Get the most accurate NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics Chapter 6 Non Competitive Market here. Updated for the 2025-26 academic session, these solutions are based on the latest NCERT textbooks for Class 12 Economics. Our expert-created answers for Class 12 Economics are available for free download in PDF format.
Detailed Chapter 6 Non Competitive Market NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics
For Class 12 students, solving NCERT textbook questions is the most effective way to build a strong conceptual foundation. Our Class 12 Economics solutions follow a detailed, step-by-step approach to ensure you understand the logic behind every answer. Practicing these Chapter 6 Non Competitive Market solutions will improve your exam performance.
Class 12 Economics Chapter 6 Non Competitive Market NCERT Solutions PDF
Question. Explain why the demand curve facing a firm under monopolistic competition is negatively sloped?
Answer:
1. The demand curve of a firm under monopolistic competition is negatively sloped because of product differentiation.
2. The product of the sellers are differentiated but close substitutes of one another.
3. Each seller has some degree of monopoly power of ‘Making’ the price. But since there are many close substitutes available, the result is downward sloping and elastic demand curve.
Question. What is the reason for the long run equilibrium of a firm in monopolistic competition to be associated with zero profit?
Answer:
1. The reason why firm in monopolistic competition earns zero profit in the long run is free entry and exit of firm.
2. If firm earns super-normal profits in the short run then new entry will take place in the long run. If the firm is incurring losses in the short run, firm will leave in the longrun.
3. The result is zero abnormal profits in the long run.
Question. What is the value of MR when the demand curve is elastic?
Answer:
The relationship between MR and elasticity of demand is given by –
MR = P (1 – 1/Ed)
When demand curve is elastic, i.e. Ed > 1, the MR will be positive because for any value of Ed, 1/Ed will be less than 1.
The graph representing it is given below –
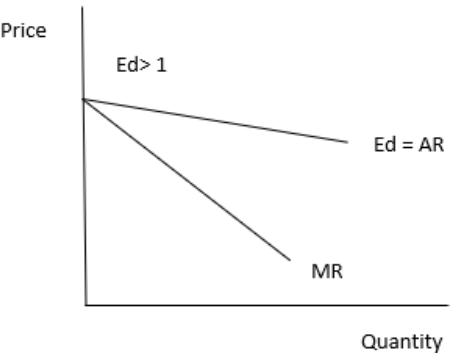
Question. List the three different ways in which oligopoly firms may behave.
Answer: Oligopoly firm may—:
1. Cooperate with each other and formally have a contract or written document of their policies.
2. Cooperate with each other but have tacit (informal) understanding.
3. Not cooperate with each other.
Question. What is meant by prices being rigid? How can oligopoly behaviour lead to such an outcome?
Answer:
1. Price rigidity refers to a situation in which whether there is change in demand and supply, the price tends to stay fixed.
2. In an oligopolistic market firms. Are in a position to influence the prices.
3. However, they stick to their prices in order to avoid a price war. If a firm tries to reduce the price the rivals will also react by reducing their prices. So, it will be of no benefit.
4. Likewise, if a firm tries to raise the price other firms will not do so. As a result, the firm which intended to raise the price will lose its customers. So, oligopoly behaviour leads
to price rigidity in an oligopolistic market.
MORE QUESTIONS SOLVED
I. Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Define monopoly.
Answer: ‘Mono’ means single and ‘poly’ means seller, i.e., single seller. Monopoly is a market situation where there is a single firm selling the commodity and there is no close substitute of the commodity sold by the monopolist.
Question. Under which market form, firm is a price-maker?
Answer: Monopoly.
Question. What are the shapes of AR and MR curves under monopoly?
Answer: Both AR and MR curves slope downward s. ‘
Question. How many firms are there in a monopoly market?
Answer: One firm.
Question. What is a price-maker firm?
Answer: A price maker firm is one to fix the price itself because of its monopoly power.
Question. What does Monopolistic Competition mean?
Answer: It refers to a market situation in which there are many firms which sell closely related but differentiated products.
Question. Why is the demand curve under monopoly less elastic as compared to the demand curve under monopolistic competition?
Answer: Demand curve under monopoly is less elastic as compared to the demand curve under monopolistic competition due to absence of close substitutes in monopoly.
Question. Define product differentiation.
Answer: Product differentiation refers to differentiating the products on the : basis of brand, size, colour, shape, etc.
Question. In which form of market there is product differentiation?
Answer: Monopolistic competition.
Question. Give the meaning of ‘Oligopoly’.
Answer: Oligopoly is a market situation in which an industry has only a few firms (or few large firms producing most of its output) mutually dependent for taking decisions about price and output.
II. Multiple Choice Questions
Question. Which one of the following statement is not a characteristic of monopolistic competition?
(a) Ease of entry into the industry.
(b) Product differentiation.
(c) A relatively large number of sellers.
(d) A homogenous product.
Answer: (d)
Question. All of the following are characteristics of a monopoly except:———————–.
(a) There is a single firm.
(b) The firm is a price-taker.
(c) The firm produces a unique product.
(d) The existence of some advertising.
Answer: (b)
Question. Oligopolistic industries are characterized by—
(a) A few dominant firms and substantial barriers to entry.
(b) A few large firms and no entry barriers.
(c) A large number of small firms and no entry barriers.
(d) One dominant firm and low entry barriers.
Answer: (a)
Question. Monopolistic competition differs from perfect competition primarily becaus—
(a) in monopolistic competition firms can differentiate their products.
(b) in perfect competition firms can differentiate their products.
(c) in monopolistic competition entry into the industry is blocked.
(d) in monopolistic competition there are relatively few barriers to entry.
Answer: (a)
Question. In which form of the market structure is the degree of control over the price of its product by a firm very large?
(a) Monopoly
(b) Imperfect Competition
(c) Oligopoly
(d) Perfect competition
Answer: (a)
Question. Under which one of the following forms of market structure does a firm have no control over the price of its product?
(a) Monopoly
(b) Monopolistic competition
(c) Oligopoly
(d) Perfect competition
Answer: (d)
Question. Price discrimination will be profitable only if the elasticity of demand in different sub markets is:
(a) Uniform
(b) Different
(c) Less
(d) Zero
Answer: (b)
Question. Suppose that the demand curve for the XYZ Co. slopes downward and to the right. We can conclude that
(a) The firm operates in a perfectly competitive market.
(b) The firm can sell all that it wants to at the established market price.
(c) The XYZ Co. is not a price taker in the market because it must lower the price to sell additional units of output.
(d) The XYZ Co. will not be able to maximise profits because price and revenue are subject to change.
Answer: (c)
Question. One characteristic not typical of Oligopolistic industry is its:
(a) Horizontal demand curve.
(b) Too much importance to non-price competition.
(c) Price leadership.
(d) A small number of firms in the industry.
Answer: (a)
Question. A Monopolist is a price:
(a) Maker
(b) Taker
(c) Adjuster
(d) None of these.
Answer: (a)
Question. Price discrimination is one of the features of
(a) monopolistic competition
(b) monopoly
(c) perfect competition
(d) oligopoly
Answer: (b)
Question. Pure oligopoly is based on the————– products.
(a) differentiated
(b) homogeneous
(c) unrelated
(d) None of these
Answer: (b)
Question. The firm and the industry are one and the same in————-.
(a) perfect competition
(b) monopolistic competition
(c) duopoly
(d) monopoly
Answer: (d)
Question. The demand curve of a monopoly firm will be———————–.
(a) upward sloping
(b) downward sloping
(c) horizontal (d) vertical
Answer: (b)
III. Short Answer Type Questions
Question. A monopolist can sell any quantity he likes at a price. Give reasons with true or false.
Answer: False: A monopolist cannot sell any quantity he likes at a price.
1. A monopolist faces a downward sloping demand curve because of price discrimination which means that a monopolist can sell more quantity only by lowering the price.
2. A monopolist controls only the supply of the product and not the demand of the product.
Question. Why AR curve (demand curve) under monopolistic competition is more elastic than AR curve under monopoly?
Answer:
1. AR curve under both the markets slope downwards.
2. However, AR curve under monopolistic competition is more elastic as compared to AR curve under monopoly because of presence of close substitutes.
3. AR curve is less elastic in monopoly because of no close substitutes.
Question. Explain the feature of few firms in an oligopoly market.
Answer:
1. The number of sellers in an oligopoly market is small—when there are two or more than two, but not many sellers.
2. What matters is that these few sellers account for most of the industry’s sales.
3. These “few” sellers consciously dominate the industry and indulge in intense competition. Each firm is aware of that it possesses a large degree of monopoly power.
4. For example, the market for mobile service provider in India is an oligopolistic structure as there are only few producers of mobile service provider. There exists severe competition among different firms and each firm tries to manipulate both prices and volume of production to outsmart each other.
Question. Explain the main features of barriers to the entry of firms.
Answer:
1. The main reason why the number of firms is small is that there are barriers which prevent entry of firms into industry.
2. Patents, large capital, control over the crucial raw material etc. prevent new firms from entering into industry.
3. Only those who are able to cross these barriers are able to enter.
Question. Give reasons for the following statements:
1. Demand curve facing a perfectly competitive firm is a horizontal straight line.
2. Demand curve facing a monopolistic competitive firm is a downward sloping curve.
3. Demand curve facing a monopoly firm is less elastic than that curve facing a monopolistic competitive firm.
Answer:
1. Under perfect competition, every firm is a price-taker firm. The price is set by industry demand and supply. Therefore, every firm faces a horizontal straight line demand curve indicating that it can sell any quantity at the given price.
2. A monopolistic competitive firm has to design its own pricing strategy. It can expect to sell larger quantity at a lower price, and vice-versa. Hence, its demand curve slopes downwards.
3. A monopolist is the only producer of a good which has no close substitutes. A monopolistic competitive firm, on the other hand, produces a good that has several
close substitutes. Hence, the demand curve facing a monopolistic competitive firm is more elastic than that faced by a monopoly firm.
Question. Draw a demand curve in different market situation and also compare its elasticity of demand.
Answer: (i) In monopolistic competition a firm can sell more quantity of a commodity only by lowering the price. When price falls means Average Revenue falls and when Average Revenue falls, Marginal Revenue also falls but at a much faster rate, i.e.,AR > MR. Total Revenue increases but at a diminishing rate. At point Q where Marginal Revenue = 0, Total Revenue is maximum and constant. After point Q when MR is negative, TR starts falling.
(i) Monopolistic Compe- tition: As we know, in monopolistic competition close substitutes are produced. So, demand fluctuates more propor- tionately than the price of the commodity. So, we are having more than unit elastic demand.
(ii) Monopoly: As we know in monopoly no close substitute are produced. That is why demand fluctuates less proportionately than the price of the commodity. So, we are having less than unitary elastic demand.
Question. Give reasons for the following statements:
1. A perfectly competitive firm is a price-taker.
2. Product differentiation is a characteristic feature of a monopolistic competitive market,
3. A monopolist cannot fix both the quantity that he likes to produce and the price at which he would like to sell.
Answer:
1. In a perfectly competitive market there are a large number of producers of a product.
All of them produce a homogeneous product. Therefore, all the firms have to sell at the same price. This price is determined by industry demand and supply.
2. In a monopolistic competitive market there is a large number of producers. But each of these producers produces a product which is somewhat different from what others
do. At least, the producers make all the attempts to influence the consumer with the idea that their product is better than the product of the rival producers.
3. A monopolist is faced with a downward sloping curve. He can sell a larger quantity at a lower price; or alternatively, he may charge a higher price and be satisfied with lower quantity. He has to make a choice between the two alternatives.
Question. Explain any two sources of restricted entry under monopoly.
Answer:
1. Grant of patent rights
(i) When a company introduces a new product or new technology it applies to the government to grant it patent certificate by which it gets exclusive rights to produce new product or use new technology.
(ii) Patent rights prevent others to produce the same product or use the same technology without obtaining license from the concerned company. Patent rights are granted by the government for a certain number of years.
2. Licensing by Government :
A monopoly market emerges when government gives a firm license, i.e. exclusive legal rights to produce a given product or service in a particular area or region.
Question. What is meant by price rigidity, under oligopoly.
Answer:
1. Price rigidity refers to a situation in which whether there is change in demand and supply the price tends to stay fixed.
2. If a firm tries to reduce the price the rivals will also react by reducing their prices. Likewise, if it tries to raise the price, other firms will not do so. It will lead to loss of customers for the firm which intended to raise the price.
IV. TRUE OR FALSE
Giving reasons, state whether the following statements are true or false.
Question. Under monopoly all firms can sell at any price.
Answer: False: Under monopoly there is only one firm.
Question. In monopoly, firm is different from industry.
Answer: False: There is only one firm in monopoly market, so there exists no difference between firm and industry.
Question. Under monopoly new firms can enter the industry to raise the supply.
Answer: False: In monopoly, no other firm can enter into industry because of barrier created by monopoly firm.
Question. Under monopoly a firm sells the goods at a single price.
Answer: False: Under monopoly a firm can sell all of its output at different prices due to it’s complete control over supply and market.
Question. Under monopolistic competition there is only one seller of the product.
Answer: False: Under monopolistic competition, there are large number of buyers and also large number of sellers.
Question. Under monopolistic competition price discrimination can be made easily.
Answer: False: There is no possibility of price discrimination in the sales of goods in this market because of product differentiation.
Question. Under monopolistic competition, all the customers have perfect knowledge of the market conditions.
Answer: False: under monopolistic competition there is a large variety of a single product, so they do not get perfect knowledge of the market conditions.
Question. Under oligopoly, there are large number of buyers and sellers.
Answer: False: In oligopoly there are a few sellers and a large number of buyers
Question. Under monopolistic competition, a firm faces a perfectly elastic demand curve.
Answer: False: Monopolistic competitive firm faces downward sloping demand curve as it can sell more only by lowering the price.
V. Long Answer Type Questions
Question. Compare between perfect competition and monopoly.
Answer:
| BASIS FOR COMPARISON | MONOPOLY | PERFECT COMPETITION | |
| Meaning | Monopoly is such a market situation, where only one seller exists in the market. Hence, there is no competition and so the seller controls the supply and price. | Perfect Competition implies fair and direct competition between the sellers. | |
| Supply | As there is just one seller. So, the supply of goods is controlled by him. | As there are a large number of sellers, a single seller cannot control the supply. | |
| Demand | Inelastic Demand | Perfectly Elastic | |
| Number of Sellers | One | Many | |
|
No close substitutes for the product. | The product offered by different sellers is homogeneous in all respects. | |
| Entry and Exit | There are restrictions on entry and exit. Therefore a firm can make abnormal profits and losses in the long run. | The firm is free to enter and exit the market. Hence, it results in the absence of abnormal profits and losses in the long run. | |
| Price | The firm is a price-maker. So, the firm and industry are one and the same thing. Monopolist charges different prices for different groups of people. | Firms are price-takers. This is because the industry determines the price. The price is determined by demand and supply forces. | |
| Level of Knowledge | Buyers and sellers do not possess complete knowledge about the market condition. | Buyers and sellers have perfect knowledge about the market condition. | |
| Incurrence of selling cost | Incurred | Not incurred | |
| Profit | Firms earn supernormal profit | Firms earn a normal profit |
Question. Compare between perfect competition and monopolistic competition.
Answer:
| BASIS FOR COMPARISON | PERFECT COMPETITION | MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION |
| Meaning | A market structure, where there are many sellers selling similar goods to the buyers, is perfect competition. | Monopolistic Competition is a market structure, where there are numerous sellers, selling close substitute goods to the buyers. |
| Product | Standardized | Differentiated |
| Price | Determined by demand and supply forces, for the whole industry. | Every firm offer products to customers at its own price. |
| Entry and Exit | No barrier | Few barriers |
| Demand Curve slope | Horizontal, perfectly elastic. | Downward sloping, relatively elastic. |
| Relation between AR and MR | AR = MR | AR > MR |
| Situation | Unrealistic | Realistic |
Question. Compare between monopoly and monopolistic competition.
Answer:
| Monopoly | Basis | Monopolistic Competition |
| Monopoly refers to a market situation where there is a single seller selling a product which has no close substitutes. | Meaning | Monopolistic Competition refers to a market situation in which there are large number of firms selling closely related but differentiated products. |
| There is a single seller and the monopolist has full control over the supply. | Number of Sellers | There are large number of sellers. So, a firm does not have much impact on activities of other firms. |
| There are no close substitutes of the product. So, there is no competition from new and existing products | Nature Product | Products are differentiated on the basis of brand, size, colour, shape etc. So, a firm is in a position to influence the price. |
| There is restriction on entry and exit. So, a firm can earn abnormal profits in the long run. | Entry or Exit | Although there is freedom of entry and exit but it is possible only for a competitive firm to enter or leave the industry. |
| Monopolist is a price-maker as firm and industry are one and the same thing. | Price | Firm is neither a price-taker nor a price- maker but has partial control over price due to product differentiation. |
| Downward sloping demand curve is less elastic due to absence of close substitutes. | Demand Curve | Firm is neither a price-taker nor a price- maker but has partial control over price due to product differentiation. |
| Low selling costs are incurred | Selling Cost | Heavy selling costs are incurred on sales promotion. |
VI. Higher Order Thinking Skills
Question. Demand curve facing a monopoly firm is a constraint for the monopolist.” Comment.
Answer:
1. A monopoly firm has market power and is itself a price-maker. It can choose any price, it likes.
2. Unlike perfect competition where as output increases, price remains unchanged.
3. In monopoly as output increases or decreases, price changes according to what consumers are willing to pay along the demand curve. It produces and supplies a product to satisfy the entire market.
4. It is because a monopoly firm faces the entire demand of the market, that market demand curve is said to be a constraint facing a monopoly firm.
Question. Explain the implication of the following: The feature of ‘no close substitutes’ under monopoly.
Answer:No close substitute:
1. A monopolist produces all the output in a particular market. So, there is no close substitute in monopoly.
2. The monopolist is a ‘price-maker’. It does not mean that monopolist can fix both price and the quantity demanded. If he fixes a high price, less commodity will be demanded.
3. Implication: The result is an inelastic demand curve as shown in Figure. The demand curve is a constraint facing a monopoly firm. Demand curve is also the price line and the AR curve. Since AR is downward sloping, MR lies below AR curve and is twice as steep as the AR curve.
Question. Distinguish between cooperative and non-cooperative oligopoly.
Or
Differentiate between collusive and non-collusive oligopoly.
Answer:
| BASIS FOR COMPARISON | COLLUSIVE OLIGOPOLY | NON-COLLUSIVE OLIGOPOLY |
| Meaning | A Collusive Oligopoly is one in which the firms cooperate and not compete, with one another with respect to price and output. | A Non-Collusive Oligopoly is one wherein each firm in the industry pursues a price and output policy that is independent of competitors. |
| Profit | Collective profit | Individual profit |
| Objective | To reduce competition and to create and maintain entry barriers. | To maintain competition and to work independently as a normal business. |
| Price and Output decision | Mutual or Interdependent | Independent |
| Formation of monopoly | Yes | No |
| Price benefit | Consumers receive fewer price benefits, due to monopoly. | Consumers receive price benefits due to competition between sellers. |
| Brand Loyalty | No need to incur expenses to create brand loyalty. | No need to incur expenses to create brand loyalty. |
Question. What do you mean by duopoly?
Answer: When there are only two firms producing a product, it is called duopoly. Under duopoly it is assumed that the product sold by the two firms is homogeneous and there is no substitute for it. It is a special case of oligopoly.
Question. Which features of monopolistic competition are monopolistic in nature?
Answer:The features of monopolistic competition are:
1. Product differentiation
2. Downward sloping AR and MR curves.
Question. Which features of monopolistic competition are competitive in nature?
Answer: The features of monopolistic competition, which are competitive in nature are:
1. Large number of sellers; and
2. Freedom of entry and exit.
Question. What is the importance of monopoly?
Answer:
1. Patent rights encourage discovery and invention of new product and technique.
2. Public monopolies (like railways, etc) protect the rights and interest of the public and saves them from exploitation.
Question. Discuss the relationship between total revenue, average revenue and marginal revenue under perfect competition and monopolistic competition. Use diagrams.
Answer: (1) In perfect competition, a firm is not in a position to influence the price; it has to sell its output at the same price. Hence, AR curve and MR curve will be a straight line parallel to X-axis. As a consequence TR increases at constant prices as shown below.
(i) In monopolistic competition a firm can sell more quantity of a commodity only by lowering the price. When price falls means Average Revenue falls and when Average Revenue falls, Marginal Revenue also falls but at a much faster rate, i.e.,AR > MR. Total Revenue increases but at a diminishing rate. At point Q where Marginal Revenue = 0, Total Revenue is maximum and constant. After point Q when MR is negative, TR starts falling.
VII. Value Based Questions
Question. In spite of having monopoly why the Indian Railways has not increased the fare for many years?
Answer: Indian Railway is a major public sector undertaking and its main motive is social welfare not the profit. Value: Social welfare
Question. How to reduce the incidence of selling cost under monopolistic competition because of which price tends to be higher than what it would have been if production cost would have been the sole basis?
Answer: The cost incurred on advertisement and salesmanship constitutes selling cost which affects the minds of buyers in favour of certain commodities. In this situation buyers should care for intrinsic value and utility. This way the role of selling cost will be reduced.
Value: Analytic
Question. Under oligopoly though firms are free to take decisions about price and quantity to be sold but they do not change the price and hence buyers are deprived of the benefit of fall in price. Comment.
Answer: Oligopoly firms are mutually dependent and therefore while fixing the price and the output they are guided by the reactions of other firms. As such price tends to be rigid and the consumers suffer.
Value: Critical thinking
Question. Although there are few (more than one) firms in oligopoly. Even these firms can enjoy monopoly power. How?
Answer: Firms in oligopoly form cartel and in this way these firms can control over prices.
Value: Critical thinking
VIII. Application Based Questions
Question. How the efficiency may increase if two firms merge?
Answer:
1. Suppose that initially there are two firms in an industry and both are same but inefficient.
2. Their MC curves are at a high level and consequently they charge a higher price and produce less.
3. They realize, however, that if they merge with each other – and thereby become a monopoly—they can reduce their cost.
4. For instance, one firm may have excellent technical manpower but may not have good marketing skills, whereas the other may not have good technical manpower but possesses superior marketing knowledge by merging the resulting monopoly firms MC curve will be at a lower level and thus it will be more efficient firm.
5. This, by itself will induce the monopoly to charge a price which is less and produce a quantity which is greater than when both firms were competing with each other.
Question. Selling cost is a nail in the coffin of consumer’s sovereignty. How?
Answer:
1. Selling cost is the expenses which are incurred for promoting sales or inducing customers to buy a good of a particular brand.
2. Theoretically, a consumer is the king because whatever he desires/ demands is produced/supplied,
3. But in reality this is not so. Advertisement and salesmanship bias his mind in favour of certain commodities which otherwise may not be good.
Question. “A day without selling costs is nearly impossible”. Comment.
Answer:
1. The given statement is correct. It is the expenses which are incurred for promoting sales or inducing customers to buy a good of a particular brand.
2. This includes, the cost of advertisement through newspaper, television and radio and cost on each other sales promotional activities.
3. As selling costs by the firms in the form of various promotional tools have become a routine activity and the firm generally persuades or lures the customer to avail from one brand to another.
Question. Average revenue will always be equal to marginal revenue in all market conditions. Defend or refute.
Answer: Refute: MR and AR will be equal only for a perfectly competitive firm, because it is faced with a horizontal straight line demand curve. Under all other market conditions MR will always be less than AR.
Question. Price discrimination should be socially desirable. How?
Answer: There should be an approach on the part of the Monopoly Firm to fix lower prices for poor people and backward areas for its product.
Question. If the firm in the toothpaste industry have the following market shares, which market structure would best describe the industry?
| Market Share | (% of market) |
| Toothpaste | 18.7 |
| Dentipaste | 14.3 |
| Shinibright | 11.6 |
| I can't believe its not toothpaste | 9.4 |
| Brighter than white | 8.8 |
| Pastystuff | 7.4 |
| Others | 29.8 |
Answer: Oligopoly market best describes the market structure of toothpaste industry.
Question. Suppose that the demand curve for the XYZ Company slopes downward and to the right. Would you conclude that the firm is a price taker or a price maker? Give
reasons.
Answer: 1. Since the demand curve of XYZ Co. is downward sloping, it has to lower its price to sell additional units of output.
2. But in perfect competition the demand curve is parallel to x-axis as the firm can sell any amount of the output at the same price.
3. Hence, XYZ Co. is not a price- taker but a price maker.
Question. Because of product differentiation under monopolistic competition, price tends to be higher than what it ought to have been in real terms and hence consumers suffer. How?
Answer:
1. Product differentiation is created by artificial differences such as change in colour, fragrance, certain features etc.
2. But as such all the products are close substitutes to each other,
3. This feature of product differentiation results in the downward sloping demand curve because of which prices tend to be more and hence the consumers suffer.
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 1 Introduction to Economics |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 2 Demand |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 2 Elasticity of Demand |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 3 Cost |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 3 Production |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 4 Perfect Competition |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 4 Producer Equilibrium |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 4 Revenue |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 4 Supply |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 6 Non Competitive Market |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 1 Introduction to Macroand its Concepts |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 2 National Income and Related Aggregates |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 3 Banking |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 3 Money |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 4 Aggregate Demand and Its Related Concepts |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 4 National Income Determination and Multiplier |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 5 Government Budget and the Economy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 6 Balance of Payment |
| NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 6 Foreign Exchange Rate |
Important Practice Resources for Class 12 Economics
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics Chapter 6 Non Competitive Market
Students can now access the NCERT Solutions for Chapter 6 Non Competitive Market prepared by teachers on our website. These solutions cover all questions in exercise in your Class 12 Economics textbook. Each answer is updated based on the current academic session as per the latest NCERT syllabus.
Detailed Explanations for Chapter 6 Non Competitive Market
Our expert teachers have provided step-by-step explanations for all the difficult questions in the Class 12 Economics chapter. Along with the final answers, we have also explained the concept behind it to help you build stronger understanding of each topic. This will be really helpful for Class 12 students who want to understand both theoretical and practical questions. By studying these NCERT Questions and Answers your basic concepts will improve a lot.
Benefits of using Economics Class 12 Solved Papers
Using our Economics solutions regularly students will be able to improve their logical thinking and problem-solving speed. These Class 12 solutions are a guide for self-study and homework assistance. Along with the chapter-wise solutions, you should also refer to our Revision Notes and Sample Papers for Chapter 6 Non Competitive Market to get a complete preparation experience.
The complete and updated is available for free on StudiesToday.com. These solutions for Class 12 Economics are as per latest NCERT curriculum.
Yes, our experts have revised the as per 2026 exam pattern. All textbook exercises have been solved and have added explanation about how the Economics concepts are applied in case-study and assertion-reasoning questions.
Toppers recommend using NCERT language because NCERT marking schemes are strictly based on textbook definitions. Our will help students to get full marks in the theory paper.
Yes, we provide bilingual support for Class 12 Economics. You can access in both English and Hindi medium.
Yes, you can download the entire in printable PDF format for offline study on any device.

