SOCIETY, LAW AND ETHICS
Introduction
Information forms the intellectual capital for a person. Some ethical issues involved with the usage and availability of information are:
i. Intellectual property rights
ii. Plagiarism
iii. Digital property rights
Intellectual property rights
These are the rights of the owner of information to decide how much information is to be exchanged, shared or distributed. Also it gives the owner to decide the price for doing (exchanging/sharing/distributing) so.
The intellectual property rights must be protected because:
i. Ensures new ideas and technologies are widely distributes
ii. Encourages individuals and business to create new software and improve the existing application.
iii. Promotes investment in the national economy
Plagiarism
It is stealing someone else’s intellectual work such as idea, literary work or academic work etc. and representing it as your own work without giving credit to creator or without citing the source of information.
Digital right management
It is used to protect your software from being scraped for source code using decompilers etc.
• Digital property (digital assets)
It refers to any information about you or created by you that exists in digital form, either online or on an electronic storage device.
• Measures to protect digital property
a. Anti-temper solution
b. Legal clauses
c. Limit the sharing of software code
Licensing
A software license is a document that provides legally binding guidelines to the person who holds it for the use and distribution of software. It typically provide end users with the right to make one or more copies of the software without violating copyrights. It also defines the responsibilities of the parties entering into the license agreement and may impose restrictions on how the software can be used. Software licensing terms and conditions usually include fair use of the software, the limitations of liability, warranties and disclaimers and protections.
• Creative commons: Creative Commons (CC) is an internationally active non-profit organization to provide free licenses for creators to use it when making their work available to the public in advance under certain conditions. CC licenses allow the creator of the work to select how they want others to use the work. When a creator releases their work under a CC license, members of the public know what they can and can’t do with the work.
• General Public License: General Public License (GNU GPL), is the most commonly used free software license, written by Richard Stallman in 1989 of Free Software Foundation for GNU Project. This license allows software to be freely used modified,and redistributed by anyone. WordPress is also an example of software released under the GPL license, that’s why it can be used, modified, and extended by anyone.
• Apache License: The Apache License is a free and open source software (FOSS) licensing agreement from the Apache Software Foundation (ASF). The main features are copy, modify and distribute the covered software in source and/or binary forms, all copies, modified or unmodified, are accompanied by a copy of the license.
Open Source
Open source means any program whose source code is made available publically for use or modification as users or other developers see fit. Open source software is usually made freely available.
Eg: Open source software: python, java, linux, mongodb etc
Open data
Open data is data which can be accessed, used and shared by anyone to bring about social, economic and environmental benefits. Open data becomes usable when made available in a common, machine-readable format.
• Open source terminologies and definitions:
a. Free Software: They are freely accessible and can be freely used, changed, improved, copied and distributed by all and payments are not needed for free Software.
b. Open Source Software: Software whose source code is available to the user and it can be modified and redistributed without any limitation .OSS may come free of cost but nominal charges have to be paid for support of Software and development of Software.
c. Proprietary Software: Proprietary Software is neither open nor freely available, normally the source code of the Proprietary Software is not available but further distribution and modification is possible by special permission by the developer.
d. Freeware: Freeware are the software freely available, which permit redistribution but not modification (their source code is not available). Freeware is distributed in Binary Form (ready to run) without any licensing fees.
e. Shareware: Software for which license fee is payable after some time limit, its source code is not available and modification to the software are not allowed.
• Privacy
It is the protection of personal information given online.
Online fraud
Fraud committed using the internet is called online fraud. Online fraud occurs in many forms such as non-delivered goods,non-existent goods, stealing information, fraudulent payments.
• Preventive measures to stop online fraud
a. Strong security mechanism by the e-commerce site and payment gateways to prevent stealing of crucial information.
b. Official guidelines and safeguards on the selling of users’s data to third parties.
c. A monitoring official body that ensures the delivery of goods/services as promised.
Cybercrime
Any criminal offense that is facilitated by the use of electronic device, computer or internet is called cybercrime. Eg: Information Theft, scams, illegal downloads etc.
• Phishing
It is the practice of attempting to acquire sensitive information from individuals over the internet by means of deception.Figure shows how phishing attack is carried out.
• Scams
Any fraudulent business practice that extracts money from an unsuspecting, ignorant person is called scams.
Measures to avoid online scams
i. Never enter personal information or any financial information on unsecure website.
ii. Never replays to emails from any unknown or unreliable source.
iii. Never respond to an e-mail or advertising claiming you won something.
• Illegal download
Illegal downloading refers to obtaining files for which you don’t have the right to use or download from the internet.
• Child pornography
It is considered to be any depiction of a minor or an individual who appears to be a minor who is engaged in sexual or sexually related conduct. This includes pictures, videos, and computer-generated content. Even altering an image or video so that it appears to be a minor can be considered child pornography.
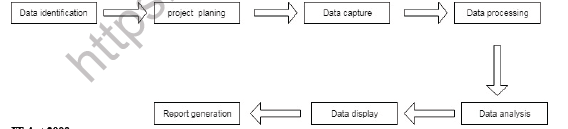
Cyber forensics (digital forensics)
It refers to methods used for interpretation of computer media for digital evidence.
Digital forensic investigation process
Please click on below link to download CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Society Law and Ethics Notes

