Get the most accurate NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics Chapter 4 Revenue here. Updated for the 2025-26 academic session, these solutions are based on the latest NCERT textbooks for Class 12 Economics. Our expert-created answers for Class 12 Economics are available for free download in PDF format.
Detailed Chapter 4 Revenue NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics
For Class 12 students, solving NCERT textbook questions is the most effective way to build a strong conceptual foundation. Our Class 12 Economics solutions follow a detailed, step-by-step approach to ensure you understand the logic behind every answer. Practicing these Chapter 4 Revenue solutions will improve your exam performance.
Class 12 Economics Chapter 4 Revenue NCERT Solutions PDF
Question. How are the total revenue of a firm, market price, and the quantity sold by the firm related to each other?
Answer: Total Revenue = Market Price x Quantity sold
Question. Compute the total revenue, marginal revenue and average revenue schedules in the following table. Market price of each unit of good is Rs. 10.
| Quantity sold | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| TR | ||||||
| MR | ||||||
| AR |
Answer:
| QUANTITY SOLD | TR | MR | AR |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| 1 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| 2 | 20 | 10 | 10 |
| 3 | 30 | 10 | 10 |
| 4 | 40 | 10 | 10 |
| 5 | 50 | 10 | 10 |
| 6 | 60 | 10 | 10 |
Question. What would be the shape of the demand curve so that the total revenue curve is
(a) A positively sloped straight line passing through the origin?
(b) A horizontal line?
Answer:
(a) If the total revenue curve is a positively sloped straight line passing through the origin, then the slope of the demand curve will be a horizontal line parallel to the x-axis. This happens when prices are constant.
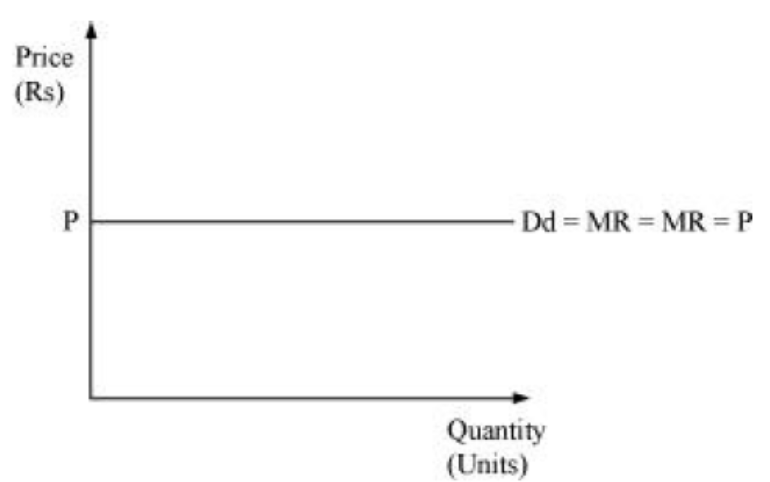
(b) If the total revenue curve is a horizontal line, then the demand curve will be downward sloping. Firms can increase their volume by decreasing the price i.e., AR falls with increase in sales
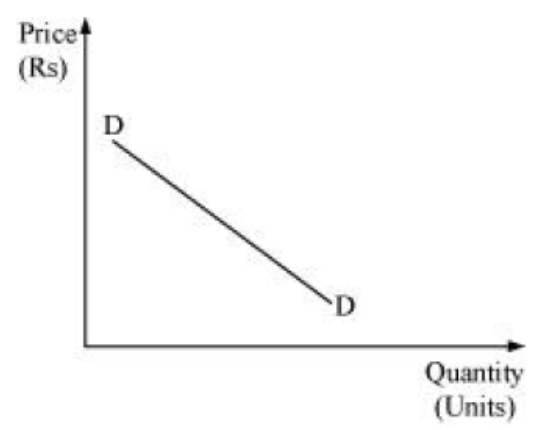
Question. Comment on the shape of the MR curve in case the TR curve is a (i) positively sloped straight line, (ii) horizontal straight line.
Answer: (i) When TR curve is positively sloped straight line, MR is a horizontal line. MR coincides with the demand curve. Price or AR is constant at each level of output.
When AR is constant, MR is also constant.
(ii) When TR is a horizontal straight line, MR is zero. It is because horizontal TR means when price falls, quantity demanded rises in the same proportion. Thus, MR is zero. MR curve coincides with the x-axis
Question. From the schedule provided below calculate the total revenue, demand curve and the price elasticity of demand:
| Quantity | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| Marginal Revenue | 10 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | -5 |
Answer:
| Quantity | MR | TR | AR | Ed = ΔQ/ΔP x P/Q |
| 1 | 10 | 10 | 10 | - |
| 2 | 6 | 16 | 8 | 5 |
| 3 | 2 | 18 | 6 | 2 |
| 4 | 2 | 20 | 5 | 2 |
| 5 | 2 | 22 | 4.4 | 2.5 |
| 6 | 0 | 22 | 3.6 | 1 |
| 7 | 0 | 22 | 3.1 | 1.2 |
| 8 | 0 | 22 | 2.7 | 1.1 |
| 9 | -5 | 17 | 1.9 | 0.38 |
MORE QUESTIONS SOLVED
I. Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Give the meaning of revenue. Or
Define revenue.
Answer: Revenue of a firm refers to receipts from the sale of output in a given period.
Question. Define total revenue.
Answer: The amount received from the sale of given amount of output is known as Total Revenue.
For example, if a firm sells 100 chairs at a price of? 200 per chair, The total revenue will be
100 Chairs x Rs. 200 = Rs 20,000.
Question.Define average revenue.
Answer: The per unit amount received from the sale of given amount of output.
Question. Define marginal revenue.
Answer: The amount received from the sale of additional unit of output is known as Marginal Revenue.
Question. How is MR derived from TR?
Answer: MRn=TRn - TRn-1
Question. What change in TR will result in a decrease in MR?
Answer: When TR increases at a diminishing rate.
Question. When TR falls, what happens to MR?
Answer: MR is negative.
Question. How does TR change with the output when MR is zero?
Answer: Then, TR is maximum and constant.
Question. What is the behaviour of average revenue in a market in which a firm can sell more only by lowering the price?
Answer: Average revenue will fall.
Question. What is the behaviour of Marginal Revenue in a market in which a firm can sell any quantity of the output it produces at a given price?
Answer: Marginal revenue remains constant.
II. Multiple Choice Questions
Question. Assume that when price is Rs.20, the quantity demanded is 9 units, and when price is Rs.19 the quantity demanded is 10 units. Based on this information what is the marginal revenue resulting from an increase in output from 9 units to 10 units.
(a) Rs.20
(b)Rs.19
(c) Rs.10
(d) Rs. 1
Answer: (c)
Question. Assume that when price is Rs.20, the quantity demanded is 15 units and when price is Rs.18, the quantity demanded is 16 units. Based on this information what is the marginal revenue resulting from an increase in output from 15 units to 16 units?
(a) Rs. 18
(b) Rs.16
(c) Rs.12
(d) Rs. 28
Answer: (c)
Question. Marginal Revenue is equal to:
(a) The change in price divided by the change in output.
(b) The change in quantity divided by the change in price.
(c) The change in P * Q due to a one unit change in output.
(d) Price, but only if the firm is a price searcher.
Answer: (c)
Question. Total revenue =
(a) Price x quantity
(b) Price x income
(c) Income x quantity
(d) None of these.
Answer: (a)
Question. Average revenue is the revenue earned
(a) per unit of input
(b) per unit of output
(c) different units of input
(d) different units of output
Answer: (b)
Question. AR can be symbolically written as:
(a) MR/Q
(b) Price x quantity
(c) TR/Q
(d) None of these.
Answer: (c)
Question. AR is also known as:
(a) Price
(b) Income
(c) Revenue
(d) None of these.
Answer: (a)
Question. Marginal revenue can be defined as the change in total revenue resulting from—
(a) purchase of an additional unit of a commodity
(b) sale of an additional unit of a commodity
(c) sale of subsequent units of a product
(d) None of these.
Answer: (b)
Question. When price remains constant at all level of output, total revenue—
(a) increases at increasing rate
(b) increases at diminishing rate
(c) increases at constant rate
(d) None of these.
Answer: (c)
Question. How does TR change with output when MR is negative?
(a) TR falls with the increase in output
(b) TR rise with the increase in output
(c) TR falls with the decrease in output
(d) None of these.
Answer: (a)
Question. Average revenue curve is also known as:
(a) Profit Curve
(b) Demand Curve
(c) Average Cost Curve
(d) Indifference Curve
Answer: (b)
III. Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Calculate Average Revenue (AR) and Marginal Revenue (MR).
| Units sold Q | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| TR (Rs) | 20 | 36 | 48 | 56 | 60 | 60 | 56 |
Answer:
| Units sold Q | TR(Rs) | AR(Rs) | MR(Rs) |
| 1 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| 2 | 36 | 18 | 16 |
| 3 | 48 | 16 | 12 |
| 4 | 56 | 14 | 8 |
| 5 | 60 | 12 | 4 |
| 6 | 60 | 10 | 0 |
| 7 | 56 | 8 | -4 |
Question. Calculate TR and AR from the following data.
| Units sold Q | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| MR (Rs) | 14 | 10 | 7 | 5 | 0 | -3 | -5 |
Answer:
| Units sold Q | MR (Rs) | TR =∑MR | AR (Rs) |
| 1 | 14 | 14+0=14 | 14 |
| 2 | 10 | 14+10=24 | 12 |
| 3 | 7 | 24+7=31 | 10.33 |
| 4 | 5 | 31+5=36 | 9 |
| 5 | 0 | 36+0=36 | 7.2 |
| 6 | -3 | 36-3=33 | 5.5 |
| 7 | -5 | 35-5=28 | 4 |
Question. Calculate TR and MR from the following data.
| Units sold | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | - |
| AR (Rs) | 25 | 23 | 21 | 19 | 18 | 15 | - |
Answer:
| Units sold Q | AR (Rs) | TR(Rs) | MR (Rs) |
| 1 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 2 | 23 | 46 | 21 |
| 3 | 21 | 63 | 17 |
| 4 | 19 | 76 | 13 |
| 5 | 18 | 90 | 14 |
| 6 | 15 | 90 | 0 |
| - | - | - | - |
Question. Complete the following table
|
Price(Rs) |
12 | 10 | 8 | 6 |
| Output | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| TR(Rs) | - | - | - | - |
| MR(Rs) | - | - | - | - |
Answer:
| Price(Rs) | Output Units |
TR(Rs) P×Q |
MR(Rs) TRn-TRn-1 |
| 12 | 1 | 12 | 12 |
| 10 | 2 | 20 | 8 |
| 8 | 3 | 24 | 4 |
| 6 | 4 | 24 | 0 |
Question. Complete the following table.
| Price(Rs) | 10 | 9 | 6 | 4 |
| Output Units | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| TR(Rs) | - | - | - | - |
| MR(Rs) | - | - | - | - |
Answer:
| Price(Rs) | Output Units | TR(Rs) P×Q |
MR(Rs) TRn-TRn-1 |
| 10 | 1 | 10 | 10 |
| 9 | 2 | 18 | 8 |
| 6 | 3 | 18 | 0 |
| 4 | 4 | 16 | -2 |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 1 Introduction to Economics |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 2 Demand |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 2 Elasticity of Demand |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 3 Cost |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 3 Production |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 4 Perfect Competition |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 4 Producer Equilibrium |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 4 Revenue |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 4 Supply |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 6 Non Competitive Market |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 1 Introduction to Macroand its Concepts |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 2 National Income and Related Aggregates |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 3 Banking |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 3 Money |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 4 Aggregate Demand and Its Related Concepts |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 4 National Income Determination and Multiplier |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 5 Government Budget and the Economy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 6 Balance of Payment |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 6 Foreign Exchange Rate |
Important Practice Resources for Class 12 Economics
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 4 Revenue
Students can now access the NCERT Solutions for Chapter 4 Revenue prepared by teachers on our website. These solutions cover all questions in exercise in your Class 12 Economics textbook. Each answer is updated based on the current academic session as per the latest NCERT syllabus.
Detailed Explanations for Chapter 4 Revenue
Our expert teachers have provided step-by-step explanations for all the difficult questions in the Class 12 Economics chapter. Along with the final answers, we have also explained the concept behind it to help you build stronger understanding of each topic. This will be really helpful for Class 12 students who want to understand both theoretical and practical questions. By studying these NCERT Questions and Answers your basic concepts will improve a lot.
Benefits of using Economics Class 12 Solved Papers
Using our Economics solutions regularly students will be able to improve their logical thinking and problem-solving speed. These Class 12 solutions are a guide for self-study and homework assistance. Along with the chapter-wise solutions, you should also refer to our Revision Notes and Sample Papers for Chapter 4 Revenue to get a complete preparation experience.
The complete and updated is available for free on StudiesToday.com. These solutions for Class 12 Economics are as per latest NCERT curriculum.
Yes, our experts have revised the as per 2026 exam pattern. All textbook exercises have been solved and have added explanation about how the Economics concepts are applied in case-study and assertion-reasoning questions.
Toppers recommend using NCERT language because NCERT marking schemes are strictly based on textbook definitions. Our will help students to get full marks in the theory paper.
Yes, we provide bilingual support for Class 12 Economics. You can access in both English and Hindi medium.
Yes, you can download the entire in printable PDF format for offline study on any device.

