Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 8 Science Cell Structure And Functions Worksheet. Students and teachers of Class 8 Science can get free printable Worksheets for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Functions in PDF format prepared as per the latest syllabus and examination pattern in your schools. Class 8 students should practice questions and answers given here for Science in Class 8 which will help them to improve your knowledge of all important chapters and its topics. Students should also download free pdf of Class 8 Science Worksheets prepared by teachers as per the latest Science books and syllabus issued this academic year and solve important problems with solutions on daily basis to get more score in school exams and tests
Worksheet for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Functions
Class 8 Science students should download to the following Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Functions Class 8 worksheet in PDF. This test paper with questions and answers for Class 8 will be very useful for exams and help you to score good marks
Class 8 Science Worksheet for Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Functions
Question. Which of the following is the main difference between onion peel cells and human cheek cells?
(A) Presence of mitochondria in onion peel cells only
(B) presence of cell wall in onion peel cells only
(C) Absence of plasma membrane in cheek cells
(D) Absence of endoplasmic reticulum in cheek cells
Answer. B
Question. The brain and spinal cord are made up of
(A) Nervous tissue
(B) Epithelial tissue
(C) Muscular tissue
(D)Connective tissue
Answer. A
Question. Red blood cells
(A) have two nuclei
(B) have a cell wall
(C) have pigment-containing plastids
(D) do not have a nucleus
Answer. D
Question. Centrioles are found in
(A) onion peel cells
(B) human cheek cells
(C) all plant cells
(D) none of these
Answer. B
Question. Cartilage and bone are type of:
(A) epithelial tissue
(B) skeletal tissue
(C) muscular tissue
(D) nervous tissue
Answer. B
Question. Muscles involved in the movement of the arm are:
(A) striated
(B) nonstriated
(C) cardiac
(D) smooth
Answer. A
Question. Blood is a type of:
(A) epithelial tissue
(B) nervous tissue
(C) connective tissue
(D) muscular tissue
Answer. C
Question. The network of tube-like structure running through the cytoplasm is called
(A) Golgi complex
(B) mitochondria
(C) endoplasmic reticulum
(D) ribosomes
Answer. C
Question. Cheek cells are
(A) epithelial cells
(B) epidermal cells
(C) vascular cells
(D) guard cells
Answer. A
Question. The cell wall in plant cells is made up of
(A) Proteins
(B) Facts
(C) Plasma
(D) Cellulose
Answer. D
Question. The semipermeable membrane in the plant cell allows the diffusion of:
(A) solute molecules
(B) solvent molecules
(C) solute and solvent molecules
(D) none of these
Answer. B
Question. Biological membrane includes
(A) only nuclear membrane
(B) only membranes of Golgi complex
(C) only mitochondrial membrane
(D) all the intracellular membranes along with plasma membrane
Answer. D
Question. Entry of water into root hairs is an examples of :
(A) diffusion
(B) imbibition
(C) osmosis
(D) plasmolysis
Answer. C
Ture & False type questions.
Question. All living organisms consists of cells.
Answer. True
Question. The main function of ribosomes is to synthesize proteins.
Answer. True
Question. Plastids are the sites of photosynthesis.
Answer. True
Question. Chloroplasts are colourless plastids.
Answer. False
Question. Prokaryotic cells lack nuclear envelope
Answer. True
Question. Make a sketch of the human nerve cell. What funtion do nerve cells perform?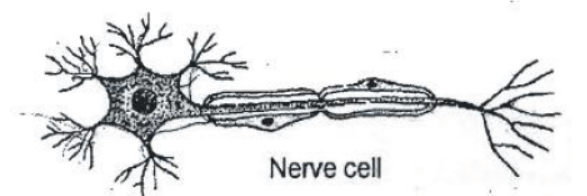
Answer. Functions of human nerve cell:
(i) Nerve cells receive message from different parts of body.
(ii) They further transfer these messages to brain and accordingly brain send commands for functioning of different organs of body.
Question. Write short notes on the following:
(i) Cytoplasm (ii) Nucleus of a cell
Answer. (i) Cytoplasm: Cytoplasm is a jelly like substance which is present between the cell membrane and the nucleus. Various other organelles of cells are present in the cytoplasm. Cytoplasm is made up of chemical substances like carbohydrates, proteins and water. These chemical substances are present in cells of all types and sizes. Cytoplasm contains many important tiny substances called Organelles.
(ii) Nucleus of a cell: Nulceus is the master of the cell. It commands all the functioning of the cell. It is generally located in the center of the cell and is spherical in shape. A membrane called nuclear membrane separates it from cytoplasm. It contains the genetic material DNA and RNA in it. This porous membrane allows the transfer of material in the nucleus and cytoplasm. Nucleus contains a dense body called Nucleolus which actually contains Chromosomes, the genetic material.
Question. Which part of the cell contains organelles?
Answer. Cytoplasm.
Question. State a difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
Answer. Prokaryotes do not have a well designed nuclear membrane while, eukaryotes have a well designed nuclear membrane.
Question. Where are the chromosomes found in cell? State their functions?
Answer. Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of a cell. Their function is to carry characteristic features of parent cells to the daughter cell means, from parent to offspring.
Question. Cells are the basic structural units of living organism. Explain.
Answer. In Biology, the basic unit of which all living thins are composed is knows as cell. The cell is the smallest structural unit of living matter that is capable of functioning independently. A single cell can be a complete organism in itself, as in bacteria and protozoAnswer. A unicellular organism also captures and digests food, respires, excretes, grows, and reproduces. Similar functions in multi-cellular organisms are carried out by groups of specialized cell which are organized into tissues and organs such as, the higher plants and animals. Hence, ‘cell’ is known as the basic structural and functional unit of life.
Question. Explain why chloroplast are found only in plant cells.
Answer. Chloroplasts are found only in plant cells because they are required for photosynthesis.
Q1. Fill Ups:
i. Cells were first observed in cork by ________________.
ii. ___________________ is the longest cell in our body.
iii. ______________ is the smallest cell known with a size of ____________ micrometer.
iv. ______________ is present in plant cell but absent in animal cell while, ___________ is present in animal cell and absent in plant cell.
v. ________________ in human blood is a single cell.
vi. A _______________ is a group of cells performing a specific function.
vii. _______________ are used to colour parts of the cell to study their details.
viii. The plastids responsible for green color of leaves is ____________________.
ix. __________ controls the transfer of a hereditary characteristic from parents to offspring.
x. _____________________ cells having nuclear material without nuclear membrane.
xi. The cells, like onion cells and cheek cells are example of __________________cells.
xii. ___________________ is a structure that contains more than one type of tissues.
xiii. The porous membrane that allows the movement of materials between the cytoplasm and the inside of the nucleus is ________________________________.
xiv. The porous membrane that allows the movement of materials both inward and outward from the cells is ______________________________.
xv. Basic structural units of living organisms are _________ .
xvi. Protoplasm which is between nucleus and plasma membrane is_____________________.
xvii. _______________ and _____________ are cell organelles in a human cell.
Q2. Name Parts of Nucleus.
Q3. Give the functions of the following:
1. Nucleus 4. Cell Membrane
2. Plastids 5. Pseudopodia
3. Genes
Q4. Give the detailed structure of the nucleus of a cell?
Q5. Name any branched cell found in human body?
Q6. What are common similarities between all organisms?
Q7. Categorize the Organisms Based Upon their Cell.
Q8. Name the Largest and Smallest Single Cell in the World.
Q9. Define Protoplasm.
Q10.Few school students went for an educational trip to a nearby pond. There they divided themselves in groups of five and collected few samples of soil and pond water. Students brought the samples back to the school to study the microbes present in it.
(a) Name the instrument that is used to study microbes?
(b) Students found presence of Amoeba in the pond water sample. What kind of organism is Amoeba?
(c) What is the advantage of pseudopodia in an Amoeba?
(d) What values are expected from a student for a team work?
Q11. Choose the correct option:
1. Term used for the entire content of the living cell
a) Cytoplasm
b) Protoplasm
c) Nucleoplasm
d) Karyoplasm
2. Which of the following is absent in an animal cell:
a) Cell Wall
b) Plastids
c) Large Vacuoles
d) All of these
3. Cytoplasm is present in this region:
a) B/w Nuclear membrane and cell membrane
b) Inside the nucleus
c) Within the entire cell, including nucleus
d) None of these
4. Choose the correct sequence:
a) Tissue Cells Organ Organism
b) Cells Tissue Organ Organism
c) Organ Tissue Cell Organism
d) Cell Organ Tissue Organism
5. To enter or leave a cell, substances must pass through
a) cytoplasm
b) protoplasm
c) nucleus
d) plasma membrane
6. Bacterial cell are prokaryotic; in comparison to a typical eukaryotic cell they would
a) be smaller
b) have a smaller nucleus.
c) lacks a plasma membrane.
d) Have a greater variety of organelles
7. Which of the following clues would tell you whether a cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
a) the presence or absence of a rigid cell wall
b) whether or not the cell has cytoplasm
c) the presence or absence of chloroplast
d) whether or not the cell contains organized nucleus
1. Basic structural units of living organisms are _________
2. Three ways in which cells differ are ________________, _______________ and ____________
3. Largest animal cell is __________________________
4. Name 2 cells which change shape continuously ____________________, ______________________
5. Smallest cell is _______________________________
6. A unicellular Algae _________________________
7. An egg consists ________________________, _________________________
8. Long and branched cell in human body is _________________________
9. 3 basic cell parts are ______________________, __________________ and ____________________
10. Animal Cell is bounded by _____________________
11. Outer layer in plant cell is _______________________
12. Function of cell membrane and cell wall- ________________________________
13. Suicide bags of the cell.________________
14. Boss of the cell is ____________________
15. Power house of the cell is _______________________
16. Chloroplasts are found only in ____________
17. Protoplasm which is between nucleus and plasma membrane is _____________________
18. Non-Living component of the cell wall._______________________
19. Instrument used in biology lab to magnify objects_______________
20. Cells lacking nuclear membrane are (Prokaryotic cells/ Eukaryotic cells)
Worksheet for CBSE Science Class 8 Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Functions
We hope students liked the above worksheet for Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Functions designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 8 Science released by CBSE. Students of Class 8 should download in Pdf format and practice the questions and solutions given in the above worksheet for Class 8 Science on a daily basis. All the latest worksheets with answers have been developed for Science by referring to the most important and regularly asked topics that the students should learn and practice to get better scores in their class tests and examinations. Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to the NCERT book for Class 8 Science to develop the Science Class 8 worksheet. After solving the questions given in the worksheet which have been developed as per the latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 8 Science designed by our teachers. We have also provided a lot of MCQ questions for Class 8 Science in the worksheet so that you can solve questions relating to all topics given in each chapter.
You can download the CBSE Printable worksheets for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Functions for latest session from StudiesToday.com
There is no charge for the Printable worksheets for Class 8 CBSE Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Functions you can download everything free
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all latest NCERT Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Functions Class 8 Science test sheets with answers based on the latest books for the current academic session
CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Functions worksheets cover all topics as per the latest syllabus for current academic year.
Regular practice with Class 8 Science worksheets can help you understand all concepts better, you can identify weak areas, and improve your speed and accuracy.

