Please refer to CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Excretory Products And Their Elimination. Download HOTS questions and answers for Class 11 Biology. Read CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs for Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination below and download in pdf. High Order Thinking Skills questions come in exams for Biology in Class 11 and if prepared properly can help you to score more marks. You can refer to more chapter wise Class 11 Biology HOTS Questions with solutions and also get latest topic wise important study material as per NCERT book for Class 11 Biology and all other subjects for free on Studiestoday designed as per latest CBSE, NCERT and KVS syllabus and pattern for Class 11
Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination Class 11 Biology HOTS
Class 11 Biology students should refer to the following high order thinking skills questions with answers for Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination in Class 11. These HOTS questions with answers for Class 11 Biology will come in exams and help you to score good marks
HOTS Questions Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination Class 11 Biology with Answers
MCQ Questions for NCERT Class 11 Biology Excretory Products and Their Elimination
Ques. Select the option which shows correct matching of animal with its excretory organ and excretory product.
Animal Excretory organ Excretory product
(a) Labeo (Rohu) Nephridial tubes Ammonia
(b) Salamander Kidneys Urea
(c) Peacock Kidneys Urea
(d) Housefly Renal tubules Uric acid
Answer: B
Ques. Which one of the following options gives the correct categorization of six animals according to the type of nitrogenous waste they give out?
Ammonotelic Ureotelic Uricotelic
(a) Pigeon,humans Aquatic amphibia, lizards Cockroach,frog
(b) Frog,lizards Aquatic amphibia, humans Cockroach, pigeon
(c) Aquatic amphibia Frog,humans Pigeon,lizards,cockroach
(d) Aquatic amphibia Cockroach, humans Frog, pigeon, lizards
Answer: C
Ques. Which one of the following characteristics is common both in humans and adult frogs?
(a) Four chambered heart
(b) Internal fertilisation
(c) Nucleated RBCs
(d) Ureotelic mode of excretion
Answer: D
Ques. Uricotelic mode of excreting nitrogenous wastes is found in
(a) reptiles and birds
(b) birds and annelids
(c) amphibians and reptiles
(d) insects and amphibians.
Answer: A
Ques. The principal nitrogenous excretory compound in humans is synthesised
(a) in kidneys but eliminated mostly through liver
(b) in kidneys as well as eliminated by kidneys
(c) in liver and also eliminated by the same through bile
(d) in the liver, but eliminated mostly through kidneys.
Answer: D
Ques. Uric acid is the chief nitrogenous component of the excretory products of
(a) earthworm
(b) cockroach
(c) frog
(d) man.
Answer: B
Ques. In ornithine cycle, which of the following wastes are removed from the blood?
(a) CO2 and urea
(b) Ammonia and urea
(c) CO2 and ammonia
(d) Urea and urine
Answer: C
Ques. Uricotelism is found in
(a) mammals and birds
(b) fish and fresh water protozoans
(c) birds, land reptiles and insects
(d) frogs and toads.
Answer: C
Ques. Conversion of ammonia to urea is done by
(a) ornithine cycle
(b) arginine cycle
(c) fumaric cycle
(d) citrulline cycle.
Answer: A
Ques. In ureotelic animals, urea is formed by
(a) Krebs’ cycle
(b) EM pathway
(c) Ornithine cycle
(d) Cori cycle.
Answer: C
Ques. The ornithine cycle removes two waste products from the blood in liver. These products are
(a) CO2 and ammonia
(b) ammonia and uric acid
(c) CO2 and urea
(d) ammonia and urea.
Answer: A
Ques. Two examples in which the nitrogenous wastes are excreted from body in the form of uric acid are
(a) birds and lizards
(b) frogs and cartilaginous fish
(c) insects and bony fish
(d) mammals and molluscs.
Answer: A
Ques. Nitrogenous waste products are eliminated mainly as
(a) urea in tadpole and ammonia in adult frog
(b) ammonia in tadpole and urea in adult frog
(c) urea in both tadpole and adult frog
(d) urea in tadpole and uric acid in adult frog.
Answer: B
Ques. Which one of the following is not a part of a renal pyramid?
(a) Peritubular capillaries
(b) Convoluted tubules
(c) Collecting ducts
(d) Loop of Henle
Answer: C
Ques. The basic functional unit of human kidney is
(a) nephridia
(b) Henle’s loop
(c) nephron
(d) pyramid.
Answer: C
Ques. Which one of the four parts mentioned below does not constitute a part of single uriniferous tubule?
(a) Distal convoluted tubule
(b) Collecting duct
(c) Bowman’s capsule
(d) Loop of Henle
Answer: B
Question. A crustacean lobster eliminates excretory matter from the body with the help of
(a) contractile vacuole
(b) flame cells
(c) nephridia
(d) none of these.
Answer. D
Question. The function of renin is
(a) stimulation of corpus luteum
(b) vasodilation
(c) to reduce blood pressure
(d) degradation of angiotensinogen.
Answer. D
Question. At a time about how much blood is passed through the artificial kidney?
(a) 1000 mL
(b) 200 mL
(c) 500 mL
(d) 400 mL
Answer. C
Question. Mammals have
(a) opisthonephric kidneys and ureotelic excretion
(b) mesonephric kidneys and ureotelic excretion
(c) metanephric kidneys and ureotelic excretion
(d) metanephric kidneys and ammonotelic excretion.
Answer. C
Question. What will happen if one kidney is removed from the body of a human being?
(a) Death due to poisoning
(b) Uremia and death
(c) Stoppage of urination
(d) The person will survive and remain normal
Answer. D
Question. Uriniferous tubules are mainly concerned with
(a) concentration of urine
(b) passage of urine
(c) reabsorption of useful substances from glomerular filtrate
(d) removal of urea from blood.
Answer. D
Question. Diuresis is the condition in which
(a) the excretory volume of urine increases
(b) the excretory volume of urine decreases
(c) the kidneys fail to excrete urine
(d) the water balance of the body is disturbed.
Answer. A
Question. Match the column I with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.
Column I Column II
(Excretory structure) (Organism)
A. Nephridia 1. Fasciola
B. Flame cells 2. Pheretima
C. General body surface 3. Periplaneta
D. Malpighian tubules 4. Hydra
A B C D
(a) 2 1 4 3
(b) 1 2 3 4
(c) 3 4 1 2
(d) 4 3 2 1
Answer. A
Question. Refer to the given figure of nephron andselect the correct option.
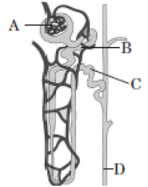
(a) A-glomerulus - a tuft of capillaries formed by afferent arteriole.
(b) B-PCT- only reabsorption of HCO3 – and selective secretion of H+ and K+ occurs here.
(c) C-DCT - almost all glucose, amino acids, water, Na+, K+ and uric acid are absorbed here.
(d) D-Collecting duct-extends from the cortex of the kidney to the inner parts of medulla. Large amount of water is secreted in this region.
Answer. A
Question. Which is not correct with respect to human kidney?
(a) The peripheral region is called cortex and central medulla.
(b) Malpighian corpuscles are present in the cortex region.
(c) Blood enters into glomerulus through efferent arterioles.
(d) The concave part of kidney is called hilum.
Answer. C
Question. Refer to the given figure and select the correct option representing the osmolarity at P, Q, R and S.
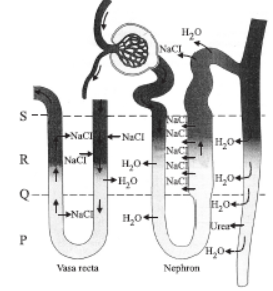
P Q R S
(mOsmolL–1) (mOsmolL–1) (mOsmolL–1) (mOsmolL–1)
(a) 1200 900 600 300
(b) 900 1200 300 600
(c) 300 600 900 1200
(d) 1200 300 900 600
Answer. A
Question. A fall in glomerular filtration rate (GFR) activates
(a) juxtaglomerular cells to release renin
(b) adrenal cortex to release aldosterone
(c) adrenal medulla to release adrenaline
(d) posterior pituitary to release vasopressin.
Answer. A
Question. Deficiency of ADH leads to
(a) formation of copious quantity of dilute urine
(b) frequent micturition
(c) feeling insatiably thirsty
(d) all of these.
Answer. D
Read the following passage and answer questions from 46 to 50 given below.
Kidneys, filter unwanted substances from the blood and produce urine. Urine formation includes glomerular filtration, selective reabsorption and tubular secretion shown in the figure.
These processes occurs in Malphigian corpuscle (Glomerulus and Bowman’s Capsule) and renal tubules comprising proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle, distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct.
Question. Which of the following do not pass the lumen of Bowman’s capsule during glomerular filtration?
(a) Creatinine
(b) Glucose
(c) Water
(d) Proteins
Answer. D
Question. Which of the following hormone increases the reabsorption of Na+ in PCT?
(a) Antidiuretic hormone
(b) Angiotensin II
(c) Aldosterone
(d) Atrial Natriuretic factor
Answer. B
Question. Select the incorrect statement regardingmechanism of urine formation in human.
(a) The glomerular filtration rate is about 125 mL per minute.
(b) The ultrafiltration is opposed by the colloidal osmotic pressure of plasma.
(c) Aldosterone induces greater reabsorption of sodium.
(d) The counter current system contributes in diluting the urine.
Answer. D
Question. Which of the following are reabsorbed in the proximal convoluted tubule ?
(a) Sulphates, sodium, chlorides
(b) Creatinine, phosphates, vitamins
(c) Sulphates, creatine, chlorides
(d) Bicarbonates, glucose, hormones
Answer. D
Question. Kidneys help in the conservation of useful materials and excretion of wastes and therefore they receive 20% of the heart’s output of blood (as much as the heart and brain combined). On a percentage basis, which substance is most completely reabsorbed by the kidneys?
(a) Water
(b) Glucose
(c) Urea
(d) Sodium
Answer. B
Assertion & Reasoning Based MCQs
For question numbers 51-60, two statements are given-one labelled Assertion and the other labelled Reason.
Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false but reason is true.
Question. Assertion : If human urine is allowed to stand for some time, it smells strongly of ammonia.
Reason : Main constituent of human urine is ammonia.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : Malpighian tubules are excretory organs in most of the insects.
Reason : Malpighian tubules help in the removal of nitrogenous wastes in cockroaches.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : During micturition, urine is prevented from flowing back into the ureters.
Reason : Urethral sphincters relax during micturition.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : Hemodialysis can save and prolong the life of uremic patients.
Reason : Waste products like urea are removed from the blood by the process of hemodialysis.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : Birds can considerably reduce water loss in the urine.
Reason : Birds store urine along with faeces in the cloaca.
Answer. B
Important Questions for NCERT Class 11 Biology Excretory Products and Their Elimination
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Which component of plasma is absent in dialysis fluid?
Answer. Nitrogenous wastes are absent in the dialysis fluid.
Question. Which part of the body is connected to the dialyzer to withdraw blood for dialysis?
Answer. Radial artery
Question. What is the value of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) in a healthy individual?
Answer. Approximately 125 mL/minute, i.e., 180 litres per day.
Question. How is the hormone angiotensin II activated?
Answer. Enzyme called renin is secreted by juxtaglomerular cells which converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin I which is further converted into angiotensin II.
Question. Which part of loop of Henle is impermeable to water?
Answer. Ascending limb of loop of Henle.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Mention the function of the following in regulation of kidney function.
(i) ADH (ii) ANF (iii) Renin
Answer. The following play an important role in the functioning of kidneys– (i) ADH : Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) is secreted by hypothalamus of the brain and released into the blood from the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland. The release of ADH is triggered when osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus detect an increase in the osmolarity of the blood above a set point of 300 mosmL–1. In this situation, the osmoreceptor cells also promote thirst. It increases the reabsorption of water in the DCT and collecting duct. (ii) ANF : Atrial natriuretic factor is another hormone which opposes the regulation by RAAS. The walls of the atria of the heart release ANF in response to an increase in blood volume and pressure. ANF inhibits release of renin from the JGA and thereby inhibits NaCl reabsorption by the collecting duct and reduces aldosterone release from the adrenal gland. Thus ADH and ANF regulate the function of the kidneys. As a result, they control body fluid osmolarity, salt concentration, blood pressure and blood volume. (iii) Renin : The smooth muscle cells of both the afferent and efferent arterioles are swollen and contain dark granules. These cells are called juxtaglomerular cells. The granules are composed mainly of inactive renin. It means renin is secreted by juxtaglomerular cells. Renin converts angiotensinogen into angiotensin I and further to angiotensin II. The latter increases blood pressure. It also stimulates the secretion of aldosterone by the adrenal cortex thus inducing the reabsorption of sodium ions by the DCT and that of water through collecting ducts.
Question. Aquatic animals generally are ammonotelic in nature whereas terrestrial forms are not. Comment.
Answer. Aquatic animals like bony fishes, aquatic amphibians and aquatic insects excrete ammonia, i.e., they are ammonotelic in nature. This is because ammonia is highly toxic and is readily soluble in water. It is generally excreted by diffusion across body surfaces or through gill surfaces (in fish) as ammonium ions. Excretion of nitrogenous wastes in the form of ammonia requires a lot of water. Terrestrial animals cannot afford to lose so much of water, thus they convert ammonia into urea or uric acid which are less toxic and can be stored in body for longer. Terrestrial amphibians and mammals mainly excrete urea and are called ureotelic animals while reptiles, birds, land snails excrete uric acid and are called uricotelic animals. Urea and uric acid are less soluble in water and can be excreted with lesser loss of water. Thus, terrestrial adaptation necessitated the production of urea and uric acid for conservation of water.
Question. How are the following materials reabsorbed in the proximal convoluted tubule?
(a) Glucose
(b) Amino acids
(c) Urea
(d) Chloride
Answer. (a) Glucose - Active transport (b) Amino acid - Active transport (c) Urea - Diffusion (d) Chloride - Diffusion
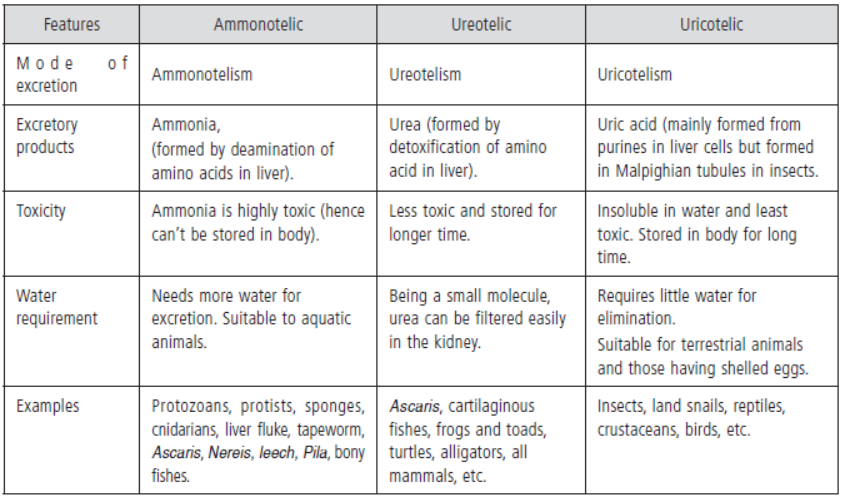
Question. Differentiate among ammonotelic, ureotelic and uricotelic animals. Give two examples in each case.
Answer. Differences among ammonotelic, ureotelic and uricotelic is given below :
Question. (a) What is the relationship between length of loop of Henle and concentration of urine?
(b) What is the maximum osmotic difference that can be created by the Na-K pump in the ascending limb of loop of Henle?
Answer. (a) In different mammals, the concentration of urine is directly related to the length of loop of Henle. The function of the loop of Henle is to conserve water. More the length of loop of Henle more is absorption of water and this results in more concentrated urine. (b) The thick part of the ascending limb of loop of Henle is virtually impermeable to water, but large amounts of sodium, chloride, potassium, and other ions are actively transported from the tubule into the medullary interstitium. Therefore, fluid in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle becomes very dilute, falling to a concentration of about 100 mOsmol/l.
Question. Why is skin an accessory excretory organ?
Answer. Skin plays a major role in excretion. It helps the body to get rid of excess of water, salts and waste such as ammonia in aquatic animals. The mammalian skin possesses sweat glands and sebaceous glands that play excretory roles. The secretion of sweat glands (sweat) is an aqueous fluid containing sodium chloride, lactic acid, urea, amino acids and glucose. Control of sweat lost is an example of homeostatic control for regulating the body temperature according to the variation in the ambient temperature. Sebum from sebaceous glands eliminates sterols, fatty acids and some other hydrocarbons. They are mainly meant for lubrication of hair and skin, but some constituents are concerned with excretion like waxes and sterols.
Question. Fill in the blanks at (A), (B), (C), (D), (E) and (F) and complete the flow chart.
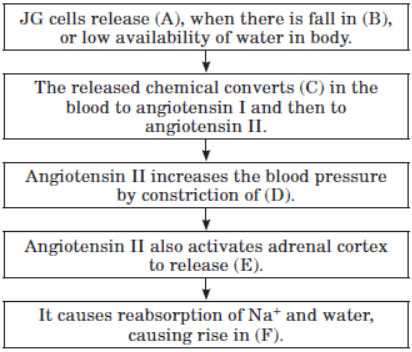
Answer. (A) - Renin (B) - Glomerular filtration rate (C) - Angiotensinogen (D) - Arterioles (E) - Aldosterone (F) - Blood volume
Question. Glomerular filtration is autoregulated. Justify.
Answer. Glomerular filtration is autoregulated by the following mechanisms: (i) Myogenic mechanism : An increase in blood pressure increases blood flow to the glomerulus by stretching afferent arteriole. When the wall of the arteriole contracts, the diameter of the afferent arteriole is reduced that increases the flow of blood. (ii) Juxtaglomerular mechanism : Juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) cells secrete enzymes like renin that modulate blood pressure and thus renal blood flow. This also regulates GFR. (iii) Neural control : Blood vessels of the kidney are innervated by nerve fibres of sympathetic neural system. When activated, the nerve fibres bring about constriction of renal arteries and cause decrease in renal flow and GFR.
Long Answer Type Questions
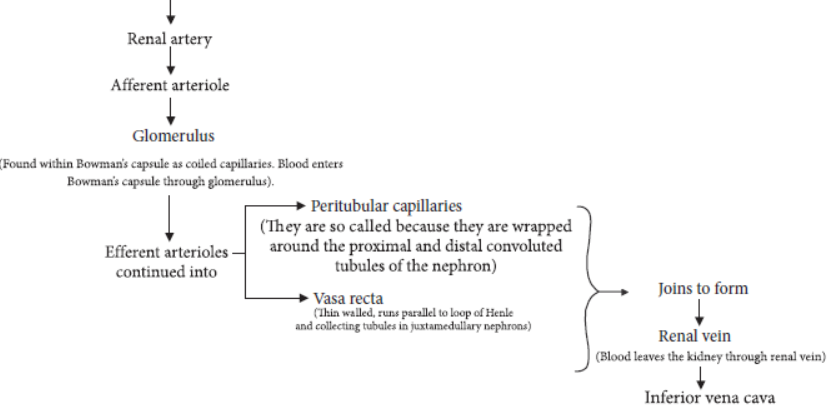
Question. (a) With the help of a self explanatory flow chart, display the path followed by the blood in the kidney.
(b) Differentiate between descending and ascending limbs of loop of Henle.
Answer. (a) The flow of blood in the kidneys can be represented as: (IMG 158) (b) Differences between descending limb and ascending limb of loop of Henle are :
Question. What is the role played by following hormones in regulating the urine formation?
(a) Aldosterone
(b) Angiotensin II
(c) Atrial natriuretic factor
Answer. (a) Aldosterone is a hormone secreted by the outer layer of the adrenal gland (cortex part), a gland which is situated above the kidneys. The release of aldosterone is controlled by low levels of sodium in body. When aldosterone is present in the blood, more Na+ from the filtrate is reabsorbed by the epithelial cells of the collecting duct. Retaining Na+, raises the osmotic pressure of the blood and reduces water loss from the body. When aldosterone is absent, some Na+ remains in the filtrate and is excreted with the urine. (b) As blood pressure decreases, the cells of juxtaglomerular apparatus release an enzyme renin and activate the Renin- Angiotensin-Aldosterone pathway (RAAS). Renin converts angiotensinogen into angiotensin I and then converts angiotensin I into angiotensin II, a peptide hormone that is the active form. Angiotensin II has the following effects: – Increases the release of aldosterone – Raises blood pressure directly by constricting blood vessels – Stimulates sodium reabsorption by the distal convoluted tubules. These changes assist in restoring extracellular fluid volume and in stabilising blood pressure. (c) Atrial natriuretic factor (ANF) a peptide hormone produced by the atria of heart, increases sodium excretion and decreases blood pressure and blood volume. ANF is released into the bloodstream in response to stretching of the atrial muscle cells by increased blood volume. ANF has the following physiological effects: – Inhibits the release of renin from JGA. – Inhibits the collecting ducts from reabsorbing sodium, both directly and indirectly (by inhibiting aldosterone secretion).
Questions. What stimulates the release of aldosterone? How does aldosterone increase the blood pressure and regulate GFR?
Answer-Angiotensin-II
Questions. What is stimulus for the cells of JGA to release renin?
Answer-Glomerular blood pressure falls.
Questions. Why tubular secretion an important step in urine formation?
Answer-maintains ionic balance and pH of body fluids.
Questions. Give the technical term for each of the following. Inflamation of glomeruli of kidney.
b. Formation of insoluble masses of crystallized salts.
c. Accumulation of urea in the blood.
d. The process of artificial removal of urea from blood.
Answer-a. Glomerulo-nephritis
b. Renal calculi
c. Uremia
d. HemoDialysis
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs The Living World |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Biological Classification |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Plant Kingdom |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Animal Kingdom |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Structural Organisation In Animals |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Cell And Its Structure |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Biomolecule |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Cell Cycle And Cell Division |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Transport In Plants |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Mineral Nutrition |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Photosynthesis in Higher Plants |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Respiration in Plants |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Plant Growth and Development |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Digestion And Absorption |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Breathing and Exchanger of gases |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Body Fluids And Circulation |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Excretory Products And Their Elimination |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Locomotion And Movement |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Neural Control and Coordination |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology HOTs Chemical Co-Ordination And Integration |
HOTS for Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination Biology Class 11
Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to NCERT book for Class 11 Biology to develop the Biology Class 11 HOTS. If you download HOTS with answers for the above chapter you will get higher and better marks in Class 11 test and exams in the current year as you will be able to have stronger understanding of all concepts. High Order Thinking Skills questions practice of Biology and its study material will help students to have stronger understanding of all concepts and also make them expert on all critical topics. You can easily download and save all HOTS for Class 11 Biology also from www.studiestoday.com without paying anything in Pdf format. After solving the questions given in the HOTS which have been developed as per latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 11 Biology designed by our teachers. We have also provided lot of MCQ questions for Class 11 Biology in the HOTS so that you can solve questions relating to all topics given in each chapter. After solving these you should also refer to Class 11 Biology MCQ Test for the same chapter
You can download the CBSE HOTS for Class 11 Biology Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the HOTS issued by CBSE for Class 11 Biology Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination have been made available here for latest academic session
HOTS stands for "Higher Order Thinking Skills" in Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination Class 11 Biology. It refers to questions that require critical thinking, analysis, and application of knowledge
Regular revision of HOTS given on studiestoday for Class 11 subject Biology Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, HOTS questions are important for Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination Class 11 Biology exams as it helps to assess your ability to think critically, apply concepts, and display understanding of the subject.

