NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings have been provided below and is also available in Pdf for free download. The NCERT solutions for Class 9 Science have been prepared as per the latest syllabus, NCERT books and examination pattern suggested in Class 9 by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. Questions given in NCERT book for Class 9 Science are an important part of exams for Class 9 Science and if answered properly can help you to get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise answers for NCERT Class 9 Science and also download more latest study material for all subjects. Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings is an important topic in Class 9, please refer to answers provided below to help you score better in exams
Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions
Class 9 Science students should refer to the following NCERT questions with answers for Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings in Class 9. These NCERT Solutions with answers for Class 9 Science will come in exams and help you to score good marks
Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science
Class IX Science
Chapter 1 – Matter in Our Surroundings
Question 1: Which of the following are matter?
Chair, air, love, smell, hate, almonds, thought, cold, cold drink, smell of perfume.
Answer: Anything that occupies space and has mass is called matter. Matter can exist in three physical states—solid, liquid, and gaseous.
Chair and almond are forms of matter in the solid state.
Cold drink is a liquid state of matter.
Air and smell of perfume are gaseous states of matter.
Note: The sense of smell is not matter. However, the smell or odour of a substance is classified as matter. The smell of any substance (say, perfume) is the gaseous form of that substance which our olfactory system can detect (even at very low concentrations). Hence, smell of perfume is matter.
Question 2: Give reasons for the following observation: The smell of hot sizzling food reaches you several metres away, but to get the smell from cold food you have to go close.
Answer: Solids diffuse at a very slow rate. But, if the temperature of the solid is increased, then the rate of diffusion of the solid particles into air increases. This is due to an increase in the kinetic energy of solid particles. Hence, the smell of hot sizzling food reaches us even at a distance, but to get the smell from cold food we have to go close.
Question 3: A diver is able to cut through water in a swimming pool. Which property of matter does this observation show?
Answer: The ability of a diver to cut through water in a swimming pool shows that matter is made up of particles.
Question 4: What are the characteristics of particles of matter?
Answer: The characteristics of particles of matter are:
(i) Particles of matter have spaces between them.
(ii) Particles of matter are continuously moving.
(iii) Particles of mater attract each other.
Exercise:
Question 1: The mass per unit volume of a substance is called density (density = mass/volume).
Arrange the following in order of increasing density − air, exhaust from chimney, honey, water, chalk, cotton, and iron.
Answer: The given substances in the increasing order of their densities can be represented as:
Air < Exhaust from chimney < Cotton < Water < Honey < Chalk < Iron
Question 2: (a) Tabulate the differences in the characteristics of states of matter.
(b) Comment upon the following: rigidity, compressibility, fluidity, filling a gas container, shape, kinetic energy, and density.
Answer:
(a) The differences in the characteristics of states of matter are given in the following table.
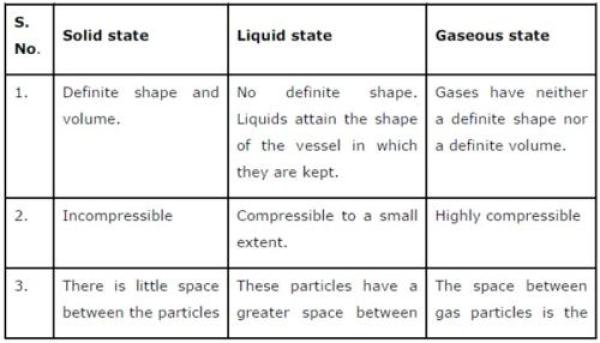
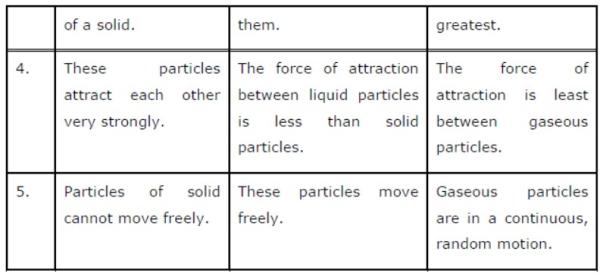
(b) Rigidity can be expressed as the tendency of matter to resist a change in shape.
Compressibility is the ability to be reduced to a lower volume when force is applied.
Fluidity is the ability to flow.
By filling a gas container we mean the attainment of shape of the container by gas.
Shape defines a definite boundary.
Kinetic energy is the energy possessed by a particle due to its motion.
Density is mass per unit volume.
Question 3:
Give reasons:
(a) A gas fills completely the vessel in which it is kept.
(b) A gas exerts pressure on the walls of the container.
(c) A wooden table should be called a solid.
(d) We can easily move our hand in air, but to do the same through a solid block of wood, we need a karate expert.
Answer:
(a) There is little attraction between particles of gas. Thus, gas particles movefreely in all directions. Therefore, gas completely fills the vessel in which it is kept.
(b) Particles of gas move randomly in all directions at high speed. As a result, theparticles hit each other and also hit the walls of the container with a force.
Therefore, gas exerts pressure on the walls of the container.
(c) A wooden table has a definite shape and volume. It is very rigid and cannot be compressed i.e., it has the characteristics of a solid. Hence, a wooden table should be called a solid.
(d) Particles of air have large spaces between them. On the other hand, wood has little space between its particles. Also, it is rigid. For this reason, we can easily move our hands in air, but to do the same through a solid block of wood, we need a karate expert.
Question 4: Liquids generally have lower density as compared to solids. But you must have observed that ice floats on water. Find out why.
Answer:
The mass per unit volume of a substance is called density (density = mass/volume).
As the volume of a substance increases, its density decreases.
Though ice is a solid, it has large number of empty spaces between its particles.
These spaces are larger as compared to the spaces present between the particles of water. Thus, the volume of ice is greater than that of water. Hence, the density of ice is less than that of water. A substance with lower density than water can float on water. Therefore, ice floats on water.
Chapter 1 – Matter in Our Surroundings
Question 1: Convert the following temperature to Celsius scale:
(a) 300 K
(b) 573 K
Answer:
(a) 300 K = (300 − 273)°C
= 27°C
(b)573 K = (573 − 273)°C
= 300°C
Question 2: What is the physical state of water at:
(a) 250°C
(b) 100°C
Answer:
(a) Water at 250°C exists in gaseous state.
(b) At 100°C, water can exist in both liquid and gaseous form. At this temperature, after getting the heat equal to the latent heat of vaporization, water starts changing from liquid state to gaseous state.
Question 3: For any substance, why does the temperature remain constant during the change of state?
Answer: During a change of state, the temperature remains constant. This is because all the heat supplied to increase the temperature is utilised in changing the state by overcoming the forces of attraction between the particles. Therefore, this heat does not contribute in increasing the temperature of the substance.
Question 4: Suggest a method to liquefy atmospheric gases.
Answer: By applying pressure and reducing the temperature, atmospheric gases can be liquefied.
Chapter 1 – Matter in Our Surroundings
Question 1: Why does a desert cooler cool better on a hot dry day?
Answer:
When a liquid evaporates, the particles of the liquid absorb energy from the surroundings to compensate the loss of energy during evaporation. This makes the surroundings cool.
In a desert cooler, the water inside it is made to evaporate. This leads to absorption of energy from the surroundings, thereby cooling the surroundings. Again, we know that evaporation depends on the amount of water vapour present in air (humidity). If the amount of water vapour present in air is less, then evaporation is more. On a hot dry day, the amount of water vapour present in air is less. Thus, water present inside the desert cooler evaporates more, thereby cooling the surroundings more.
That is why a desert cooler cools better on a hot dry day.
Question 2: How does water kept in an earthen pot (matka) become cool during summers?
Answer:
There are some pores in an earthen pot through which the liquid inside the pot evaporates. This evaporation makes the water inside the pot cool. In this way, water kept in an earthen pot becomes cool during summers.
Question 3: Why does our palm feel cold when we put some acetone or petrol or perfume on it?
Answer:
When we put some acetone or petrol or perfume on our palm, it evaporates. During evaporation, particles of the liquid absorb energy from the surrounding or the surface of the palm to compensate for the loss of energy, making the surroundings cool. Hence, our palm feels cold when we put some acetone or petrol or perfume on it.
Question 4: Why are we able to sip hot tea or milk faster from a saucer than a cup?
Answer: A liquid has a larger surface area in a saucer than in a cup. Thus, it evaporates faster and cools faster in a saucer than in a cup. For this reason, we are able to sip hot tea or milk faster from a saucer than a cup.
Question 5: What type of clothes should we wear in summers?
Answer: We should wear cotton clothes in summers. During summers, we sweat more. On the other hand, cotton is a good absorber of water. Thus, it absorbs sweat from our body and exposes the liquid to the atmosphere, making evaporation faster. During this evaporation, particles on the surface of the liquid gain energy from our body surface, making the body cool.
Chapter 1 – Matter in Our Surroundings
Question 1: Convert the following temperatures to Celsius scale.
(a) 300 K
(b) 573 K
Answer: Kelvin is an SI unit of temperature, where 0°C = 273.16 K (approximately 273 K)
(a) 300 K = (300 − 273) °C
= 27 °C
(b) 573 K = (573 − 273) °C
= 300 °C
Question 2: Convert the following temperatures to Kelvin scale.
(a) 25°C
(b) 373°C
Answer: Kelvin is an SI unit of temperature, where 0°C = 273.16 K (approximately 273 K)
(a) 25 °C = (25 + 273) K
= 298 K
(b) 373 °C = (373 + 273) K
= 646 K
Question 3: Give reason for the following observations.
(a) Naphthalene balls disappear with time without leaving any solid.
(b) We can get the smell of perfume sitting several metres away.
Answer: (a) Naphthalene undergoes sublimation easily i.e., the change of state of naphthalene from solid to gas takes place easily. Thus, naphthalene balls disappear with time without leaving any solid.
(b) Gaseous particles possess high speed and large spaces between them. Particles of perfume diffuse into these gaseous particles at a very fast rate and reach our nostrils. This enables us to smell the perfume from a distance.
Question 4: Arrange the following substances in increasing order of forces of attraction between particles−− water, sugar, oxygen.
Answer: Sugar is a solid; the forces of attraction between the particles of sugar are strong.
Water is a liquid; the forces of attraction here are weaker than sugar. Oxygen is a gas; the forces of attraction are the weakest in gases.
Thus, the increasing order of forces of attraction between the particles of water, sugar and oxygen is Oxygen < Water < Sugar
Question 5: What is the physical state of water at−−
(a) 25°C
(b) 0°C
(c) 100°C
Answer:
(a) Water at 25°C is present in the liquid state.
(b) At 0 °C, water can exist as both solid and liquid. At this temperature, after getting the heat equal to the latent heat of fusion, the solid form of water i.e., ice starts changing into its liquid form i.e., water.
(c) At 100 °C, water can exist as both liquid and gas. At this temperature, after getting the heat equal to the latent heat of vaporization, water starts changing from its liquid state to its gaseous state, i.e., water vapours.
Question 6: Give two reasons to justify−
(a) water at room temperature is a liquid.
(b) an iron almirah is a solid at room temperature.
Answer:
(a) At room temperature (25 °C), water is a liquid because it has the following characteristic of liquid:
(i) At room temperature, water has no shape but has a fixed volume that is, it occupies the shape of the container in which it is kept.
(ii) At room temperature, water flows.
(b) An iron almirah is a solid at room temperature (25 °C) because:
(i) it has a definite shape and volume like a solid at room temperature.
(ii) it is rigid as solid at room temperature.
Question 7: Why is ice at 273 K more effective in cooling than water at the same temperature?
Answer: Ice at 273 K has less energy than water (although both are at the same temperature). Water possesses the additional latent heat of fusion. Hence, at 273 K, ice is more effective in cooling than water.
Question 8: What produces more severe burns, boiling water or steam?
Answer: Steam has more energy than boiling water. It possesses the additional latent heat of vaporization. Therefore, burns produced by steam are more severe than those produced by boiling water.
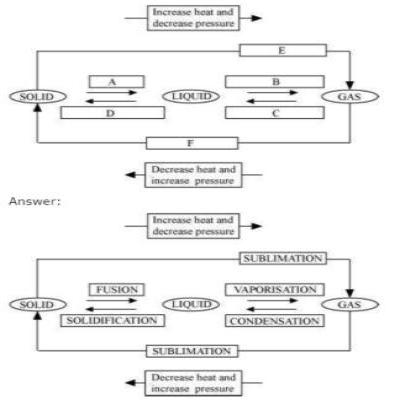
Question 9: Name A, B, C, D, E and F in the following diagram showing change in its state.
Question. People sometimes add salt to the water in which eggs are to be boiled. What is the MAIN reason for this?
(a) Adding salt to the water before the egg is cooked makes the egg tastier.
(b) Adding salt to the water increases its boiling point and cooks the egg better.
(c) Adding salt to the water reduces the water temperature cooking the egg faster.
(d) Adding salt to the water kills micro organisms making the egg safer to eat.
Answer : B
Question. Rama suspects that the LPG cylinder is leaking, and immediately turns the cylinder valve to the OFF position. What should she do next?
(a) Switch on all lights
(b) Switch off all lights.
(c) Open all the windows
(d) Close all the windows
Answer : C
Question. A lump of bread dough in a baking tin contains air and carbon dioxide released by the yeast cells. When heated the dough rises to about twice its size. In this case, the increase in temperature has resulted in _____________.
(a) an increase in volume while the pressure remained constant
(b) an increase of pressure while the volume remained constant
(c) an increase in both volume and pressure
(d) a decrease in both volume and pressure.
Answer : A
Question. When a substance changes from LIQUID to GASEOUS state, it is said to EVAPORATE. Some substances change from SOLID to GASEOUS state without passing through the LIQUID state. They are then said to
(a) evaporate
(b) condense
(c) diffuse
(d) sublime
Answer : D
Question. Both AIR CONDITIONERS and AIR COOLERS can be used to cool rooms. What is the main difference in the effect they produce?
(a) They are basically the same, but air conditioners cool much more
(b) Air conditioners control the humidity of the room also, unlike air coolers.
(c) They are basically the same, but air coolers can be used only for a few hours at a stretch.
(d) They are basically the same, but air coolers can be used only for a few hours at a stretch.
Answer : B
Question. Mercury can vaporize if heated. This means that with enough heat mercury can__________.
(a) be destroyed
(b) become water vapour
(c) be changed into a gas
(d) change from a liquid to a solid.
Answer : C
Question. A student wishes to test whether adding a substance (called an anti-freeze) to water lowers the freezing point of the water. Measuring which of these variables will help her arrive at a conclusion?
(a) Amount of water put into the container
(b) Amount of anti-freeze added to the water
(c) Temperature at which the mixture freezes
(d) Type of thermometer used to make the measurement
Answer : C
Question. The density of water is 1 g/cc. Ice floats on water with 90% of its volume inside the water. What will be the mass of a cube of ice of side 3 cm?
(a) 27 g
(b) 30 g
(c) 24.3 g
(d) 25.3 g
Answer : C
Question. The figure shows the amount of water in a graduated test-tube. The curved surface shown is called the meniscus. What is the correct reading of the volume of liquid?
(a) 7.1 ml
(b) 7.2 ml
(c) 6.8 ml
(d) 6.6 ml
Answer : D
Question. Many modern tanks for water and liquid fuels are made spherical in nature. What could be the reason behind this?
(a) It is easier to build spherical tanks compared to tanks of other shapes
(b) For a given surface area, spherical tanks enclose maximum volume
(c) It is easier to transport spherical tanks when repairs, etc. are required
(d) Liquids get preserved better when they are stored in spherical tanks.
Answer : B
Question. Ramesh has to pour out boiling hot water into a glass. He has four glasses of the same size but of different THICKNESSES. Which of them is LEAST LIKELY to break, if hot water is poured into it?
Answer : A
Question. A box is made by cutting and folding a thick sheet having a pattern drawn on it as shown.What will the face OPPOSITE TO THE FACE MARKED 'X' look like
Answer : B
Question. A box is made by cutting and folding a thick sheet having a pattern drawn on it as shown. How many faces of the cube will have a complete circle?
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 3
Answer : B
Question. Setup P below shows an egg being boiled. In setup Q, a similar arrangement is used, but inside an apparatus which creates near-vacuum conditions. Will the egg in setup Q get cooked faster?
(a) Yes, lower pressure lowers the boiling point, so the water and egg will boil earlier than setup P.
(b) No, lower pressure raises the boiling point, so the water and egg will boil later than setup P.
(c) No, lower pressure lowers the boiling point; the water will boil away quickly but the egg will not boil
(d) Yes, lower pressure raises the boiling point, so the water will get hotter and the egg will boil faster
Answer : C
Question. Which phase change at standard temperature and pressure represents sublimation?
(a) CO(s) - CO(g)
(b) H(l) - H(g)
(c) CO(l) - CO(g)
(d) H(s) - H(l)
Answer : A
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 4 Structure of the Atom |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organisms |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 8 Motion |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 9 Force and Laws of Motion |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Work and Energy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 12 Sound |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Why Do We Fall Ill |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources |
NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
The above provided NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings is available on our website www.studiestoday.com for free download in Pdf. You can read the solutions to all questions given in your Class 9 Science textbook online or you can easily download them in pdf. The answers to each question in Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings of Science Class 9 has been designed based on the latest syllabus released for the current year. We have also provided detailed explanations for all difficult topics in Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 chapter of Science so that it can be easier for students to understand all answers. These solutions of Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings NCERT Questions given in your textbook for Class 9 Science have been designed to help students understand the difficult topics of Science in an easy manner. These will also help to build a strong foundation in the Science. There is a combination of theoretical and practical questions relating to all chapters in Science to check the overall learning of the students of Class 9.
You can download the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the NCERT Solutions issued for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings have been made available here for latest academic session
Regular revision of NCERT Solutions given on studiestoday for Class 9 subject Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all latest NCERT Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 Science solutions based on the latest books for the current academic session
Yes, NCERT solutions for Class 9 Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings Science are available in multiple languages, including English, Hindi
All questions given in the end of the chapter Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings have been answered by our teachers

