WATER
Introduction
Water is one of the most useful substances on the Earth. Without water, life could not exist on Earth. This is because water is the most important constituent of living things. It is also the home of many organisms that live in it. In general, water is life.
1.1 Properties of Water
Water has various properties that make its unique chemical compound. But these properties can be generalized as chemical and physical properties.
A. Physical properties of water
Physical properties are the features by which we distinguish a substance from other substances using sense organs. Color, odor, taste, density, boiling point, and melting points are physical properties of substance. Some of the physical properties are specific and constant for given substance. These physical properties include density, boiling point and melting point. The physical properties of water are the following.
A. Density of water
Density is the mass of the substance divided by its volume.
Thus, density = Volume/mass ,In short, ρ = v/m
where ρ (rho) = density, m = mass, v = Volume
Therefore, density is the mass per unit volume of a substance. It is expressed in the unit gram/cubic centimeter or kilogram/ meter cubic. Density is a characteristic property of substance and it’s used to identify the material (substance).
The density of water at 40C is 1 gram/milliliter or 1 gram/cubic centimeter. The density of water changes as temperature changes. As the temperature decreases below 40C the density of water decreases. That is why ice floats on liquid water.
B. Color of water: Pure water is colorless, odorless, tasteless and transparent.
C. States of water: You already know that matter exists in three states.
1. Solid state 2. Liquid state3. Gas state
Solids have a definite shape and volume. Liquids have no definite shape they will assume the shape of their container but a definite volume while gases have neither definite shape nor definite volume. Depending on temperature and pressure water can exist in the three states of matter. It exists as liquid (water) at standard temperature and pressure. On cooling (decreasing temperature below 00c) water exists as ice (solid) while boiling changes it to water vapor (gas). The change of one state of water to another is a physical change because it involves change of shape only. Therefore, the existence of water in the three states of matter is a physical property.
d) Boiling point of water
The boiling point of water is the temperature at which water changes into steam (water vapor). Water has the ability to boil at higher and lower altitudes. The boiling point of water at sea level is 1000c. Its boiling point decreases at higher altitudes due to decrease in atmospheric (air) pressure.
e) Melting point of water
Meting point of water is the temperature at which ice (solid water) changes into liquid water. The melting point of ice is 00c. Melting of ice is also a physical change as it involves only change of shape.
A. Chemical properties of water
Chemical properties are the characteristics features observed when a substance changes into another new substance completely different from the original one. Some of the chemical properties of water are the following.
1. Water is a neutral compound
In chapter one you learnt that oxides are classified as acidic, basic, neutral, per & amphoteric oxides. We also mentioned that neutral oxides do not react with acids and bases to form salt and water. Moreover, water solution of a neutral oxide is neither acidic nor basic in property. Thus, water is an example of neutral oxide. It is neither acidic nor basic. The neutrality of water can be confirmed using indicator papers. If we dip a red or blue litmus paper into a beaker of pure water, the paper does not show any changes of color. This is because water is neutral.
b) Reaction of water with other chemicals
Water forms useful substances when combined with other chemicals. This chemical property is due to the formation of new substance when water combines with other chemicals.
Examples
1. Water + Potassium → Potassium hydroxide
2. Water + Sodium → Sodium hydroxide
3. Water + Carbon dioxide → Carbonic acid
4. Water + cement + Sand → Concrete
5. Water + digested food + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide+ Energy
6. Water + Carbon dioxide Sunlight Carbohydrate + oxygen
Chlorophyll
2 Sources of Water
Rain, rivers, lakes, ponds, sea, springs, wells etc. are the main sources of natural water. None of these natural sources of water is pure.
1) Rain Originally, rain-water is the purest form of natural water. But while falling down through the atmosphere it gets mixed with dust particles, germs and gaseous air pollutants released from factories.
2) Lakes and rivers these sources of water contain many soluble minerals and insoluble impurities, germs, harmful chemicals and wastes from factories and households and germs.
3) Ponds contain all types of soluble and suspended impurities & germs.
4) Sea or Ocean the biggest source of water on the Earth. It is the impurest form of all natural waters. It contains all types of impurities. It’s saline.(salty)
3. Pollution of Water
Water gets polluted whenever household wastes, chemicals from industries, insecticides, herbicides, sewage water, unwanted by product chemicals from factories & harmful gaseous air pollutants mix with pure water. Pollution kills fish and other aquatic organisms. It also makes the water unsafe for certain uses.
4. Water purification processes
Water from various sources contains impurities and germs. So, it must be purified before drinking. In Ethiopia the purified water comes from Legadedi, Gefersa and Akaki underground water wells.
Water of small rivers, springs and rain are stored in a reservoir called dam. Aquatic algae grow on the surface of water stored in dam and remove organic substances that cause odor. Then certain amount of water transferred to small dam for purification solid matters settle down. Finally chlorine is added to kill germs after the water goes to other storages. The purity of water is again checked in the laboratory and send to our house through pipes.
4.1 Water purification methods
Water purification is the process of removing dissolved chemical compounds, insoluble solids float on or suspended in water and germs to make the water fit for drinking and other uses. To make the water free from these impurities and germs we can use different purification methods.
1) Decantation
Decantation removes settle able solid impurities from water. Decanted water still may contain fine particles and germs which are invisible to naked eye. Thus, decanted water is not purified or safe to drink.
Process of decantation
1) Collect the water to be purified in a jar
2) Leave the jar undisturbed for a while
3) Settle able solid impurities settle at the bottom of the jar below the clear water.
4) Pour the clear water in another container gently.
2) Filtration
Filtration is another method of purifying water. It is a method of separating insoluble solid impurities from water by passing it through a perforated layer of filter paper, cotton layer, fine cloth or a layer of sand. The filter paper is fold into funnel shape and placed on the mouth of clean glass beaker.
Then pour the dirty water on to filter paper. The solid impurity remain in the filter paper is called residue while the pure liquid passing through filter paper and collected in the beaker is called filtrate. The filtered water is not safe to drink as it may still contain germs.
3) Boiling
Boiling the water kills germs present in it. The water which is decanted and filtered must be boiled in order to make it completely safe for drink.
4) Adding chlorine and potassium permanganate
Adding chlorine or potassium permanganate to the water before supply kills germs.
3.5 Water-Born Diseases
As we learnt at the beginning of this chapter, water is a very useful resource. We can not live without water. Fresh water sources like streams, rivers, lakes and springs are very essential for our survival. The water we use for drinking, bathing, cleaning and washing can get contaminated by
o Wastes from house holds
o Dead animals dump into rivers and streams
o Sewages
o Industrial wastes
o Animal wastes (e.g. cow dung, horse dung)
o Human wastes etc.
A contaminated water can spread a number of water- borne diseases like cholera, amoebiasis, gardiasis, ascariasis typhoid etc
1. Cholera
Cholera is a good example of water-born disease. It is caused by a bacterium called vibrio-cholerae. It is a communicable disease. Drinking contaminated water, or washing food or utensils in it, is the most common means of transmission of water borne diseases. Direct contamination of food with faeces from infected person as a result of poor personal and community hygiene is also the possible means of transmission of the diseases. Cholera commonly occurs as epidemic in areas
1. where community hygiene is poor
2. affected by flooding and earth quake.
Vibrio-cholerae multiplies in our intestine and release powerful toxins. The toxins result in violent inflammation of the intestine and produce a watery diarrhea. Unless and other wise immediate medical treatment is taken, the toxins lead to death due to the loss of water with mineral salts from the body. Thus, dehydration (class of water) is rapid and quick resulting in death.
Symptoms of Cholera
1. Inflammation of the gut
2. Severe diarrhea /” rice water”/
3. Dehydration and loss of mineral salt make the body deathly cold and damp.
Prevention of cholera
Cholera is one of the epidemic diseases which needs prompt international and national actions to prevent its spread. Cholera can be prevented by
1. Provision of clean drinking water
2. High standards of public and personal hygiene
3. Proper sewage treatment & sanitation
4. Vaccination etc.
2. Amoebiasis
Amoebiasis is also known as amoebic dysentery. It is caused by single celled protozoa called Ent amoeba histolytica. The most common means of transmission of amoebiasis are
• Drinking contaminated water
• Uncooked food/fruits and vegetables/
• Washing food or utensils with contaminated water
• Unhygienic food handling and preparation
Symptoms of amoebic dysentery
A. Diarrhea with loss of blood in stools C. Fever
B. Nausea D. Vomiting
Prevention of Amoebic dysentery
i. Provision of clean drinking water
ii. Hygienic food preparation and handling
iii. Wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly with pure water before use.
3. Giardiasis
Giardiasis is caused by protozoa called giardia. The protozoa cause dysentery some what similar to amoebiasis. The disease transmits from person to person through contact under poor hygienic conditions. Other means of transmission include
i. Drinking contaminated water
ii. Washing food like vegetables and fruits & utensils with contaminated water.
iii. Unhygienic food preparation & handling
4. Ascariasis
Ascariasis is caused by a parasitic worm called ascariasis. Children are invariably infected with ascariasis. This is because their hands can easily be contaminated with ascariasis eggs while playing in dirty areas. The eggs are attached to their hands and swallowed if they eat with dirty hands. Thus washing hands before meal is very important. The worms attach themselves to the small intestine and absorb digested food from the host.
Symptoms of ascariasis
i. Nausea
ii. Blotted belly
iii. Loss of appetite
iv. General body weakness
5. Bilharziasis
Bilharziasis is /schistosomiasis/ is a water-borne disease caused by a parasitic worm called bilharzias /schist- soma/. The adult worms live in the blood vessels of infected person associated with intestine and bladder. Bilharzia is a tropical disease /occurs in the warmer part of Africa, Latin America and Far East/ which makes people feel ill and unable to work properly.
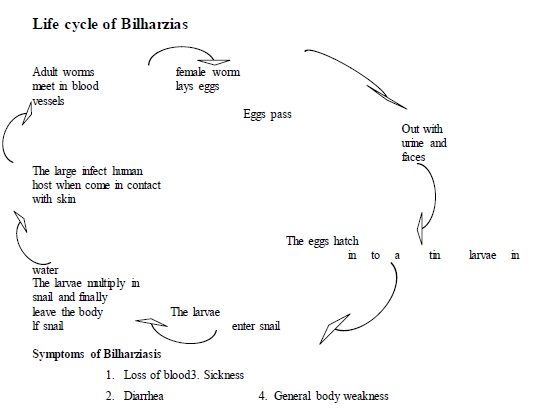
3.6.1 Prevention of Water-Borne Diseases
Most of the water-borne diseases are infectious. More than 1.2 billion people worldwide do not have access to pure water. Thus, they are highly vulnerable to water-borne diseases. To prevent water-borne diseases, the water we use for drinking, cleaning, bathing and washing should be clean and pure. If you are not sure the purity of the water you should boil it for a while to kill germs and parasitic worms. In general, to prevent water-borne diseases one should take the following measures.
i. Use water only from water tap or filter and boil non-tap waters.
ii. Use clean and covered vessels/containers/ for storage of water.
iii. High standards of public and community hygienic. Do not defecate in /around rivers and streams. Use sanitary latrine and dispose wastes properly in land fill.
iv. Never bath in dirty water.
v. Use clean water to prepare and wash food and utensils.
vi. Cook foods thoroughly before you eat.
I Tick the right answer.
a. The season with longer nights and shorter days.
summer winter rainy season
b. The soil which has large particles with lot of space between them.
sandy soil loamy soil clayey soil
c. The gas used by the plants to make food.
oxygen carbon dioxide nitrogen
d. The soil used to make pots.
sandy soil clayey soil loamy soil
II Name the following.
a. Fast blowing wind . : ________________________ .
b. The soft rock used to write on a slate. : ________________________ .
c. Rotten plants and animals found in the soil. : ________________________ .
d. The mixture of sand and clay. : ________________________ .
e. Solid form of water. : ________________________
III. Differentiate between Summer season and Winter season.
Summer season Winter season
1. 1.
2. 2.
IV. Look at the picture and answer the following questions.
a. Identify the picture _______________________
b. Label the process in the given box.
V. Answer the following questions.
1. What is water cycle ?
2. Why is soil important for living things?
VI. Give reason.
1. Gardeners like loamy soil
VII. Life Skill.
Water is very precious and it is very important to save . There are many ways to conserve water.
Put a tick for the right option.
a. Leave the tap open while brushing your teeth. _______
b. Rain water harvesting . _______
c. Building dams . _________
d. Take longer shower. _______
Q.1 Draw and label the diagram and also answer the related questions.

1. What is the Function of root?
Ans:________________________
2. What is the function of root?
Ans:________________________
3. What is the function of stem?
Ans:_______________________
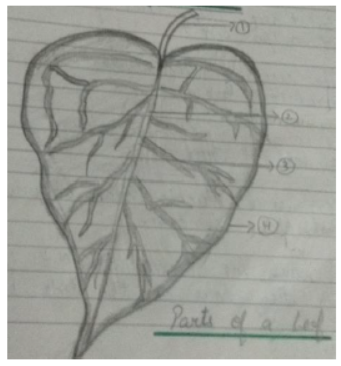
1. Why leaf is called the kitchen of plants?
Ans:________________________
2. What is photosynthesis?
Ans: :________________________
3. Give two examples of food stored in leaves.
Ans:1.__________’
2.__________
Q.1 Choose the correct answer:-
a. Animal that swallows its food.
Snake ( ) frog ( ) rabbit ( )
b. Animals that has long and sticky tongue.
frog ( ) dog ( ) Rat ( )
c. Animals that gnaw its food.
Rat ( ) Squirrel ( ) both of these ( )
d. Animal that chew cud.
Cat ( ) Cow ( ) Elephant ( )
e. Animal that lap milk and water.
Cat ( ) dog ( ) both of these ( )
f. Animal that eats or drinks by its trunk.
Elephant ( ) goat ( ) fox ( )
g. An insect that has long sucking tube to suck nectar.
Mosquito ( ) leech ( ) butterfly ( )
h. An insect that suck blood from the bodies of other animals.
Mosquito ( ) leech ( ) both of these ( )
i. Animal that swallow soil.
Snake ( ) earthworm( ) horse( )
j. Animal that swallow grass.
Cow ( ) dog ( ) camel ( )
Please click on below link to download CBSE Class 3 Science Worksheet P

