ASSIGNMENT - PHYSICS
CLASS IX
1. A car travels from stop A to stop B with a speed of 30 km/h and then returns back to A with a speed of 50 km/h. Find : (i) Displacement of the car. (ii) Average speed of the car.
2. An object starts linear motion with a velocity ‘u’ and under uniform acceleration ‘a’ it acquires a velocity ‘v’ in time ‘t’. Draw its velocity time graph. From this graph obtain the following equations.
(a) v=u+at (b) s=ut+½at2
3. Why is glass or chinaware packed with straw ?
4. The velocity–time graph of a car is given below. The car weighs 1000 kg. (i) What is the distance travelled by the car in the first 2 seconds ? (ii) What is the braking force at the end of 5 seconds to bring the car to a stop within one second ?
5. A man throws a ball of mass 0.5 kg vertically upward with a velocity of 25 m/s. Find : (a) the initial momentum of the ball (b) momentum of the ball at the half way mark of the maximum height
6. The velocity-time graph of an ascending passenger lift is as in the figure shown below.
Identify the kind of motion of lift represented by lines OA and BC. (ii) Calculate the acceleration of the lift :
(a) During the first two seconds. (b) Between the 3rd and 10th second. (c) During the last two seconds.
7. (a) State Newton‟s third law of motion. Give two examples to illustrate it.
(b) Explain why a cricketer moves his hands backwards while catching a fast moving cricket ball.
8. In a high jump athletic event the athletes are made to fall on a cushioned bed. Why ?
9. If a stone is thrown vertically upwards to a height of 19.6m, calculate
(i) the velocity with which it was thrown and (ii) time taken by it to reach the highest point. Take g = 10m/s2
10. For how much time should the force of 400N be exerted on a body of mass 8kg to increase its velocity from 150 m/s to 300 m/s ?
11. Look at the diagram above and answer the following questions :
(a) When a force is applied through the free end of the spring balance A, the reading on the spring balance A is 15 gwt. What will be the reading of spring balance B ? Write reasons for your answer.
(b) Name the force which balance A exerts on balance B and the force of balance B on balance A.
12. (a) State the law of conservation of momentum.
(b) A body of mass 2 kg, initially moving with a velocity of 10m/s, collides with another body of mass 5 kg at rest. After collision velocity of first body becomes 1m/s. Find the velocity of second body
13. (a) ‘Lactometers are used to determine the purity of a sample of milk’. State the principle on which this instrument is based on.
(b) Write two factors on which the buoyant force acting on a body when immersed in a liquid depends.
14. An object has a mass of 30 kg. What is its weight (i) on the moon (ii) on another planet ? The value of ‘g’ on moon is 1/6 the value of ‘g’ on the earth. The value of ‘g’ on the planet is 3 times the value of ‘g’ on the earth. Take (ge=10 m/s2)
15. (a) Tabulate any two differences between mass and weight.
(b) A body weighs 30 kg on the surface of earth. How much would it weigh on the surface of a planet whose mass is the mass of earth and radius is half that of earth.
16. Give any two differences between G and g’
17. What happens to the gravitational force between two objects, if :
(i) the mass of an object is doubled. (ii) the distance between the objects is tripled. (iii) mass of both the objects is doubled.
18. A stone is dropped from the edge of a 4.9 m high roof. Find out the following : (i) Time taken to fall 4.9m ?
(ii) Velocity just before it reaches the ground. (iii) What is its acceleration after 1 s and 2 s from start ?
19. From the given data infer whether the given object will float or sink in the given solution?
Find:
i) will a bar of gold sink in mercury? ii) will a piece of platinum float on gasoline?
iii) will a block of paraffin sink in gasoline? iv)Will a piece of platinum sink in mercury?
20. (a) Define one joule of energy.
(b) Two cars X and Y of masses m1 and m2 accelerate from rest in linear direction. The mass of Y is twice of X. The acceleration due to car X is 1 ms-2. After a time of t seconds it is noticed that the Kinetic energy of X is twice of Kinetic energy of Y. Calculate the acceleration produced by the car Y.
21. (a) State and prove law of conservation of energy for a freely falling body.
(b) What is the power expended by the engine of the car mass 1.5 tonnes which increases the velocity of the car from 36 km/hr to 72 km/hr in 20 seconds.
22. (a) Define Kinetic energy and derive an expression for it.
(b) How many joules of energy make one KWh.
(c) A bullet of mass 50 gm is fired from a gun. It leaves the barrel with a velocity of 100 m/s in 0.01 seconds. Calculate the power expended by the gun in firing the bullet.
23. A child of mass 35kg is sitting on a trolley of mass 5 kg. The trolley is given a push by applying a force so that begins to move with a speed of 4m/s. The trolley comes to rest after covering a distance of 16 m. Find
(i) the work done on the trolley (ii) the work done by the trolley before coming the nest.
24. Define commercial unit of energy. Derive relationship between this unit of energy and SI unit of energy. An electrical device of 500 W is used for 10 hours per day. Calculate the energy consumed in the month of April.
25. The frequency of a sound source is 600 Hz. The speed of sound in a medium is 330 m/s. What will be the linear distance between an adjacent crest and trough.
26. (a) What is an echo ? (b) For how long does the sensation of a sound persist in our brain ? (c) Echo is not heard in a small room. why ? (d) Why are ceilings of concert halls, conference halls and cinema halls are curved?
27. (a) What is the role of hammer bone, anvil bone, stirrup bone and cochlea of human ear in hearing a sound ?
(b) Write a difference between pitch of sound and loudness. (c) The depth of sea at a point is 15300 m. Find out after what time the sound signal sent by a SONAR device fitted in the ship will reach the sea bed from that point. Take the speed of sound in sea water as 1530 m/s.
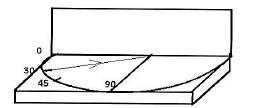
28. In an experiment to verify the laws of reflection of sound for the given angle of incidence what is the angle of reflection ?
29. A pulse is generated at one end of the slinky of length 10m. The pulse returns back to its point of generation in 10 seconds. The velocity of the pulse in the slinky will be : (a) 4 m/s (b) 3 m/s (c) 2 m/s (d) 1 m/s
30. A longitudinal pulse is produced in a slinky. The frequency of the pulse is 60 Hz and it travels at a speed of
30 cm/s. What is the separation between consecutive compressions?
31. A pulse was created in a slinky of length 8m. It was observed that it returned after reflection at the point of creation 5 times in 10s.What is the speed of pulse through slinky ?
32. A bat can hear sound of frequencies up to 120 KHz of the speed of sound in air 360 m/s, determine the wavelength of sound at this frequency.
33. An object of mass 2 kg is sliding with a constant velocity of 4 m/s on a friction less horizontal table. The force required to keep the object moving with the same velocity is:
(a) 32 N (b) 0 N (c) 2 N (d) 8 N
34. Read the paragraph and answer the questions that follow.
In a rocket, a large volume of gases produced by the combustion of fuel is allowed to escape through its tail nozzle in the downward direction with the tremendous speed and makes the rocket to move upward.
a) Which law is involved in the above situation?
b) Give another application of the above stated law.
c) Why don’t the forces involved in the above law cancel each other?
d) Why do passengers get a backward jerk when a bus suddenly begins to move?
35. How much time will be required to perform 520 J of work at the rate of 20 W?
(a) 24s (b) 16s (c) 20 s (d) 26 s
36. The distance between two bodies becomes 6 times more than the usual distance. The F becomes
a. 36 times b. 6 times c. 12 times d. 1/36 times
37. Which part of human ear converts sound vibrations into electrical signals
a. Hammer b. Stirrup c. Tympanic membrane d. Cochlea
Please click on below link to download CBSE Class 9 Science Worksheet Set C

