CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology Principles and Processes VBQs read and download in pdf. Value Based Questions come in exams for Biology in Class 12 and are easy to learn and helpful in scoring good marks. You can refer to more chapter wise VBQs for Class 12 Biology and also get latest topic wise very useful study material as per latest NCERT book for Class 12 Biology and all other subjects for free on Studiestoday designed as per latest Class 12 CBSE, NCERT and KVS syllabus and examination pattern
VBQ for Class 12 Biology Chapter 09 Biotechnology Principles and Processes
Class 12 Biology students should refer to the following value based questions with answers for Chapter 09 Biotechnology Principles and Processes in Class 12. These VBQ questions with answers for Class 12 Biology will come in exams and help you to score good marks
Chapter 09 Biotechnology Principles and Processes VBQ Questions Class 12 Biology with Answers
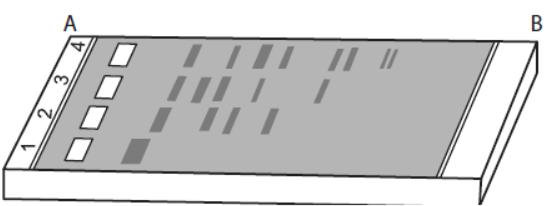
Question. Study the given figure carefully and select the correct statements regarding this. (Image 125)
I. It represents typical agarose gel electrophoresis showing differential migration ofDNAfragments.
II. Lane 1 contains undigestedDNAfragments.
III. Lanes 2 to 4contain digestedDNAfragment.
IV. SmallestDNAbands are present atAposition and largestDNAbands are present atBposition.
(a) I, II and III
(b) I, II and IV
(c) II and III
(d) III and IV
Answer : A
Question. Read the statements about gene gun method.
I. This method is also known as biolistic technique.
II. In this method, cells are bombarded with high velocity microparticles of gold or tungsten coated withDNAin plants.
III. Important crop plants like maize, rice and wheat have now been transformed by this method.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) I and II
(b) I and III
(c) II and III
(d) I, II and III
Answer : D
Question. Identify the correct statements.
I. The first recombinantDNAwas constructed by using a piece of DNAfrom plasmid carrying antibioticresistance gene in the bacterium Salmonella typhimurium and linked it to the plasmid of E. coli.
II. When cut by the same restriction enzyme, the resultant DNAfragments have the same kind of sticky ends and these can be joined together usingDNAligases.
III. The presence of more than one recognition sites within the vector will generate several fragments, which will complicate the gene cloning.
(a) I, II and III
(b) I and II
(c) Only I
(d) II and III
Answer : A
Question. Read the statements.
I. In the process of recombinantDNAtechnology, after several treatment the purifiedDNAis precipitated by adding chilled acetone.
II. The bacterial/plant, animal cell is broken down by enzymes to releaseDNA, along with RNA, proteins, polysaccharides and lipids.
Choose the correct option for above statements.
(a) I is true, but II is false
(b) I is false, but II is true
(c) I and II are true
(d) I and II are false
Answer : B
Question. Which of the following statements are correct with respect to a bioreactor?
I. It can process small volume of culture.
II. It provides optimum temperature, pH, salt, vitamins and oxygen.
III. Sparged stirred-tank bioreactor is a stirred type reactor in which air is bubbled.
Choose the correct option.
(a) I and II
(b) I and III
(c) II and III
(d) I, II and III
Answer : C
Question. Consider the following statements.
I. Bioreactors are vessels of large volumes in which raw materials are biologically converted into specific products.
II. One of the most commonlyused bioreactor is of stirring type.
III. Shake flasks are used for growing andmixing the desiredmaterials on a small scale in the laboratory.
IV. Alarge scale production of desired biotechnological product is done by using ‘bioreactors’.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) I and II
(b) I and III
(c) I, II and III
(d) I, II, III and IV
Answer : D
Question. Which statement is correct?
I. The downstream processing and quality control testing vary from product to product.
II. In bioreactors, raw materials are biologically converted into specific products.
III. Large amount of recombinant protein can be produced by gene cloning.
IV. pBR322 vector was constructed by usingDNA derived from naturally occurring plasmids of E. coli.
(a) I, II and III
(b) Only IV
(c) II, III and IV
(d) All of these
Answer : D
Question. Which statement is incorrect ?
I. Retroviruses have also been disarmed and are now
used to deliver desirable genes into animals cells.
II. Downstream processing is one of the steps ofR-DNA technology.
III. DNAis a negatively charged molecule.
IV. The presence of chromogenic substrate gives blue colour colonies, if the plasmid in the bacteria does not have an insert.
(a) I and II
(b) I, III and IV
(c) All of these
(d) None of these
Answer : D
Question. For selectable marker.
I. It helps to select the host cells which contain the vector and eliminate the non-transformants.
II. Genes encoding resistance to antibiotics like ampicillin, chloramphenicol, tetracycline or kanamycin, are useful selectablemarkers forE.coli.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) Only I
(b) Only II
(c) I and II
(d) None of these
Answer : C
Question. I. DNAbeing a hydrophilic molecule cannot pass through cell membranes.
II. The bacteria should be made competent to accept the DNAmolecule.
The correct option regarding the above statements is
(a) I is true, but II is false
(b) II is true, but I is false
(c) I and II are true
(d) I and II are false
Answer : C
Question. Why foreign DNA cannot pass through cell membrane?
(a) DNA is hydrophobic
(b) DNA is hydrophilic
(c) DNA is rich in proteins
(d) DNA is heavy
Answer : B
Question. The treatment of host cell with divalent cation leads to the
(a) change in permeability of DNA
(b) increased efficiency with which DNA enters the bacterium
(c) decreased efficiency with which DNA enters the bacterium
(d) change in permeability of host
Answer : B
Question. Which vector can clone only a small fragment of DNA?
(a) Bacterial artificial chromosome
(b) Yeast artificial chromosome
(c) Plasmid
(d) Cosmid
Answer : C
Question. The DNA used as a carrier for transferring a fragment of foreign DNA into a suitable host is called
(a) cloning vector
(b) vehicle DNA
(c) gene carrier
(d) All of these
Answer : D
Question. Which of the following is a plasmid vector?
(a) pBR322
(b) Bam II
(c) SaI I
(d) Eco RI
Answer : A
Question. The method which is used to introduce recombinant DNA into animal cell?
(a) Gene gun method
(b) Changing permeability of host
(c) Biolistic method
(d) Microinjection
Answer : D
Question. Which of the following methods(s) is used to introduce foreign DNA into plant host cells?
(a) Gene gun method
(b) Gel electrophoresis
(c) Elution
(d) Extension
Answer : A
Question. For transformation, microparticles coated with DNA to be bombarded with gene gun are made up of
(a) silver or platinum
(b) platinum or zinc
(c) silicon or platinum
(d) gold or tungsten
Answer : D
Question. DNA transfer with high velocity micro particles is present in
(a) biolistics
(b) hybridisation
(c) tissue culture
(d) vegetative propagation
Answer : A
Question. The different steps involved in the process of recombinant DNA technology are given below randomly? Arrange these in correct order.
I. Extraction of the desired gene product.
II. Amplification of the gene of interest.
III. Isolation of a desiredDNAfragment.
IV. Ligation of theDNAfragment into a vector.
V. Insertion of recombinantDNAinto the host.
Correct order is
(a) I, II, III, IV and V
(b) III, II, IV, V and I
(c) II, IV, V, III and I
(d) I, IV, V, III and II
Answer : B
Question. In bacterial cells, the membrane is digested with the help of enzyme
(a) cellulase
(b) lysozyme
(c) chitinase
(d) lipase
Answer : B
Question. Primers are
(a) small chemically synthesised oligonucleotides of about 10-18 nucleotides that are complementary to the region of template DNA
(b) chemically synthesised oligonucleotides of about 10-18 nucleotides that are not complementary to the region of template DNA
(c) the double-stranded DNA that need to be amplified
(d) specific sequences present on recombinant DNA
Answer : A
Question. The Taq polymerase enzyme is obtained from
(a) Thiobacillus ferroxidans
(b) Bacillus subtilis
(c) Pseudomonas subtilis
(d) Thermus aquaticus
Answer : D
Question. A single PCR amplification cycle involves
(a) denaturation
(b) extension
(c) annealing
(d) All of these
Answer : D
Question. In gel electrophoresis, restriction enzyme digested DNA is loaded in wells near
(a) anode
(b) cathode
(c) centre of gel
(d) any where in the gel
Answer : B
Question. Stirred-tank bioreactors are advantageous over shake flasks because they
(a) provide high temperature and pH
(b) provide better aeration and mixing properties
(c) do not allow the entry of CO2
(d) are easy to operate
Answer : B
Question. Simple stirred-tank bioreactor is given below. Identify
A, B, C, D and E. (Image 100)
Answer : A
Question. The components of a bioreactor are
I. an agitator system.
II. an oxygen delivery system.
III. foam control system.
IV. temperature control system.
V. pH control system.
VI. sampling ports towithdrawcultures periodically.
Choose the correct option.
(a) I, II, III, IV and V
(b) II, IV, V and VI
(c) I, II, III, IV and VI
(d) All of these
Answer : D
Question. The process of separation and purification of expressed protein before marketing is called
(a) upstream processing
(b) downstream processing
(c) bioprocessing
(d) post-production processing
Answer : B
Question. Which of the following is not a component of downstream processing?
(a) Separation
(b) Purification
(c) Preservation
(d) Expression
Answer : D
I. Assertion and Reason
In each of the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is given followed by corresponding statement of Reason (R). Of the statements, mark the correct answer as
(a) If both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) If both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) If A is true, but R is false
(d) If A is false, but R is true
Question. Assertion (A) Biotechnology deals with techniques that use living organism to produce products useful for humans.
Reason (R) It uses only a unicellular organism.
Answer : C
Question. Assertion (A) Maintenance of sterile environment is essential for manufacture of biotechnological products.
Reason (R) This is to enable growth of desired prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells.
Answer : A
Question. Assertion (A) Origin of replication is an essential part of a vector.
Reason (R) Ori is responsible for initiating replication.
Answer : A
Question. Assertion (A) Foreign DNA and vector DNA cut with the help of ligase.
Reason (R) Ligase acts by forming phosphodiester bonds.
Answer : D
Question. Assertion (A) In gel electrophoresis, DNA fragments are separated.
Reason (R) DNA is negatively charged, so it moves towards anode under electric field.
Answer : A
Question. Assertion (A) Restriction endonucleases are also called ‘molecular scissors’.
Reason (R) When fragments generated by restriction endonucleases are mixed, they join together due to their sticky ends.
Answer : B
Question. Assertion (A) All endonucleases cut DNA at specific sites.
Reason (R) Endonucleases were discovered from viruses.
Answer : C
Question. Assertion (A) The tumour inducing plasmid (Ti plasmid) of Agrobacterium tumefaciens acts as a cloning vector in recombinant DNA technology.
Reason (R) The Ti plasmid which is used in the mechanisms of delivering genes to a cell remains pathogenic.
Answer : C
Question. Assertion (A) Use of chitinase enzyme is necessary for isolation of DNA from fungal cells.
Reason (R) Fungal cell wall is made up of chitin and chitinase is able to digest it.
Answer : A
Statement Based Questions
Question. Which one is a true statement regarding DNA polymerase used in PCR?
(a) It is used to ligate introduced DNA in recipient cells
(b) It serves as a selectable marker
(c) It is isolated from a virus
(d) It remains active at high temperature
Answer : D
Question. Following statements describe the characteristics of the enzyme restriction endonulease. Identify the incorrect statement. NEET 2019
(a) The enzyme binds DNA at specific sites and cuts only one of the two strands
(b) The enzyme cuts the sugar-phosphate backbone at specific sites on each strand
(c) The enzyme recognises a specific palindromic nucleotide sequence in the DNA
(d) The enzyme cuts DNA molecules at identified position within the DNA
Answer : A
Question. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
(a) Nucleic acid is fragmented by nucleases
(b) Construction of recombinant DNA involves cleaning DNA segments with endonuclease and rejoining with ligase
(c) Genetic engineering is making artificial limbs and diagnostic instruments
(d) Ti plasmid transforms cells of plants
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
(a) DNA being a hydrophilic molecule cannot pass through cell membranes
(b) Agrobacterium tumefaciens delivers a piece of DNA known as ‘Z-DNA’ which transforms normal plant cells into tumour cells and directs these tumour cells to produce chemicals against pathogens
(c) Retrovirus, adenovirus, papillomavirus are also now used as cloning vectors in animal because of their ability to transform normal cells into cancerous cell
(d) In genetic engineering, DNA from different sources are cut with the same restriction enzymes so that both DNA fragments have same kind of sticky ends
Answer : B
Question. Consider the following statements and select the correct option.
(a) A soil inhabiting plant bacterium, Agrobacterium tumefaciens, a pathogen of several dicot plants is able to transfer a piece of DNA known as T-DNA
(b) The T-DNA causes tumours
(c) Tumour formation is induced by Ti plasmid
(d) All of the above
Answer : D
Question. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
(a) Each restriction endonuclease recognises a specific palindromic nucleotide sequence
(b) Specific base sequence is known as recognition sequence
(c) Restriction enzymes cannot cut DNA
(d) Restriction enzymes belong to enzymes called nucleases
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
(a) EcoRI cuts the DNA between bases G and A
(b) Making multiple identical copies of any template DNA is called cloning
(c) pBR322 is a natural plasmid
(d) Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a natural genetic engineer
Answer : C
Question. Choose the incorrect statement.
(a) Ori also controls the copy numbers of the linked DNA
(b) If a foreign DNA ligates at the Bam HI site of tetracycline resistance gene in the vector pBR322, the recombinant plasmid loses the tetracycline resistance due to insertion of foreign DNA
(c) Copy number refers to the number of copies of plasmid present in a cell
(d) Copy number of plasmid varies from 50-100 per cell
Answer : D
Question. Which of the statements given is incorrect?
(a) In microinjection method, foreign DNA is directly injected into the nucleus of animal cell by using microneedles
(b) Microinjection method is used in oocytes, eggs and embryo
(c) Electroporation is the formation of temporary pores in the plasma membrane of host cell by using lysozyme or calcium chloride
(d) In chemical mediated gene transfer method, certain chemicals such as Ca phosphate help foreign DNA to enter the host cell
Answer : C
Question. Consider the following statements.
I. RecombinantDNAtechnology popularly known as genetic engineering is a stream of biotechnology which deals with the manipulation of genetic material by manin vitro.
II. pBR322 is the first artificial cloning vector developed in 1977 by Boliver and Rodriquez from E. coli plasmid.
III. Restriction enzymes belong to a class of enzymes called nucleases.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) I and II
(b) I and III
(c) II and III
(d) I, II and III
Answer : D
Question. Given below are four statements pertaining to separation of DNA fragments using gel electrophoresis. Identify the incorrect statements.
I. DNAis negatively charged molecule and so it is loaded on gel towards the anode terminal.
II. DNAfragments travel along the surface of the gel whose concentration does not affect movement of DNA.
III. Smaller the size ofDNAfragment larger is the distance it travels through it.
IV. PureDNAcan be visualised directly by exposing UV-radiation.
Select the correct option from the following.
(a) I, III and IV
(b) I, II and III
(c) II, III and IV
(d) I, II and IV
Answer : D
Question. Study the given figure carefully and select the correct statements regarding this. (Image 125)
I. It represents typical agarose gel electrophoresis showing differential migration ofDNAfragments.
II. Lane 1 contains undigestedDNAfragments.
III. Lanes 2 to 4contain digestedDNAfragment.
IV. SmallestDNAbands are present atAposition and largestDNAbands are present atBposition.
(a) I, II and III
(b) I, II and IV
(c) II and III
(d) III and IV
Answer : A
Question. Read the statements about gene gun method.
I. This method is also known as biolistic technique.
II. In this method, cells are bombarded with high velocity microparticles of gold or tungsten coated withDNAin plants.
III. Important crop plants like maize, rice and wheat have now been transformed by this method.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) I and II
(b) I and III
(c) II and III
(d) I, II and III
Answer : D
Question. Identify the correct statements.
I. The first recombinantDNAwas constructed by using a piece of DNAfrom plasmid carrying antibioticresistance gene in the bacterium Salmonella typhimurium and linked it to the plasmid of E. coli.
II. When cut by the same restriction enzyme, the resultant DNAfragments have the same kind of sticky ends and these can be joined together usingDNAligases.
III. The presence of more than one recognition sites within the vector will generate several fragments, which will complicate the gene cloning.
(a) I, II and III
(b) I and II
(c) Only I
(d) II and III
Answer : A
Question. Read the statements.
I. In the process of recombinantDNAtechnology, after several treatment the purifiedDNAis precipitated by adding chilled acetone.
II. The bacterial/plant, animal cell is broken down by enzymes to releaseDNA, along with RNA, proteins, polysaccharides and lipids.
Choose the correct option for above statements.
(a) I is true, but II is false
(b) I is false, but II is true
(c) I and II are true
(d) I and II are false
Answer : B
Question. Which of the following statements are correct with respect to a bioreactor?
I. It can process small volume of culture.
II. It provides optimum temperature, pH, salt, vitamins and oxygen.
III. Sparged stirred-tank bioreactor is a stirred type reactor in which air is bubbled.
Choose the correct option.
(a) I and II
(b) I and III
(c) II and III
(d) I, II and III
Answer : C
Question. Consider the following statements.
I. Bioreactors are vessels of large volumes in which raw materials are biologically converted into specific products.
II. One of the most commonlyused bioreactor is of stirring type.
III. Shake flasks are used for growing andmixing the desiredmaterials on a small scale in the laboratory.
IV. Alarge scale production of desired biotechnological product is done by using ‘bioreactors’.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) I and II
(b) I and III
(c) I, II and III
(d) I, II, III and IV
Answer : D
Question. Which statement is correct?
I. The downstream processing and quality control testing vary from product to product.
II. In bioreactors, raw materials are biologically converted into specific products.
III. Large amount of recombinant protein can be produced by gene cloning.
IV. pBR322 vector was constructed by usingDNA derived from naturally occurring plasmids of E. coli.
(a) I, II and III
(b) Only IV
(c) II, III and IV
(d) All of these
Answer : D
Question. Which statement is incorrect ?
I. Retroviruses have also been disarmed and are now
used to deliver desirable genes into animals cells.
II. Downstream processing is one of the steps ofR-DNA technology.
III. DNAis a negatively charged molecule.
IV. The presence of chromogenic substrate gives blue colour colonies, if the plasmid in the bacteria does not have an insert.
(a) I and II
(b) I, III and IV
(c) All of these
(d) None of these
Answer : D
Question. For selectable marker.
I. It helps to select the host cells which contain the vector and eliminate the non-transformants.
II. Genes encoding resistance to antibiotics like ampicillin, chloramphenicol, tetracycline or kanamycin, are useful selectablemarkers forE.coli.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) Only I
(b) Only II
(c) I and II
(d) None of these
Answer : C
Question. I. DNAbeing a hydrophilic molecule cannot pass through cell membranes.
II. The bacteria should be made competent to accept the DNAmolecule.
The correct option regarding the above statements is
(a) I is true, but II is false
(b) II is true, but I is false
(c) I and II are true
(d) I and II are false
Answer : C
Long Answer Questions
Question. List the steps involved in rDNA technology.
Answer. Steps in rDNA technology:
(i) Isolation of DNA.
(ii) Fragmentation of DNA by restriction endonucleases.
(iii) Isolation of the desired DNA fragments.
(iv) Amplification of the gene of interest.
(v) Ligation of the DNA fragment into a vector using DNA ligase.
(vi) Transfer of recombinant DNA into the host organism.
(vii) Culturing the host cell on a suitable medium on a large scale.
(viii) Extraction of the desired product.
(ix) Downstream processing of the products as finished products are ready for marketing.
Question. List the key tools used in recombinant DNA technology.
Answer. The key tools used in recombinant DNA technology are:
(i) Restriction enzymes
(ii) Polymerase enzyme
(iii) Ligase enzyme
(iv) Vectors
(v) Host organism/cell.
Question. (a) Explain the significance of ‘palindromic nucleotide sequence’ in the formation of recombinant DNA.
(b) Write the use of restriction endonuclease in the above process.
Answer. (a) Palindromic nucleotide sequence is the recognition (specific) sequence present both on the vector and on a desired or alien DNA for the action of the same (specific) restriction endonuclease to act upon.
(b) (i) Every endonuclease inspects the entire DNA sequence for the palindromic recognition sequence.
(ii) On finding the palindrome, the endonuclease binds to the DNA.
(iii) It cuts the opposite strands of DNA in the sugar–phosphate backbone; a little away from the centre of the palindrome sites but between the same bases on both strands.
(iv) This results in the formation of single stranded overhanging stretches at the end of each strand called sticky ends.
(v) The sticky ends facilitate the action of the enzyme DNA ligase by readily forming hydrogen bonds with complementary strands.
Question. Explain three basic steps to be followed during genetic modification of an organism.
Answer. The three basic steps are:
(i) Identification of DNA with desirable genes.
(ii) Introduction of the identified DNA into the host.
(iii) Maintenance of introduced DNA in the host and transfer of the DNA to its progeny.
Question. Explain the action of the restriction endonuclease EcoRI.
Answer. (i) The recognition sequence shows palindrome character in which the sequence of base pairs
read the same on both the DNA strands, i.e., same in 5′ → 3′ or 3′ → 5′ directions, e.g.,
5′ — G A A T T C — 3′
3′ — C T T A A G — 5′
(ii) The restriction endonuclease acts on specified length of a DNA and binds to the DNA at the recognition sequence.
(iii) It cuts the opposite double helix of DNA in the sugar-phosphate backbones, a little away from the centre of the palindrome sites.
(iv) There are overhanging stretches called sticky ends on each strand, which form hydrogen bonds with their complementary cut counterparts. This stickiness of the ends facilitates the action of the enzyme DNA ligase.
Question. (a) What is EcoRI? What does ‘R’ represent in this?
(b) Explain its action.
Answer. (a) EcoRI is a restriction endonuclease, obtained from an E. coli bacterium.
R represents the name of the strain.
(b) It cuts the DNA between bases G and A on both the strands only when the sequence GAATTC is present in DNA.
Question. (a) Name the selectable markers in the cloning vector pBR322? Mention the role they play.
(b) Why is the coding sequence of an enzyme β-galactosidase is a preferred selectable marker in comparison to the ones named above?
Answer. (a) Selectable markers are ampR/ampicillin resistance genes and tetR/tetracycline resistance gene. They help in identifying and eliminating non-transformants/non-recombinants and selectively permitting the growth of the transformants/recombinants.
(b) This is because it is simpler and less cumbersome. In the presence of chromogenic substrate recombinants form colourless colonies and non-recombinants form blue in colonies.
Question. (a) In pBR322, foreign DNA has to be introduced in tetR region. From the restriction enzymes given below, which one should be used and why?
PvuI, EcoRI, BamHI
(b) Give reasons, why the other two enzymes cannot be used.
Answer. (a) BamHI should be used, as restriction site for this enzyme is present in tetR region.
(b) PvuI will not be used, as restriction site for this enzyme is present in ampR region (not in tetR).EcoRI will not be used, as restriction site for this enzyme is not present in selectable marker tetR.
Question. Why are genes encoding resistance to antibiotics considered useful selectable markers for E. coli cloning vector? Explain with the help of one example.
Answer. Genes encoding resistance to antibodies are considered useful selectable markers for E. coli cloning vector.
If a recombinant DNA bearing gene for resistance to an antibiotic (e.g., ampicillin) is transferred into E. coli cells, the host cells become transformed into ampicillin-resistant cells. If these transformed cells are spread on agar plates containing ampicillin, only transformants will grow, and the non-transformed recipient cells will die as they do not contain the gene for ampicillin resistance. Thus, transformed cells can be selected. The gene for ampicillin resistance, in this case, is a useful selectable marker.
Question. How does β-galactosidase coding sequence act as a selectable marker? Explain. Why is it a preferred selectable marker to antibiotic resistance genes?
Answer. When a recombinant DNA is inserted within the coding sequence of the enzyme β-galactosidase,it results into inactivation of the enzyme. The presence of a chromogenic substrate gives blue coloured colonies if the plasmid in the bacteria does not have an insert, whereas presence of insert do not produce any colour.
Selection of recombinants due to inactivation of antibiotics is a cumbersome procedure because it requires simultaneous plating on two plates having different antibiotics. Therefore, selectable markers are preferred for selection of recombinants.
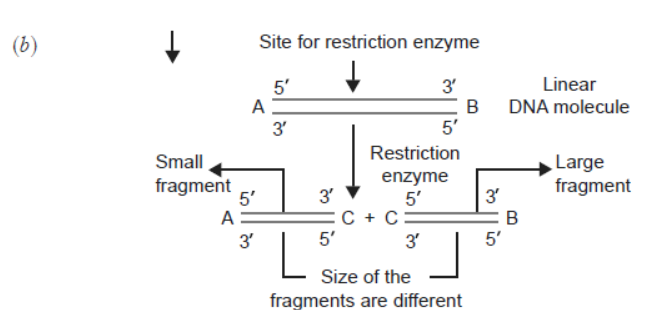
Question. A plasmid DNA and a linear DNA (both of the same size) have one site for a restriction endonuclease. When cut and separated on agarose gel electrophoresis, plasmid shows one DNA band while linear DNA shows two fragments. Explain.
Answer. It is because plasmid is a circular DNA molecule. When cut with enzyme, it becomes linear but does not get fragmented. Whereas, a linear DNA molecule gets cut into two fragments. Hence, a single DNA band is observed for plasmid while two DNA bands are observed for linear DNA in agarose gel.
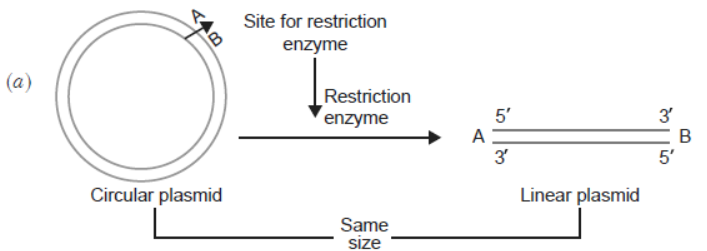
Question.
(a) Mark the positive and negative terminals.
(b) What is the charge carried by DNA molecule and how does it help in its separation?
(c) How the separated DNA fragments are finally isolated?
Answer. (a) Positive terminal – ‘B’
Negative terminal – ‘A’
(b) DNA is negatively charged. Because of its negative charge, DNA moves towards the positive electrode (anode).
(c) The separated DNA fragments are separated by elution. The separated bands of DNA are cut out from the agarose gel and extracted from the gel piece.
Question. A mixture of fragmented DNA was electrophoresed in agarose gel. After staining the gel with ethidium bromide, no DNA bands were observed. What could be the reason?
Answer. The reasons that could be possible are as follows:
(i) DNA sample that was loaded on the gel may have got contaminated with nuclease (exo- or endo- or both) and completely degraded.
(ii) Electrodes were put in opposite orientation in the gel assembly, i.e., anode towards the wells (where DNA sample is loaded). Since DNA molecules are negatively charged, they move towards anode and hence move out of the gel instead of moving into the matrix of gel.
(iii) Ethidium bromide was not added at all or was not added in sufficient concentration and so DNA was not visible.
(iv) After staining with Ethidium bromide it was not observed under UV.
Question. (a) Why must a cell be made ‘competent’ in biotechnology experiments? How does calcium ion help in doing so?
(b) State the role of ‘biolistic gun’ in biotechnology experiments.
Answer. (a) A cell must be made competent so that it can take up the hydrophilic DNA from the external medium. Divalent calcium ions increases the efficiency, of DNA entering the cell through pores in the cell wall.
(b) Biolistic gun is used to introduce alien DNA into the plant cell by bombarding them with high velocity microparticles (gold or tungsten coated with DNA).
Question. What is Ti plasmid? Name the organism where it is found. How does it help in genetic engineering?
Answer. An extra-chromosomal DNA which delivers gene of interest into variety of plants and act as cloning vector is called Ti plasmid. They are present in Agrobacterium tumifaciens. Ti plasmid vectors are used for genetic transformation in many dicot plants. The tumour inducing (Ti) plasmid of Agrobacterium tumifaciens has been modified into a cloning vector which is no more pathogenic to the plants but is still able to use the mechanisms to deliver genes of interest into a variety of plants.
Question. Expand the following and mention one application of each:
(i) PCR (ii) ELISA
Answer. Expansion Application
(i) PCR Polymerase Chain Reaction Amplification of gene of interest/In forensic study
(ii) ELISA Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay Diagnostic test for AIDS
Question. How can a bioreactor be made to function at optimal state in order to obtain a desired foreign gene product? Explain.
Answer. A stirred-tank bioreactor is the most commonly used bioreactor. It comes with a curved base to facilitate the mixing of the reactor contents. The stirrer facilitates even mixing and oxygen availability throughout the bioreactor. The bioreactor has an agitator system, an oxygen delivery system and a foam control system, a temperature control system, pH control system and sampling port so that volumes of the cultures can be withdrawn periodically.
Question. Explain the importance of (a) ori, (b) ampR and (c) rop in the E. coli vector shown below:
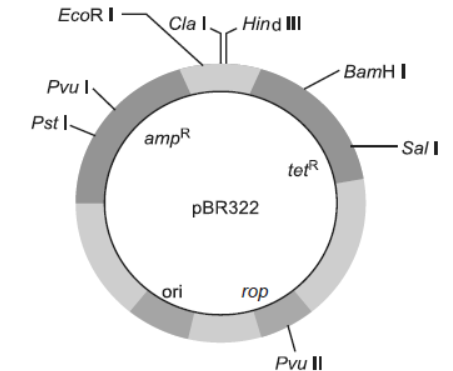
Answer. (a) ori: Ori is a sequence from where replication starts and any piece of DNA when linked to this sequence can be made to replicate within the host cells. It is also responsible for controlling the copy number of the linked DNA.
(b) ampR: The ligation of alien DNA is carried out at a restriction site present in any antibiotic resistance gene.
(c) rop: It codes for the proteins involved in the replication of the plasmid.
Question. Describe the roles of heat, primers and the bacterium Thermus aquaticus in the process of PCR.
Answer.
- Heat denatures or helps in separation of DNA into two strands.
- Primer–Enzyme DNA Polymerase extend the primers using the nucleotides provided in the reaction and the genomic DNA as template.
- Thermus aquaticus: It is the source of thermostable DNA polymerase or Taq polymerase.
Question. A schematic representation of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) up to the extension stage is given below. Answer the questions that follow:
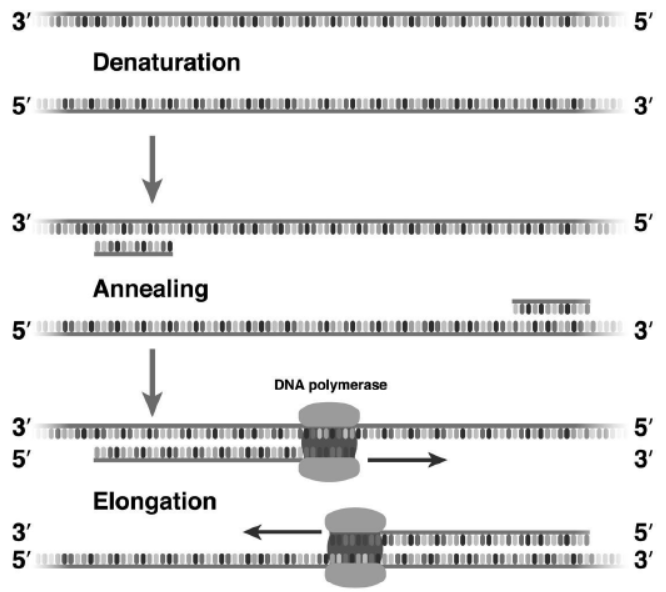
(i) Name the process ‘a’. (ii) Identify ‘b’
(iii) Identify ‘c’ and mention its importance in PCR.
Answer. (i) a—Denaturation process
(ii) b—Primers
(iii) c—Taq DNA polymerase. Taq polymerase is a thermostable enzyme which remains active during the high temperature required for extension of DNA.
Question. (a) List the three steps involved in Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR).
(b) Name the source organism of Taq polymerase. Explain the specific role of this enzyme in PCR.
Answer. (a) The three steps involved in polymerase chain reaction (PCR):
(i) Denaturation of double stranded DNA (dsDNA) at high temperature.
(ii) Annealing of two sets of primers.
(iii) Extension of primers to form dsDNA by Taq polymerase and deoxynucleotides.
(b) Source organism of Taq polymerase is the bacterium Thermus aquaticus. This enzyme is heat tolerant and can repeatedly amplify DNA at high temperatures.
Question. Name two commonly used bioreactors. State the importance of using a bioreactor.
Answer. Two commonly used bioreactors are simple stirred tank bioreactor and sparged stirred tank bioreactor.
A bioreactor is used for
(i) processing large volumes of culture.
(ii) large scale production of recombinant proteins.
(iii) biologically converting raw materials into specific products.
Question. “A very small sample of tissue or even a drop of blood can help determine paternity”. Provide a scientific explanation to substantiate the statement.
Answer. (i) DNA from all cells of an individual shows the same degree of polymorphism and therefore becomes a useful identification tool.
(ii) Polymorphs are heritable and the child inherits 50% of the chromosome from each parent.
(iii) With the help of PCR, the small amount of DNA from blood can be amplified and be used in DNA finger printing to identify the paternity
Question. (i) Describe the characteristics that a cloning vector must possess.
(ii) Why DNA cannot pass through the cell membrane? Explain. How is a bacterial cell made ‘competent’ to take up recombinant DNA from the medium?
Answer. (i) A cloning vector must have the following characteristics:
(a) ori or origin of replication which can make large number of copies
(b) Selectable marker i.e., genes encoding for an antibiotic resistance or genes encoding for α-galactosidase.
(c) Recognition site for the restriction enzyme to recognise.
(ii) DNA is a hydrophilic molecule, therefore it cannot pass through the cell membrane.
The bacterial cells can be made competent by treating them with a specific concentration of a divalent ion like calcium. The cells are then incubated on ice followed by a heat shock by placing them briefly at 42°C and then putting back on ice.
Question. If a desired gene is identified in an organism for some experiments, explain the process of the following:
(i) Cutting this desired gene at specific location.
(ii) Synthesis of multiple copies of this desired gene.
Answer. (i) The desired gene is cut using the enzymes restriction endonucleases. Firstly, the restriction endonucleases that recognise the palindromic nucleotide sequence of the desired gene is identified. The endonuclease inspects the entire DNA sequences to find and recognise the site. It cuts each of the double helix at a specific point which is a little away from the centre of the palindromic site. The cutting site is between the same two bases on the opposite strands. This results in over-hanging single stranded stretches which act as sticky ends.
(ii) Multiple copies of the desired gene is synthesised by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method. In this method, the desired gene is synthesised in vitro. The double stranded DNA
is denatured using high temperature of 95°C and the strands are separated. Each separated strand acts as template.
Two sets of oligonucleotide primers are annealed to the denatured DNA strands. The thermostable Taq polymerase extends the primers, using nucleotides provided in the reaction mixture. Finally the amplified fragments are ligated into recipient cells.
Question. Which methodology is used while sequencing the total DNA from a cell? Explain it in detail.
Answer. Methodology used:
- Sequence Annotation – total DNA from a cell is isolated, converted into random fragments of relatively smaller sizes, and cloned in suitable host using specialized vectors.
- The cloning resulted into amplification of each piece of DNA fragment.
- The fragments were sequenced using automated DNA sequencers, these sequences are then arranged based on some overlapping regions (present in them).
- This requires generation of overlapping fragments (for sequencing).
- Specialised computer based programmes were developed, and these sequences were subsequently annotated and assigned to each chromosome.
Question. For selection of recombinants, insertional inactivation of antibiotic marker has been superceded by insertional inactivation of a marker gene coding for a chromogenic substrate.
Give reasons.
Answer. Selection of recombinants due to inactivation of antibiotics is a laborious process as it requires:
(i) a vector with two antibiotic resistance markers,
(ii) preparation of two kinds of media plates, with one antibiotic each.
Transformed cells are first plated on the antibiotic plate which has not been insertionally inactivated (say, ampicillin) and incubated overnight for growth of transformants. For selection of recombinants, these transformants are replica-plated on second antibiotic (say, tetracycline) plate (which got inactivated due to insertion of gene). Non-recombinants grow on both the plates (one carrying ampicillin and the other carrying tetracycline) while recombinants will grow only on ampicillin plate.
This entire exercise is laborious and takes more time (two overnight incubation) as well. However, if we choose insertional inactivation of a marker that produces colour in the presence of a chromogenic compound, we can distinguish between the recombinants and non-recombinants on a single medium plate (containing one antibiotic and the chromogenic compound) after overnight growth.
Question. (a) Explain how recombinants and non-recombinants are differentiated on the basis of colour production in the presence of a chromogenic substrate. Name that procedure.
(b) Describe the temperature treatment that enhances the bacteria to take up the rDNA.
Answer. (a) The procedure is called insertional inactivation.
In this method recombinants and non-recombinants are differentiated on the basis of the ability to produce colour in the presence of a chromosomic substrate. In this method, a rDNA is inserted in an enzyme – b-galactosidase which leads to inactivation of the enzyme which does not produce colour due to insertion.
(b) (i) Host cells are incubated with rDNA on ice.
(ii) Followed by placing them briefly at 42°C.
(iii) Then transfer them back on ice.
This enables the host cells (bacteria) to take up the rDNA.
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants VBQs |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Human Reproduction VBQs |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Reproductive Health VBQs |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Principles of Inheritance and Variation VBQs |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Molecular Basis of Inheritance VBQs |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution VBQs |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Human Health and Diseases VBQs |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Microbes in Human Welfare VBQs |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology Principles and Processes VBQs |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology and Its Application VBQs |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Organisms and Populations VBQs |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem VBQs |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biodiversity and Conservation VBQs |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Reproduction in Organisms VBQs |
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production VBQs |
VBQs for Chapter 09 Biotechnology Principles and Processes Class 12 Biology
We hope students liked the above VBQs for Chapter 09 Biotechnology Principles and Processes designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 12 Biology released by CBSE. Students of Class 12 should download the Value Based Questions and Answers in Pdf format and practice the questions and solutions given in above Class 12 Biology VBQs Questions on daily basis. All latest VBQs with answers have been developed for Biology by referring to the most important and regularly asked topics which the students should learn and practice to get better score in school tests and examinations. Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to NCERT book for Class 12 Biology to develop the Biology Class 12 VBQs. After solving the questions given in the VBQs which have been developed as per latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 12 Biology designed by our teachers. We have also provided a lot of other VBQs for Class 12 Biology which you can use to further make yourself better in Biology.
You can download the CBSE VBQs for Class 12 Biology Chapter 09 Biotechnology Principles and Processes for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the VBQs issued by CBSE for Chapter 09 Biotechnology Principles and Processes Class 12 Biology have been made available here for latest academic session
There is no charge for the VBQs and their answers for Class 12 CBSE Biology Chapter 09 Biotechnology Principles and Processes you can download everything free
Regular revision of VBQs given on studiestoday for Class 12 subject Biology Chapter 09 Biotechnology Principles and Processes can help you to score better marks in exams
Value Based Questions (VBQs) for Class 12 Biology Chapter 09 Biotechnology Principles and Processes help to test the ability of students to apply learnings to various situations in life.

