Please refer to CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Photosynthesis in Higher Plants. Download HOTS questions and answers for Class 11 Biology. Read CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs for Chapter 13 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants below and download in pdf. High Order Thinking Skills questions come in exams for Biology in Class 11 and if prepared properly can help you to score more marks. You can refer to more chapter wise Class 11 Biology HOTS Questions with solutions and also get latest topic wise important study material as per NCERT book for Class 11 Biology and all other subjects for free on Studiestoday designed as per latest CBSE, NCERT and KVS syllabus and pattern for Class 11
Chapter 13 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Class 11 Biology HOTS
Class 11 Biology students should refer to the following high order thinking skills questions with answers for Chapter 13 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants in Class 11. These HOTS questions with answers for Class 11 Biology will come in exams and help you to score good marks
HOTS Questions Chapter 13 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Class 11 Biology with Answers
Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
Important Questions for NCERT Class 11 Biology Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
Ques. One scientist cultured Cladophora in a suspension of Azotobacter and illuminated the culture by splitting light through a prism. He observed that bacteria accumulated mainly in the region of
(a) violet and green light
(b) indigo and green light
(c) orange and yellow light
(d) blue and red light.
Answer: D
Question. Basic feature of Kranz anatomy of C4 plants is
(a) chloroplasts in mesophyll cells are granal whereas in bundle-sheath they are agranal, that favours light reaction and carbon reactions separately.
(b) presence of granal chloroplasts in mesophyll and epidermal cells
(c) presence of typical granal chloroplasts in bundle sheath cells and rudimentary chloroplasts in mesophyll cells
(d) presence of rudimentary chloroplasts in bundle sheath cells and typical granal chloroplasts in mesophyll cells.
Answer. A
Question. Non-cyclic photophosphorylation is also known as
(a) photolysis
(b) photorespiration
(c) Z-scheme
(d) biosynthetic phase.
Answer. C
Question. In PS II, active chlorophyll is
(a) P680
(b) P700
(c) P673
(d) P720.\
Answer. A
Question. Photosynthesis in C4 plants is relatively less limited by atmospheric CO2 because
(a) there is effective pumping of CO2 into bundle sheath cells
(b) RuBisCO in C4 plants has higher affinity for CO2
(c) four carbon acids are primary initial CO2 fixation products
(d) primary fixation of CO2 is mediated via PEP carboxylase.
Answer. D
Question. Which one of the following is false about the activities associated with PS-I and PS-II in non-cyclic photophosphorylation?
(a) Water is oxidised in PS-II, but not PS-I.
(b) Photons (light) are needed to activate both PS I and PS-II.
(c) Photolysis of water, formation of ATP and NADPH occur.
(d) Production of NADPH + H+ is associated with PS-II, not with PS-I.
Answer. D
Question. Calvin cycle has three stages.
1. Reduction during which carbohydrate is formed at the expense of photochemically made ATP and NADPH.
2. Regeneration during which carbon dioxide acceptor 1, 5-RuBP is formed.
3. Carboxylation during which CO2 combines with 1,5 RuBP.
Identify the correct sequence.
(a) 3, 1, 2
(b) 3, 2, 1
(c) 1, 2, 3
(d) 2, 1, 3
Answer. A
Question. The carbon dioxide acceptor in Calvin cycle/ C3 plants is
(a) Phosphoenol pyruvate (PEP)
(b) Ribulose-1, 5-biphosphate (RuBP)
(c) Phosphoglyceric acid (PGA)
(d) Ribulose monophosphate (RMP).
Answer. B
Question. Carbon in carbon dioxide is radioactively labelled. The product in which radioactive carbon can be traced in C3 plants is
(a) PEP
(b) RuBP
(c) PGAL
(d) PGA.
Answer. D
Question. Glucose synthesis occurs during which stage of C3 cycle?
(a) Carboxylation
(b) Oxygenation
(c) Reduction
(d) Regeneration
Answer. C
Question. Match the following and choose the correct combination from the option given.
Column I Column II
A. Thylakoid of chloroplast (i) Kreb’s cycle
B. Stroma of chloroplast (ii) Light reaction
C. Cytoplasm (iii) Dark reaction
D. Mitochondrial matrix (iv) Glycolysis
(a) A-(iv), B-(iii), C-(ii), D-(i)
(b) A-(i), B-(ii), C-(iv), D-(iii)
(c) A-(iv), B-(i), C-(iii), D-(ii)
(d) A-(ii), B-(iii), C-(iv), D-(i)
Answer. D
Question. Law of limiting factor is
(a) law of maximum
(b) law of minimum
(c) law of optimum
(d) all of these.
Answer. B
Question. A point at which illuminated plant parts stop absorbing CO2 from their environment, is known as
(a) CO2 compensation point
(b) CO2 saturation point
(c) CO2 optimum point
(d) CO2 limiting point.
Answer. A
Question. Plant factors affecting photosynthesis include
(a) number, age, size and orientation of leaves, mesophyll cells and chloroplast, internal CO2 conc., the amount of chlorophyll
(b) nature of leaves, size of mesophyll cells and light only
(c) mesophyll cells and temperature only
(d) quantity of chlorophyll, size of leaves only.
Answer. A
Ques. Oxygen is not produced during photosynthesis by
(a) Green sulphur bacteria
(b) Nostoc
(c) Cycas
(d) Chara.
Answer: A
Ques. Anoxygenic photosynthesis is characteristic of
(a) Rhodospirillum
(b) Spirogyra
(c) Chlamydomonas
(d) Ulva.
Answer: A
Ques. Oxygenic photosynthesis occurs in
(a) Oscillatoria
(b) Rhodospirillum
(c) Chlorobium
(d) Chromatium.
Answer: A
Ques. Stroma in the chloroplasts of higher plant contains
(a) light-dependent reaction enzymes
(b) ribosomes
(c) chlorophyll
(d) light-independent reaction enzymes.
Answer: D
Ques. Emerson’s enhancement effect and Red drop have been instrumental in the discovery of
(a) photophosphorylation and cyclic electron transport
(b) oxidative phosphorylation
(c) photophosphorylation and non-cyclic electron transport
(d) two photosystems operating simultaneously.
Answer: D
Ques. Chromatophores take part in
(a) movement
(b) respiration
(c) photosynthesis
(d) growth.
Answer: C
Ques. Which fractions of the visible spectrum of solar radiations are primarily absorbed by carotenoids of the higher plants?
(a) Blue and green
(b) Green and red
(c) Red and violet
(d) Violet and blue
Answer: D
Ques. Which element is located at the centre of the porphyrin ring in chlorophyll ?
(a) Calcium
(b) Magnesium
(c) Potassium
(d) Manganese
Answer: B
Ques. Chlorophyll a molecule at its carbon atom 3 of the pyrrole ring II has one of the following
(a) carboxylic group
(b) magnesium
(c) aldehyde group
(d) methyl group.
Answer: D
Ques. The core metal of chlorophyll is
(a) Ni
(b) Cu
(c) Fe
(d) Mg.
Answer: D
Ques. Chlorophyll a occurs in
(a) all photosynthetic autotrophs
(b) in all higher plants
(c) all oxygen liberating autotrophs
(d) all plants except fungi.
Answer: C
Ques. Photosynthetic pigments found in the chloroplasts occur in
(a) thylakoid membranes
(b) plastoglobules
(c) matrix
(d) chloroplast envelope.
Answer: A
Ques. The size of chlorophyll molecule is
(a) head 15 × 15 Å, tail 25 Å
(b) head 20 × 20 Å, tail 25 Å
(c) head 15 × 15 Å, tail 20 Å
(d) head 10 × 12 Å, tail 25 Å.
Answer: C
Ques. Which of the following is not a product of light reaction of photosynthesis?
(a) ATP
(b) NADH
(c) NADPH
(d) Oxygen
Answer: B
Ques. Which of the following absorb light energy for photosynthesis?
(a) Chlorophyll
(b) Water molecule
(c) O2
(d) RuBP
Answer: A
Ques. The first step for initiation of photosynthesis will be
(a) photolysis of water
(b) excitement of chlorophyll molecules due to absorption of light
(c) ATP formation
(d) glucose formation.
Answer: B
Ques. NADPH2 is generated through
(a) photosystem II
(b) anaerobic respiration
(c) glycolysis
(d) photosystem I.
Answer: D
Ques. Which of the following pigments acts as a reactioncentre during photosynthesis?
(a) Carotene
(b) Phytochrome
(c) P700
(d) Cytochrome
Answer: C
Case II : Read the following passage and answer questions from 46 to 50 given below:
Photosynthetic reactions which are dependent on the products of light reaction are calledb biosynthetic phase or dark reactions. There are two main pathways -−Calvin cycle and C4 (dicarboxylic acid) cycle in which assimilatory power (ATP and NADPH) produced during photochemical phase is used in fixation andre duction of carbon dioxide.
Question. In C3 cycle, ATP and NADH required for production of one glucose respectively are
(a) 12 and 18
(b) 18 and 12
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 3 and 2.
Answer. B
Question. Which one of following is a special feature of C4 plants?
(a) They tolerate high temperature.
(b) They have lesser productivity of biomass.
(c) They show less response to high light intensity.
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer. A
Question. Bundle sheath cells in C4 plants have
(a) thick walls, large intercellular spaces, large number of chloroplasts
(b) thin walls, no intercellular spaces, large number of chloroplasts
(c) thin walls, large intercellular spaces, no chloroplasts
(d) thick walls, no intercellular spaces, large number of chloroplasts.
Answer. D
Question. Where do Calvin pathway takes place in C3 and C4 plants?
(a) It takes place in mesophyll cells of both C3 and C4 plants.
(b) If takes place is mesophyll cells of C3 plant and bundle sheath cells of C4 plant.
(c) Bundle sheath cells of C3 plant and mesophyll cells of C4 plant.
(d) It takes place in bundle sheath cells of C3 and C4 plants.
Answer. B
Question. Read the given statements and answer the follwing questions.
Statement 1 : In C4 plants, OAA is formed in mesophyll cells.
Statement 2 : Mesophyll cells of C4 plants have enzyme PEP case but lack RuBisCO.
(a) Both statements 1 and 2 are true.
(b) Statement 1 is true but statement 2 is false.
(c) Statement 1 is false but statement 2 is true.
(d) Both statements 1 and 2 are false.
Answer. A
Assertion & Reasoning Based MCQs For question numbers 51-60, two statements are given-one labelled Assertion and the other labelled Reason. Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false but reason is true.
Question. Assertion : Plastoquinones act as link between two photosystems.
Reason : The donor of electrons for both photosystems is water.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : Quantum conversion occurs during light reaction.
Reason : Light reaction generates energy-rich compounds.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : A plant growing in complete dark will show only dark reactions.
Reason : Dark reaction produces assimilatory power.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : Plants showing Calvin-Benson pathway are called C3 plants.
Reason : Plants showing Hatch-Slack pathway are called C4 plants.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : Plants utilising first RuBP in CO2-fixations are called C3 plants.
Reason : Plants utilising first PEP in CO2- fixations are called C4 plants.
Answer. B
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. What would happen to the rate of photosynthesis in C3 plants if CO2 concentration level almost doubles from its present level in the atmosphere?
Answer. If the CO2 concentration in C3plants almost get doubles from its present level in the atmosphere, plants will eventually grow much faster and lead to higher productivity due to higher rate of photosynthesis but then show a decline if CO2 concentration increases.
Question. Why photosynthesis is an oxidation reduction process?
Answer. Photosynthesis is an oxidation reduction process continues because water is oxidised to oxygen and carbon is reduced to carbohydrate.
Question. Where do the electrons move from the electron acceptor of PS-II in the Z-scheme?
Answer. The electrons move to downstream components of ETC and finally to PS-I from the electron acceptor of the PS-II in the Z-scheme.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Suppose there are plants having high concentration of chlorophyll-b, but lack chlorophyll-a, will they carry out photosynthesis? Why or why not?
Answer. No, plants will not carry out photosynthesis, as reaction centre is formed by chlorophyll a. The other chlorophyll and accessory pigments absorb different wavelengths of light and pass on the energy to reaction centre for more efficient photosynthesis.
Question. Fill in the blanks at A, B, C, D, E and F and complete the C4 pathway/Hatch-Slack pathway. (Img 40)
Answer. A - Mesophyll cell, B-Phosphoenol pyruvate (PEP), C4 acid, D-Bundle sheath cells, E-Pyruvate, F-Phosphoglyceric acid (PGA).
Question. How does water stress affect/decrease the rate of photosynthesis?
Answer. Water stress causes closure of stomata and decreases the availablity of CO2 for photosynthesis. Water stress also causes wilting of leaves, thus reducing the surface area of leaves for metabolic functions.
Question. Cyanobacteria and some other photosynthetic bacteria do not have chloroplasts. How do they conduct photosynthesis?
Answer. Cyanobacteria and some other photosynthetic bacteria have thylakoids suspended freely in the cytoplasm (i.e., they are not enclosed in membrane) and also have bacteriochlorophyll to conduct photosynthesis.
Question. List the differences between C3 and C4 pathways of dark reaction.
Answer. The differences between C3 and C4 pathways of dark reaction are as follows:
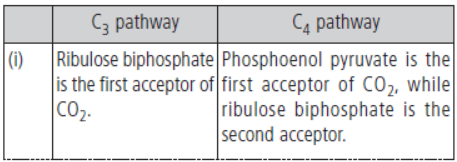
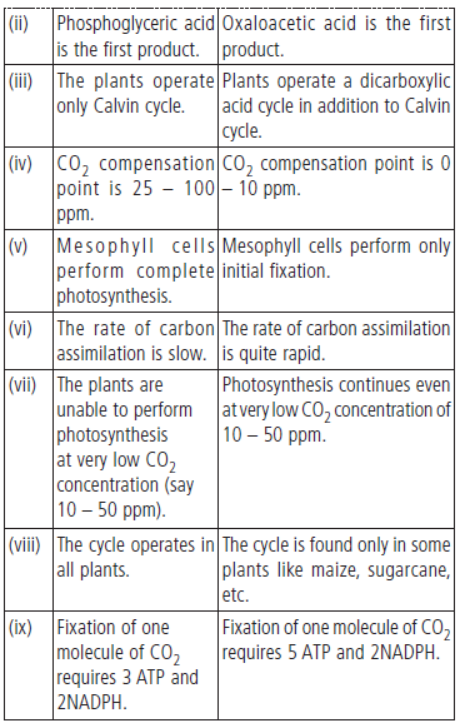
Question. Name the necessary components of the electron transport that process in the light reaction of photosynthesis.
Answer. The necessary components of the electron transport that process in the light reaction of photosynthesis are cytochrome b, cytochrome f, plastoquinone, plastocyanin, ferredoxin, and NADP+.
Question. Why is the lumen of thylakoids acidic while, the stroma is alkaline in nature?
Answer. The acidic nature of lumen of thylakoids is due to the accumulation of protons by the spliting of water. The same does not occurs in stroma so, it has alkaline nature.
Question. What is photorespiration?
Answer. Photorespiration is the light dependent process of oxygenation of ribulose biphosphate (RuBP) and release of carbon dioxide by the photosynthetic organs of a plant.
Question. Tomatoes, carrots and chillies are red in colour due to the presence of one pigment? Is it a photosynthetic pigment?---M---G1---
Answer. The pigments are chromoplasts ; these are fat soluble carotinoid pigments like carotenes and xanthophylls. These are called accessory pigments; they absorb light and transfer energy to Chlorophyll a.
Question. Which property of the pigment is responsible for its ability to initiate the process of photosynthesis? Why is the rate of photosynthesis higher in the red and blue region of spectrum of light?
Answer. The wave length of light: the visible light lies between the wave lengths of UV and IR. The most efficient is red light for photosynthesis. Green lights less effective. Maximum photosynthesis takes place in red and blue regions of spectrum of light. Chl a and b absorb mostly blue and red light.
Question. Why not photorespiration does take place in C4 plants?
Answer. The reason is that they have a mechanism that increases the concentration of CO2 at the enzyme site. It occurs when C4 acid from mesophyll cell is broken down in bundle sheath cells and releases CO2, hence increasing CO2 concentration intra cellular. It also ensures that RUBISCO acts as carboxylase to minimize oxygenase activity of it.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. (a) Name the first stable compound formed in sugarcane plant during CO2 fixation. (b) Describe Hatch and Slack pathway of CO2 fixation?
Answer. (a) : Sugarcane is a C4 plant, so first stable compound formed in this plant during CO2 fixation is oxaloacetic acid. (b) Mechanism of C4 pathway (or Dicarboxylic acid pathway or Hatch and Slack pathway) can be illustrated as follows: It involves following steps: (i) Initial fixation : In C4 plants, initial fixation of CO2 or carboxylation occurs in mesophyll cells. The chloroplasts of mesophyll cells possess enzyme PEP carboxylase (or PEP case) for initial fixation of CO2. The primary acceptor of CO2 is phosphoenol pyruvate or PEP. It combines with CO2 in the presence of PEP carboxylase (or PEPcase) to form oxaloacetic acid or oxaloacetate (OAA). (Img 49) (ii) Transport : Malic acid or aspartic acid is translocated to bundle sheath cells through plasmodesmata. Inside the bundle sheath cells they are decarboxylated (and deaminated in case of aspartic acid) to form pyruvate and CO2. Since a number of mesophyll cells are feeding bundle sheath cells, the latter come to have a carbon dioxide concentrations several times that of atmosphere. (Img 49) (iii) Final Fixation : CO2 released in bundle sheath cells is fixed through Calvin cycle. RuBP of Calvin cycle is called secondary or final acceptor of CO2 in C4 plants. (iv) Regeneration of PEP : Pyruvate and PEP formed in bundle sheath cells are sent back to mesophyll cells. Here, pyruvate is changed to phosphoenol pyruvate. Energy is required for this that is provided by ATP. The latter is changed into AMP (adenosine monophosphate). Pyruvate + ATP + H3PO4 Phosphopyruvate dikinase PEP + AMP + PPi Conversion of AMP to ATP requires double the energy than energisation of ADP to ATP. Therefore, actual requirement of energy is equal to two molecules of ATP. So, the overall reaction of Hatch and Slack pathway is as follows: 6 PEP + 6RuBP + 6CO2 + 30 ATP + 12 NADPH → 6 PEP + 6 RuBP + C6H12O6 + 30 ADP + 30 H3PO4 + 12 NADP.
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs The Living World |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Biological Classification |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Plant Kingdom |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Animal Kingdom |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Structural Organisation In Animals |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Cell And Its Structure |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Biomolecule |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Cell Cycle And Cell Division |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Transport In Plants |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Mineral Nutrition |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Photosynthesis in Higher Plants |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Respiration in Plants |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Plant Growth and Development |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Digestion And Absorption |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Breathing and Exchanger of gases |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Body Fluids And Circulation |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Excretory Products And Their Elimination |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Locomotion And Movement |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Neural Control and Coordination |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Chemical Co-Ordination And Integration |
HOTS for Chapter 13 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Biology Class 11
Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to NCERT book for Class 11 Biology to develop the Biology Class 11 HOTS. If you download HOTS with answers for the above chapter you will get higher and better marks in Class 11 test and exams in the current year as you will be able to have stronger understanding of all concepts. High Order Thinking Skills questions practice of Biology and its study material will help students to have stronger understanding of all concepts and also make them expert on all critical topics. You can easily download and save all HOTS for Class 11 Biology also from www.studiestoday.com without paying anything in Pdf format. After solving the questions given in the HOTS which have been developed as per latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 11 Biology designed by our teachers. We have also provided lot of MCQ questions for Class 11 Biology in the HOTS so that you can solve questions relating to all topics given in each chapter. After solving these you should also refer to Class 11 Biology MCQ Test for the same chapter
You can download the CBSE HOTS for Class 11 Biology Chapter 13 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the HOTS issued by CBSE for Class 11 Biology Chapter 13 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants have been made available here for latest academic session
HOTS stands for "Higher Order Thinking Skills" in Chapter 13 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Class 11 Biology. It refers to questions that require critical thinking, analysis, and application of knowledge
Regular revision of HOTS given on studiestoday for Class 11 subject Biology Chapter 13 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, HOTS questions are important for Chapter 13 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Class 11 Biology exams as it helps to assess your ability to think critically, apply concepts, and display understanding of the subject.

