UNIT - 2
SOLUTIONS
1 Marks Questions
1. A 500 gm of toothpaste sample has 0.2 g of fluoride concentration. What is the concentration of fluoride in terms of ppm level?
2. Two liquids A and B boil at 1350C and 1850C respectively. Which of them has a higher vapour pressure at 800C?
3. Write the possible structural arrangement of a mixture of chloroform and acetone to form a solution.
4. What is Van’t Hoff’s factor for a compound which undergoes tetramerization in an organic solvent?
5. Aquatic species are more comfortable in cold waters rather than in warm water. Give reason.
2 marks questions
6. RBC’s are placed in the given solutions as in figure (i)and (ii). What happens to RBC in test tube (i) and test tube (ii).
7. Given below is the sketch of a plant carrying out a process.
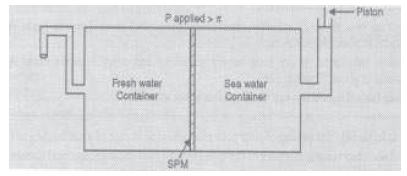
(i) Name the process occurring in the above plant.
(ii) To which container does the net flow of the solvent takes place?
(iii) Name one SPM which can be used in this plant.
(iv) Give one practical use of the plant.
8. A solution of sucrose (Molar mass 342 g mol-1) is prepared by dissolving 68.4 g in 1000 g of water. What is the
(i) Vapour pressure of the solution at 293k .
(ii) Osmotic pressure at 293k.
(iii) Boiling point of the solution.
(iv) Freezing point of the solution.
The vapour pressure of the water at 293k is 0.023atm. kb=0.52k kg mol-1 & kf=1.86k kg mol-1 . Assume the solution to behave ideally.
9. Why calculations based on colligative properties of solutions sometimes do gives abnormal molecular mass values for solute? What are the nature of the abnormalities. 2g of C6H5COOH dissolved in 25g of benzene shows a depression
in freezing point equal to 1.62k. Molal depression constant for benzene is 4.9k kg mol-1. What is the Percentage(%) of association of acid, if it forms a dimer in solution?
10. Assuming complete dissociation, calculate the freezing point of a solution prepared by dissolving 6 g of glaubers salt (Na2SO4.10H2O) in 0.100 kg of H2O. Given kf = 1.86k kg mol-1 Atomic mass of H2O : 18 , Na : 23 , S : 32 , O : 16 , H : 1 all in amu units.
3 Marks Questions
11. A) Addition of HgI2 to aq. KI solution shows an increase in the vapour pressure why?
B) A person suffering from high blood pressure is advised to take minimum quantity of common salt. Give reason.
12. A) Why the vapour pressure of a solution of glucose in water lower than that of water?
B) 0.1 molal solution of glucose and NaCl respectively. Which one will have higher boiling point?
13. H2S, a toxic gas with rotten egg like smell is used for qualitative analysis. If the solubility of H2S in water at STP is 0.195 m, calculate Henry’s law constant (kH=282 bar)
14. Examine the following illustrations and answer the following questions.
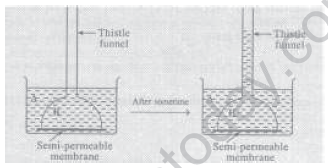
1) Identify the liquid A (pure water or sugar solution).
2) Identify the liquid B (pure water or sugar solution).
3) Why the level of liquid in thistle funnel has risen after sometime?
4) Name the phenomenon involved in this experiment and define it.
15. A storage battery contains a solution of H2SO4 38% by weight. At this concentration van’t Hoff factor is 2.50. At what temperature will the battery contents freeze? (kf for water =1.86k kg/ mol)
16. Following are the graphs for the vapour pressure of two component system as a function of composition. Answer the following questions.
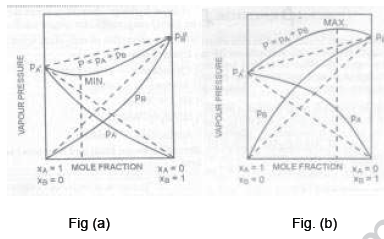
(i) What type of deviation is shown in fig.(a) and (b)?
(ii) Give one example of solutions showing deviations in fig ( a) (b).
(iii) What change in the volume and temperature is observed in solutions of this type?
17. How does osmotic pressure depend on temperature and atmospheric pressure, what is the molar concentration of solute particles in the human blood, if the osmotic pressure is 7.2 atm at the body temperature of 370C?
18. The vapour pressure of dilute aqueous solution of glucose (C6H12O6) is 750 mm of mercury at 373K. Calculate
1) Molality
2) Mole fraction of the solute
5 Marks Questions
19. The elements A and B form purely covalent compounds having molecular formulae AB2 and AB4. When dissolved in 20g of benzene, 1g of AB2 lowers the freezing point by 2.3K, whereas 1g of AB4 lowers it by 1.3K. the molal depression constant for benzene is 5.1 K kg/mol, calculate the atomic mass of A and atomic mass of B. (A=25.59, B=42.64)
20. a) Why constant boiling mixtures behave like a single component when subjected to distillation.
b) What type of Azeotropic mixtures are formed by the following solution
i) H2O and HCl ii) H2O and C2H5OH
c) Give one practical application of depression of freezing point?
d) A Solid solution is formed between two substances. One whose particles are very large and the other particles are very small. What type of solid solution is this likely to be?
e) Write the Raoults Law for each component of a binary solution and show that the total vapour pressure of the solution may be expressed as P = P0A + (P0B – P0A) XB
21. Vapour pressure of pure benzene at a certain temperature is 640 mm Hg. A non-volatile non-electrolyte solid weighing 2.175g is added to 39.0 of benzene. The vapour pressure of solution is 600 mm Hg. What is the molecular mass of
solid substance? (65.9g mol-1 )
22. The degree of dissociation of Ca(NO3 )2 in dilute solution aqueous solution containing 7.0g of the solute per 100g of water at 1000 C is 70 percent. If the vapour pressure of water at 1000 C is 760mm, calculate the vapour pressure of
the solution. (746.02mm)
23. What mass of a non-volatile solute urea (NH2CONH2) need to be dissolved in 100g of water in order to decrease the vapour pressure of water by 25%? also calculate the molality of the solution. (18.52m)
24. 8.0575 X 10-2 kg of Glauber’s salt is dissolved in water to obtain 1 dm3 of a solution of density 1077.2 kg m-3. Calculate the molarity, molality & mole fraction of Na2SO4 in the solution. (0.2508m, 0.0045, 0.25M)
25. To 500 cm3 of water 3.0 X 10-3 kg of acetic acid is added. If 23% of acetic acid is dissociated, what will be the depression in freezing point? Kf and density of water are 1.86 K kg mol-1 & 0.997 g cm-3 respectively.(0.229K)
1 - MARK QUESTIONS
1. Why a person suffering from high blood pressure is advised to take minimum quantity of common salt ? 1
2. What happens to vapour pressure of water, if a table spoon of glucose is added to it ? 1
3. Equimolar solutions of glucose and sodium chloride are not isotonic. Why ? 1
4. Two liquids A and B boil at 145oC and 190oC respectively. Which of them has a higher vapour pressure at 80oC. 1
5. Semipermeable membrane of cupric ferrocyanide is not used for studying osmosis in non aqueous solutions. Why ? 1
6. Why is camphor preferred as a solvent in the determination of ΔTf ? 1
7. Addition of HgI2 to aq KI solution shows an increase in the vapour pressure. Why ? 1
2 - MARKS QUESTIONS
8. Arrange the following in the order of increasing i. boiling points and ii. freezing points
a. 1M aq acetic acid b. 1M aq NaCl c. 1M aq Na2SO4 d. 1M aq AlCl3 2
9. Calculate the number of moles of methanol in 5 L in its 2m solution, if the density of the solution is 0.981 kgL-1 2
10. Calculate the amount of ice that will separate out on cooling a solution containing 50 g of ethylene glycol in 200 g of water to – 9.3oC. 2
11. The temperature at a hill station is – 10oC. Will it be suitable to add ethylene glycol to water in the radiator sol that the solution is 30 % by mass. Why ? 2
12. A 45 % solution of sucrose is isotonic with 3 % solution of an unknown substance. Calculate the molecular mass of the unknown substance. 2
13. An electrolyte AB is 50 % ionized in aq solution. Calculate the freezing point of 1m aq solution.
3 - MARKS QUESTIONS
14. 75.2 g of phenol is dissolved in solvent of Kf = 14. If the depression in freezing point is 7K, find the % of phenol that dimerises ? 3
15. A solution of 3.8 g Sulphuyr in CS2 ( boiling point 46.3 oC ) boils at 46.66 oC. What is the formula of Sulphur molecule in this solution. Kb for CS2 = 2.40 kg mol-1 3
16. An aqueous solution of 1.248 g of Barium chloride ( molar mass = 208.34 g mol-1 ) in 100 g of water is found to boil at 100.0832oC. Calculate the degree of dissociation of BaCl2 . Kb of water = 0.52 K kg mol-1 3
17. The storage battery contains a solution of sulphuric acid 38 % by mass. At this concentration vant Hoff factor is 2.50. At what temperature will the battery condense freeze ? Kf for water = 1.86 K kg mol-1

