NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds have been provided below and is also available in Pdf for free download. The NCERT solutions for Class 10 Science have been prepared as per the latest syllabus, NCERT books and examination pattern suggested in Class 10 by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. Questions given in NCERT book for Class 10 Science are an important part of exams for Class 10 Science and if answered properly can help you to get higher marks. Refer to more Chapter-wise answers for NCERT Class 10 Science and also download more latest study material for all subjects. Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds is an important topic in Class 10, please refer to answers provided below to help you score better in exams
Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds Class 10 Science NCERT Solutions
Class 10 Science students should refer to the following NCERT questions with answers for Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds in Class 10. These NCERT Solutions with answers for Class 10 Science will come in exams and help you to score good marks
Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
Question. Which of the following is not an use of graphite ?
(A) dry lubricant
(B) electrodes
(C) black paints
(D) high precision thermometers
Answer : D
Question. Which of the following is the chemically inactive allotropic form of carbon ?
(A) diamond
(B) coal
(C) charcoal
(D) animal charcoal
Answer : A
Question. Which of the following properties is not true regarding organic compounds ?
(A) They are generally covalent compounds.
(B) They have high melting and boiling points.
(C) They are generally insoluble in water.
(D) They generally show isomerism
Answer : B
Question. The scientist who gave vital force theory was -
(A) Berzelius
(B) Avogadro
(C) Wohler
(D) Lavoisier
Answer : A
Question. Which one of the following is not an organic compound ?
(A) Hexane
(B) Urea
(C) Ammonia
(D) Ethyl alcohol
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following statements is/are true for fullerene ?
(A) It is a non-crystalline form of carbon.
(B) It was discovered by Buckminster fuller.
(C) All the fullerenes have even number of atoms
(D) All of these
Answer : C
Question. In diamond, the bonding between carbon atoms is -
(A) Co-ordinate
(B) Ionic
(C) Electrostatic
(D) Covalent
Answer : D
Question. Graphite is a soft solid lubricant extremly difficult to melt. The reason for this anomalous behaviour is that graphite -
(A) has carbon atoms arranged in large plates of rings of strongly bonded carbon atoms with weak interplate bonds.
(B) is a non-crystalline substance
(C) is an allotropic form of carbon
(D) has molecules of variable molecular masses like polymers.
Answer : A
Question. The number of sigma and pi bonds in the structure, CH2 = CH – C CH
(A) 7 and 3
(B) 6 and 2
(C) 4 and 3
(D) All are sigma bonds
Answer : A
Question. Number of & bonds in benzene are :
(A) 6 , 3
(B) 3 , 3
(C) 12 , 3
(D) 6 , 6
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following is an unsaturated compound ?
(A) C6H14
(B) CH3OH
(C) C3H7OH
(D) C4H8
Answer : D
Question. The functional group, present in CH3COOC2H5 is -
(A) ketonic
(B) aldehydic
(C) ester
(D) carboxylic
Answer : C
Question. C ≅ C bond length is -
(A) 1.54 Å
(B) 1.20 Å
(C) 1.34 Å
(D) 1.39 Å
Answer : B
Question. Which of the following hydrocarbon does not exhibit position isomerism ?
(A) C2H4
(B) C3H6
(C) C3H4
(D) All of these
Answer : D
Question. Which of the following forms a homologus series -
(A) Ethane, ethylene, acetylene
(B) Ethane, propane, butanol
(C) methanal, ethanol, propanoic acid
(D) Butane, 2-Methylbutane, 2,3-Dimethyl butane
Answer : D
Question. The compound which can show chain iosmerism is -
(A) CH4
(B) CH3CH3
(C) CH3CH2CH3
(D) CH3CH2CH2CH3
Answer : D
Question. Which of the following statement is/are true about characteristic properties of alkanes ?
(A) Boiling point increases with molecular mass.
(B) All alkane are saturated hydrocarbons.
(C) They mostly show substitution reactions with halogens.
(D) All of these
Answer : D
Question. Methane is insoluble in -
(A) ether
(B) water
(C) alcohol
(D) carbon tetrachloride
Answer : B
Question. Soaps are sodium salts of fatty acids, RCOONa;
e.g. C17H35COO-Na+. It gives an insoluble precipitate/layer with
(A) Ca2+(aq)
(B) Mg2+(aq)
(C) HCl(aq)
(D) All of these
Answer : D
Question. The IUPAC name of CH3 – C(CH3) (OH) CH2 – CH(CH3) CH3 is -
(A) 2,4-Dimethylpentan-2-ol
(B) 2,4- Dimethylpentan-4-ol
(C) 2,2-Dimethylbutane
(D) Butanol-2-one
Answer : A
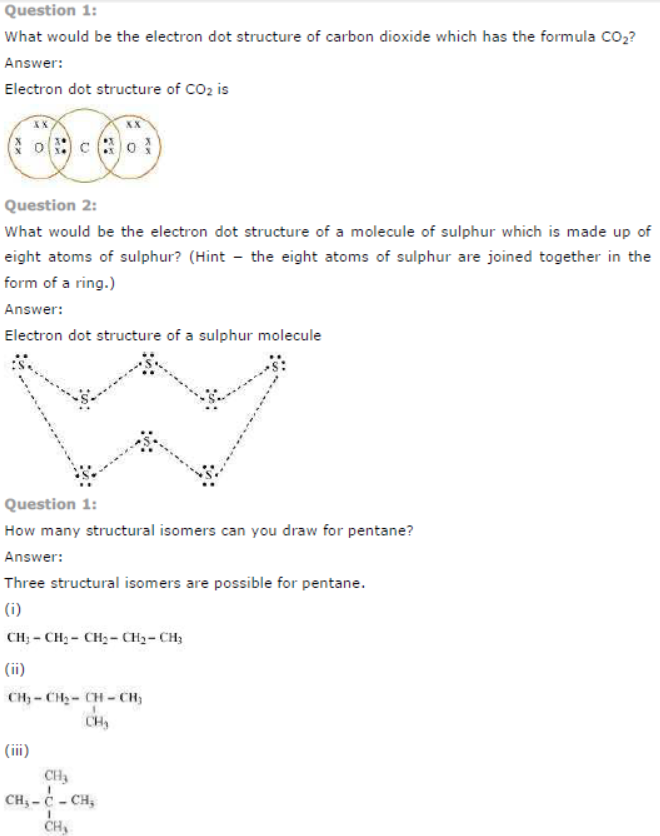
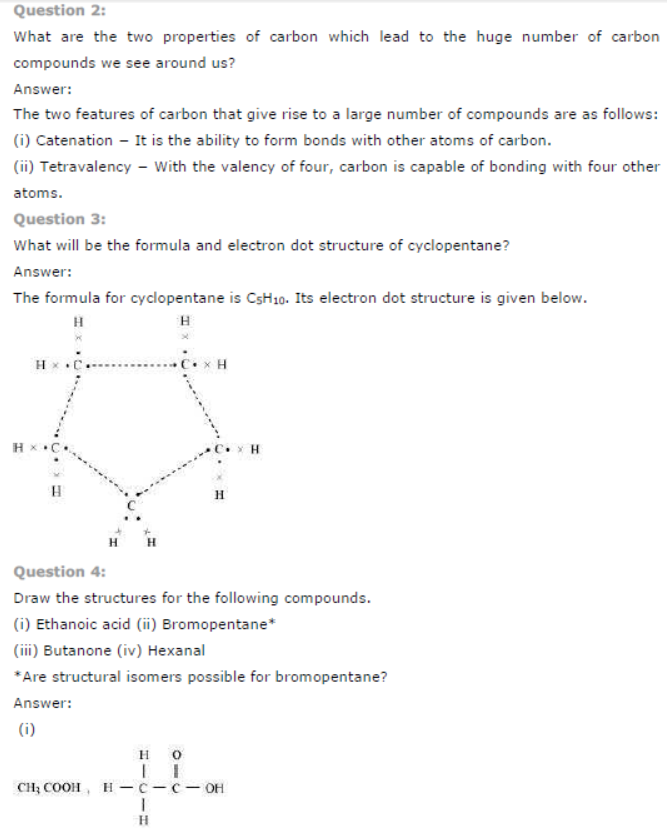

Question : Why is the conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid an oxidation reaction?
Answer:
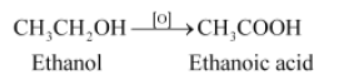
Since the conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid involves the addition of oxygen to ethanol, it is an oxidation reaction.
Question : A mixture of oxygen and ethyne is burnt for welding. Can you tell why a mixture of ethyne and air is not used?
Answer:
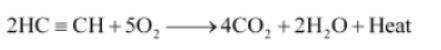
When ethyne is burnt in air, it gives a sooty flame. This is due to incomplete combustion caused by limited supply of air. However, if ethyne is burnt with oxygen, it gives a clean flame with temperature 3000°C because of complete combustion. This oxy-acetylene flame is used for welding. It is not possible to attain such a high temperature without mixing oxygen. This is the reason why a mixture of ethyne and air is not used.
Question : How would you distinguish experimentally between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid?
Answer: We can distinguish between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid on the basis of their reaction with carbonates and hydrogen carbonates. Acid reacts with carbonate and hydrogen carbonate to evolve CO2 gas that turns lime water milky.
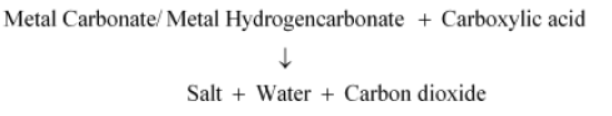
Alcohols, on the other hand, do not react with carbonates and hydrogen carbonates.
Question : What are oxidising agents?
Answer: Some substances such as alkaline potassium permanganate and acidified potassium dichromate are capable of adding oxygen to others. These are known as oxidising agents.
Question : Would you be able to check if water is hard by using a detergent?
Answer: Detergents are ammonium or sulphonate salts of long chain carboxylic acids. Unlike soap, they do not react with calcium and magnesium ions present in hard water to form scum. They give a good amount of lather irrespective of whether the water is hard or soft. This means that detergents can be used in both soft and hard water. Therefore, it cannot be used to check whether the water is hard or not.
Question : People use a variety of methods to wash clothes. Usually after adding the soap, they ‘beat’ the clothes on a stone, or beat it with a paddle, scrub with a brush or the mixture is agitated in a washing machine. Why is agitation necessary to get clean clothes?
Answer: A soap molecule has two parts namely hydrophobic and hydrophilic. With the help of these, it attaches to the grease or dirt particle and forms a cluster called micelle. These micelles remain suspended as a colloid. To remove these micelles (entrapping the dirt),it is necessary to agitate clothes.
Question : Ethane, with the molecular formula C2H6 has
(a) 6 covalent bonds.
(b) 7 covalent bonds.
(c) 8 covalent bonds.
(d) 9 covalent bonds.
Answer: (b) Ethane has 7 covalent bonds.
Question : Butanone is a four-carbon compound with the functional group
(a) carboxylic acid.
(b) aldehyde.
(c) ketone.
(d) alcohol.
Answer: (c) The functional group of butanone is ketone.
Question : While cooking, if the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the outside, it means that
(a) the food is not cooked completely.
(b) the fuel is not burning completely.
(c) the fuel is wet.
(d) the fuel is burning completely.
Answer: (b) While cooking, if the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the outside, then it means that the fuel is not burning completely.
Question : Explain the nature of the covalent bond using the bond formation in CH3Cl.
Answer: Carbon can neither lose four of its electrons nor gain four electrons as both the processes require extra amount of energy and would make the system unstable.
Therefore, it completes its octet by sharing its four electrons with other carbon atoms or with atoms of other elements. The bonds that are formed by sharing electrons are known as covalent bonds. In covalent bonding, both the atoms share the valence electrons, i.e., the shared electrons belong to the valence shells of both the atoms.
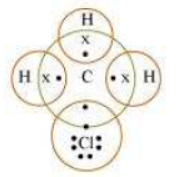
Here, carbon requires 4 electrons to complete its octet, while each hydrogen atom requires one electron to complete its duplet. Also, chlorine requires an electron to complete the octet. Therefore, all of these share the electrons and as a result, carbon forms 3 bonds with hydrogen and one with chlorine.
Question : Draw the electron dot structures for
(a) ethanoic acid.
(b) H2S.
(c) propanone.
(d) F2.
Answer:
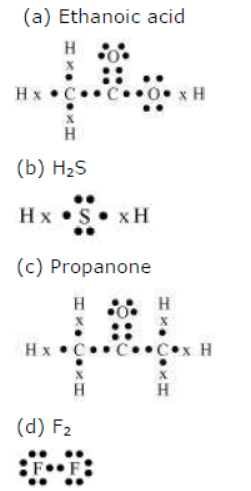
Question : What is a homologous series? Explain with an example.
Answer: A homologous series is a series of carbon compounds that have different numbers of carbon atoms but contain the same functional group.
For example, methane, ethane, propane, butane, etc. are all part of the alkane homologous series. The general formula of this series is CnH2n+2.
Methane CH4
Ethane CH3CH3
Propane CH3CH2CH3
Butane CH3CH2CH2CH3
It can be noticed that there is a difference of −CH2 unit between each successive compound.
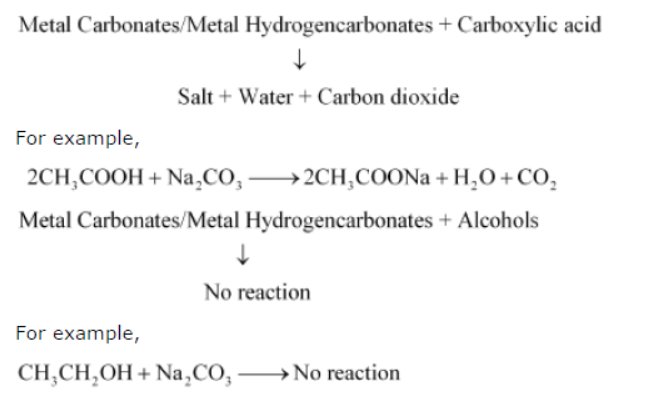
Question : How can ethanol and ethanoic acid be differentiated on the basis of their physical and chemical properties?
Answer:
• Ethanol is a liquid at room temperature with a pleasant odour while ethanoic acid has vinegar-like smell. The melting point of ethanoic acid is 17°C. This is below room temperature and hence, it freezes during winters.
• Ethanoic acid reacts with metal carbonates and metal hydrogencarbonates to form salt, water, and carbon dioxide gas while ethanol does not react with them.
Question : In the electrolytic refining of a metal M, what would you take as the anode, the cathode and the electrolyte?
Answer: In the electrolytic refining of a metal M:
Anode → Impure metal M
Cathode → Thin strip of pure metal M
Electrolyte → Solution of salt of the metal M
Question : Why are carbon and its compounds used as fuels for most applications?
Answer: Most of the carbon compounds give a lot of heat and light when burnt in air. Saturated hydrocarbons burn with a clean flame and no smoke is produced. The carbon
compounds, used as a fuel, have high calorific values. Therefore, carbon and its compounds are used as fuels for most applications.
Question : Explain the formation of scum when hard water is treated with soap.
Answer: Soap does not work properly when the water is hard. A soap is a sodium or potassium salt of long chain fatty acids. Hard water contains salts of calcium and magnesium. When soap is added to hard water, calcium and magnesium ions present in water displace sodium or potassium ions from the soap molecules forming an insoluble substance called scum. A lot of soap is wasted in the process.
Question : What change will you observe if you test soap with litmus paper (red and blue)?
Answer: Since soap is basic in nature, it will turn red litmus blue. However, the colour of blue litmus will remain blue.
Question : What is hydrogenation? What is its industrial application?
Answer: Hydrogenation is the process of addition of hydrogen. Unsaturated hydrocarbons are added with hydrogen in the presence of palladium and nickel catalysts to give saturated hydrocarbons.
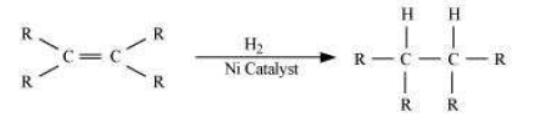
This reaction is applied in the hydrogenation of vegetables oils, which contain long chains of unsaturated carbons.
Question : Which of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition reactions:
C2H6, C3H8, C3H6, C2H2 and CH4.
Answer: Unsaturated hydrocarbons undergo addition reactions. Being unsaturated hydrocarbons,C3H6 and C2H2 undergo addition reactions.
Question : Give a test that can be used to differentiate chemically between butter and cooking oil.
Answer: Butter contains saturated fats. Therefore, it cannot be hydrogenated. On the other hand, oil has unsaturated fats. That is why it can be hydrogenated to saturated fats (solids).
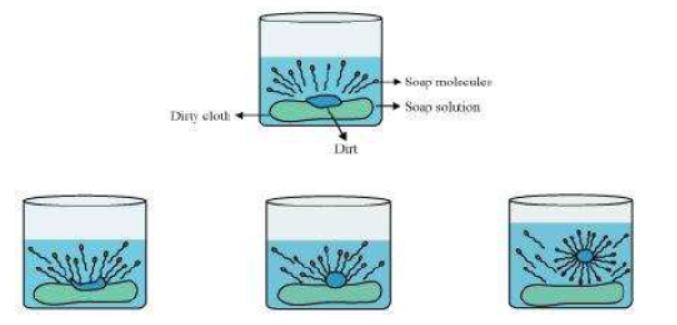
Question : Explain the mechanism of the cleaning action of soaps.
Answer: Cleansing action of soaps:
The dirt present on clothes is organic in nature and insoluble in water. Therefore, it cannot be removed by only washing with water. When soap is dissolved in water, its hydrophobic ends attach themselves to the dirt and remove it from the cloth. Then, the molecules of soap arrange themselves in micelle formation and trap the dirt at the centre of the cluster. These micelles remain suspended in the water. Hence, the dust particles are easily rinsed away by water.
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids Bases and Salts |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non metals |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control and Coordination |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric current |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 14 Sources of Energy |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment |
| NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources |
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds
The above provided NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds is available on our website www.studiestoday.com for free download in Pdf. You can read the solutions to all questions given in your Class 10 Science textbook online or you can easily download them in pdf. The answers to each question in Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds of Science Class 10 has been designed based on the latest syllabus released for the current year. We have also provided detailed explanations for all difficult topics in Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds Class 10 chapter of Science so that it can be easier for students to understand all answers. These solutions of Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds NCERT Questions given in your textbook for Class 10 Science have been designed to help students understand the difficult topics of Science in an easy manner. These will also help to build a strong foundation in the Science. There is a combination of theoretical and practical questions relating to all chapters in Science to check the overall learning of the students of Class 10.
You can download the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the NCERT Solutions issued for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds have been made available here for latest academic session
Regular revision of NCERT Solutions given on studiestoday for Class 10 subject Science Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all latest NCERT Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds Class 10 Science solutions based on the latest books for the current academic session
Yes, NCERT solutions for Class 10 Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds Science are available in multiple languages, including English, Hindi
All questions given in the end of the chapter Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds have been answered by our teachers

