NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life have been provided below and is also available in Pdf for free download. The NCERT solutions for Class 9 Science have been prepared as per the latest syllabus, NCERT books and examination pattern suggested in Class 9 by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. Questions given in NCERT book for Class 9 Science are an important part of exams for Class 9 Science and if answered properly can help you to get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise answers for NCERT Class 9 Science and also download more latest study material for all subjects. Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life is an important topic in Class 9, please refer to answers provided below to help you score better in exams
Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions
Class 9 Science students should refer to the following NCERT questions with answers for Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life in Class 9. These NCERT Solutions with answers for Class 9 Science will come in exams and help you to score good marks
Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science
Chapter 5 – The Fundamental Unit of Life
Question 1: Who discovered cells and how?
Answer: Cells were discovered in 1665 by an English Botanist, Robert Hooke. He used a primitive microscope to observe cells in a cork slice.
Question 2: Why is the cell called the structural and functional unit of life?
Answer: Cells constitute various components of plants and animals. A cell is the smallest unit of life and is capable of all living functions. Cells are the building blocks of life. This is the reason why cells are referred to as the basic structural and functional units of life. All cells vary in their shape, size, and activity they perform. In fact, the shape and size of the cell is related to the specific functions they perform.
Chapter 5 – The Fundamental Unit of Life
Question 1: How do substances like CO2 and water move in and out of the cell? Discuss.
Answer:
Thecell membrane is selectively permeable and regulates themovement of substances in and out of the cell. Movement of CO2:
CO2 is produced during cellular respiration. Therefore, it is present in high concentrations inside the cell. This CO2 must be excreted out of the cell. In the cell’s external environment, the concentration of CO2 is low as compared to that inside the cell. Therefore, according to the principle of diffusion, CO2 moves from a region of higher concentration (inside the cell) towards a region of lower concentration (outside the cell). Similarly, O2 enters the cell by the process of diffusion when the concentration of O2 inside the cell is low as compared to its surroundings.
Movement of water:
Water moves from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration through the plasma membrane. The plasma membrane acts as a semi-permeable membrane, and this movement of water is known as osmosis. However, the movement of water across the plasma membrane of the cell is affected by the amount of substance dissolved in water.
Question 2: Why is the plasma membrane called a selectively permeable membrane?
Answer: Thecell membraneor the plasma membraneis known as a selectively permeable membrane because it regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell. This means that the plasma membrane allows the entry of only some substances and prevents the movement of some other materials.
Chapter 5 – The Fundamental Unit of Life
Question 1: Fill in the gaps in the following table illustrating differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
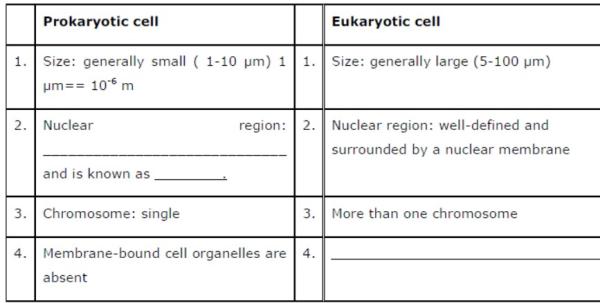
Answer :
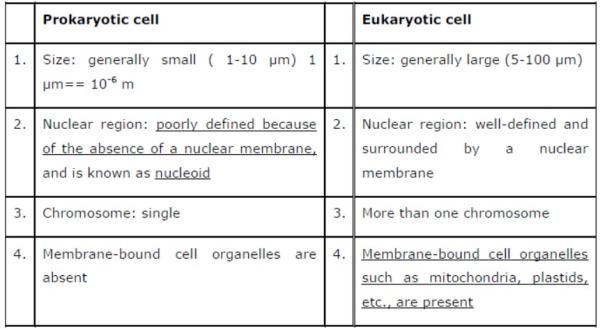
Chapter 5 – The Fundamental Unit of Life
Question 1: Can you name the two organelles we have studied that contain their own genetic material?
Answer: Mitochondriaandplastids are the two organelles that contain their own genetic material. Both these organelles have their own DNA and ribosomes.
Question 2: If the organisation of a cell is destroyed due to some physical or chemical influence, what will happen?
Answer: Cell is the smallest unit of life, which is capable of all living functions. If the organisation of a cell is destroyed due to some physical or chemical influence, then the ability of the cell to perform all living functions such as respiration, nutrition, excretion, etc. would be affected.
Question 3: Why are lysosomes known as suicide bags?
Answer: Lysosomes are membrane-bound vesicular structures that contain powerful digestive enzymes. These enzymes are capable of breaking down any foreign food particle or microbes entering the cell. Sometimes, lysosomes can cause self-destruction of a cell by releasing these digestive enzymes within the cells. Hence, they are also known as ‘suicidal bags’.
Question 4: Where are proteins synthesized inside the cell?
Answer: Ribosomesare the site for protein synthesis. Ribosomes are very small structures found either in a free state, suspended in the cytoplasm, or attached to the surface
of the endoplasmic reticulum. They are composed of ribonucleic acids and proteins.
Chapter 5 – The Fundamental Unit of Life
Question 1: Make a comparison and write down ways in which plant cells are different from animal cells.
Answer: Animal cell
• Animal cells are generally small in size.
• Cell wall is absent.
• Except the protozoan Euglena, no animal cell possesses plastids.
• Vacuoles are smaller in size.
Plant cell
• Plants cells are usually larger than animal cells.
• Cell wall is present.
• Plastids (chromoplasts and leucoplasts) are present.
• Vacuoles are larger in size.
Question 2: How is a prokaryotic cell different from a eukaryotic cell?
Answer: Prokaryotic cell
1. Most prokaryotic cells are unicellular.
2. Size of the cell is generally small (0.5-5 8m).
3. Nuclear region is poorly defined due to the absence of a nuclear membrane or the cell lacks true nucleus.
4. It contains a single chromosome.
5. Nucleolus is absent.
6. Membrane-bound cell organelles such as plastids, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, etc. are absent
7. Cell division occurs only by mitosis.
8. Prokaryotic cells are found in bacteria and blue-green algae.
Eukaryotic cell
1. Most eukaryotic cells are multicellular.
2. Size of the cell is generally large (50- 1008m).
3. Nuclear region is well-defined and is surrounded by a nuclear membrane, or true nucleus bound by a nuclear membrane is present in the cell.
4. It contains more than one chromosome.
5. Nucleolus is present.
6. Cell organelles such as mitochondria, plastids, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, etc. are present.
7. Cell division occurs by mitosis and meiosis.
8. Eukaryotic cells are found in fungi, plants, and animal cells.
Question 3: What would happen if the plasma membrane ruptures or breaks down?
Answer: If the plasma membrane of a cell is ruptured, then the cell will die. The plasma membrane regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell by diffusion or osmosis. Thus, if the plasma membrane is ruptured, then the cell might leak out its contents.
Question 4: What would happen to the life of a cell if there was no Golgi apparatus?
Answer: If there was no Golgi apparatus in the cell, then most activities performed by the Golgi apparatus will not take place.
(i) Membranes of the Golgi apparatus are often connected to ER membranes. It collects simpler molecules and combines them to make more complex molecules. These are then packaged in small vesicles and are either stored in the cell or sent out as per the requirement. Thus, if the Golgi apparatus is absent in the cell, then the above process of storage, modification, and packaging of products will not be possible.
(ii) The formation of complex sugars from simple sugars will not be possible as this takes place with the help of enzymes present in Golgi bodies.
(iii) The Golgi apparatus is involved in the formation of lysosomes or peroxisomes. Thus, if the Golgi body is absent in a cell, the synthesis of lysosomes or peroxisomes will not be possible in the cell.
Question 5: Which organelle is known as the powerhouse of the cell? Why?
Answer: Mitochondriaare known as the powerhouse of cells. Mitochondria create energy for the cell, and this process of creating energy for the cell is known as cellular respiration. Most chemical reactions involved in cellular respiration occur in the mitochondria. The energy required for various chemical activities needed for life is released by the mitochondria in the form of ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) molecules. For this reason, mitochondria are known as the powerhouse of cells.
Question 6: Where do the lipids and proteins constituting the cell membrane get synthesized?
Answer: Lipids and proteinsconstituting the cell membrane are synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum. SER (Smooth endoplasmic reticulum) helps in the manufacturing of lipids. RER (Rough endoplasmic reticulum) has particles attached to its surface, called ribosomes. These ribosomes are the site for protein synthesis.
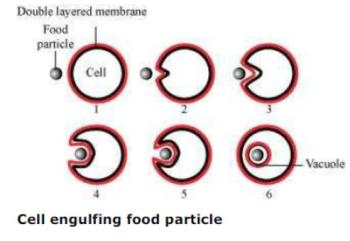
Question 7: How does an Amoeba obtain its food?
Answer: Amoebaobtains its food through the process of endocytosis. The flexibility of the cell membrane enables the cell to engulf the solid particles of food and other materials from its external environment.
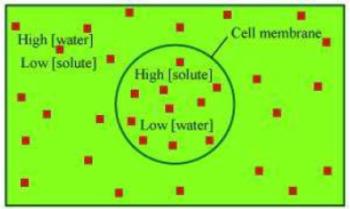
Question 8: What is osmosis?
Answer:The movement of water molecules from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration through a selectively permeable membrane is called osmosis. It is a special case of diffusion, where the medium is water. For example, if the medium surrounding the cell has a higher water concentration than the cell i.e., if the solution is a dilute solution, then the cell will gain water by osmosis.
Movement of water inside the cell
Question 9: Carry out the following osmosis experiment:
Take four peeled potato halves and scoop each one out to make potato cups. One of these potato cups should be made from a boiled potato. Put each potato cup in a trough containing water. Now,
(a) Keep cup A empty
(b) Put one teaspoon sugar in cup B
(c) Put one teaspoon salt in cup C
(d) Put one teaspoon sugar in the boiled potato cup D.
Keep these for two hours. Then observe the four potato cups and answer the following:
(i) Explain why water gathers in the hollowed portion of B and C.
(ii) Why is potato A necessary for this experiment?
(iii) Explain why water does not gather in the hollowed out portions of A and D.
Answer Discussion
Experimental set up
(i) Water gathers in the hollowed portions of set-up B and C because water enters the potato as a result of osmosis. Since the medium surrounding the cell has a higher water concentration than the cell, the water moves inside by osmosis. Hence, water gathers in the hollowed portions of the potato cup.
(ii) Potato A in the experiment acts as a control set-up. No water gathers in the hollowed portions of potato A.
(iii) Water does not gather in the hollowed portions of potato A because potato cup A is empty. It is a control set-up in the experiment. Water is not able to enter potato D because the potato used here is boiled. Boiling denatures the proteins present in the cell membrane and thus, disrupts the cell membrane. For osmosis, a semi-permeable membrane is required, which is disrupted in this case. Therefore, osmosis will not occur. Hence, water does not enter the boiled potato cup.
Question. Sunil views a slide of onion root cells in a compound microscope under low power objective. He wants to increase the magnification to see the slide better. His teacher tells him to centre the portion of the slide he wants to see in the field of view, before he shifts to the high power objective. This is important because_________
(a) Under high power a smaller area of the slide is observed.
(b) Under high power a larger area of the slide is observed.
(c) Under high power the entire slide is magnified
(d) Under high power focussing is not possible at all.
Answer : A
Question. The diameter of a field of view while using a 10X objective in a microscope is determined to be 2 millimetres (mm). From the picture of the cells as observed in the picture, the average length of each cell is about: (1mm = 1000 micrometres)
(a) 250 micrometres
(b) 1000 micrometres
(c) 2000 micrometres
(d) 4000 micrometres
Answer : B
Question. The table below describes some of the organelles visible in a cell under a microscope. Identify the type of organism to which the cell belongs.
| Cell organelle | Description |
| Cell wall | Present |
| Vacuole | Large |
| Centriole | Not visible |
| Nucleus | Present |
(a) It is the cell of an animal.
(b) It is the cell of a plant.
(c) It is the cell of a bacterium
(d) It is the cell of a virus.
Answer : B
Question. Outer surfaces of some cells are folded into finger-like projections as shown in the figure here.Which of the following could be the function of such folded surfaces
(a) to increase the energy production in the cell
(b) to increase the rate of cell division of the cell
(c) to increase the absorption of nutrients by the cell
(d) to help the cell move about much more effectively
Answer : C
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 4 Structure of the Atom |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organisms |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 8 Motion |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 9 Force and Laws of Motion |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Work and Energy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 12 Sound |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Why Do We Fall Ill |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources |
| NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources |
NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life
The above provided NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life is available on our website for free download in Pdf. You can read the solutions to all questions given in your Class 9 Science textbook online or you can easily download them in pdf. The answers to each question in Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life of Science Class 9 has been designed based on the latest syllabus released for the current year. We have also provided detailed explanations for all difficult topics in Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 chapter of Science so that it can be easier for students to understand all answers. These solutions of Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life NCERT Questions given in your textbook for Class 9 Science have been designed to help students understand the difficult topics of Science in an easy manner. These will also help to build a strong foundation in the Science. There is a combination of theoretical and practical questions relating to all chapters in Science to check the overall learning of the students of Class 9.
You can download the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the NCERT Solutions issued for Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life have been made available here for latest academic session
Regular revision of NCERT Solutions given on studiestoday for Class 9 subject Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all latest NCERT Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 Science solutions based on the latest books for the current academic session
Yes, NCERT solutions for Class 9 Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life Science are available in multiple languages, including English, Hindi
All questions given in the end of the chapter Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life have been answered by our teachers

