b) Cross pollination : The transfer of pollen grains from anther of flower of one plant to stigma of another flower of different plant but of same species is called cross pollination.
Question. Hormones are powerful. It takes only a tiny amount to cause big changes in cells or even your whole body. That is why too much or too little of a certain hormone can be serious. Laboratory tests can measure the hormone levels in your blood, urine, or saliva.
(i) Name the part of the brain that regulates the release of hormones.
(ii) Name any two endocrine glands that are common in both males and females.
(iii) Name the endocrine gland which is present only in the males. Also, name the hormone that is produced by this gland.
(iv) Name the endocrine gland which is present only in the females and the hormone that is produced by this gland.
Ans. (i) The part of the brain that controls and regulates the release of hormones is the hypothalamus.
(ii) Pituitary gland and thyroid gland.
(iii) Testis which produces a hormone named testosterone is present only in males.
(iv) Ovary which produces the hormones progesterone and estrogen is the endocrine gland which is present only in the females.
Question. Why is the number of sperms produced always more than the number of eggs Produced?
Ans. A single ejaculation produces about 400 million sperms.
Sperms are motile in nature and they have to travel long distance to reach the egg for fertilisation. They also compete with each other to reach the egg, very few are able to climb
through uterus to reach oviduct whereas rest die and are absorbed on the way. Only one sperm in the end fuses with egg so to fertilise a single egg million number of sperms are
produced.
Question. Draw the diagram of a flower and label the four whorls. Write the names of gametes producing organs in the flower.
Ans. Anther of stamen produce male gametes and ovary pistil produce female gametes.
Question. The sexual act always has the potential to lead to pregnancy.
Pregnancy will make major demands on the body and the mind of the woman, and if she is not ready for it, her health will be adversely affected. Therefore, many ways have been devised to avoid pregnancy. 217
(i) Name any two bacterial diseases that are caused due to unprotected sex.
(ii) How a pill helps in preventing pregnancy?
(iii) What is vasectomy?
(iv) What are the common side-effects of using contraceptive pills?
Ans. (i) The two bacterial diseases that are caused due to unprotected sex are gonorrhea and syphilis.
(ii) The pill helps in preventing pregnancy as it prevents the release of the ovum, by changing the hormonal balance.
(iii) Vasectomy is the surgical process by which the vas deferens is cut. This prevents the sperms from reaching the ejaculatory duct.
(iv) The common side-effects of using contraceptive pills areirritation, nausea, and mood swings.
Question. How does binary fission differ from multiple fission?
Ans.
Question. Distinguish between a gamete and zygote?
Ans.
Question. Study the table given below and answer the questions.
(i) What are STDs?
(ii) Which of the bacteria is responsible for causing syphilis?
(iii) Name the contraceptive device that is commonly used by the males?
(iv) What is the part of the male reproductive organ that is cut in the process of vasectomy?
Ans. (i) There are a number of diseases that are caused by sexual intercourses. These diseases are called STDs “Sexually transmitted disease”.
(ii) Treponema pallidum is the bacterium that causes a disease called syphilis in humans.
(iii) The contraceptive device that is commonly used by the males is the condom.
(iv) The vas deferens is cut in the process of vasectomy. This prevents the sperms from reaching the ejaculatory duct.
Question. To perform an experiment to identify the different parts of an embryo of a dicot seed, first of all you require a dicot seed. Select dicot seeds from the following group.
Wheat, gram, maize, pea, barley, ground-nut.
(i) Wheat, gram and pea
(ii) Gram, pea and ground-nut
(iii) Maize, pea and barley
(i) Gram, maize and ground-nut
Ans. (ii) Gram, pea and ground-nut.
Question. Are binary fission and budding faster processes of reproduction when compared to sexual reproduction? Justify.
Ans. Yes, binary fission and budding are faster processes of reproduction when compared to sexual reproduction because in sexual reproduction there are lot of events like formation of gametes, fusion of gametes, development of a zygote to a young one etc.
Question. Name the type of asexual reproduction in which two individuals are formed from a single parent and the parental identity is lost.
Draw the initial and the final stages of this type of reproduction.
State the event with which this reproduction starts.
Ans. Binary fission is the type of asexual reproduction in which two individuals are formed from a single parent and the parental identity is lost.
This reproduction starts with elongation of Nucleus.
Question. Answer the following questions:
(i) A slide showing several amoeba was given to a student and was asked to focus the Amoeba undergoing binary fission. What will the student look for to correctly focus on a dividing Amoeba?
(ii) How can you identify the daughter cells which are formed due to binary fission in amoeba?
Ans. (i) Student should observe the Amoeba which will have a elongated nucleus along with a constriction in the middle of cytoplasm.
(ii) The daughter cells would be smaller in size than their respective parent cells.
Question. Answer the following questions:
(i) Name the remaining structure after removing the testa from water soaked gram seed.
(ii) How many cotyledons are present in the embryo of gram?
Ans. (i) Full mature embryo
(ii) Two cotyledons
Question. A student is made to observe two permanent slides. He was asked to identify the mode of reproduction in the respective organism. The student observed the following slides:
Ans. Slide I is showing budding in yeast and slide II is showing the process of binary fission in Amoeba.
Question. Ravi took three bread slices and kept the three pieces of the slices in the following gconditi ons.
(i) Slice 1 in a dried and dark place.
(ii) Slice 2 in a moist and dark place.
(iii) Slice 3 in moist and in refrigerator.
What would he observe in each of the above conditions?
Ans. In slice 1, no spores will develop as there is lack of moisture. In slice 2, white spongy mass like structures with black spots will be seen as both moisture and darkness favours the growth of bread moulds. In slice 3, there will be no formation of spores even though moisture is present because the low temperature in refrigerator does not favour the growth of spores.
Question. A student noticed that an organism by mistake was cut in two parts. After sometime both the parts developed into new individuals.
(i) Name the mode of reproduction used by the organism.
(ii) State the type of cells which carry this process.
(iii) Write examples of two organisms which multiply by this process.
Ans. (i) Regeneration method of asexual mode of reproduction.
(ii) Specialised regenerative cells.
(iii) Planaria and Hydra multiply by this process.
Question. Draw a labelled diagram of the longitudinal section of a flower.
Ans.
Question. Study the diagram and answer the following questions.
(i) What does the figure indicate?
(ii) Label the parts A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H.
(iii) Mention the role of parts B, E?
Ans. (i) The figure indicates fertilisation process in flowering plant.
(ii) A – Pollen grains, B – Stigma, C – Male gametes, D – Style, E – Pollen tube, F – Ovule, G – Ovary, H – Embryo sac
(iii) Stigma is the part of carpel which receives pollen grains during pollination. Pollen tube contains the male gamete which passes through the style and finally reaches the ovary.
It carries the male gametes towards female gametes for fertilisation.
Question. Answer the following:
(i) Complete the sentence by filling in X and Y. The ovary contains the X and the X contains the Y.
(ii) If a farmer wishes to develop a mango with characters of two related species, what method of vegetative propagation should he use?
Ans. (i) X is Ovule, Y is embryo sac which contain egg cell and two polar nuclei.
(ii) Grafting method is used.
Question. Ram and Shyam went for a trip to Botanical garden. They saw some plants with beautifully coloured and scented flowers. They wondered why some flowers were beautifully coloured and scented. Then they saw in a flower bed, rose plants with same coloured flowers and of same size. Next day when they went to school they asked teacher about that.
(a) Why flowers are beautifully coloured and scented?
(b) Why all the flowers in the flower bed were of same size and colour?
Ans. (a) Flowers are beautifully coloured and scented to attract insects for pollination. Pollination would lead to fertilization and finally formation of fruits and seeds.
(b) Rose plants might have propagated by vegetative propagation so they resemble their parents i.e., all the rose plants are of same size and of same colour.
Question. (i) Dissolve about 10 gm of sugar in 100 mL of water.
(ii) Take 20 mL of this solution in a test tube and add a pinch of yeast granules to it.
(iii) Put a cotton plug on the mouth of the test tube and keep it in a warm place.
(iv) After 1 or 2 hours, put a small drop of yeast culture from the test tube on a slide and cover it with a cover slip.
Observe the slide under a microscope.
Ans. Formation of yeast cells by budding process could be seen.
Some may show a chain of yeast cells attached to each other.
Question. It is a well known fact that pregnant woman’s health is a backbone of every family, society and thus nation.
(i) Which tissue is responsible for providing nutrition from mother to growing embryo?
(ii) According to you, what can likely be the measures to maintain woman health during pregnancy.
Ans. (i) Placenta is responsible for providing nutrition from mother to growing embryo.
(ii) Following measures should be maintain for the proper health of woman during pregnancy:
(a) Well balanced and proper nutritious diet.
(b) She should not take alcohol, smoke cigarette.
(c) She must be kept stress free away from family problems.
(d) Regular check-ups and visits to doctor.
(e) Avoid use of excess medicines and do light exercises.
Please refer to link below for CBSE Class 10 Biology HOTs-How do organisms reproduce.
MCQ Questions for NCERT Class 10 Science How Do Organisms Reproduce
Question. Length of pollen tube exhibits the distance from
(a) pollen grain to stigma
(b) pollen grain to style
(c) pollen grain through the style to the ovule
(d) stigma to style
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following processes is represented in the following figure?
(a) Multiple fission
(b) Binary fission
(c) Sporulation
(d) Vegetative propagation
Answer : A
Question. The following figure shows
(a) binary fission in Hydra
(b) budding in yeast
(c) fragmentation in Hydra
(d) budding in Hydra
Answer : D
Question. The following diagram represents
(a) budding in Hydra
(b) fragmentation in Spirogyra
(c) binary fission in Spirogyra
(d) budding in yeast
Answer : B
Question. Which of the following organisms reproduce through asexual means?
(a) Goat
(b) Yeast
(c) Dog
(d) Banana
Answer : B , D
Question. Why does testes lie in the scrotum outside the body cavity in human males?
(a) Because it helps in transfer of gametes
(b) Because it helps in storage of sperms
(c) Because it helps in mating
(d) Because it helps in formation of sperm
Answer : D
Question. In the following figure parts A, B and C represent
(a) stigma, pollen tube and ovarywall respectively
(b) stigma, pollen grain ad ovule respectively
(c) pollen grain, pollen tube and ovary wall respectively
(d) pollen grain, ovary and pollen tube respectively
Answer : C
Question. Reproduction is essential for living organisms to order to
(a) keep the individual organism alive.
(b) fulfill their energy requirement.
(b) maintain growth.
(d) continue the species generation after generation.
Answer: D
Question. The correct sequence of reproductive stages seen in flowering plants is :
(a) gametes, zygote, embryo, seedling
(b) zygote, gametes, embryo, seedling
(b) seedling, embryo, zygote, gametes
(d) gametes, embryo, zygote, seedling
Answer: A
Question. Offspring formed by asexual method of reproduction have greater similarity among themselves because
(i) Asexual reproduction involves only one parent.
(ii) Asexual reproduction does not involve gametes.
(iii) Asexual reproduction occurs before sexual reproduction.
(iv) Asexual reproduction occurs after sexual reproduction.
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Answer: A
Question. Name the part labelled X in the diagram that produces fluids which help the sperm to swim.
(a) Prostate gland
(b) Scrotum
(b) Urethra
(d) Ureter
Answer: A
Question. Which of the following statements are true for flowers?
(i) Flowers are always bisexual.
(ii) They are the sexual reproductive organs.
(iii) They are produced in all groups of plants.
(iv) After fertilisation they give rise to fruits.
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Answer: D
Question. The male human reproductive system consists of the testes and the male accessory glands.
Which of the following statements about male accessory glands is false?
(a) The prostate gland also synthesises sperm.
(b) The prostate gland and seminal vesicles are found outside the testes.
(b) The secretions of prostate gland and seminal vesicles make semen fluid and provide nutrition.
(d) Male accessory glands contribute to semen.
Answer: A
Question. Which of the following is not a part of the female reproductive system in human beings?
(a) Ovary
(b) Uterus
(b) Vas deferens
(d) Fallopian tube
Answer: C
Question. The diagram shows the female reproductive system during the fertile period of the menstrual cycle. Select what happens in the ovary during this time?
(a) Implantation occurs.
(b) Fertilisation takes place.
(b) A sperm fuses (joins) with an egg.
(d) An egg is released.
Answer: D
Question. Which of the following statements are incorrect?
(a) The umbilical cord is the conduit between the foetus and the placenta.
(b) The placenta can exchange materials between the foetus and the mother.
(b) Antibodies cannot reach the foetus through the mother’s placenta.
(d) All of the above.
Answer: C
Question. On observing an embryo of a pea seed, a student listed its various parts as given below :
Micropyle, Cotyledon, Plumule, Testa, Radicle, Tegmen On examining the list the teacher remarked that out of these only three parts belong to embryo. Select these three parts* :
(a) Testa, Radicle, Cotyledon
(b) Tegmen, Radicle, Micropyle
(b) Cotyledon, Plumule, Radicle
(d) Cotyledon, Plumule, Testa
Answer: C
Question. Offspring formed as a result of sexual reproduction exhibit more variations because:
(a) sexual reproduction is a lengthy process.
(b) genetic material comes from two parents of the same species.
(b) genetic material comes from two parents of different species.
(d) genetic material comes from many parents.
Answer: B
Question. The figure is given alongside shows the human male reproductive organs. Which structures make sperms and seminal fluid?
(a) V makes sperms and X makes seminal fluid
(b) W makes sperms and Y makes seminal fluid
(b) X makes sperms and W makes seminal fluid
(d) Y makes sperms and V makes seminal fluid
Answer: D
Question. Which of the following is considered a barrier form of contraception?
(a) Vasectomy
(b) Femidom
(b) Copper T
(d) Silver T
Answer: B
Question. Vegetative propagation refers to formation of new plants from
(a) stem, roots and flowers
(b) stem, roots and leaves
(b) stem, flowers and fruits
(d) stem, leaves and flowers
Answer: B
Question. To perform an experiment to identify the different parts of an embryo of a dicot seed, first of all you require a dicot seed. Select dicot seeds from the following group*.
Wheat, Gram, Maize, Pea, Barley, Ground-nut
(a) Wheat, Gram and Pea
(b) Gram, Pea and Ground-nut
(b) Maize, Pea and Barley
(d) Gram, Maize and Ground-nut
Answer: B
Question. Which of the functions are performed by the ovaries?
(a) Formation of ovum
(b) Secretion of Progesterone
(b) Secretion of Estrogen
(d) All of the above
Answer: D
Question. Characters transmitted from parents to offspring are present in
(a) cytoplasm
(b) ribosome
(b) golgi bodies
(d) genes
Answer: D
Question. In human females an event that reflects onset of reproductive phase is :
(a) growth of body
(b) change in voice
(b) changes in hair pattern
(d) menstruation
Answer: D
Assertion and Reasoning Based Questions :
Question. Assertion: The flower of papaya is called unisexual flower.
Reason:The flower contains stamens only as a sex organ.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) If assertion is true, but reason is false.
(d) If assertion is false, but reason is true.
Answer: C
Question. Assertion: XX chromosome give rise to female child whereas XY give rise to male child.
Reason: The Y chromosome in males is smaller than X chromosome.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) If assertion is true, but reason is false.
(d) If assertion is false, but reason is true.
Answer: B
Question. Assertion: Lumen of fallopian tube is lined by ciliated epithelium.
Reason: Ciliated epithelium helps in moving the zygote towards the uterus for implantation.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) If assertion is true, but reason is false.
(d) If assertion is false, but reason is true.
Answer: A
Question. Assertion: Non flowering plants cannot reproduce sexually.
Reason: Flower is only reproductive part of the plant that can produce gametes.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) If assertion is true, but reason is false.
(d) If assertion is false, but reason is true.
Answer: A
Question. Assertion: High chances of fertilisation is during the mid of the menstrual cycle.
Reason: Sperms are very active during that time.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) If assertion is true, but reason is false.
(d) If assertion is false, but reason is true.
Answer: C
Question. Assertion: The testes descend into the scrotum just before birth.
Reason: Human males have 2 testes in the body.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) If assertion is true, but reason is false.
(d) If assertion is false, but reason is true.
Answer: B
Question. Assertion: Copper-T can be used as a contraceptive method.
Reason: It prevents from sexually transmitted disease.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) If assertion is true, but reason is false.
(d) If assertion is false, but reason is true.
Answer: C
Question. Assertion: Male is responsible for the sex determination in humans.
Reason: It has similar kind of chromosomes XX.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) If assertion is true, but reason is false.
(d) If assertion is false, but reason is true.
Answer: C
Question. Assertion: Meiosis takes place only in gametes.
Reason: To restore the total number of chromosomes in offspring.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) If assertion is true, but reason is false.
(d) If assertion is false, but reason is true.
Answer: A
Question. Assertion: Placenta is connected to the embryo through an umbilical cord which helps in the transport of substances to and from the embryo.
Reason: Placenta acts as an endocrine tissue.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) If assertion is true, but reason is false.
(d) If assertion is false, but reason is true.
Answer: B
Very Short Answer Type Questions :
Question. Why is cell division considered as a type of reproduction in unicellular organisms?
Answer : Cell division results in the formation of two daughter cells, i.e., it results in the production of more individuals of the organism like the process of reproduction.
Question. Why is fertilisation in flowering plants not possible without pollination?
Answer : Pollination allows pollen grains to reach carpel which contains the egg. Thus, fertilisation which involves fusion of male and female germ cells can occur only after pollination.
Question. Name the parts in human body where sperms and eggs are produced.
Answer : Sperms are produced in testes (males) and eggs are produced in ovary (female).
Question. Mention any one limitation of vegetative propagation.
Answer : One limitation of vegetative propagation is that it does not show genetic variation.
Question. Why copper - T cannot protect a woman from sexually transmitted diseases?
Answer : Copper-T is an intrauterine device which acts as contraceptive but does not provide protection against sexually transmitted diseases as it does not provide any barrier against mixing of body fluids from two individuals.
Question. What is the function of pollen grains in flowers?
Answer : Pollen grains produce male gametes which fertilise the egg cell present in the ovule.
Question. How regeneration is carried out?
Answer : Regeneration is carried out by specialised cells which proliferate and make large numbers of cells. From this mass of cells, different cells undergo changes to become various
cell types and tissues.
Question. Name the parts of a bisexual flower that are not directly involved in reproduction.
Answer : The parts of a bisexual flower that are not directly involved in reproduction are : sepals (calyx), petals (corolla) and thalamus.
Question. Name any two type of asexual reproduction.
Answer : (i) Fragmentation (ii) Budding
Question. What changes occur in the flower after fertilisation?
Answer : After fertilisation, the flower withers. The sepals and the petals dry up, the ovary converts into fruit, the ovule forms the seed and the zygote forms the embryo which is enclosed
in the seed.
Question. How population growth can be prevented?
Answer : Population growth can be prevented by family planning programmes which involve various types of birth control measures like mechanical, chemical, surgical and natural methods.
Question. Name the information source of making proteins in the cell. State two basic events in reproduction.
Answer : The DNA in the cell nucleus is the information source of making proteins. The two basic events in reproduction are:
(i) Creation of a DNA copy,
(ii) Additional cellular apparatus by the cell involved in the process.
Question. What is regeneration? State a reason why a more complex organism cannot give rise to new individuals through this method.
Answer : Regeneration is the ability of a fully differentiated organism to give rise to new individual organisms from its body parts. More complex organisms cannot give rise to new individuals through regeneration because:
(i) their body is highly complicated.
(ii) there are specific organs to do specific functions.
(iii) there is a labour division in the body of complex organisms.
(iv) regeneration is carried out by specialised cells which are not present in complex organisms.
Question. State what type of method is used for growing jasmine plant.
Answer : Artificial methods of vegetative propagation like layering is used for growing jasmine plant.
Question. Name the largest cell present in the human body.
Answer : The largest cell present in the human body is ovum.
Question. What is ‘reproduction’? Mention the importance of DNA copying inreproduction.
Answer : Reproduction is the process of producing new individuals of the same species by existing organisms of a species, i.e. parents. The importance of DNA copying in reproduction are as follows:
(i) DNA copying is called DNA replication. In this process, one copy each of replicated DNA will be passed to daughter cells.
(ii) Variations may be introduced during DNA copying. This inbuilt tendency for variation during reproduction forms the basis of evolution.
Question. “Variations that confer an advantage to an individual organism only will survive in a population.” Justify.
Answer : It is because the chances of survival depend on the nature of variations and different individuals have different kinds of advantages.
For example, a bacteria that can withstand heat will survive better in a heat wave, i.e. the organisms that are fit in the competitive environment and with great variations will be able to survive and adapt. Thus, more offsprings and population with genetic variations will survive.
Question. Can you consider cell division as a type of reproduction in unicellular organisms? Justify.
Answer: Yes, cell division can be considered as a type of reproduction in unicellular organisms because through cell division two or more daughter cells are produced from a parent cell.
Question. What would be the ratio of chromosome number between an egg and its zygote? How is the sperm genetically different from the egg?
Answer: The ratio of chromosome number between an egg and its zygote is 1 : 2. Sperms are of two types 50% of sperms have X chromosome and rest 50% Y chromosomes. But eggs have only one type of chromosome i.e., X chromosome.
Question. What is the effect of DNA copying which is not perfectly accurate in the reproduction process?
Answer: If DNA copying is not perfectly accurate in the reproduction process it would lead to variations in the populations which may prove a better survival option to the species.
Question. Name the types of asexual reproduction in which two individuals are formed from a single parent and the parental identity is lost.
Write the first step from where such a type of reproduction begins.
Answer: Binary fission is a type of asexual reproduction in which two individuals are formed from a single parent and the parental identity is lost. The reproduction starts from Karyokinesis i.e., division of nucleus.
Question. What is the end product of double fertilisation?
Answer: In double fertilisation one of the male gametes fuse with egg cell to form a zygote whereas the other male gamete fuses with two polar nuclei to form primary endosperm that provides nourishment to the growing embryo.
Question. Write any two precautions while studying different parts of an embryo of a dicot seed?
Answer: Two precautions are:
(a) The slide should first be observed under low power magnification compound microscope and then under high power magnification compound microscope.
(b) The slides should be focused properly.
Question. Name three dicot seeds. Seeds on germination give rise to _______ and __________.
Answer: The three dicot seeds are gram, peas and beans.Seeds on germination give rise to plumule and radicle.
Question. Is the chromosome number of zygote, embryonal cells and adult of a particular organism always constant? How is the constancy maintained in these three stages?
Answer: Yes, the chromosome number of zygote, embryonal cells and adult of a particular organism is always constant. This is because zygote is diploid and it undergoes mitotic divisions to form embryonal cells and finally adult and during mitosis the chromosome number remains constant.
Question. Colonies of yeast fail to multiply in water but multiply in sugar solution. Give one reason for this.
Answer: Sugar solution provides energy which cannot be provided by water for the growth of yeast colonies.
Question. Where is the zygote located in the flower after fertilisation?
Answer: Zygote is located inside the ovule which is present in the ovary part of the pistil.
Question. List two advantages of practising vegetative propagation in plants. Select two plants raised by this method from the list given below:
Banana, Gram, Pea, Rose, Tomato, Wheat.
Answer : Advantages of vegetative propagation are:
1. Plants raised by vegetative propa-gation can bear fruits and flowers earlier.
2. Plants produced are genetically similar.
Banana and Rose can be raised by vegetative method.
Question. Name one sexually transmitted disease each caused due to bacterial infection and viral infection. How can these be prevented?
Answer : Sexually transmitted disease caused due to
(i) Bacterial infection is gonorrhoea, and
(ii) Viral infection is AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome). These diseases can be prevented by responsible sexual behaviour such as use of condom during intercourse, etc.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. What happens when the egg is not fertilised in human females?
Answer : One egg is produced every month by one of the ovaries. The uterus prepares itself every month to receive and nurture the growing embryo. The lining thickens and is richly supplied with blood to nourish the growing embryo. If the egg is not fertilised, this lining is not needed any longer. So, the lining slowly breaks and comes out through the vagina as blood and mucus. This cycle takes place roughly every month and is known as menstruation. It usually lasts for about two to eight days.
Question. Do you think sex-education is necessary in schools?
Answer : A correct knowledge about reproductive organs, adolescence related changes, sexually transmitted diseases, etc., will save the young minds from myths and misconceptions about sex related aspects and help them to lead a reproductively healthy life. Thus, sex-education is necessary in schools.
Question. Pollination brings male gamete in close proximity to the female reproductive part.
Answer : Pollination is the process of transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a flower to the stigma of the same or another flower. Pollen grains bear male gametes which are carried to the ovary of a flower with the help of pollen tubes. Hence, pollination brings male gametes in close proximity to the female reproductive part.
Question. How Spirogyra reproduces?
Answer : Spirogyra reproduces through the fragmentation process.
Fragmentation is the mode of reproduction in which parent body breaks into two or more fragments and each fragment develops into a new individual. It is a method of reproduction in many filamentous algae, mycelial fungi and thalloid bryophytes. The given figure shows the process of fragmentation in Spirogyra.
Question. How do insects help in pollination?
Answer : In entomophily (insect pollination), when an insect visits a flower for nectar, the pollen grains get deposited on the body of insect. When this insect visits another flower, some
of the pollen grains stick to stigma of another flower. This leads to pollination.
Question. Why do multicellular organisms use complex way of reproduction?
Answer : In multicellular organisms, cells are organised into specialised groups; tissues, organs or organ systems, each of which occupy specific locations in the body. In such an
organised condition cell-by-cell division would be impossible. Hence, multicellular organisms need complex methods of reproduction.
Question. Describe the role of prostate gland, seminal vesicle and testes in the human male reproductive system.
Answer : Prostate glands - Secretion of the prostate gland nourishes and activates the spermatozoa to swim. Seminal Vesicles - They produce an alkaline secretion which forms 60% of the volume of semen. Alkaline nature of the removal fluid helps to neutralise the acidic environment of the male urethra as well as that of female reproductive tract which otherwise would inactive and kill sperms. Testes are responsible for producing sperm and secreting male sex hormones e.g., testosterone.
Question. Why is variation so important?
Answer : Variation is so important because
(i) Populations of organisms normally live and interact with definite kinds of ecological niches. If there is an alteration in the ecological conditions of such places, the population of organisms will get damaged and may be wiped out. The variants of the organisms, however, may have better chances of survival. The surviving individuals may reproduce and
develop a kind of population which is suited to the changed niche.
(ii) It makes some individuals better fitted in the struggle of existence.
(iii) It helps the individuals to adapt themselves according to the changing environment.
(iv) It allows breeders to improve races of useful plants and animals for increase resistance, better yield, quicker growth and lesser input.
(v) Preadaptation caused by the presence of neutral variations are extremely useful for survival against sudden changes in environment e.g., resistance against a new pesticide or antibiotic.
(vi) It constitutes raw material for evolution.
(vii) It gives each organism a distinct individuality.
Question. (a) In the human body what is the role of (i) seminal vesicles, and (ii) prostate gland?
(b) List two functions performed by testis in human beings.
Answer : (a) The role of seminal vesicles and the prostate gland are as follows:
(i) Seminal vesicles produce seminal plasma which is in the form of fluid makes the transport of sperms smooth.
(ii) Prostate gland secretes prostatic fluid that keeps the sperms alive and helps them to swim vigorously.
(b) Two functions performed by testis in human beings are as follows:
(i) Formation of sperms takes place in testis.
(ii) They secrete the hormone testosterone which regulates the formation of sperms and brings changes in appearance of boys at the time of puberty.
Question. What is reproduction? What are its two types? Which one of the two confers new characteristics on the offsprings and how?
Answer : Reproduction is the process of producing new individuals of the same species by existing organisms of a species, z.e. parents. Its two types are: Asexual reproduction and Sexual reproduction.
Sexual reproduction confers new characteristics on the offspring due to variation in DNA copying.
Question. What is the effect of DNA copying which is not perfectly accurate on the reproduction process?
Answer : DNA copying is not perfectly accurate and the resultant errors are a source of variations in populations of organisms.
Question. State the method used for growing rose plants.
Answer : Artificial methods of vegetative propagation like cutting are used to grow rose plants.
Question. How does growing embryo get nutrition from the mother’s blood?
Answer : The embryo gets nutrition from the mother’s blood with the help of a special tissue called placenta. This is a disc which is embedded in the uterine wall and transfers glucose and oxygen from the mother to the embryo.
Question. List any four reasons for vegetative propagation being practised in the growth of some type of plants.
Answer :
(i) Vegetative propagation is a cheaper, easier and more rapid method of propagation in plants than growing plants from their seeds.
(ii) Better quality of plants can be maintained by this method.
(iii) It results in propagation of those plants which do not produce viable seeds or produce seeds with prolonged period of dormancy.
(iv) The plants generated from vegetative means are more uniform and genetically similar to the parent stock.
Question. Write any two differences between binary fission and multiple fission in a tabular form as observed in cells of organisms.
Answer :

Question. Mention the mode of reproduction used by
(a) Amoeba (b) Planaria.
Answer : Mode of reproduction used by
(a) Amoeba is Binary fission. (b) Planaria is Regeneration.
Question. State one genetically different feature between sperms and eggs of humans. What is its consequence?
Answer : The sex chromosome of human male is XY. A sperm of human male carries either an X chromosome or one Y chromosome.
The sex chromosome of human female is XX and hence, the egg always carries the X chromosome.
If a sperm carrying X chromosome fertilises an egg which carries X chromosome, then the’ child born will be a girl. If a sperm carrying Y chromosome fertilises an egg which carries X chromosome, then the child born will be a boy.
Question. List two advantages of vegetative reproduction practised in case of an orange plant.
Answer : Two advantages of practising vegetative reproduction in orange plants are:
(i) The oranges produced are similar in size and shape.
(ii) Many oranges do not produce viable seeds and hence, vegetative method is good alternative.
Question. Define the term puberty. List two changes observed in girls at the time of puberty.
Answer : The period, when the rate of general body growth begins to slow down and reproductive tissues begin to mature, is called puberty.
Two changes observed in girls at the time of puberty are:
(i) The breast size begin to increase,
(ii) Menstruation starts.
Question. Differentiate between ‘self-pollination’ and ‘cross-pollination’. Describe double fertilisation in plants.
Answer :
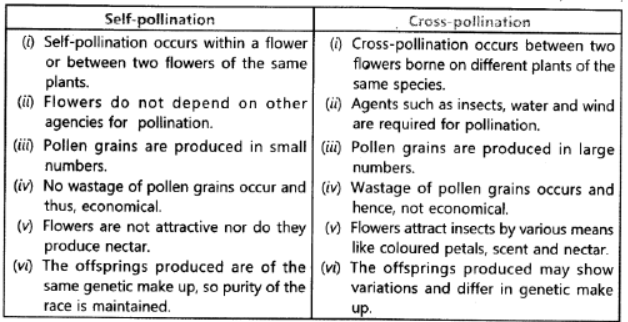
During fertilisation in plants, the following events take place:
(i) One of the male gamete fuses with the female gamete present in the embryo sac.
(ii) The other male gamete fuses with the two polar nuclei in the embryo sac.
The first fusion product gives rise to the zygote while the second one forms the endosperm. The process of two fusions occurring in the embryo sac is called double fertilisation.
Question. What is meant by asexual reproduction? List its any two different forms.
Answer : Asexual reproduction is the process of producing new organism from a single parent without the involvement of sex cells. Fission and fragmentation are two different forms of asexual reproduction.
Question. Name an organism which reproduces by spore formation. List three conditions favourable for spores to germinate and grow.
Answer : Rhizopus reproduces by spore formation. Conditions favourable for spore formation are: (i) Cool place, (ii) Moist place and (iii) Dark place.
Question. “DNA copies generated during reproduction will be similar but may not be identical to the original.” Justify this statement.
Answer : DNA copies generated will be similar, but may not be identical to the original as some variations are so drastic that new DNA copy cannot work with the cellular apparatus it inherits. Such a newborn cell will simply die. Therefore, there could be many other variations in the DNA copies that would not lead to such a drastic outcome. Thus, the surviving cells are similar but slightly different from each other. This tendency of variation during reproduction is the basis for evolution.
Question. Why is DNA copying an essential part of the process of reproduction?
Answer : DNA copying is an essential part of the process of reproduction because:
(i) DNA copying provides cellular apparatus in the daughter cells.
(ii) DNA in daughter cells will be able to control the functioning of daughter cells. (iii)DNA copies will retain the traits.
Question. List the parts of human male reproductive system which contribute fluid to the semen. State two advantages semen offers to the sperms.
Answer : Prostate glands and seminal vesicles add fluid in the vas deferens. This makes transportation of sperms easier and also provides nutrition to the sperms.
Question. Name the two types of germ-cells present in human beings. How do they structurally differ from each other? Give two differences.
Answer : The two types of germ-cells present in human beings are sperm and ova. The sperm of human have either X or Y chromosome. The ova always carry X chromosome. The sperm is structurally long with a tail. The ova is round in structure.
Question. List any four modes of asexual reproduction.
Answer : Four modes of asexual reproduction are—Binary fission in Amoeba, Fragmentation in Spirogyra, Regeneration in Planaria and Budding in Hydra.
Question. Define the terms unisexual and bisexual giving one example of each.
Answer : Unisexual is the plant whose flowers contain either stamens or carpels but not both.
Example: Papaya, Watermelon.
Bisexual is the plant whose flowers contain both stamens and carpels. Example: Hibiscus, Mustard.
Question. (i) What is fertilisation? Distinguish between external fertilisation and internal fertilisation.
(ii) What is the site of fertilisation in human beings?
Answer : (i) Fertilisation is defined as the fusion of a male gamete (sperm) with a female gamete (an ovum or egg) to form a zygote during sexual reproduction.
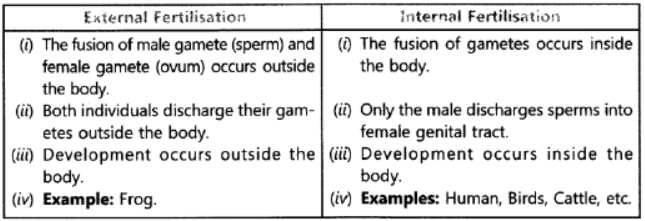
(ii) The site of fertilisation in human beings is in the fallopian tube of female reproductive system.
Question. Illustrate the following with the help of suitable diagrams:
(i) Regeneration in Planaria.
(ii) Budding in Hydra.
Answer :
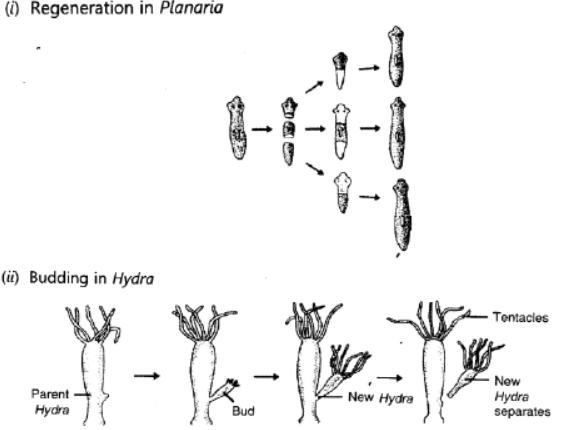
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. What is the significance of sexual mode of reproduction?
Answer : Sexual reproduction may be defined as the production of offsprings (new individuals) by the fusion of two gametes (usually one from male parent and the other from female
parent) to form a diploid zygote which develops into a mature organism. Gamete formation involves meiosis or reduction division. The gamete mother cell is diploid (2n), i.e., it has two sets of chromosomes. This single diploid cell divides by meiosis to form 4 haploid (n) daughter cells. Each daughter cell becomes a gamete, either male or female. Each gamete possesses single set of chromosomes. Thus, this division involves copying of the DNA as well as the cellular apparatus. There is a stage in such nuclear division where crossing over of chromosomes take place. This is very important step which results in a slight different composition of chromosomes in gametes. Fusion of these gametes results in the formation of a slightly different individuals which show variations. The variations which lead to the appearance of such characters which fit to the changing environment result in the survival of the species. Chances of variation, therefore, are much more in sexual mode of reproduction as compared to asexual reproduction. Moreover, chances of the production of compatible generations are also more in sexual reproduction.
Question. Answer the following.
(a) Give reasons for avoiding frequent pregnancies by women.
(b) Explain the following methods of contraception giving one example of each.
(i) Barrier method
(ii) Chemical method
(iii) Surgical method
Answer : (a) Having pregnancies too frequently and giving child birth at quick succession reduce mother’s health and vitality and cause mental strain. Health of children is also affected
due to nutritional deficiencies.
(b) (i) Barrier method: These are physical devices to prevent the entry of sperm into the female genital tract during copulation. They also protect against sexually transmitted
diseases, e.g., condoms. Condoms are thin, strong rubber sheaths used by man to cover the erect penis. It is simple but effective and widely used contraceptive that has no side
effects. It checks pregnancy by preventing deposition of semen in the vagina.
(ii) Chemical method: Foam tablets, jellies, pastes, creams and spermicides are some common chemicals used by females. These are placed in vagina. These chemicals adhere
to the mucous membrane and immobilise and kill the sperms.
(iii) Surgical method: Surgical methods include – vasectomy and tubectomy. Vasectomy is a small surgical operation performed in males. It involves removal of a small portion
of the sperm duct (or vas deferens) by surgical operation. The two cut ends are then ligated (tied) with threads. This prevents the sperms from coming out. Tubectomy is done in
females where oviducts are cut and the cut ends are tied with threads.
Question. Describe the structure of human male reproductive system. Write down the role of each part.
Answer : Human male reproductive system consists of testes, scrotum, vas deferens, urethra and penis.
(a) Testes : The human male possesses two testes, which are the primary reproductive organs, lying outside the abdominal cavity. The two testes are the male gonads, which are the sites where male gametes, i.e., sperms are produced. The testes also produce the male sex hormone-testosterone.
The testes of man produce sperms from puberty onwards, throughout his life.
(b) Scrotum: The scrotum is a pouch of skin that hangs between the legs. It is divided internally into right and left scrotal sacs by a partition. The two testes lie in respective
scrotal sacs. The scrotum acts as a thermoregulator and provides an optimal temperature for the formation of sperms.
The sperms develop at a temperature 2 – 2.5°C lower than the normal body temperature.
(c) Vas deferens : This is a straight tube, about 40 cm long, which carries the sperms from epididymis towards the urethra.
(d) Urethra: It is about 20 cm long tube that arises from the urinary bladder to carry urine. It runs through the penis and opens to the outside through male genital pore. The contents
of two seminal vesicles, and sperms from vas deferens also join the urethra. Thus urethra carries urine from the bladder, as well as sperms from the vasa deferentia through the
penis.
(e) Penis: Penis is a long and thick muscular organ made up of mostly erectile tissue. At the time of sexual act, the erectile tissue gets filled with blood causing the penis to
become erect. It is inserted into the vagina of the female where sperms are ejaculated for the purpose of reproduction.
| CBSE Class 10 Science HOTs Chemical Reactions and Equations |
| CBSE Class 10 Science HOTs Acids Bases And Salts |
| CBSE Class 10 Science HOTs Metals and Non Metals |
| CBSE Class 10 Science HOTs Carbon And its Compounds |
| CBSE Class 10 Science HOTs Life Processes |
| CBSE Class 10 Science HOTs Control And Coordination |
| CBSE Class 10 Science HOTs How Do Organisms Reproduce |
| CBSE Class 10 Science HOTs Heredity |
| CBSE Class 10 Science HOTs Reflection and Refraction |
| CBSE Class 10 Science HOTs Human Eye and Colourful World |
| CBSE Class 10 Physics HOTs Electricity |
| CBSE Class 10 Science HOTs Magnetic Effects of Electric Current |
| CBSE Class 10 Science HOTs Our Environment |
| CBSE Class 10 Science HOTs Question Bank |
HOTS for Chapter 7 How do Organisms Reproduce Science Class 10
Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to NCERT book for Class 10 Science to develop the Science Class 10 HOTS. If you download HOTS with answers for the above chapter you will get higher and better marks in Class 10 test and exams in the current year as you will be able to have stronger understanding of all concepts. High Order Thinking Skills questions practice of Science and its study material will help students to have stronger understanding of all concepts and also make them expert on all critical topics. You can easily download and save all HOTS for Class 10 Science also from www.studiestoday.com without paying anything in Pdf format. After solving the questions given in the HOTS which have been developed as per latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 10 Science designed by our teachers. We have also provided lot of MCQ questions for Class 10 Science in the HOTS so that you can solve questions relating to all topics given in each chapter. After solving these you should also refer to Class 10 Science MCQ Test for the same chapter
You can download the CBSE HOTS for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 How do Organisms Reproduce for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the HOTS issued by CBSE for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 How do Organisms Reproduce have been made available here for latest academic session
HOTS stands for "Higher Order Thinking Skills" in Chapter 7 How do Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Science. It refers to questions that require critical thinking, analysis, and application of knowledge
Regular revision of HOTS given on studiestoday for Class 10 subject Science Chapter 7 How do Organisms Reproduce can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, HOTS questions are important for Chapter 7 How do Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Science exams as it helps to assess your ability to think critically, apply concepts, and display understanding of the subject.

