Very Short Answer type Chapter Controlling Class 12 Business Studies
Question. If you want to control everything you may end up controlling.
Answer: Management By Exception.
Question. Define Management Audit.
Answer: Systematic appraisal of the overall performance of the management of an organization.
Question. Why is controlling considered to be a backward looking?
Answer: Controlling involves evaluation of past activities to find out deviations from standards so it is a backward looking function.
Question. Name two types of profitability ratios?
Answer: a) Gross Profit Ratio b)Net Profit Ratio.
Question. What do you call the sales volume at which there is no profit, No loss?
Answer: Break even Point (BEP).
Question. Give 2 examples of Corrective Action.
Answer: a) Provide training b) Revive standards.
Question. Give two examples of responsibility centers.
Answer: Cost Centre, revenue center etc.
Question. Marketing department comes under which type of responsibility center.
Answer: Revenue Centre.
Question. Give the formula of Return on Investment.
Answer: Net Profit/ Total investment
Question. What do you understand by key KRAs result areas?
Answer: The areas which are critical to the success of an organization.
Question. Why planning is an empty exercise without controlling?
Answer: Planning is an empty exercise without controlling because implementation of plans and monitoring of plan depend upon controlling.
Question. Which two steps in the process of controlling are concerned with compelling events to conform to plan?
Answer: Comparison of actual performance with standards. b)Taking corrective actions.
Important Exam Questions for NCERT Class 12 Business Studies Controlling
Meaning & Definition
Controlling means ensuring that activities in an organization are performed as per the plans. Controlling also ensures that an organization’s resources are being used effectively and efficiently for the achievement of predetermined goals.
It can be defined as comparison of actual performance with the planned performance.
Nature of Controlling/Features of Controlling
1. Controlling is a goal oriented function: Controlling as a function of management ensures that the overall directions of individuals and groups are consistent with short and long range plans of the organization.
2. Controlling is an all pervasive function: Controlling is a function which is applicable to all types of organizations business and non-business and at all managerial levels.
3. Controlling is a continuous function: Control is not a one time activity. Rather, it is a dynamic process that involves constant analysis of actual and planned performance.
4. Controlling is both a backward looking as well as forward looking function: Under controlling past performance is analysed, therefore controlling is backward looking. On the basis of this past performance analysis, remedial action is taken to make future performance better, in this way controlling is forward looking.
5. Controlling is a dynamic process: Since controlling requires taking reviewable methods, changes have to be made wherever possible.
Importance of Controlling
1. Controlling helps in achieving organizational goals: The controlling function measures progress towards the organizational goals and brings to light/indicates corrective action.
2. For Evaluating/Judging accuracy of standards: A good control system enables management to verify whether the standards set are accurate or not by careful check on the changes taking place in the organizational environment.
3. Making efficient use of resources: By the process of control, a manager seeks to reduce wastage of resources.
4. Improves employee’s motivation: A good control system ensures that employees know well in advance what they are expected to do & also the standard of performance. It thus motivates & helps them to give better performance.
5. Facilitating Coordination in action: In controlling each department and employee is governed by predetermined standards which are well coordinated with one another. Control provides unity of direction.
6. Ensuring order and discipline: Controlling creates an atmosphere of order and discipline in the organization by keeping a close check on the activities of its employees.
Controlling Process
1. Setting Performance Standards: Standards are the criteria against which actual performance would be measured. Thus standards become basis for comparison and the manager insists on following of standards.
Standards can be set in both quantitative as well as qualitative terms. Is is important that standards should be flexible enough to be modified whenever required. Standards should be SMART as:
S – Simply Expressed M – Measurable
A – Attainable
R – Reasonable T – Time bounded
2. Measurement of Actual Performance: Performance should be measured in an objective and reliable manner which includes personal observation, sample checking. Performance should be measured in same terms in which standards have been established, this will facilitate comparison.
3. Comparing Actual Performance with Standard: This step involves comparison of actual performance with the standard. Such comparison will reveal the deviation between actual and desired performance. If the performance matches the standards it may be assumed that everything is under control.
4. Analysing Deviations: The deviations from the standards are assessed and analysed to identify the causes of deviations.
Deviations are analysed in the light of pre-determined deviation tolerance limit and key result areas.
a) Critical point control (CPC): It is neither economical nor easy to have a check on all the activities of an organisation. Hence, the manager should pay more attention on those activities which are important and critical to the success of an organisation. These are known as Key Result Areas- KRA’s.
Example: 2% increase in stationery cost is not critical. But 2% increase in wages Salaries is critical.
b) Management by Exception (MBE): A manager should take corrective action only when there is exceptional deviation i.e. when they cross the permissible limit or acceptable range. Deviations within acceptable range are ignored.
Example: Wastage within Normal Wastage Range may be ignored. But if wastage crosses this limit and becomes Abnormal then management should control.
5. Taking Corrective Action: The final step in the controlling process is taking corrective action. No corrective action is required when the deviations are within the acceptable limits. But where significant deviations occur corrective action is taken.
Limitations of Controlling
1. Little control on external factors: Generally no enterprise can control external factors such as government policies, technological changes, competitions etc.
2. Resistance from employees: Control is often resisted by employees. They see it as a restriction on their freedom e.g. Employees may resist and go against the use of cameras to observe them minutely.
3. Costly affair: Control is a costly affair as it involves a lot of expenditure of time and efforts.
4. Difficulty in setting quantitative standards: Control system looses some of its effectiveness, when standards cannot be defined in quantitative terms. In the absence of quantitative standards, comparison with standards becomes difficult.
MCQs for NCERT Class 12 Business Studies Controlling
Question. Which function of managment bring back the manangement cycle back to the planning function.
(a) Directing
(b) Organising
(c) Controlling
(d) Staffing
Answer : C
Question. A good control system helpls an organisatioin to.
(a) Accomplishes organisational gools.
(b) Judges accuracy of standerds.
(c) Ensure order and discipline
(d) All of the above.
Answer : D
Question. Under which step of controlling process certain pieces are checked at random for quality as sample checking.
(a) Measurement of actual performance
(b) Comparing actual performance with standards
(c) Analysing Deviations
(d) Taking corrective action.
Answer : A
Question. The plans lay down 2% increase in labour cost as an acceptable range of deviation in a manufacturing organisation, only increase in labour cost beyond 2% Should be brought to the notice of the management.
Which method of controlling deviations is mentional above.
(a) Budgetary control
(b) Critical point control
(c) Management by exception
(d) Inventory control.
Answer : C
Question. “Employees might object when they are kept under a strict watch with the help of CCTVS.” Which Limitation of controlling is indicated here’
(a) Control through CCTVS is as costly affair
(b) Organisation have little control on external factors.
(c) Selection of CCTVS instalation points is difficult and time consuming.
(d) Resistance from employees.
Answer : D
Question. In case the deviation cannot be corrected through managerial action, what should be done.
(a) Standards may have to be revised.
(b) Control through CCTVS should be ensured
(c) Existing controlling process should be changed/modified
(d) Sample checking should be done.
Answer : A
Question. In a manufacturing organisation an increase of 5% in the labour cost may be more troublesome than a 15% increase in postal charges.
Which method of controlling Deviations is mentioned in above example
(a) Budgetary control
(b) Management by exception
(c) Critical point control
(d) Inventory control
Answer : C
Question. “Controlling improves future planning by providing information derived from past experience. “This, controlling function of an organisation based on given feature is
(a) Forward looking
(b) Backward looking
(c) Forward as well as backward looking
(d) None of the above.
Answer : C
Question. Identify the basis of controlling that are provided by planning.
(a) Actual performance
(b) Key Result areas
(c) order and discipline
(d) Standard performance
Answer : D
Question. Which function of management not only helps in keeping a track on the progress of activities but also ensures that activities conform to the standards set in advance.
(a) Planning
(b) Directing
(c) organising
(d) controlling
Answer : D
True/False
Giving reason in support of your answer, state whether the following are True or False.
Question. Critical point control is an important principle of managment control based on the belief that an attempt to control everything results in controlling nothing.
Answer: False
Question. Sometime situation may arise when deviation cannot be corrected through managerial action then in such situations the standards may have to be revised.
Answer: True
Question. Controlling process is evaluative in nature as it checks whether decisions have been translated into desired action.
Answer: True
Question. Planning and controlling reinforce each other as planning improves future by providing information derived from past experiences while controlling based on facts makes planning easier.
Answer: False
Question. Once a plan becomes operational, controlling is not neccessary as events will conform to plans automatically.
Answer: False
Very Short Answer type Chapter Controlling Class 12 Business Studies
Question. Which function of management ensures that actual activities confirm to planed activities?
OR
Name the function which reviews the operations in a business unit.
Answer: Controlling
Question. There are two managers rahim and pankaj. Rahim is saying that ‘controlling is forward looking’ whereas according to pankaj ‘controlling is looking back’ . Who is correct? Explain why.
Answer: Both managers rahim and pankaj are correct and explain controlling as forward looking and looking back.
Question. Employees know well in advance what they are expected to do and what are the standards of performance on the basis of which they will be appraised, which in turn help them to give better performance. Which importance of controlling is highlighted here?
Answer: Improves employees motivation.
Question. Which function of management ensures work accomplishment according to plans? Name and explain the importance of the function.
Answer: Controlling is the function of management which ensures work accomplishment according to plans? And explain the importance of the controlling.
Question. Controlling provides direction to all activities and efforts for achieving organizational goals. Which importance of controlling is referred here? Also explain two more of its importance.
Answer: Facilitating coordination in action. Explain two more importance of controlling.
Question. “There is close and reciprocal relationship between planning and controlling”. Explain the statement through an example.
Answer: Yes, “there is close and reciprocal relationship between planning and controlling”. Without planning, there is no basis for controlling activities and without controlling planned activities cannot be implemented properly and there cannot be improvement in future plans.
Question. “Controlling is a systematic process involving a series of steps.
Answer: “Explain the process/steps of controlling.
Question. Name the concept which suggests that only significant deviations which go beyond the permissible limit should brought to the notice of management
Answer:Management by exception.
Question. Which technique of control is concerned with the contribution of actual and planed expenditure.
Answer: Budgetary control
Question. “In ideal control system is the one that checks every bit of performance”. Do you agree with this statement? Give reasons to support your answer.
Answer: No, I do not agree with this statement. Because a manager should focus on key points only and should not waste his energy in checking every bit.
Question. Abc ltd. Is manufacturing auto spare parts on large scale. The company policy is that 3% of the daily production could be defective. answer last two months it is observed that about 10-12% of production is defective. Which function of management is reinsured to correct the above case? State the procedure to be followed to correct the things.
Answer: The management function reinsured to correct the above case is controlling. The procedure to be followed is:
1) Find out the causes of deviation of defective percentage from 3 to 12.
2) Take corrective measure to control the things.
Question. “Comparing the actual performance with the laid standards, finding out the deviations and taking corrective action is an important function of a function of management”. Name the function and explain the process.
Answer: Name of the function is controlling and explain the process of controlling.
Question. What is feedback in controlling ?
Answer: Report of happening.
Question. What is the significance of standard ?
Answer: Helpful in analyzing deviation.
Question. What is deviation in controlling ?
Answer: Differences between actual performance and standard performance.
Question. Which two steps in the process of control are concerned with compelling events to conform to plan ?
Answer: Analysing deviations and taking corrective actions.
Question. What is compared with that in controlling ?
Answer: Actual performance is compared with standard.
Question. What is the last step in the process of controlling ?
Answer: Taking corrective action.
Question. What is meant by budgetary control ?
Answer: Budgetary control is a technique of managerial control in which all operations are planned in advance in the forms of budgets and actual results are compared with budgetary standards.
Question. Name the two techniques of analysing deviations ?
Answer: Critical point control and management by exception.
Question. How does controlling help in achieving organizational goals ?
Answer: Controlling helps in achieving organizational goals by correcting unfavorable deviations between actual performance and standard performance.
Question. How does controlling help in efficient utilisation of resources ?
Answer: By exercising control, a manager seeks to reduce wastage and spoilage of resources. This helps in effective and efficient utilisation of resources.
Question. How does controlling helps in ensuring order and discipline ?
Answer: Dishonest behaviour on the part of the employees is minimized by keeping a close check on their activities.
Question. Why is controlling called a backward looking function ?
Answer: Controlling finds out the deviations from the standards in that sense controlling is a backward looking function.
Question. What is critical point control ?
Answer: Key areas that are critical for the success of an organization should be the focus of control.
Question. What do you mean by ‘key result area (KRA’s) in the context of controlling ?
Answer: KRAs are the critical points which are critical to the success of an organisation.
Question. Only increase in labour cost beyond 2% should be brought to the notice of the management. Which principle of control have been highlighted by this statement ?
Answer: Control by Exception.
Short Answer Type Questions Chapter Controlling Class 12 Business Studies
Question. “Controlling is blind without Planning’ Comment.
Answer: “Controlling is blind without Planning”- Under the system of control actual performance is compared with budgetd standards to judge the effectiveness of performance. These standards are provided by planning. In the absence of standards there will be no justification left for control. Therefore it is correct to say that controlling is blind without planning.
Question. “Controlling is the last function of management”. Comment.
Answer: “Controlling is the last function of management” Comment controlling should not be mis-understood as the last function of management. The controlling functions measures actual performance against standards, finds out the deviations analyses the causes of such deviations and takes corrective actions. This process helps in formulation of future plans in the light of the past problems. Thus controlling only completes one cycle of management process and improves in the next cycle.
Question. ‘If you try to control everything, you may end up controlling nothing”. Explain.
Answer: According to the principle of ‘control by Exception” if you try to control everything, you may end up controlling nothing. Minor deviations from standards are insignificant for success. They can be ignored.
Therefore only significant deviations, which go beyond the permissible limits, should be reported to the management so that management may take corrective action to deal with the situations.
Question. “Planning is looking ahead and controlling is looking back”. Comment.
Answer: It is often said that — planning is looking ahead while controlling is looking back” However, this statement is only partially correct — Planning is deciding in the present what to do in the future, thus it is looking
ahead and it is toward looking function.
Controlling is like a past-mortem of the post activities to find out the deviations from the planned standard. Thus is a backward looking function. However future planning is guided by the past experience and corrective action initiated by controlling functions. Thus planning and controlling are both backward looking as well as forward looking function.
Question. What is ‘critical point control’ ?
Answer: A since it is neither easy nor economical to check each and every activity in an organistion, the control should focus on key result areas (KRAs). These KRAs are very essential activities for the success of organisation and act as critical point. If anything goes wrong to these critical point, the entire organisation suffers.
For Example— Increase in material cost by 10% is more harmful than 20% increase in stationery expenses. So management should focus the controlling these KRA or critical point.
This concept of also known as Management by exception.
Question. “Controlling doesn’t require any process”. Comment.
Answer: The given statement – “Control does not require any process” is not correct.
Process of management control involves the following steps.
Setting performance Standard : Standards are required to judge whether the actual performance is proceeding in the right way. Standards must be in numerical or measurable terms.
Measurement of Actual performance : Actual performance is evaluated and expressed in terms of planned standards.
Comparing Actual performance with standards : Actual performance is compared with the planned performance and deviations if any found out.
Analysing the deviations : In order to know the causes of deviations, and in order to take corrective actions, deviations are analysed.
Taking corrective Actions : If the deviations exceed the acceptable limits they should be immediately brought to the notice of management for taking corrective measures. Thus it is clear that controlling requires systematic process
Question. “An ideal control technique is one that check every bit of performance” comment.
Answer: The given statement-"A ideal technique is one that checks every bit of performance” is wrong. An ideal control technique should focus on ‘key result areas (KRAs)— It is neither economical nor easy to keep a check on each and every activity in an organisation. There may be several activities to be controlled. In practice it is not possible for management to control each and every activity due to limited time & resources.
Therefore controlling should focus on KRAs which are critical to the success of an organization. The KRAs are set as the critical point. If anything goes wrong at the critical point, the entire organization suffers. So controlling should focus on these very important activities or KRAs
Long Answer Type Questions Chapter Controlling Class 12 Business Studies
Question. Explain ‘Budgetary control’ as a technique of managerial controlling.
Answer: Budgetary control is a technique of managerial control under which different operations of an organisation are planned in advance in the form of budgets viz sales budget, cash budget, material budget, production budget etc. These budgets act as standards for comparing with the actual performance and taking necessary corrective action if need be, for attaining organizational goals
Advantages of budgetary control :—
(i) Helps in attaining targets — It helps in attaining organisational objectives by focusing on specific and time bound targets.
(ii) Optimum utilization of resources — It ensures the optimum utilisation of resources by allocating them among different departments according to their requirement.
(iii) Helps in coordination — It helps in achieving co-ordination among different departments.
(iv) Facilitates the management by exception — By stressing on the operations which deviate from the budgeted standards it helps the management to control by exceptions. However, the effectiveness of budgeting depends on how accurately estimates have been made about future.
Question. Y Ltd. Produces safety pins on a mass scale. The co.’s policy is that at the most 2% of the daily production could be defective over a three months period it has been observed that 8-10% of the production is defective. Identify the managerial function required to correct the above situation. Briefly explain the procedure to be followed for the purpose.
Answer: Here the actual deviations are more than planned acceptable deviations, so the management need to take corrective action to rectify the problems. The function of comparing actual performance with planned performance and taking corrective
action is called ‘controlling’—
The steps involved in the process of controlling are —
(i) Setting Performance Standard.
(ii) Measurement of Actual Performance.
(iii) Comparing Actual Performance with Standards.
(iv) Analysing Deviations.
(v) Taking Corrective Action and re setting the performance standard.
Question. Y Ltd. Produces safety pins on a mass scale. The company’s policy is that at the most 2% of the daily production could be defective. Over a three months period, it has been observed that 8-10% of the production is defective.
Identify the management function required to correct the above situation.
Briefly state the procedure to be followed for the purpose.
Answer: The management function required to correct the above situation is known as ‘controlling’.
Procedure to be followed for improving the quality of production :
• Find out the causes of deviations.
• Take appropriate corrective actions.
Question. X Ltd. is engaged in manufacturing machine components. The target production is 200 units per day. The company had been successfully attaining this target until two months ago. Over the last two months, it has been observed that daily production varies b/w 150 & 170 units.
Identify the management function to rectify the above situation. Briefly state the procedure to be followed so that the actual production may come up to the target production.
Answer:‘Controlling’ is the management function to rectify the above situation.
Procedure to be followed to increase the level of production
(i) Find out the causes of deviation
(ii) Take appropriate corrective action.
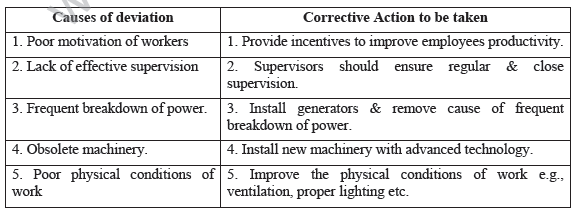
Question. “Control does not require any process”. Comment.
Answer: The given statement—“Control does not require any process”. Process of management control involves the following steps.
(i) Setting performance standards : Standards are targets against which actual performance can be measured and deviations can be found.
(ii) Measurement of actual performance : This step involves actual performance of various individuals and groups for comparing it with the standards.
(iii) Comparing actual performance with standards : After measuring the performance, the next step is to compare actual performance with the standard performance.
(iv) Analysing deviation : Control technique should focus on the key result areas only which are critical to the success of an organization.
(v) Taking corrective measures : No corrective action is required when the deviations are within the acceptable limits.
Question. Explain to a newly appointed foreman, under whose supervision school bags are being made, how he has to carry out process of control ?
Answer: The foreman should take following steps :
(i) Setting performance standards : Standards are targets against which actual performance can be measured and deviations can be found.
(ii) Measurement of actual performance : This step involves measuring actual performance of various individuals and groups for comparing it with the standards. There are several techniques for measurement of performance personal observation, sample checking, performance reports etc.
(iii) Comparing actual performance with standards : After measuring the performance, the next step is to compare actual performance with standard performance. Such comparison will reveal the deviation between actual and desired
results.
(iv) Analysing deviations : If the deviations are within reasonable limits they may be ignored. Only significant deviations from the standards should be reported to the management.
(v) Taking corrective actions : No corrective action is required when the deviations are within the acceptable limits.
Question. “An ideal control technique is one that checks every bit of performance”. Comment.
Answer: The given statement- “An ideal control technique is one that checks every bit of performance is wrong. An ideal control technique should focus on the key areas.
(i) Critical point control : There are several activities’ to be controlled. In practice, it is not possible for management to control each and every activity due to limited time.
(ii) Control by exception/management by exception : An attempt to control everything may end up by controlling nothing.
(iii) Advantages of critical point control and Management by exception : It identifies the critical problems which need timely action. The routine problems are left to the subordinate. It saves time and efforts of managers.
(iv) “Feedback” in controlling : Without the availability of feedback no action can be taken by the managers. Manager have to review the standards improve the quality of materials.
(v) “Deviation” in controlling : Deviation means the difference between actual performance and standard performance. Once the nature and magnitude to deviations are ascertained, the causes of deviations should be identified.
Question. There are two managers Rahim and Pankaj. Rahim is saying that controlling is forward looking where as according to Pankaj controlling is looking back Who correct ? Explain why ?
Answer: Both Rahim & Pankaj are partially correct. Controlling is bath backward looking as well as forward looking.
(i) Controlling is blind with out planning if the standards are not set in advance, managers have nothing to control.
(ii) Planning with out controlling in meaningless because once a plan becomes operational, controlling is necessary to monitor the progress Planning is looking ahead while controlling is looking back.
(iii) Plans are prepared for future to achieve the organizational goals. Planning is deciding in the present what to do in the future. Planning involves looking ahead and is called forward looking function.
(iv) Controlling is the process through which managers ensure that actual performance in according to planned standards. Controlling is finding out deviations from past. In this manner controlling is a backward looking function.
Question. If planning is done carefully and accordingly other functions of management are going in the right direction, then there is no need of the controlling functions of management’. Do you agree with the statement. Give reasons in support of your answer ?
Answer: No, I don’t agree with the given statement. Controlling is an indispensable function of Management Importance of Controlling.
(i) Controlling helps in achieving organizational goals Management is setting organizational goals and establishing a procedure to achieve them performance may or may not necessarily according to plans.
(ii) Controlling helps in judging accuracy of standards An efficient control system enables management to verify whether the standards set are accurate.
(iii)Controlling helps in making efficient use of resources : By exercising, a manager seeks to reduce wastage and spoilage of resources. This ensures effective and efficient utilization of resources.
(iv) Helps in motivating employees Good control system ensures to decide in advance what to do and how to do and on the basis of this their performance is evaluated.
(v) Facilitates Coordination Coordination provides direction to all activities and efforts for achieving goals.
(vi) Ensures order and discipline Controlling creates an atmosphere of order and discipline in the organization Helps to minimize dishonesty
Very Short Answer type Chapter Controlling Class 12 Business Studies
Question. Name the two techniques of Controlling.
Answer: PERT and CPM
Question. What is ‘deviation’ in Controlling Process ?
Answer: The difference between actual performances and planned performance.
Question. Name any one type of budget.
Answer: Sales Budget.
Question. How does controlling help in achieving organizational goals ?
Answer: It compares standards with actual performance, finds deviations and takes corrective action to achieve goals.
Question. How does controlling help in ensuring order and discipline ?
Answer: Dishonest behaviour on the part of the employees is minimized by keeping a close check on their activities.
Question. What is MBE ?
Answer: Management of Exceptions.
Question. Define Standard.
Answer: The criteria against which the actual performance is measured are known as standard.
Question. Why controlling is called backward looking function ?
Answer: As it involves comparing the actual performance with the planned standards which have been set in past.
Question. Name the first step in Controlling Process.
Answer: Setting up of Standards.
Question. What is Managerial Control ?
Answer: Managerial controlling is a process of setting up standards, comparing the actual performance, finding deviations and taking corrective actions.
Question. What is Feedback in Controlling ?
Answer: Report of happening.
Question. What is CPM ?
Answer: Key areas that are critical for the success of an organization should be The focus of control.
Question. What is meant by Budgetary Control ?
Answer: Budgetary control is a technique of control in which all operations are planned in advance in the form of budgets.
Question. What is the basis of Controlling Process ?
Answer: Planning is the base of controlling process.
Question. Give one corrective measure to improve the motivation level of workers.
Answer: Introduce incentives for less rate of defectives.
Short Answer Type Questions Chapter Controlling Class 12 Business Studies
Question. State any four objectives of Controlling.
Answer: Four objectives of controlling are as under :
(i) To seek planned results from subordinates.
(ii) To evaluate the progress of the work.
(iii) To detect deviations from the planned activities.
(iv) To find the causes of deviation
Question. State any three points of importance of Controlling.
Answer: Importance of controlling is as under :
(i) It helps to accomplish organizational goals.
(ii) It helps in maximum utilization of available resources at minimum cost.
(iii) Systematic evaluation of performance and consequent rewards motivate employees to put in their best efforts.
Question. How does controlling help in financial matters ?
Answer: Through controlling, managers keep tight control over finance and spend well within the budget. To access different aspects of the organizations financial position and for optimum utilization of various resources of finance, managers take recourse to financial controls. They use modern techniques for controlling such as ratio analysis, cash flow statements. etc.
Question. “Planning is meaningless without controlling.” Explain.
Answer: Planning can be successful only in the presence of control. Under the process of planning, future activities are decided beforehand. Standards are stated and determined to achieve business objectives. But to ascertain the extent to which such activities and standards have been successfully implemented and achieved, the implementation of an appropriate control system is required. Therefore, it is correct to say that planning is meaningless without control.
Question. Controlling is blind without planning.
Answer: Under the system of control, actual performance is compared with budgeted standards to judge the effectiveness of performance. These standards are provided by planning. In the absence of standards, there will be no
justification left for control. Also, planning is required to correct the deviation identified in the process of control.
Thus, without planning, controlling is blind.
Question. Explain MBE.
Answer: It implies that manager must focus attention only on factors critical to performance. Normal factors or deviation should be ignored as they can be corrected at lower levels. It is based on the maxim – “and attempt to control
everything results in nothing. Based, on this, only major deviations from standards should be reported to top-level management and other routine problems should be looked into by the subordinates.
For example, if a plan allows 5 percent decrease in the output as acceptable range of deviation then only such decrease in output should be reported to the management as 1’s well beyond 5 percent
Question. Explain the benefits of MBE.
Answer: Benefits of management by exception are as under :
(i) It saves the valuable time of the management.
(ii) It helps the management to identify important deviations which need timely action to keep the organization on the correct path.
(iii) It facilitates delegation of authority and helps in increasing morale of employees.
(iv) It helps the management to concentration on important matters beneficial for the long-term profitability of the organization.t.
Question. Define management controlling. Explain the various steps involved in controlling process.
Answer: Managerial control implies the measurement of accomplishment against the standard and the correction of deviation to assure attainment of objectives according to plans.
Steps :
* Establishment of Standards : The first step in control process is setting up of standards of performance. Standards are the criteria of performance and specify what should be accomplished. It is therefore, necessary that standards should be sat and stated in measurable terms.
* Measurement of Performance : The second step in controlling is measurement of performance. It means evaluation of work actually done and result achieved. Measurement is Most useful if actual performance is expressed in the same unit as the planned targets or standards comparison of actual and planned performance then becomes easier.
* Comparison of actual performance with standards and analysing deviation : Comparisons of actual performance with the planned target or standard involves two
steps :
(a) finding the extent of deviation
(b) identifying the causes of such deviations.
* If performance falls short of standards, managers must find out the extent of deviation generally, minor deviations do not require managerial attention. To save time, managers concentrate on major deviations only.
* Taking corrective action : The purpose of control is not only to detect errors and defects in performance of work but also to adopt remedial measures. Corrective actions are therefore, initiated on the basis of factors causing deviations between standards and actual results.
* Corrective action may involve a change in methods, machinery rules or procedure, improving physical conditions of work, or changing the nature of supervision may also be necessary at times. Where the deviations cannot be rectified through managerial action, the standards may have to be revised.
Long Answer Type Questions Chapter Controlling Class 12 Business Studies
Question. ‘If planning is done carefully and accordingly other functions of management are going in right direction then there is no need of the controlling function of management.’ Do you agree with the statement ? Justify your answer.
Answer: Importance of Controlling :
8.4 Importance of Controlling
Controlling is an indispensable function of management. Just as road signals are essential to ensure accident-free and smooth traffic, managerial controlling is necessary for the smooth running of business.
“Control is the soul of business management.” A good control system helps an organization in the following ways :
1. Controlling helps in achieving organizational goals : The first steps in management is setting organizational goals and establishing a procedure to achieve them. The objective may be in terms of a target profit, target sales or target production. However, actual performance may or may not necessarily be according to plan. If deviation are detected early, remedial action can be taken and the desired target is ultimately achieved. This will only happen if there is a control mechanism which detects and corrects deviations between actual and desired results.
2. Controlling helps in judging accuracy of standards : An efficient control system enables management to verify whether the standards set are accurate and objective by keeping a careful check on the changes taking place in the organization and in the environment.
3. Controlling helps in making efficient use of resources : By exercising control, a manager seeks to reduce wastage and spoilage of resources. Each activity is performed in accordance with predetermined standards. This ensures effective and efficient utilization of resources.
4. Controlling helps in improving employees motivation : A good control system ensures that employees know well in advance what they are expected to do and what are the standards of performance on the basis of which their performance will be evaluated. It, thus, motivates them and helps them to give better performance.
5. Controlling ensures order and discipline : Controlling creates an atmosphere of order and discipline in the organization. It helps to minimize dishonest behaviour on the part of employees by keeping a close check on their activities.
6. Controlling facilitates coordination in action : Controlling provides direction to all activities and efforts for achieving organizational goals. Each department and employee is governed by predetermined standards which are well coordinated with one another. This helps is accomplishing the overall organizational objectives
Question. How are planning and controlling interdependent and inter-linked ?
Answer: The given statement is wrong. Controlling is an indispensable function of management. Rest is same to answer 3 in above.
Question. Taking corrective action is the last step in the process of management (a) Name the function (b) Explain the steps involved in this process.
Answer: Planning and controlling are interrelated and interdependent as follows :
(i) Planning is the basis for controlling Planning is the basis for controlling too. In the absence of plans it is not possible to measure and assess performance. For example, if the output is 500 units, the manager can know whether it is adequate or not only when there is a standard output set up by the planners. Thus, planning provides the base for comparison of actual performance with the budget performance.
(ii) Controlling helps in planning : Without effective controlling, activities can not be properly planned. Planning is guided by past experiences and corrective measures suggested by controlling.
(iii) Effective controlling helps in formulation of future plans Controlling helps in revising plans to reap maximum benefits at minimum cost. Controlling ensures improvement in future performance.
(iv) Finding out deviations and cause there of effectiveness of planning can be measured with the help of controlling. Planning is based on fore cast about future conditions. Controlling sets standards and finds out deviations from
standards. After that corrective actions are to be taken by controlling function.

