NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric current have been provided below and is also available in Pdf for free download. The NCERT solutions for Class 10 Science have been prepared as per the latest syllabus, NCERT books and examination pattern suggested in Class 10 by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. Questions given in NCERT book for Class 10 Science are an important part of exams for Class 10 Science and if answered properly can help you to get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise answers for NCERT Class 10 Science and also download more latest study material for all subjects. Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric current is an important topic in Class 10, please refer to answers provided below to help you score better in exams
Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric current Class 10 Science NCERT Solutions
Class 10 Science students should refer to the following NCERT questions with answers for Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric current in Class 10. These NCERT Solutions with answers for Class 10 Science will come in exams and help you to score good marks
Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric current NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
Question : Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet?
Answer: A compass needle is a small bar magnet. When it is brought near a bar magnet, its magnetic field lines interact with that of the bar magnet. Hence, a compass needle shows a deflection when brought near the bar magnet.
Question : Draw magnetic field lines around a bar magnet.
Answer: Magnetic field lines of a bar magnet emerge from the north pole and terminate at the south pole. Inside the magnet, the field lines emerge from the south pole and terminate at the north pole, as shown in the given figure.
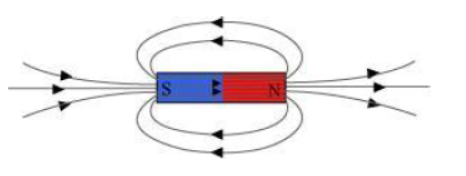
Question : List the properties of magnetic lines of force.
Answer: The properties of magnetic lines of force are as follows.
(a) Magnetic field lines emerge from the north pole.
(b) They merge at the south pole.
(c) The direction of field lines inside the magnet is from the south pole to the north pole.
(d) Magnetic lines do not intersect with each other.
Question : Why don’t two magnetic lines of force intersect each other?
Answer: If two field lines of a magnet intersect, then at the point of intersection, the compass needle points in two different directions. This is not possible. Hence, two field lines do not intersect each other.
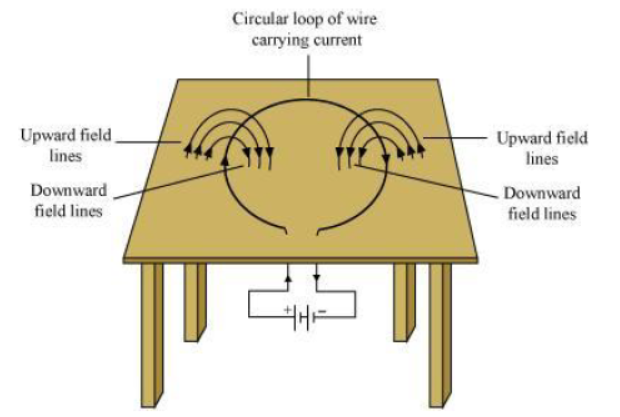
Question : Consider a circular loop of wire lying in the plane of the table. Let the current pass through the loop clockwise. Apply the right-hand rule to find out the direction of the magnetic field inside and outside the loop.
Answer: Inside the loop = Pierce inside the table
Outside the loop = Appear to emerge out from the table
For downward direction of current flowing in the circular loop, the direction of magnetic field lines will be as if they are emerging from the table outside the loop and merging in the table inside the loop. Similarly, for upward direction of current flowing in the circular loop, the direction of magnetic field lines will be as if they are emerging from the table outside the loop and merging in the table inside the loop, as shown in the given figure.
Question : The magnetic field in a given region is uniform. Draw a diagram to represent it.
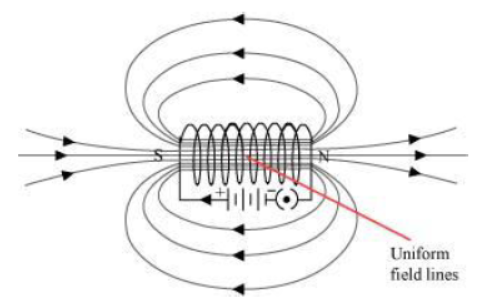
The magnetic field lines inside a current-carrying long straight solenoid are uniform.
Question : Consider a circular loop of wire lying in the plane of the table. Let the current pass through the loop clockwise. Apply the right-hand rule to find out the direction of the magnetic field inside and outside the loop.
Answer: Inside the loop = Pierce inside the table
Outside the loop = Appear to emerge out from the table
For downward direction of current flowing in the circular loop, the direction of magnetic field lines will be as if they are emerging from the table outside the loop and merging in the table inside the loop. Similarly, for upward direction of current flowing in the circular loop, the direction ofmagnetic field lines will be as if they are emerging from the table outside the loop and merging in the table inside the loop, as shown in the given figure.
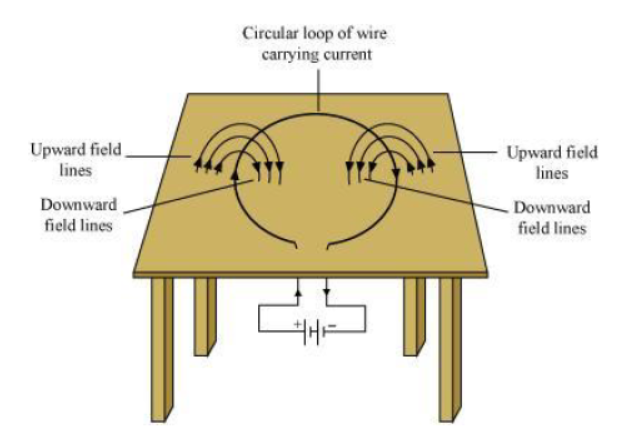
Question : The magnetic field in a given region is uniform. Draw a diagram to represent it.
Answer:
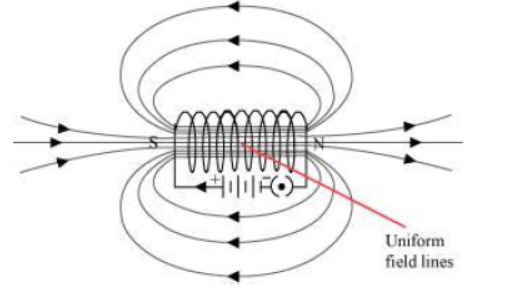
The magnetic field lines inside a current-carrying long straight solenoid are uniform.
Question : Choose the correct option.
The magnetic field inside a long straight solenoid-carrying current
(a) is zero
(b) decreases as we move towards its end
(c) increases as we move towards its end
(d) is the same at all points
Answer: (d) The magnetic field inside a long, straight, current-carrying solenoid is uniform. It is the same at all points inside the solenoid.
Question : Which of the following property of a proton can change while it moves freely in a magnetic field? (There may be more than one correct answer.)
(a) mass
(b) speed
(c) velocity
(d) momentum
Answer: (c) and (d)
When a proton enters in a region of magnetic field, it experiences a magnetic force. As a result of the force, the path of the proton becomes circular. Hence, its velocity and momentum change.
Question : State Fleming’s left-hand rule.
Answer: Fleming’s left hand rule states that if we arrange the thumb, the centre finger, and the forefinger of the left hand at right angles to each other, then the thumb points towards the direction of the magnetic force, the centre finger gives the direction of current, and the forefinger points in the direction of magnetic field.
Question : What is the principle of an electric motor?
Answer: The working principle of an electric motor is based on the magnetic effect of current. A current-carrying loop experiences a force and rotates when placed in a magnetic field. The direction of rotation of the loop is given by the Fleming’s left-hand rule.
Question : What is the role of the split ring in an electric motor?
Answer: The split ring in the electric motor acts as a commutator. The commutator reverses the direction of current flowing through the coil after each half rotation of the coil. Due to this reversal of the current, the coil continues to rotate in the same direction.
Question : Explain different ways to induce current in a coil.
Answer: The different ways to induce current in a coil are as follows:
(a) If a coil is moved rapidly between the two poles of a horse-shoe magnet, then an electric
current is induced in the coil.
(b) If a magnet is moved relative to a coil, then an electric current is induced in the coil.
Question : State the principle of an electric generator.
Answer: An electric generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction. It generates electricity by rotating a coil in a magnetic field.
Question : Name some sources of direct current.
Answer: Some sources of direct current are cell, DC generator, etc.
Question : Which sources produce alternating current?
Answer: AC generators, power plants, etc., produce alternating current.
Question : Choose the correct option.
Answer: A rectangular coil of copper wires is rotated in a magnetic field. The direction of the induced current changes once in each
(a) two revolutions(b) one revolution
(c) half revolution (d) one-fourth revolution
(c) When a rectangular coil of copper is rotated in a magnetic field, the direction of the induced current in the coil changes once in each half revolution. As a result, the direction of current in the coil remains the same.
Question : Name two safety measures commonly used in electric circuits and appliances.
Answer: Two safety measures commonly used in electric circuits and appliances are as follows:
(i) Each circuit must be connected with an electric fuse. This prevents the flow of excessive current through the circuit. When the current passing through the wire exceeds the maximum limit of the fuse element, the fuse melts to stop the flow of current through that circuit, hence protecting the appliances connected to the circuit.
(ii) Earthing is a must to prevent electric shocks. Any leakage of current in an electric appliance is transferred to the ground and people using the appliance do not get the shock.
Question : An electric oven of 2 kW is operated in a domestic electric circuit (220 V) that has a current rating of 5 A. What result do you expect? Explain.
Answer: Current drawn by the electric oven can be obtained by the expression,
p=VI
I=P/v
Where,
Current = I
Power of the oven, P = 2 kW = 2000 W
Voltage supplied, V = 220 V
I= 2000/220=9.09 A
Hence, the current drawn by the electric oven is 9.09 A, which exceeds the safe limit of the circuit. Fuse element of the electric fuse will melt and break the circuit.
Question : What precaution should be taken to avoid the overloading of domestic electric circuits?
Answer: The precautions that should be taken to avoid the overloading of domestic circuits are as follows:
(a) Too many appliances should not be connected to a single socket.
(b) Too many appliances should not be used at the same time.
(c) Faulty appliances should not be connected in the circuit.
(d) Fuse should be connected in the circuit.
Question : Which of the following correctly describes the magnetic field near a long straight wire?
(a) The field consists of straight lines perpendicular to the wire
(b) The field consists of straight lines parallel to the wire
(c) The field consists of radial lines originating from the wire
(d) The field consists of concentric circles centred on the wire
Answer: (d) The magnetic field lines, produced around a straight current-carrying conductor, are concentric circles. Their centres lie on the wire.
Question : The phenomenon of electromagnetic induction is
(a) the process of charging a body
(b) the process of generating magnetic field due to a current passing through a coil
(c) producing induced current in a coil due to relative motion between a magnet and the coil
(d) the process of rotating a coil of an electric motor
Answer: (c) When a straight coil and a magnet are moved relative to each other, a current is induced in the coil. This phenomenon is known as electromagnetic induction.
Question : The device used for producing electric current is called a
(a) generator
(b) galvanometer
(c) ammeter
(d) motor
Answer: (a) An electric generator produces electric current. It converts mechanical energy into electricity.
Question : The essential difference between an AC generator and a DC generator is that
(a) AC generator has an electromagnet while a DC generator has permanent magnet.
(b) DC generator will generate a higher voltage.
(c) AC generator will generate a higher voltage.
(d) AC generator has slip rings while the DC generator has a commutator.
Answer: (d) An AC generator has two rings called slip rings. A DC generator has two half rings called commutator. This is the main difference between both the types of generators.
Question : At the time of short circuit, the current in the circuit
(a) reduces substantially
(b) does not change
(c) increases heavily
(d) vary continuously
Answer: (c) When two naked wires of an electric circuit touch each other, the amount of current that is flowing in the circuit increases abruptly. This causes short-circuit.
Question : State whether the following statements are true or false.
(a) An electric motor converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
(b) An electric generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
(c) The field at the centre of a long circular coil carrying current will be parallel straight lines.
(d) A wire with a green insulation is usually the live wire of an electric supply.
Answer: (a) False
An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
(b) True
A generator is an electric device that generates electricity by rotating a coil in a magnetic field. It works on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
(c) True
A long circular coil is a long solenoid. The magnetic field lines inside the solenoid are parallel lines.
(d) False
Live wire has red insulation cover, whereas earth wire has green insulation colour in the domestic circuits.
Question : List three sources of magnetic fields.
Answer: Three sources of magnetic fields are as follows:
(a) Current-carrying conductors
(b) Permanent magnets
(c) Electromagnets
Question : How does a solenoid behave like a magnet? Can you determine the north and south poles of a current-carrying solenoid with the help of a bar magnet? Explain.
Answer: A solenoid is a long coil of circular loops of insulated copper wire. Magnetic field lines are produced around the solenoid when a current is allowed to flow through it. The magnetic field produced by it is similar to the magnetic field of a bar magnet. The field lines produced in a current-carrying solenoid is shown in the following figure.
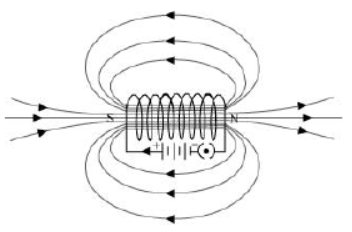
In the above figure, when the north pole of a bar magnet is brought near the end connected to the negative terminal of the battery, the solenoid repels the bar magnet. Since like poles repel each other, the end connected to the negative terminal of the battery behaves as the north pole of the solenoid and the other end behaves as a south pole. Hence, one end of the solenoid behaves as a north pole and the other end behaves as a south pole.
Question : When is the force experienced by a current-carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field largest?
Answer: The force experienced by a current-currying conductor is the maximum when the direction of current is perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field.
Question : Imagine that you are sitting in a chamber with your back to one wall. An electron beam, moving horizontally from back wall towards the front wall, is deflected by a strong magnetic field to your right side. What is the direction of magnetic field?
Answer: The direction of magnetic field is given by Fleming’s left hand rule. Magnetic field inside the chamber will be perpendicular to the direction of current (opposite to the direction of electron) and direction of deflection/force i.e., either upward or downward. The direction of current is from the front wall to the back wall because negatively charged electrons are moving from back wall to the front wall. The direction of magnetic force is rightward. Hence, using Fleming’s left hand rule, it can be concluded that the direction of magnetic field inside the chamber is downward.
Question : Imagine that you are sitting in a chamber with your back to one wall. An electron beam, moving horizontally from back wall towards the front wall, is deflected by a strong magnetic field to your right side. What is the direction of magnetic field?
Answer: The direction of magnetic field is given by Fleming’s left hand rule. Magnetic field inside the chamber will be perpendicular to the direction of current (opposite to the direction of electron) and direction of deflection/force i.e., either upward or downward. The direction of current is from the front wall to the back wall because negatively charged electrons are moving from back wall to the front wall. The direction of magnetic force is rightward. Hence, using Fleming’s left hand rule, it can be concluded that the direction of magnetic field inside the chamber is downward.
Question : Draw a labelled diagram of an electric motor. Explain its principle and working.
What is the function of a split ring in an electric motor?
Answer: An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.It works on the principle of the magnetic effect of current. A current-carrying coil rotates in a magnetic field. The following figure shows a simple electric motor.
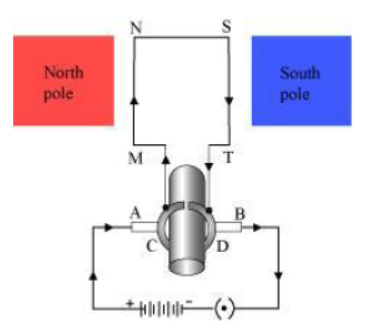
When a current is allowed to flow through the coil MNST by closing the switch, the coil starts rotating anti-clockwise. This happens because a downward force acts on length MN and at the same time, an upward force acts on length ST. As a result, the coil rotates anti-clockwise.
Current in the length MN flows fromM to N and the magnetic field acts from left to right, normal to length MN. Therefore, according to Fleming’s left hand rule, a downward force acts on the length MN. Similarly, current in the length ST flows from S to T and the magnetic field acts from left to right, normal to the flow of current. Therefore, an upward force acts on the length ST. These two forces cause the coil to rotate anti-clockwise.
After half a rotation, the position of MN and ST interchange. The half-ring D comes in contact with brush A and half-ring C comes in contact with brush B. Hence, the direction of current in the coil MNST gets reversed.
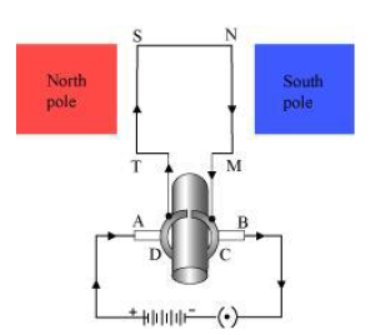
The current flows through the coil in the direction TSNM. The reversal of current through the coil MNST repeats after each half rotation. As a result, the coil rotates unidirectional. The split rings help to reverse the direction of current in the circuit. These are called the commutator.
Question : Name some devices in which electric motors are used?
Answer: Some devices in which electric motors are used are as follows:
(a) Water pumps
(b) Electric fans
(c) Electric mixers
(d) Washing machines
Question : A coil of insulated copper wire is connected to a galvanometer. What will happen if a bar magnet is (i) pushed into the coil, (ii) withdrawn from inside the coil, (iii) held stationary inside the coil?
Answer: A current induces in a solenoid if a bar magnet is moved relative to it. This is the principle of electromagnetic induction.
(i) When a bar magnet is pushed into a coil of insulated copper wire, a current is induced momentarily in the coil. As a result, the needle of the galvanometer deflects momentarily in a particular direction.
(ii) When the bar magnet is withdrawn from inside the coil of the insulated copper wire, a current is again induced momentarily in the coil in the opposite direction. As a result, the needle of the galvanometer deflects momentarily in the opposite direction.
(iii) When a bar magnet is held stationary inside the coil, no current will be induced in the coil.
Hence, galvanometer will show no deflection.
Question : Two circular coils A and B are placed closed to each other. If the current in the coil A is changed, will some current be induced in the coil B? Give reason.
Answer: Two circular coils A and B are placed close to each other. When the current in coil A is changed, the magnetic field associated with it also changes. As a result, the magnetic field around coil B also changes. This change in magnetic field lines around coil B induces an electric current in it. This is called electromagnetic induction.
Question : State the rule to determine the direction of a (i) magnetic field produced around a straight conductor-carrying current, (ii) force experienced by a current-carrying straight conductor placed in a magnetic field which is perpendicular to it, and (iii) current induced in a coil due to its rotation in a magnetic field.
Answer: (i) Maxwell’s right hand thumb rule
(ii) Fleming’s left hand rule
(iii) Fleming’s right hand rule
Question : Explain the underlying principle and working of an electric generator by drawing a labelled diagram. What is the function of brushes?
Answer: An electric generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
The principle of working of an electric generator is that when a loop is moved in a magnetic field,an electric current is induced in the coil. It generates electricity by rotating a coil in a magnetic field. The following figure shows a simple AC generator.
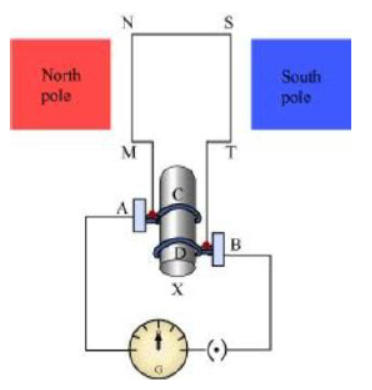
MNST →Rectangular coil
A and B → Brushes
C andD → Two slip rings
X →Axle, G → Galvanometer
If axle Xis rotated clockwise, then the length MN moves upwards while length ST moves downwards. Since the lengths MN and ST are moving in a magnetic field, a current will be induced in both of them due to electromagnetic induction. Length MN is moving upwards and the magnetic field acts from left to right. Hence, according to Fleming’s right hand rule, the direction of induced current will be from M to N. Similarly, the direction of induced current in the length ST will be from S to T.
The direction of current in the coil is MNST. Hence, the galvanometer shows a deflection in a particular direction. After half a rotation, length MN starts moving down whereas length ST starts moving upward. The direction of the induced current in the coil gets reversed as TSNM. As the direction of current gets reversed after each half rotation, the produced current is called an alternating current (AC).
To get a unidirectional current, instead of two slip rings, two split rings are used, as shown in the following figure.
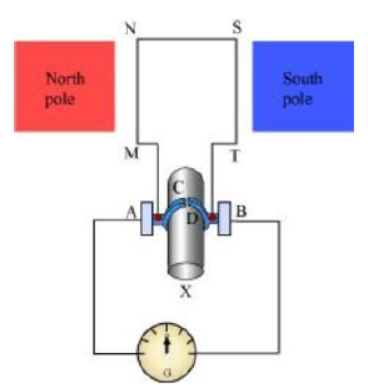
In this arrangement, brush A always remains in contact with the length of the coil that is moving up whereas brush B always remains in contact with the length that is moving down. The split rings C and D act as a commutator.
The direction of current induced in the coil will be MNST for the first rotation and TSNM in the second half of the rotation. Hence, a unidirectional current is produced from the generator called DC generator. The current is called AC current.
Question : When does an electric short circuit occur?
Answer: If the resistance of an electric circuit becomes very low, then the current flowing through the circuit becomes very high. This is caused by connecting too many appliances to a single socket or connecting high power rating appliances to the light circuits. This results in a short circuit.When the insulation of live and neutral wires undergoes wear and tear and then touches each other, the current flowing in the circuit increases abruptly. Hence, a short circuit occurs.
Question : What is the function of an earth wire?Why is it necessary to earth metallic appliances?
Answer: The metallic body of electric appliances is connected to the earth by means of earth wire so that any leakage of electric current is transferred to the ground. This prevents any electric shock to the user. That is why earthing of the electrical appliances is necessary.
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids Bases and Salts |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non metals |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control and Coordination |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric current |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 14 Sources of Energy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources |
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric current
The above provided NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric current is available on our website www.studiestoday.com for free download in Pdf. You can read the solutions to all questions given in your Class 10 Science textbook online or you can easily download them in pdf. The answers to each question in Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric current of Science Class 10 has been designed based on the latest syllabus released for the current year. We have also provided detailed explanations for all difficult topics in Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric current Class 10 chapter of Science so that it can be easier for students to understand all answers. These solutions of Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric current NCERT Questions given in your textbook for Class 10 Science have been designed to help students understand the difficult topics of Science in an easy manner. These will also help to build a strong foundation in the Science. There is a combination of theoretical and practical questions relating to all chapters in Science to check the overall learning of the students of Class 10.
You can download the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric current for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the NCERT Solutions issued for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric current have been made available here for latest academic session
Regular revision of NCERT Solutions given on studiestoday for Class 10 subject Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric current can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all latest NCERT Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric current Class 10 Science solutions based on the latest books for the current academic session
Yes, NCERT solutions for Class 10 Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric current Science are available in multiple languages, including English, Hindi
All questions given in the end of the chapter Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric current have been answered by our teachers

