Read and download the CBSE Class 12 Biology Biodiversity and Conservation VBQs. Designed for the 2025-26 academic year, these Value Based Questions (VBQs) are important for Class 12 Biology students to understand moral reasoning and life skills. Our expert teachers have created these chapter-wise resources to align with the latest CBSE, NCERT, and KVS examination patterns.
VBQ for Class 12 Biology Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation
For Class 12 students, Value Based Questions for Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation help to apply textbook concepts to real-world application. These competency-based questions with detailed answers help in scoring high marks in Class 12 while building a strong ethical foundation.
Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation Class 12 Biology VBQ Questions with Answers
Biodiversity and Conservation
Question. Three levels of biodiversity are
(a) genetic diversity, species diversity and ecological diversity
(b) species diversity, ecological diversity and habitat diversity
(c) geographical diversity, genetic diversity and habitat diversity
(d) ecological diversity, species diversity and community diversity
Answer: A
Question. Genetic diversity is the measure of
(a) varieties of the species and their relative abundance present within a region
(b) variation in the genetic information contained in the organisms
(c) diversity of the genes at community and ecosystem levels
(d) All of the above
Answer: B
Question. The medicinal plant, Rauwolfia vomitoria, growing in Himalayan ranges shows variation in terms of the potency and concentration of the chemical (reserpine), that it produces. It is an example of
(a) species diversity
(b) ecological diversity
(c) genetic diversity
(d) None of the above
Answer: C
Question. The Western Ghats have a greater amphibians diversity than the Eastern Ghats. It is an example of
(a) species diversity
(b) genetic diversity
(c) ecological diversity
(d) None of the above
Answer: A
Question. Ecological diversity exists at community level and is of three types. Select the correctly matched option for ecological diversity.
(a) Alpha diversity – Diversity between communities
(b) Beta diversity – Diversity of organisms within same community
(c) Gamma diversity – Diversity of organisms over the entire geographical area
(d) None of the above
Answer: C
Question. As estimated by Robert May, what is the total number of species present on earth?
(a) 3 million
(b) 5 million
(c) 7 million
(d) 9 million
Answer: C
Question. Which one of the following has the highest number of species in nature?
(a) Angiosperms
(b) Fungi
(c) Insects
(d) Birds
Answer: C
Question. Given below is the representation of the extent of global diversity of invertebrates. What groups the four portions (A-D) represent, respectively?
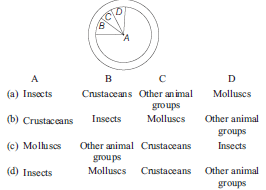
Answer: D
Question. Given below are pie diagrams I, II and III related to the proportionate number of species of major taxa of invertebrates, vertebrates and plants, respectively. Critically study and fill in the blanks A, B, C and D.
(a) A–Molluscs, B–Amphibians, C–Angiosperms, D–Gymnosperms
(b) A–Molluscs, B–Amphibians, C–Fungi, D–Angiosperms
(c) A–Turtles, B– Amphibians, C–Fungi, D–Angiosperms
(d) A–Hexapoda, B–Amphibians, C–Fungi, D–Angiosperms
Answer: B
Question. Which of the following represents maximum number of species among global biodiversity?
(a) Algae
(b) Lichens
(c) Fungi
(d) Mosses and ferns
Answer: C
Question. India is one of the ‘twelve’ megadiversity countries with ……… of genetic resources of the world.
(a) 12.1%
(b) 18.1%
(c) 38.1%
(d) 8.1%
Answer: D
Question. Biodiversity is affected by
(a) latitudinal gradients and species-area relationship
(b) species-area relationship and longitudinal gradients
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) latitudinal and longitudinal gradients
Answer: A
Question. From equator towards the poles biodiversity
(a) decreases
(b) increases
(c) remains same
(d) first decreases then increases
Answer: A
Question. Tropics (23.5°N to 23.5°S) have ....... species as compared to temperate or polar regions. The most appropriate word to fill the blank is
(a) less
(b) equal
(c) more
(d) None of these
Answer: C
Question. Arrange the following places in increasing order of biodiversities of species of birds and select the right option.
(a) Colombia®New York® Greenland® India
(b) Greenland® New York® India® Colombia
(c) New York® India® Colombia® Greenland
(d) India® Colombia® Greenland® New York
Answer: B
Question. How many times the tropical areas have vascular plants than the temperate areas have?
(a) 10
(b) 50
(c) 3
(d) 65
Answer: A
Question. The country, whose tropical rainforests possess the greatest biodiversity on earth is
(a) New York
(b) South America
(c) India
(d) England
Answer: B
Question. Given below are three statements (I-III) each with one or two blanks. Select the option, which correctly fill up to blanks.
Ecologists and evolutionary biologists have proposed various hypotheses; some important ones are
I. Speciation is generally a function of time, unlike ...A... regions subjected to frequent glaciations in the past.
...B... have remained relatively undisturbed for millions of years and thus, had a long evolutionary time for species diversification.
II. ...C... environments, unlike temperate ones, are less seasonal, relatively more constant and predictable.
Such constant environments promote niche specialisation and lead to a greater species diversity.
III. There is more solar energy available in the ...D..., which contributes to higher productivity; this in turn might contribute indirectly to greater diversity.
Choose the correct option for A, B, C and D.
(a) A–tropics, B–Tropical latitudes, C–Temperate, D–Arctic tundra
(b) A–temperate, B–Tropical latitudes, C–Tropics, D–chapparral
(c) A–tropical, B–Tropical latitudes, C–Tropics, D–chapparral
(d) A–temperate, B–Tropical latitudes, C–Tropical, D–tropics
Answer: D
Question. Alexander von Humboldt described for the first time
(a) ecological biodiveristy
(b) law of limiting factor
(c) species-area relationships
(d) population growth equation
Answer: C
Question. Alexander von Humboldt observed that, within a region species richness………with increasing explored area. The most appropriate word to fill the blank is
(a) increased
(b) decreased
(c) increased up to a limit
(d) decreased up to a limit
Answer: A
Question. The great German naturalist and geographer Alexander von Humboldt observed that within a region species richness increased with increasing explored area, but only up to a limit. In fact, relation between species richness and area for a wide variety of taxa (angiosperm plants, birds, bats, freshwater fishes) turns out to be rectangular hyperbola. Now find out correct equations shown in the graph.
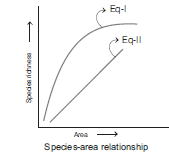
Answer: A
Question. The relationship between the species richness and the area for a wide variety of taxa appears as
(a) straight line
(b) sigmoid curve
(c) rectangular hyperbola
(d) None of these
Answer: C
Question. On a logarithmic scale, the species-area relationship is a straight line described by the equation
![]()
Answer: C
Question. In the species-area relationship, ‘S’ represents
(a) species richness
(b) slope of the line
(c) specific area
(d) special species
Answer: A
Question. In the species-area relationship, ‘Z’ represents
(a) regression coefficient
(b) enzymatic coefficient
(c) multiplication coefficient
(d) None of the above
Answer: A
Question. The value of ‘Z’ lies in the range of ...... regardless of the taxonomic group or the region. The most appropriate value to fill the blank is
(a) 0.5 to 0.7
(b) 0.3 to 0.7
(c) 0.2 to 0.3
(d) 0.1 to 0.2
Answer: D
Question. For frugivorous birds and mammals in the tropical forests of different continents, Z(slope of the line/regression coefficient) is found to be
(a) 1.15
(b) 0.1
(c) 0.5
(d) 0
Answer: A
Question. If log A = 4, Z = 0.3 and log C = 0.8, find the value of log ‘S’?
(a) 3.76
(b) 100
(c) 4.24
(d) 2
Answer: D
Question. Communities with more species tend to be more stable than those with less species. This was confirmed by
(a) Alexander von Humboldt
(b) David Tilman
(c) Paul Ehrlich
(d) Edward Wilson
Answer: B
Question. Which of the following hypothesis suggests that ecosystems are like aeroplanes where flight safety (ecosystem functioning) may or may not be compromised, depending upon which species are being lost?
(a) Gaia hypothesis
(b) Gause-exclusion hypothesis
(c) Qudum’s hypothesis
(d) Rivet popper hypothesis
Answer: D
Question. The organisation, which publishes the Red List of species is
(a) ICFRE
(b) IUCN
(c) UNEP
(d) WWF
Answer: B
Question. Antilope cervicapra (blackbuck) is categorised by IUCN as
(a) critically endangered
(b) endangered
(c) vulnerable
(d) extinct in the wild
Answer: C
Question. A species facing extremely high risk of extinction in the immediate future is called
(a) vulnerable
(b) endemic
(c) critically endangered
(d) extinct
Answer: C
Question. In natural extinction of species
(a) gradual replacement of existing species takes place
(b) human activities play an active part
(c) catastrophes, earthquakes and other natural calamities are involved
(d) None of the above
Answer: A
Question. Anthropogenic extinction is called
(a) fifth mass extinction
(b) fourth mass extinction
(c) sixth mass extinction
(d) seventh mass extinction
Answer: C
Question. The term ‘The Evil Quartet’ is related with
(a) Four major causes of forest loss
(b) Four major causes of population explosion
(c) Four major causes of air pollution
(d) Four major causes of biodiversity losses
Answer: D
Question. Which of the following is responsible for biodiversity loss?
(a) Habitat loss and fragmentation
(b) Alien species invasions
(c) Coextinctions
(d) All of the above
Answer: D
Question. Which of the following is the most important cause for animals and plants being driven to extinction?
(a) Drought and floods
(b) Economic exploitation
(c) Alien species invasion
(d) Habitat loss and fragmentation
Answer: D
Question. Many species like Steller’s sea cow and passenger pigeon have been driven to the brink of extinction. Which of the following describes this situation?
(a) Overexploitation by humans
(b) Pollution
(c) Habitat loss
(d) Competition from introduced species
Answer: A
Question. Water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) was introduced in Indian water to reduce pollution. It is an example of
(a) disturbance and degradation
(b) coextinctions
(c) alien species invasions
(d) overexploitation
Answer: C
Question. Decline in the population of Indian native fishes due to introduction of Clarias gariepinus in river Yamuna can be categoriesd as
(a) coextinction
(b) habitat fragmentation
(c) overexploitation
(d) alien species invasion
Answer: D
Question. If any extinction of a mutualistic pollinator takes place, what would be its effect on the plants where it pollinates?
(a) Decreased pollination
(b) No effect because substitute pollinator is available
(c) The plant would not be pollinated
(d) None of the above
Answer: C
Question. The reasons behind conserving biodiversity can be grouped into categories, which include
I. broadly utilitarian
II. narrowly utilitarian
III. no utilitarian
IV. ethical utilitarian
Choose the correct option.
(a) I, II, III and IV
(b) II, III and IV
(c) I, II and IV
(d) I, III and IV
Answer: C
Question. More than 25% of the drugs are derive from the plants. What benefit does this describe?
(a) Aesthetic value
(b) Ethical value
(c) Indirect economic value
(d) Direct economic value
Answer: C
Question. Exploration of molecular, genetic and species level diversity for novel products of economic importance is known as
(a) biopiracy
(b) bioenergetics
(c) bioremediation
(d) bioprospecting
Answer: D
Question. What is the sustainable use of resources?
(a) Protected strips of the land that allows organisms to migrate from one wilderness area to another
(b) A law that makes it illegal to do harm to the species that are listed as endangered or threatened
(c) The ability to use natural resources in a way that helps people to protect the ecosystem
(d) The study of the methods which help to protect biodiversity
Answer: C
Question. Conservation in the natural habitat is
(a) in situ
(b) ex situ
(c) zoo
(d) botanical garden
Answer: A
Question. Western Ghats have a large number of plant and animal species that are not found anywhere else. Which of the following terms will you use to notify such species?
(a) Endemic
(b) Vulnerable
(c) Threatened
(d) Keystone
Answer: A
Question. How many hotspots of biodiversity in the world have been identified till date by Norman Myers?
(a) 17
(b) 25
(c) 34
(d) 43
Answer: C
Question. Which one of the following areas in India, is a hotspot of biodiversity?
(a) Eastern Ghats
(b) Gangetic plain
(c) Sunderbans
(d) Western Ghats
Answer: D
Question. Conservation of hotspots are best described as
(a) conserving islands that are experiencing high rates of extinction
(b) conserving areas where native species are being replaced with introduced species
(c) conserving areas where the people are active supporters of the biological diversity
(d) conserving areas with the large members of endemic species that are disappearing rapidly
Answer: D
Question. What is the approximate percentage of the earth covered by terrestrial hotspots?
(a) 1.5% (less than 2%)
(b) 2.5%
(c) 3.5%
(d) 4.5%
Answer: A
Question. In situ strategies include
I. national parks II. wildlife sanctuaries
III. biosphere reserves IV. sacred groves
Choose the correct option.
(a) I and II
(b) II, III and IV
(c) I, II and III
(d) I, II, III and IV
Answer: D
Question. The numbers of national parks, biosphere and wildlife sanctuaries of India, respectively are
(a) 90, 14, 448
(b) 158, 62, 10
(c) 58, 412, 10
(d) 96, 412, 10
Answer: A
Question. Which one of the following is not a method of in situ conservation of biodiversity?
(a) Wildlife sanctuary
(b) Botanical garden
(c) Sacred grove
(d) Biosphere reserve
Answer: B
Question. Which of the following national parks is home to the famous musk deer or hangul?
(a) Keibul Lamjao National Park, Manipur
(b) Bandhavgarh National Park, Madhya Pradesh
(c) Eaglenest Wildlife Sanctuary, Arunachal Pradesh
(d) Dachigam National Park, Jammu and Kashmir
Answer: D
Question. Biosphere reserves differ from the national parks and wildlife sanctuaries because in the former
(a) human beings are not allowed to enter
(b) people are an integral part of the ecosystem
(c) plants are paid greater attention than the animals
(d) living organisms are brought from all over the world and preserved for posterity
Answer: B
Question. In your opinion, which is the most effective way to conserve genetic diversity of the plant of an area?
(a) By tissue culture method
(b) By creating biosphere reserve
(c) By creating botanical garden
(d) By developing seed bank
Answer: B
Question. Core zone, buffer zone and manipulation zone are found in
(a) national park
(b) sanctuary
(c) tiger reserve
(d) biosphere reserve
Answer: D
Question. The region of biosphere reserve, which is legally protected and where no human activity is allowed is known as
(a) core zone
(b) buffer zone
(c) transition zone
(d) restoration zone
Answer: A
Question. Sacred groves in India are related with
(a) aesthetic pleasure
(b) the place where threatened species are protected
(c) the place where only artificial plant breeding is allowed
(d) forest patches around the places of worship
Answer: D
Question. Sacred groves in India are found in
(a) Jaintia hills of Karnataka
(b) Western Ghat regions of Tamil Nadu
(c) Aravalli hills of Meghalaya
(d) Bastar areas of Madhya Pradesh
Answer: D
| CBSE Class 12 Biology Biodiversity and Conservation VBQs |
More free study material for Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation
VBQs for Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation Class 12 Biology
Students can now access the Value-Based Questions (VBQs) for Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation as per the latest CBSE syllabus. These questions have been designed to help Class 12 students understand the moral and practical lessons of the chapter. You should practicing these solved answers to improve improve your analytical skills and get more marks in your Biology school exams.
Expert-Approved Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation Value-Based Questions & Answers
Our teachers have followed the NCERT book for Class 12 Biology to create these important solved questions. After solving the exercises given above, you should also refer to our NCERT solutions for Class 12 Biology and read the answers prepared by our teachers.
Improve your Biology Scores
Daily practice of these Class 12 Biology value-based problems will make your concepts better and to help you further we have provided more study materials for Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation on studiestoday.com. By learning these ethical and value driven topics you will easily get better marks and also also understand the real-life application of Biology.
The latest collection of Value Based Questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation is available for free on StudiesToday.com. These questions are as per 2026 academic session to help students develop analytical and ethical reasoning skills.
Yes, all our Biology VBQs for Chapter Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation come with detailed model answers which help students to integrate factual knowledge with value-based insights to get high marks.
VBQs are important as they test student's ability to relate Biology concepts to real-life situations. For Chapter Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation these questions are as per the latest competency-based education goals.
In the current CBSE pattern for Class 12 Biology, Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation Value Based or Case-Based questions typically carry 3 to 5 marks.
Yes, you can download Class 12 Biology Chapter Chapter 13 Biodiversity and Conservation VBQs in a mobile-friendly PDF format for free.

